Coking waste water zero discharge treatment process
A technology for coking wastewater and treatment process, which is applied in water/sewage treatment, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, degassed water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing costs and reducing the amount of treated water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment
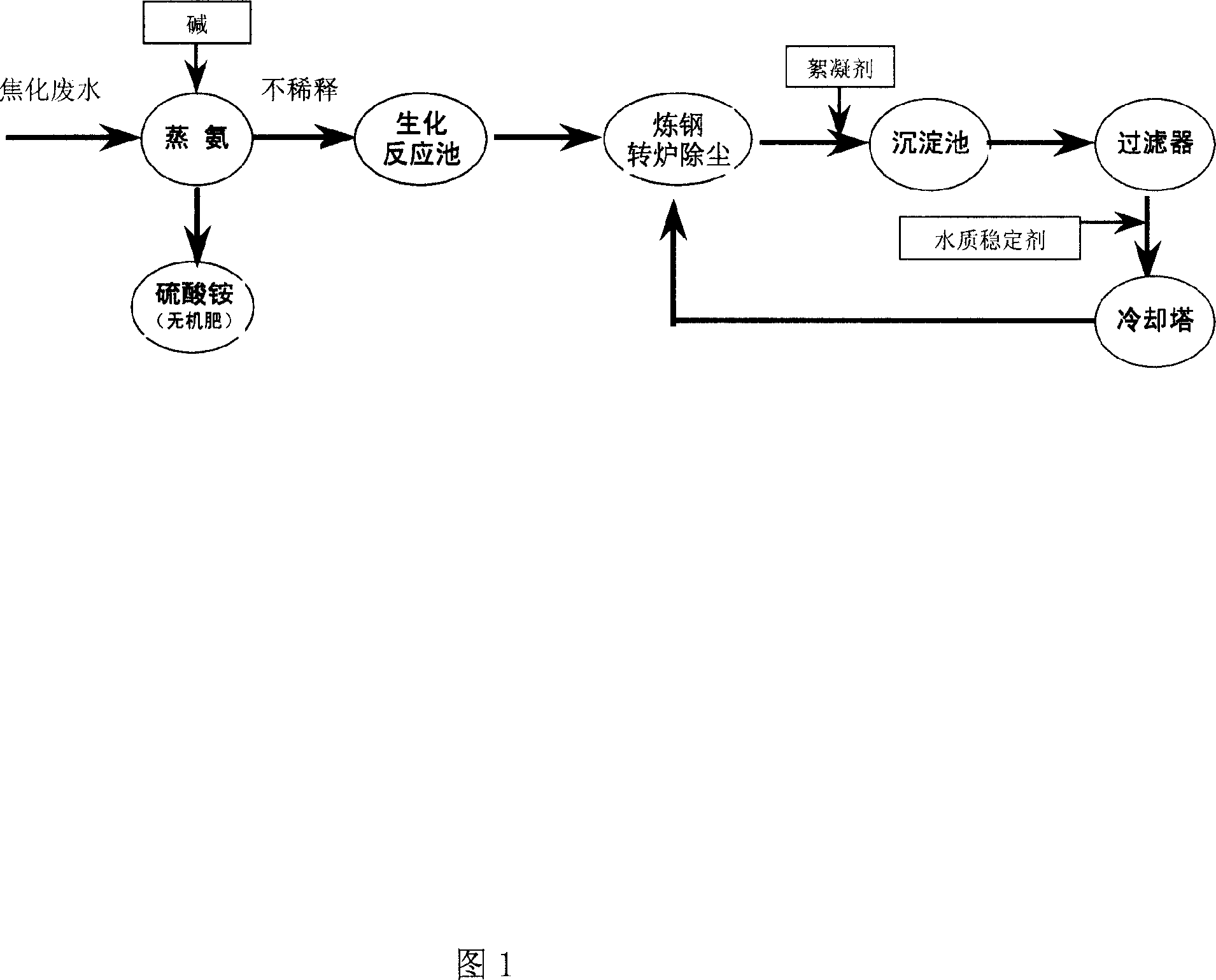
[0017] A coking plant 50m 3 / h coking wastewater zero discharge treatment process:
[0018] 1. The coking wastewater first enters the ammonia distillation unit, adds sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH=12, heats the ammonia, and recovers ammonium sulfate at the same time. The content of ammonia nitrogen in the effluent is 815mg / L, the content of phenol is 907mg / L, and the content of cyanide is 48mg / L. L, COD is 3730mg / L.
[0019] 2. The effluent from ammonia distillation directly enters the biochemical reaction tank without dilution, and biodegrades ammonia nitrogen, phenol, cyanide, COD and other pollutants. The content of ammonia nitrogen in the treated water is 111mg / L, the content of phenol is 232mg / L, and the content of cyanide is 0.78mg / L, COD is 540mg / L.
[0020] 3. The biochemical effluent is reused for steelmaking converter dust removal. Converter dust and flue gas are further degraded through adsorption, catalytic oxidation, etc. under high temperature conditions of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com