Porous rack with spherical pores and its molding prepn process
A porous scaffold and spherical technology, which is applied in the field of polymer materials and biomaterials, can solve the problems of difficult mechanical properties of scaffolds, unfavorable molding, and low porosity of scaffolds, and achieves a simple and practical preparation method, which is conducive to large-scale production, good mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
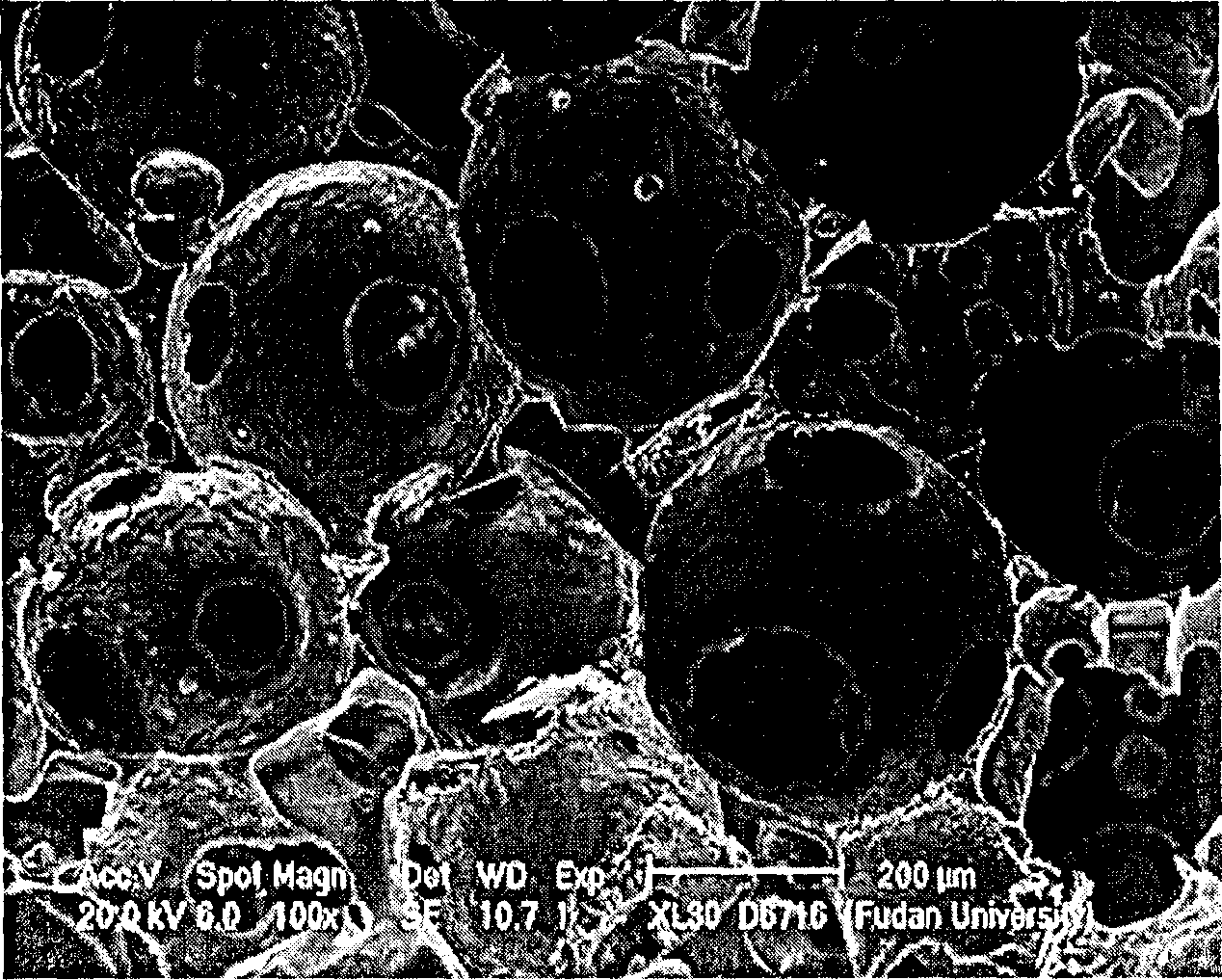
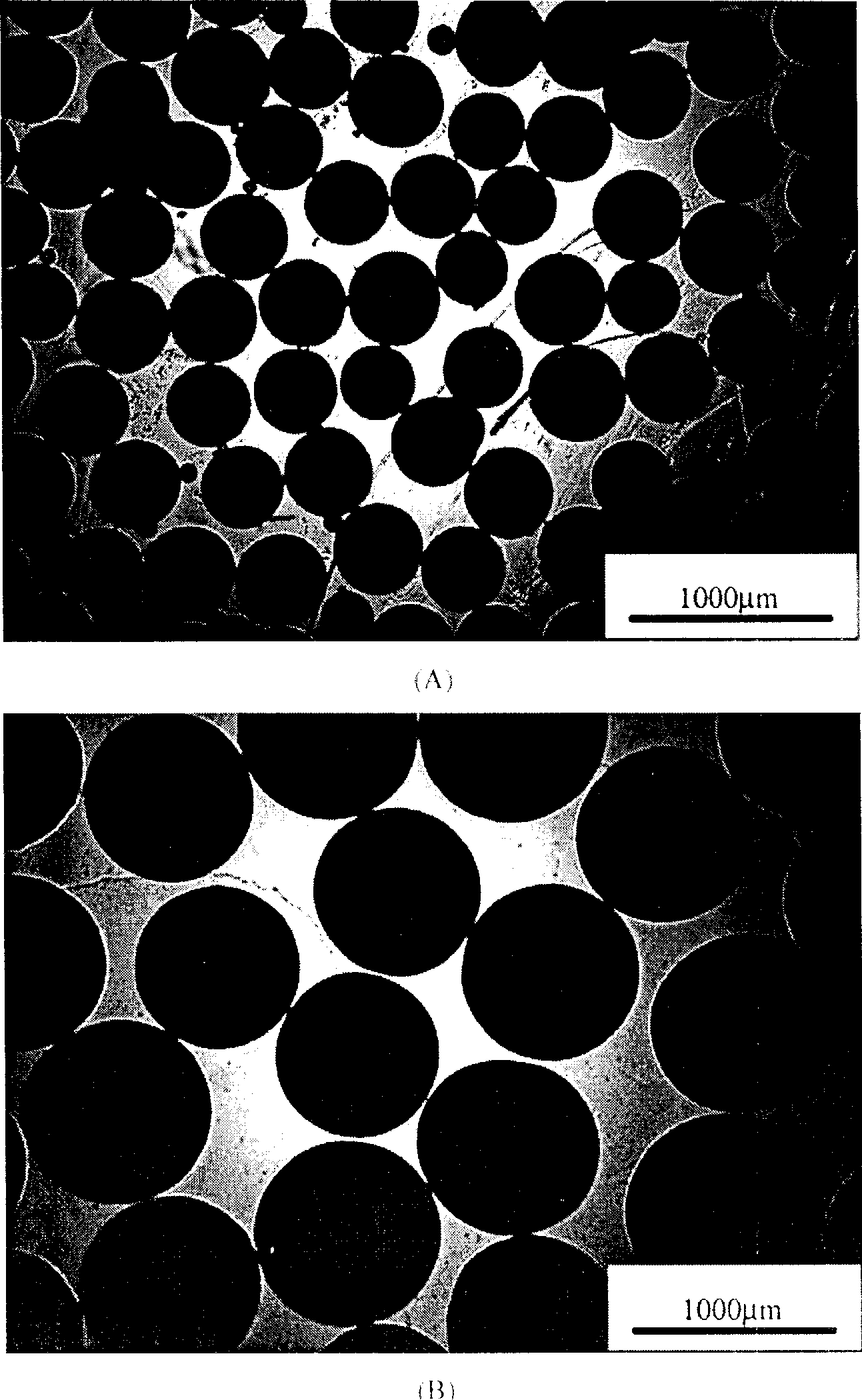
[0054] Example 1, first prepare spherical paraffin particles. Add 1g of gelatin and 20g of paraffin to 400mL of deionized water, raise the temperature to 80°C and stir evenly under 400rpm mechanical stirring, then add 300mL of ice water to quench the microspheres to keep the spherical shape. Filtered, washed several times with deionized water, dried and then sieved into different fractions of paraffin particles with different standard sieves (see figure 1 ), and stored dry for later use.
[0055] Dissolve 0.5g of PLGA85 / 15 with a molecular weight of 300,000 in 8mL of acetone, add 9.5g of spherical paraffin particles with a particle size of 355-450μm into the solution, stir evenly, and partially volatilize the solvent to make the polymer solution—the porogen The particle mixture becomes a paste; press the mixture into a pre-designed silicone rubber mold (diameter 1cm, height 1cm), apply appropriate pressure and keep it for 30 minutes; after demolding, a polymer solution with t...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2, 0.45g of PLGA85 / 15 with a molecular weight of 300,000 was dissolved in 8mL of acetone, 2.55g of paraffin spherical particles, and the particle diameter was 810-900 μm. Others were the same as in Example 1, and the pores of the porous support were interconnected (see Figure 4 ), the porosity is 89.8%, and the compressive strength is 7.1MPa.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3, 0.6g of PLGA85 / 15 with a molecular weight of 300,000 was dissolved in 10mL of acetone, 1.4g of paraffin spherical particles, the particle size was 355-450μm, the others were the same as in Example 1, and the porosity of the prepared porous scaffold was 78.4%. , The compressive strength is 15.4MPa.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com