Non-isothermal method for fabricating hollow composite parts
A non-isothermal, hollow technology, used in household components, textiles and paper, other household appliances, etc., can solve the problems of expensive heating and cooling cycles of molds, aesthetics of substandard finished products, long durability, etc., to simplify storage and handling, The effect of fast conversions and shorter cycle times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
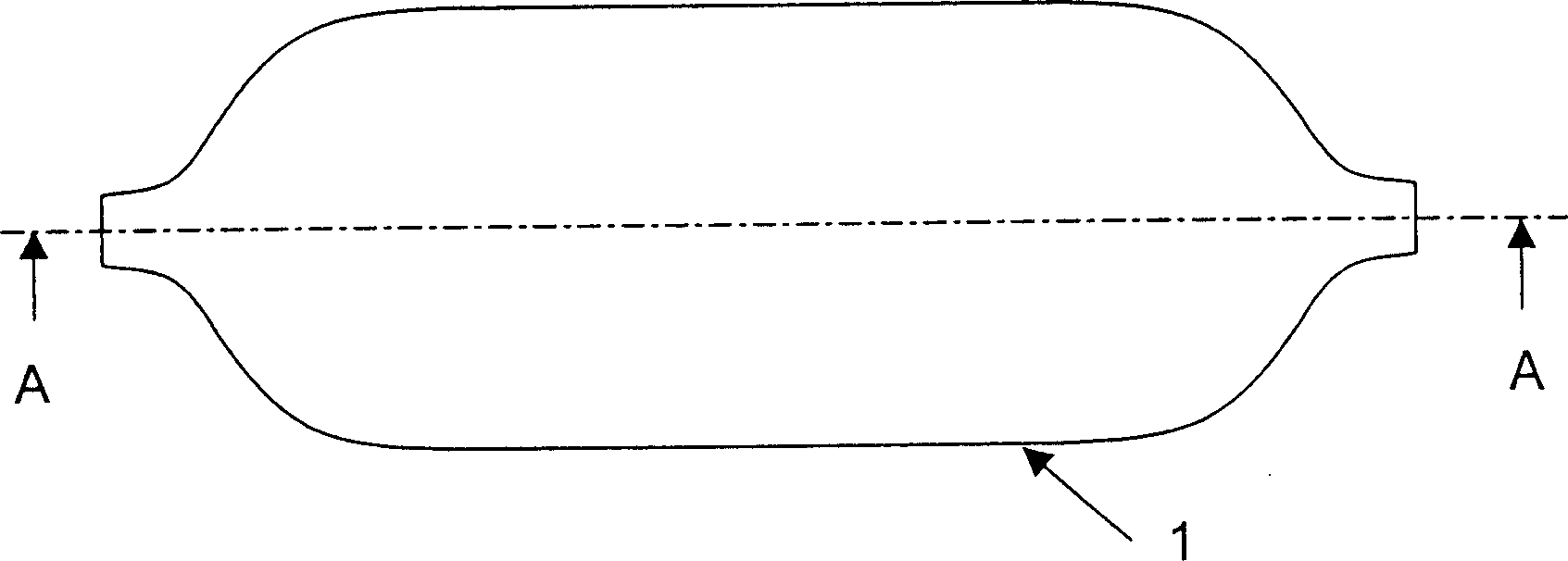
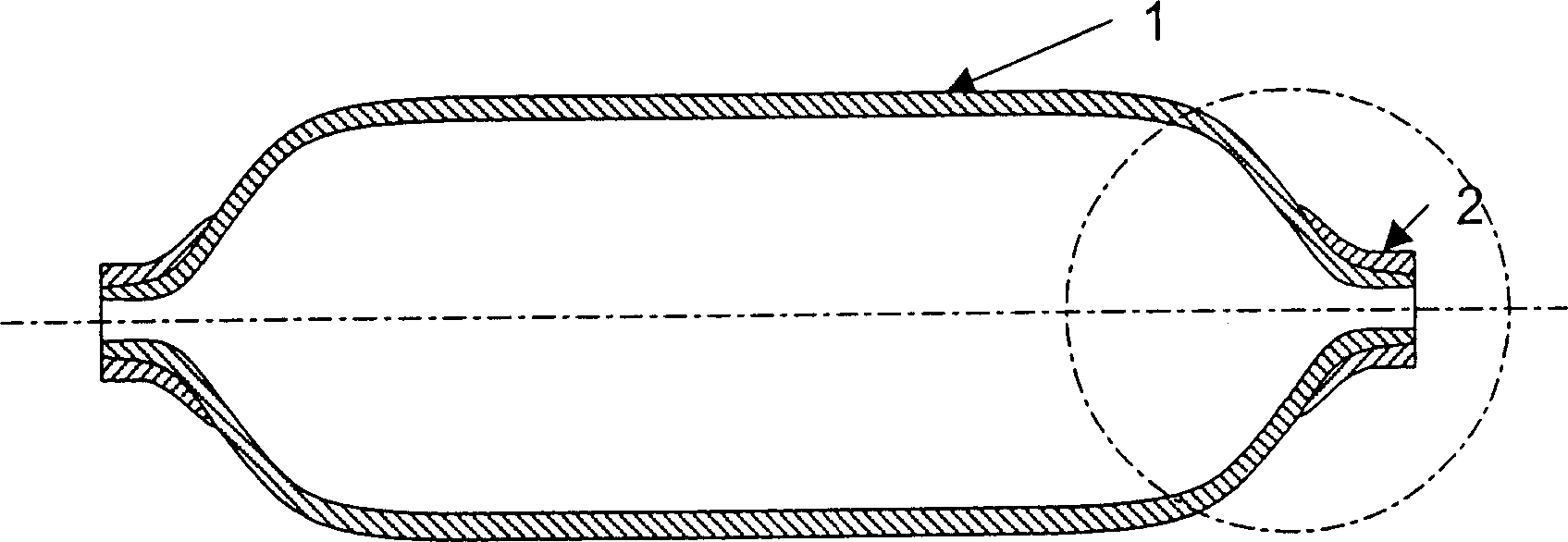
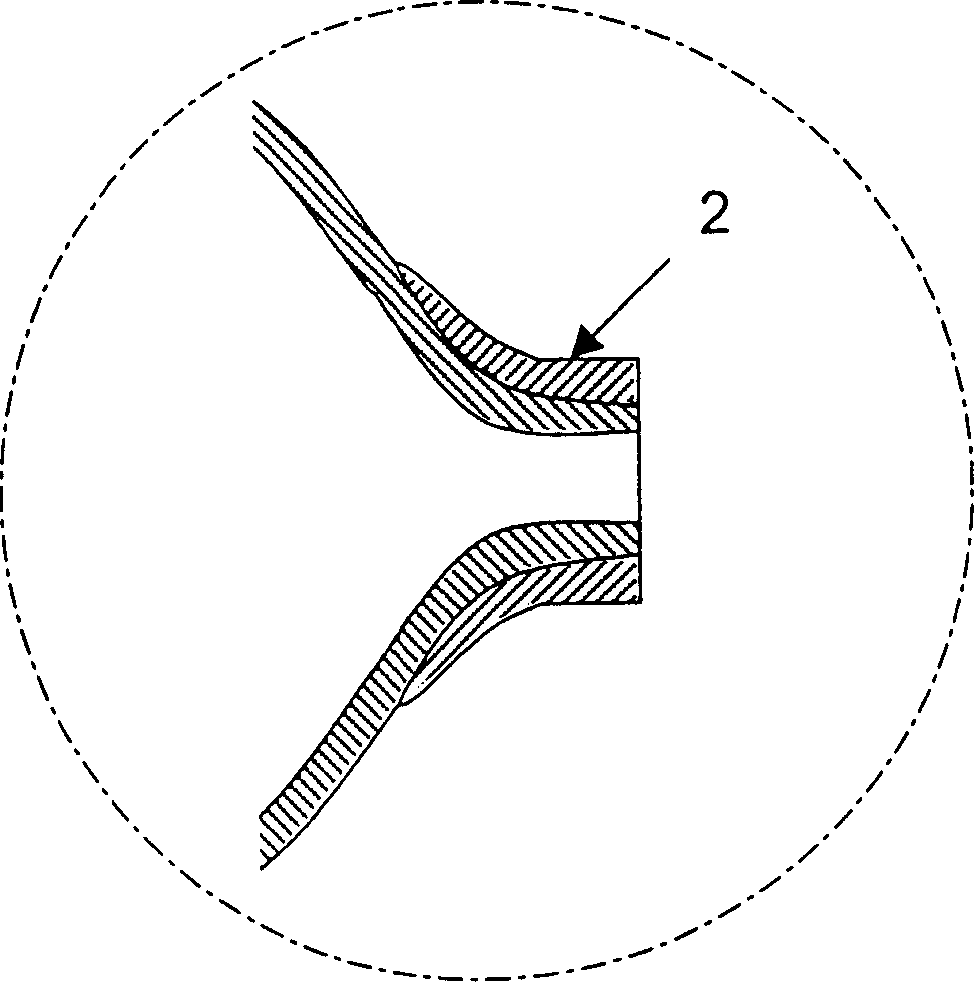
[0052] Such as figure 1 As shown, the first embodiment uses a hollow thermoplastic liner or bladder manufactured by extrusion injection molding or cast rotational molding processes. In the embodiment shown, the liner 1 or bladder is generally an elongated geometric structure that can be manufactured by extrusion injection moulding, the ends of which have one or more openings at the central axis of the part or at any other suitable location. Thus, the geometry of the bladder is not limited to rotational shapes, but any hollow thermoplastic shape capable of being manufactured by extrusion molding or cast rotational molding processes known in the art may be used. In addition to the use of thermoplastic liners1 or bladders, it is also possible to use short fiber reinforced thermoplastics or continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastics for preheating during extrusion injection molding and during non-isothermal bladder expansion molding , transfer and molding stages, the melt viscosi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com