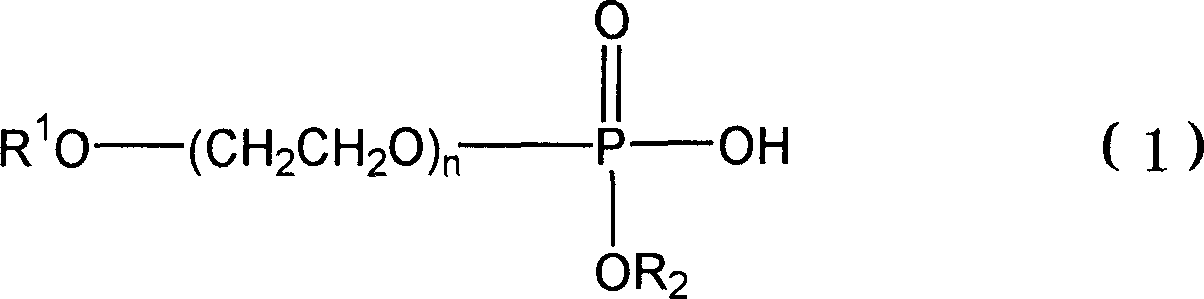
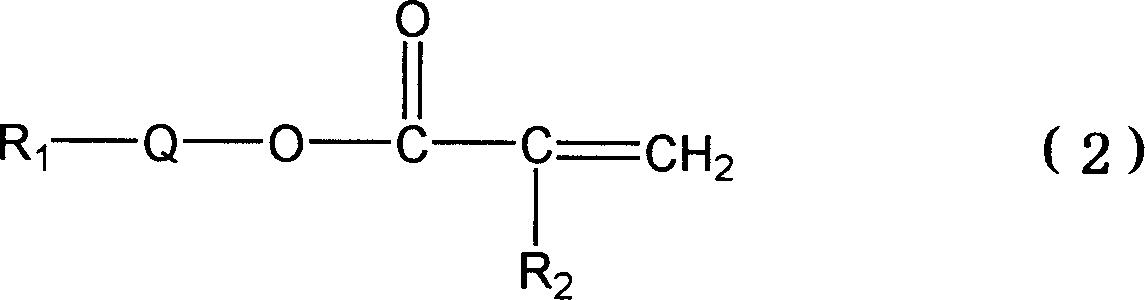
Absorbent material and absorbent article
An absorbent, vinylic technology that is used in absorbent pads, thin material handling, transportation and packaging to solve problems such as easy damage to porous structures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0023] In the production method described later, primary particles having an average particle diameter of 1 to 50 μm are first produced, and the primary particles are gradually melted in the production process, thereby forming absorbent resin particles. Such as figure 1 As shown in the electron micrograph of , by forming a structure having primary particle fusion, pores are formed in the absorbent resin particles, the surface area of the absorbent resin particles is increased, and the wettability to blood can be improved.
[0024] The pores of the water-absorbent resin used in the present invention are interstices of primary particles formed by fusion of primary particles, and are expected to adsorb blood cells in blood or move blood into the absorbent resin particles. The fine pores are generally larger than the average particle diameter of the primary particles, and the diameter thereof is 1 to 100 μm.
[0025] In the method of mercury injection in the present invention, ...
Embodiment
[0114] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically by way of examples and comparative examples. Unless otherwise specified, "%" in the following is based on weight. The various properties of the material were measured by the methods shown briefly below. Table 1 summarizes the compositions of Examples 1 to 3 and Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2.
[0115] [Measuring method of blood absorption amount]
[0116] In 20 ml of horse defibrinated blood (purchased from Japan Biomaterials Center) in a Petri dish with an inner diameter of 95 mm, 15 overlapping toilet papers (55 mm × 75 mm) were immersed, and the absorbent obtained in the examples described later was added to the paper. About 1 g of permanent resin particles was absorbed for 5 minutes, and then the swollen gel of the resin was collected and its weight was measured. The blood absorption amount (g / g) was calculated by dividing the weight of the resin particles before absorption by...
reference example 1
[0125] Reference example 1 (manufacturing example of polysuccinimide)
[0126] 96 g of maleic anhydride and 50 g of ion-exchanged water were added to a 1 L 4-necked flask equipped with a stirring device, a thermometer, a reflux device, and a nitrogen blowing device. Then, after heating to 55 degreeC and dissolving maleic anhydride, after cooling, the slurry of maleic anhydride was obtained. The system was reheated, and when it reached 55°C, 60.8 g of 28% ammonia water was added. Then, the temperature of the system was raised to 80°C. After reacting for 3 hours, the obtained aqueous solution was dried to obtain a reaction intermediate. Add 100 g of the reaction intermediate and 85% phosphoric acid into a 2 L eggplant-shaped flask, and react under reduced pressure at 200° C. in an oil bath for 4 hours using a rotary evaporator. The obtained product was washed several times with water and methanol. The weight average molecular weight of the obtained polysuccinimide measured b...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pore volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bulk density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com