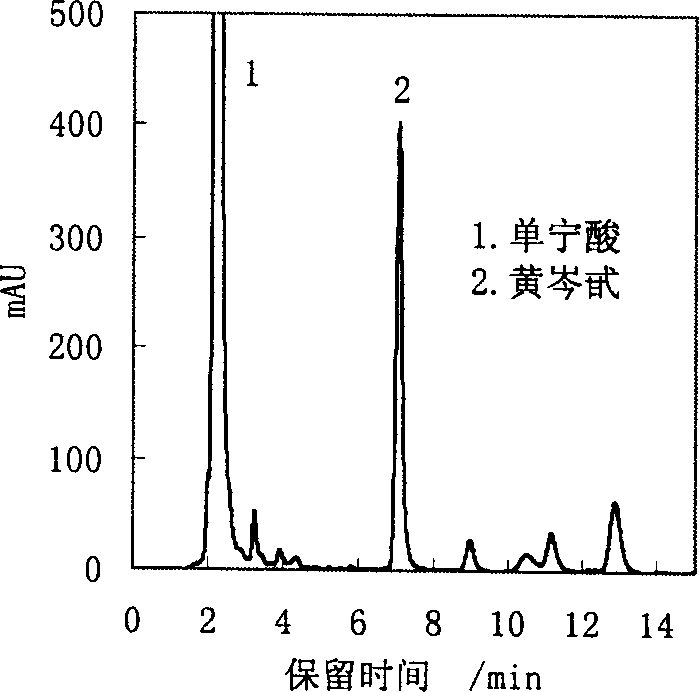
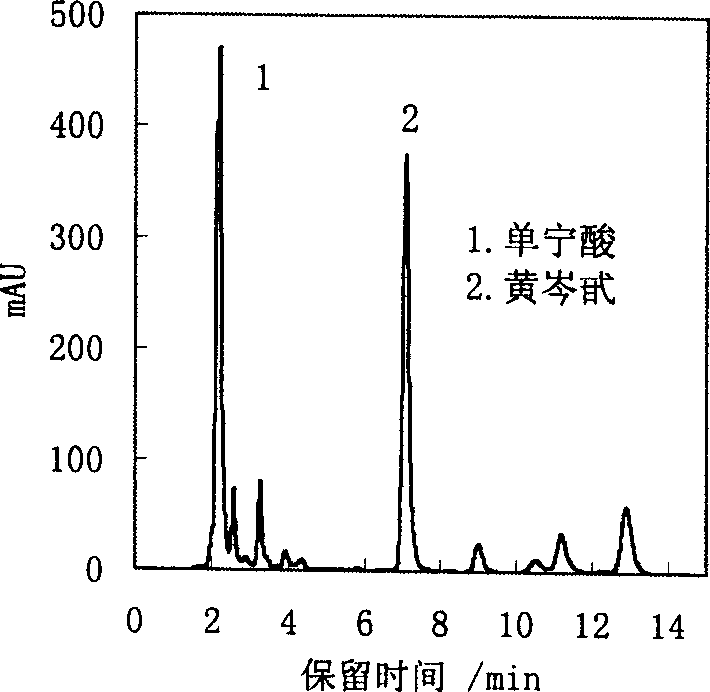
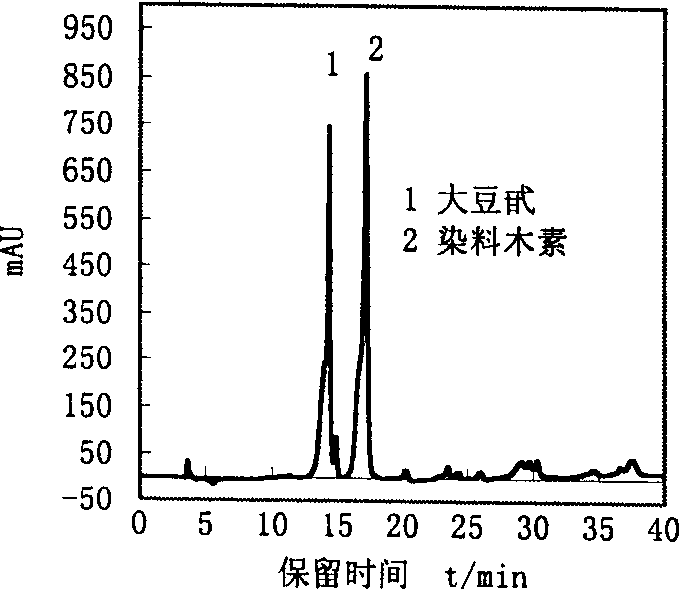
Collagen fiber adsorption material and its preparation method, and its adsorption and separation of tannin
A collagen fiber and adsorption material technology, which is applied in the fields of collagen fiber adsorption material and its preparation and adsorption and separation of tannins, and achieves the effects of wide sources, no environmental pollution and simple process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: the preparation method of formaldehyde cross-linked collagen fiber adsorption material
[0028] Step 1: Preparation of Collagen Fibers
[0029] Choose cowhide as the raw material, divide it, remove the flesh, and wash it with water to remove dirt, dissolve some soluble substances in the hide, and keep the raw hide soft and clean; use alkali to remove the interstitial fibers and destroy the disulfide bond between the hair and the keratin in the epidermis , saponification of oil to facilitate hair removal and skinning; remove the grain layer and subcutaneous layer by skinning; adjust the pH value through dealkalization, eliminate the swelling state of the skin, make the collagen functional group in a free state, and remove the remaining protein and glue Hydrolyzate and decomposed product, remove oil and saponification; then demineralize and buffer to control pH = 6.0-7.5; finally dehydrate, dry and grind to obtain granular collagen fibers with an average par...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2: Preparation method of glutaraldehyde cross-linked collagen fiber adsorption material
[0033] Step 1: Preparation of Collagen Fibers
[0034] Prepared according to the method of Example 1.
[0035] Step 2: Preparation of Collagen Fiber Adsorbent Material
[0036] Take 3.0 g of the collagen fiber obtained in the first step and fully wet it with distilled water for 12-24 hours. Put it into a solution containing 1.0 g of glutaraldehyde; add 1 g of NaCl; shake at a temperature of 25°C for 2 hours; then increase the temperature to 40°C, gradually adjust the pH to 8.5, and shake for another 2 hours. After standing overnight, the unreacted glutaraldehyde was fully washed away with distilled water the next day, and dried at a temperature of 60°C for 12-24 hours to obtain a glutaraldehyde cross-linked collagen fiber adsorption material with an average particle size of 80 μm. The shrinkage temperature measured by differential calorimeter (DSC) was 87°C.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Preparation of Oxazolidine Crosslinked Collagen Fiber Adsorbent Material
[0038] Step 1: Preparation of Collagen Fibers
[0039] Prepared according to the method of Example 1.
[0040] Step 2: Preparation of Collagen Fiber Adsorbent Material
[0041] Take 3.0 g of the collagen fiber obtained in the first step and fully wet it with distilled water for 12-24 hours. Put into 1.0g solution containing oxazolidine, adjust the pH to 5-7; shake and react at a temperature of 25°C for 2 hours; then raise the temperature to 60°C, and shake for another 4 hours. Let stand overnight, and wash away unreacted oxazolidine with distilled water the next day. Dry at a temperature of 65°C for 15-20 hours to obtain an oxazolidine cross-linked fiber adsorption material with an average particle size of 80 μm. The shrinkage temperature measured by differential calorimeter (DSC) was 85°C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com