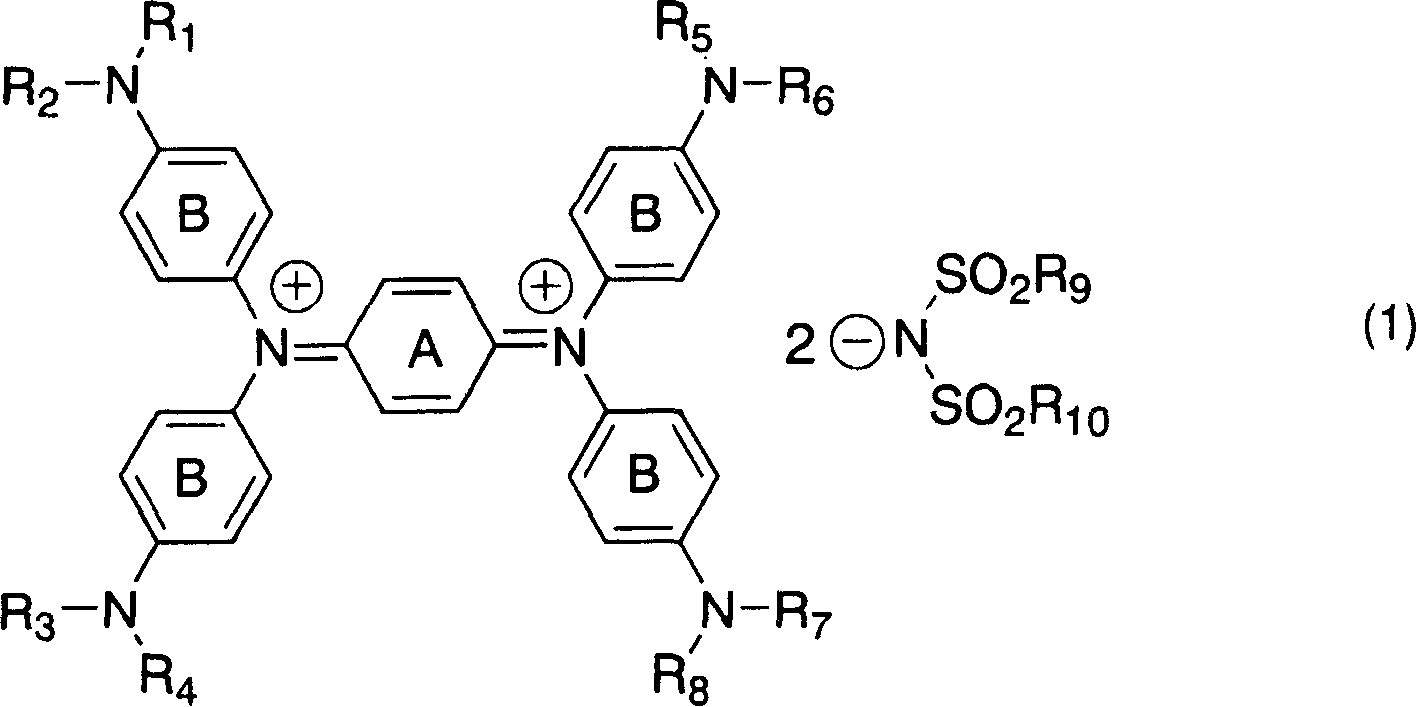
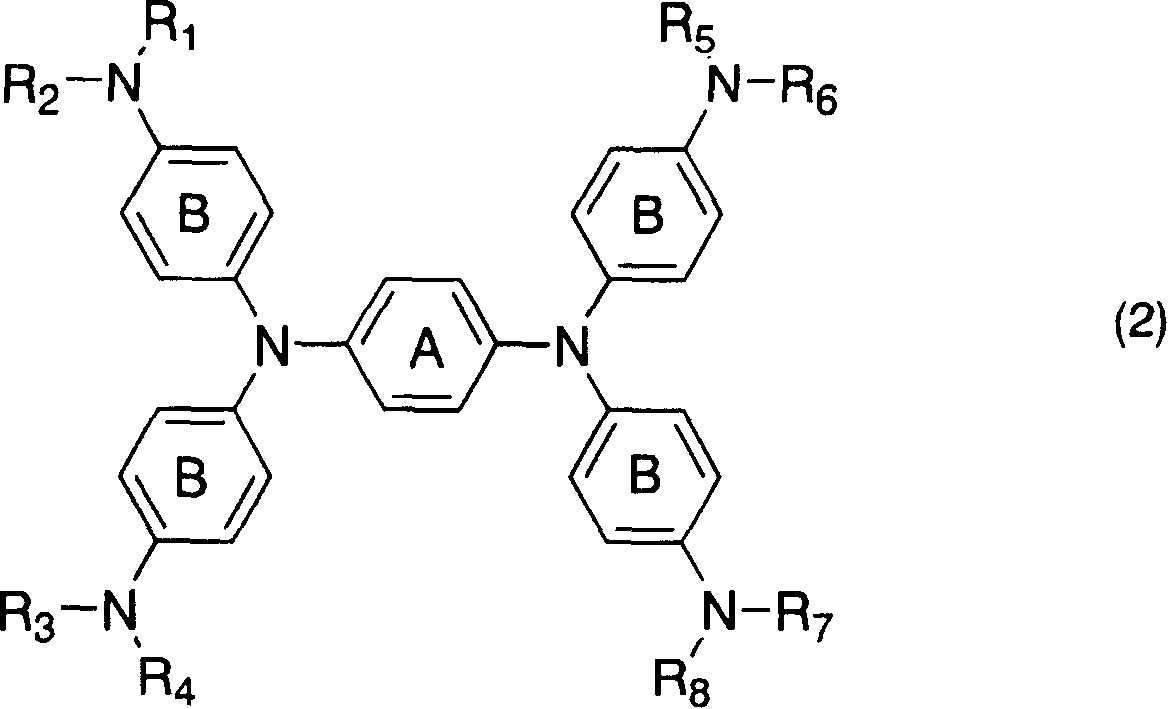
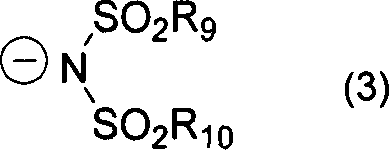Diimonium salt compound and use thereof
A compound, diimonium technology, applied in the field of diimonium compounds, can solve problems such as low molar absorption coefficient and insufficient counter ions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0122] (compound No.1 in preparation table 1)
[0123] Add 3 parts of N, N, N', N'-tetrakis[p-di(n-butyl)aminophenyl]-p-phenylenediamine to 16.5 parts of DMF, heat to 60°C for dissolution, and then dissolve the solution in 16.5 1.16 parts of silver nitrate and 2.19 parts of potassium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonate)imide in 1 part of DMF were added to the solution prepared above, heated and stirred for 30 minutes. After the insoluble matter was separated by filtration, water was added to the reaction solution, and the precipitated crystals were filtered out, washed with water, and dried to obtain 4.3 parts of the target compound No.1.
[0124] λmax: 1,102nm (in dichloromethane);
[0125] Melting point: about 170°C; thermal decomposition point (starting weight loss point): about 280°C (measured by TG-DTA)
preparation example 2
[0128] (compound No.2 in preparation table 1)
[0129] 4.3 parts of compound No.2 were obtained in the same manner as in Example 1, except that N, N, N', N'-tetrakis[p-di(isobutyl)aminophenyl]-p-phenylenediamine was used instead of N, N , N', N'-tetrakis[p-di(n-butyl)aminophenyl]-p-phenylenediamine.
[0130] λmax: 1,104nm (in dichloromethane);
[0131] Melting point: about 165°C; thermal decomposition point (starting weight loss point): about 282°C (measured by TG-DTA)
preparation example 3
[0134] (compound No.3 in preparation table 1)
[0135] Add 3.28 parts of N,N,N',N'-tetrakis[p-bis(cyanopropyl)aminophenyl]-p-phenylenediamine and 16.5 parts of DMF to a solution formed by dissolving 0.58 parts of sodium nitrate in 3 parts of water middle. The obtained reaction solution was heated to 60°C, and then 1.16 parts of silver nitrate dissolved in 16.5 parts of DMF was added to the prepared reaction solution and stirred for 30 minutes. After the insoluble matter was separated by filtration, 2.19 parts of bis(trifluoromethanesulfonic acid)imide potassium salt was added to the reaction solution, which was stirred for 3 hours and water was added. Precipitated crystals were filtered, washed with water, and dried to obtain 4.5 parts of target compound No.3.
[0136] λmax: 1,064nm (in dichloromethane);
[0137] Melting point: about 180°C; thermal decomposition point (starting weight loss point): about 282°C (measured by TG-DTA)
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com