Photovoltaic device
A photoelectric conversion device, transparent electrode technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, circuits, electrical components and other directions, can solve problems such as neglect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
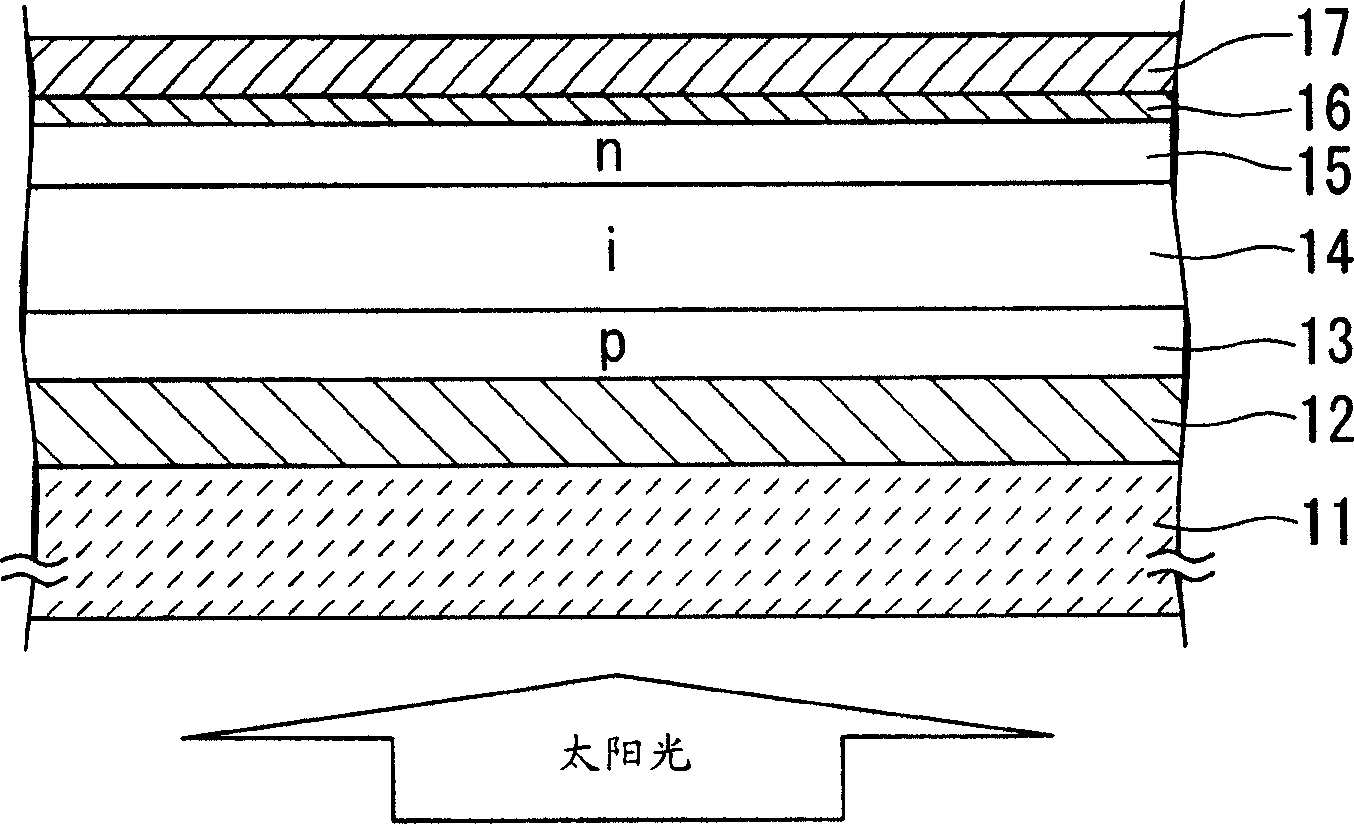
[0059] Below, refer to figure 1 A photoelectric conversion device according to a first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0060] The photoelectric conversion device of the present embodiment is of a type in which light is incident on a transparent insulating substrate, and its power generation layer is made of microcrystalline silicon.
[0061] (first process)
[0062] The first transparent electrode 12 is formed on the transparent insulating substrate 11 . On the transparent insulating substrate 11 , for example, white glass is used to indicate light transmission.
[0063] Ga (gallium)-added ZnO (zinc oxide) was used as the first transparent electrode 12 . In addition, it is preferable to form a reduction prevention film on the first transparent electrode 12 .
[0064] The transparent insulating substrate 11 was set in a DC spray coating apparatus, and a Ga-added ZnO film was formed on the transparent insulating substrate 11 by DC spray coating in a ...
no. 2 approach
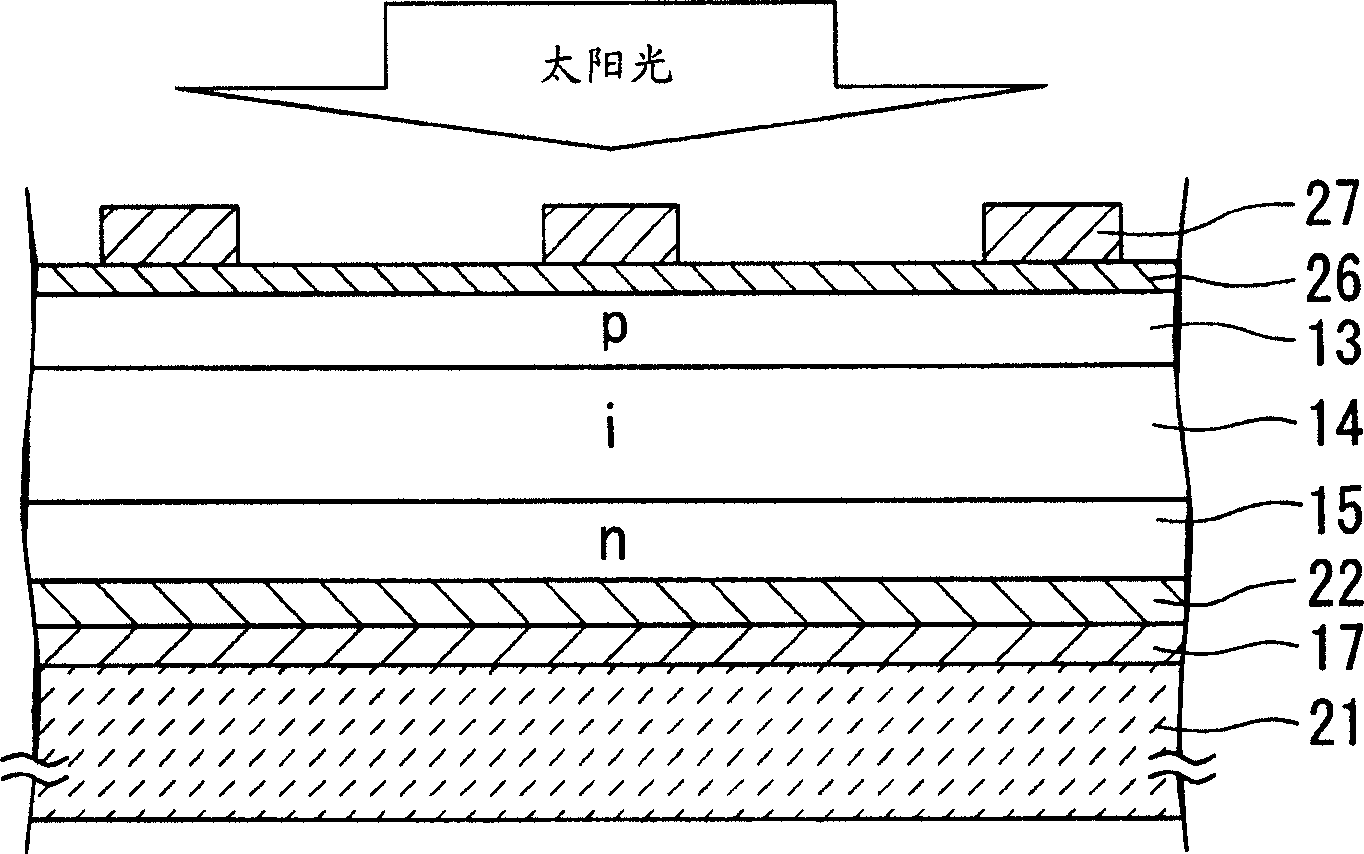
[0092] Below, refer to figure 2 A photoelectric conversion device according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0093] The photoelectric conversion device of this embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment in that the power generation layer is formed of microcrystalline silicon; the difference from the first embodiment is that it is also applicable when the insulating substrate is opaque, and that the light is transmitted from the collector in the opposite direction. Type of side incidence.
[0094] (first process)
[0095] The backside electrode 17 and the first transparent electrode 22 are formed on an opaque insulating substrate 21 that does not transmit light. For the opaque insulating substrate 21, for example, a stainless steel plate is used. Meanwhile, instead of the opaque insulating substrate 21 , soda glass (blue plate (blue plate)) may be used.
[0096] Ag or Al is used as the backside electrode 17 . As in the first...
no. 3 approach
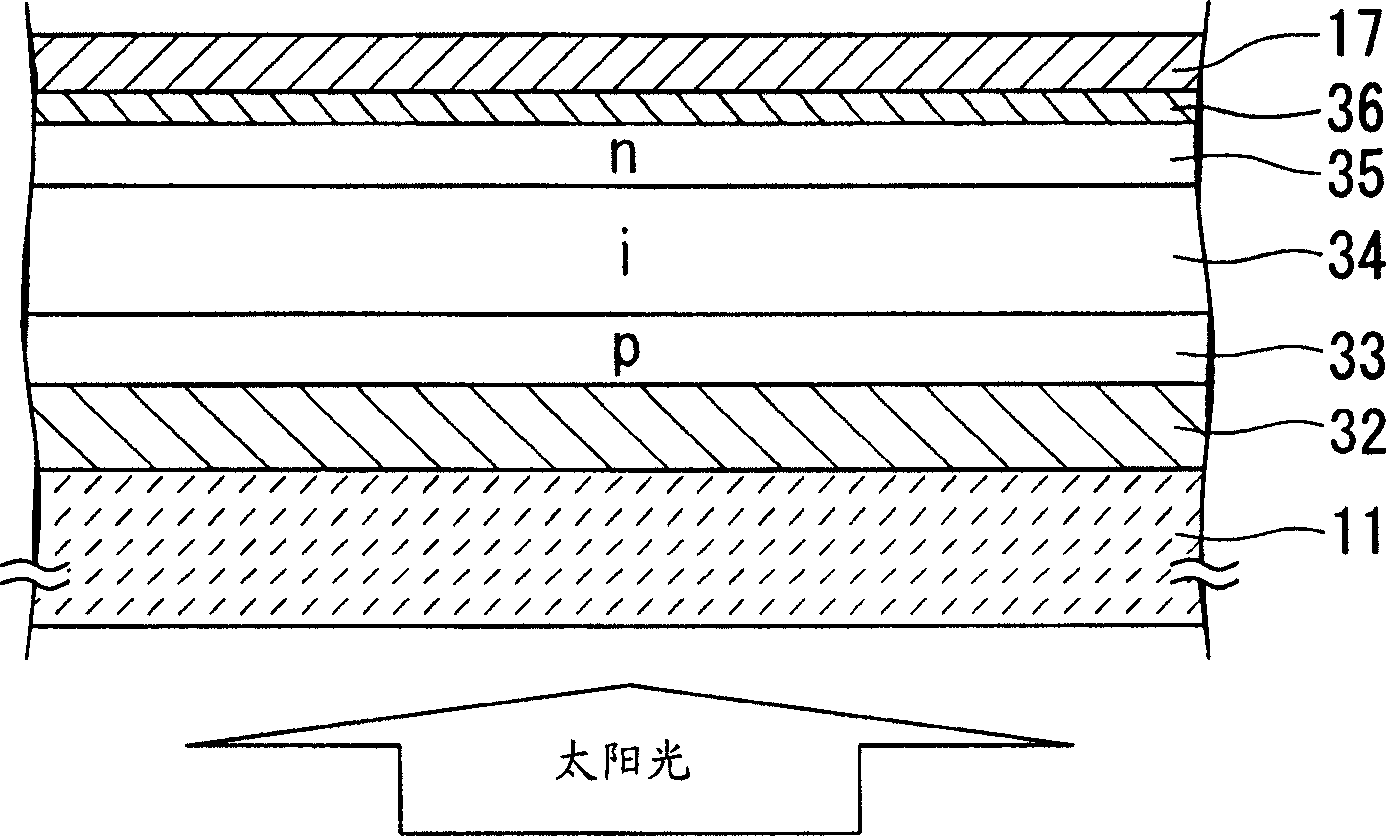
[0112] Below, refer to image 3 A photoelectric conversion device according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0113] The photoelectric conversion device of this embodiment differs from the first and second embodiments in that the power generation layer is formed of amorphous silicon, and is of the same type as the first embodiment in that light is incident on a transparent insulating substrate.
[0114] (first process)
[0115] The first transparent electrode 32 is formed on the transparent insulating substrate 11 . On the transparent insulating substrate 11 , for example, white glass is used to indicate light transmission.
[0116] Using SnO 2 (tin dioxide) as the first transparent electrode 32 .
[0117] Set the transparent insulating substrate 11 in the atmospheric pressure thermal CVD device, with SnCl 4 , water vapor (H 2 O), hydrogen fluoride (HF) as raw materials to form SnO on the transparent insulating substrate 11 2 .
[0118...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com