Glycerol channel protein gene deleted brewing microzyme strain capable of reducing glycerol output and increasing ethanol output and construction method thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and channel protein, which is applied in the field of Saccharomyces cerevisiae biological fermentation, can solve the problems of long fermentation period, environmental pollution, and high fermentation by-products, reduce the production of glycerol by-products, solve high production costs, and increase ethanol production Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] (1) Acquisition of haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae and deletion of URA3 gene
[0038] Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) can exist in nature both in haploid and diploid form. Under normal circumstances, it will sprout and multiply in the state of vegetative body; the vegetative body can be haploid (n) It can exist as a diploid (2n); it can only reproduce sexually under certain environmental conditions. One ascus produces four ascus buns, two of which are type a and two are type α. .
[0039] The formation of ascospores in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Take appropriate amount of newly activated diploid S. cerevisiae cells and spread them evenly on the ascospore-producing medium with potassium acetate, and culture them at 28°C for 2 days. Scrape an appropriate amount of yeast cells from the coating, dissolve them in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube filled with 50μl sterile water, add 5μl zymolyase at a concentration of 15mg / ml to digest the ascos wall at 37°C for 20min to form Sacc...
Embodiment 2
[0068] (1) Acquisition of haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae and deletion of URA3 gene
[0069] Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospore formation: Take appropriate amount of newly activated diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) cells uniformly spread on potassium acetate ascospore production medium, culture at 26 ℃ for 3 days, in the medium yeast Scrape an appropriate amount of yeast cells from the coating, dissolve them in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube containing 50μl of sterile water, add 10μl of zymolyase at a concentration of 10mg / ml to digest the ascosal wall at 37°C for 10min to form Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospores Solution
[0070] Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospore resolution: slowly add 1ml of sterile water to the centrifuge tube containing the ascospore solution of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, invert for 4min, take 50μl of the liquid, drop it on the edge of the YPD plate, tilt the plate to make the cells The liquid forms a strip on the edge of the plate. After drying, the...
Embodiment 3
[0083] (1) Acquisition of haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae and deletion of URA3 gene
[0084] Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospore formation: Take appropriate amount of newly activated diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S. cerevisiae) cells uniformly spread on potassium acetate ascospore production medium, culture at 30 ℃ for 2 days, in the medium yeast Scrape an appropriate amount of yeast cells from the coating, dissolve them in a 1.5ml centrifuge tube containing 50μl of sterile water, add 3μl of zymolyase at a concentration of 20mg / ml to digest the ascus wall at 37°C for 30min to form Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospores Solution
[0085] Resolution of ascospores of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the steps are the same as in Example 2;
[0086] Deletion of URA3 gene of KAM-19 strain: the same steps as in Example 1;
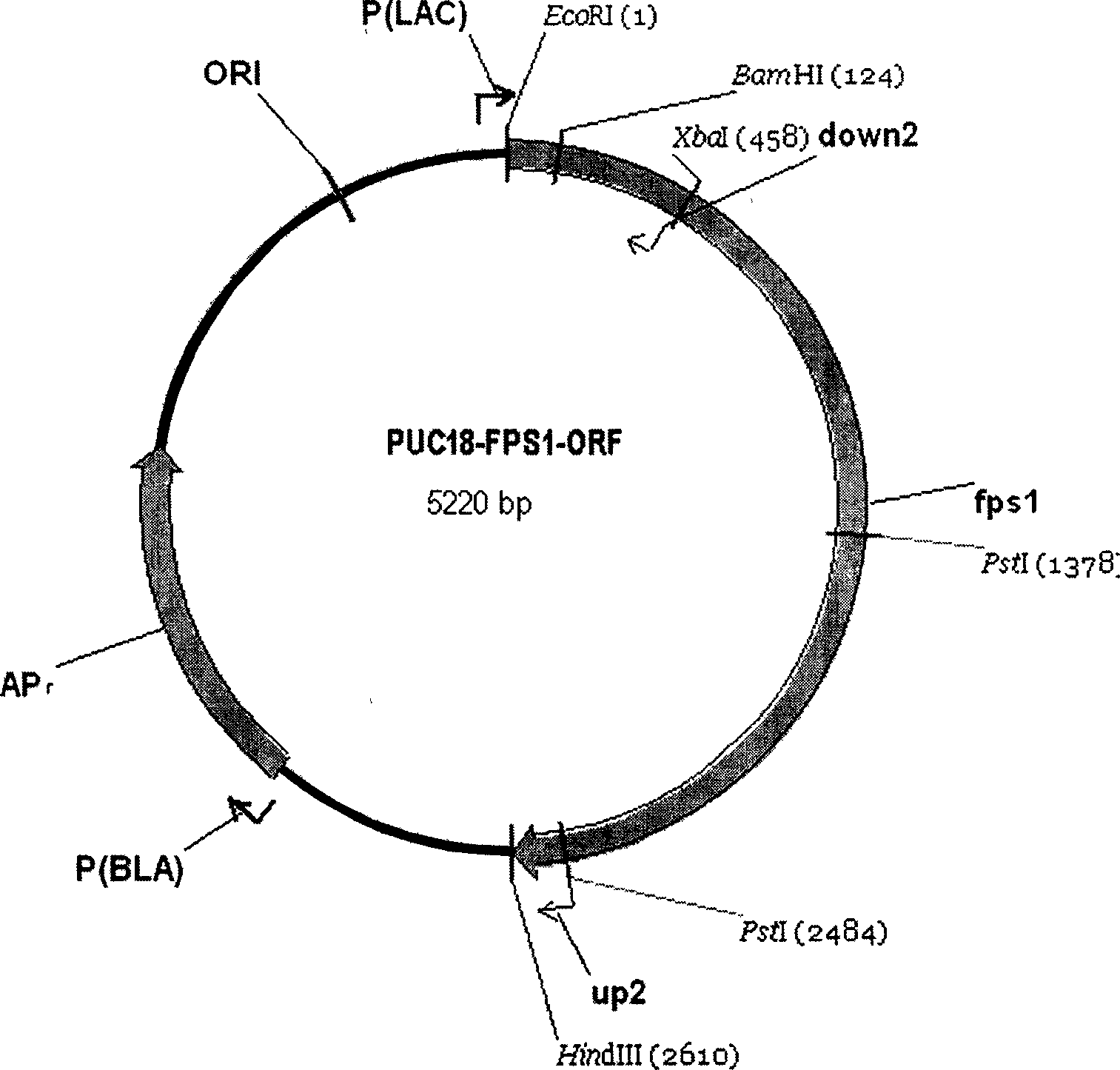
[0087] (2) Construction of PUC18-FPS1-ORF plasmid
[0088] Preparation of yeast chromosomes: the steps are the same as in Example 2;
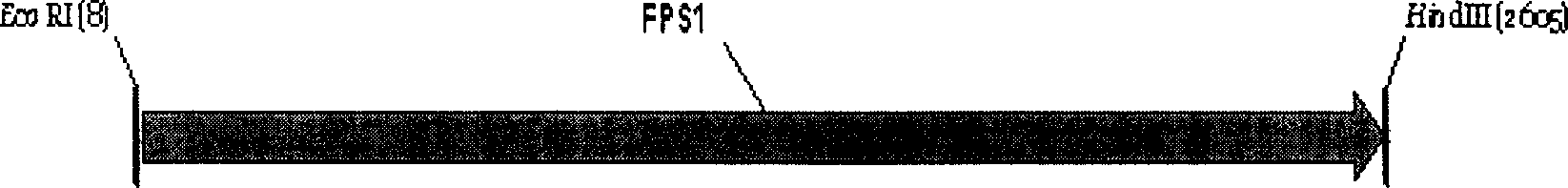
[0089] Amplify the FPS1-ORF gene: the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com