Synthetic fibers modified with PTFE to improve performance
a synthetic fiber and performance technology, applied in the field of synthetic fibers modified with ptfe to improve performance, can solve the problems of poor ultraviolet (uv) resistance characteristics, many polyesters, teraphthalates, and difficulties in achieving optimal performance, and achieve the effects of improving the bonding coating substrate conditions, improving the bonding effect, and enhancing the fiber and/or fabric dullness and resistance to abrasion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
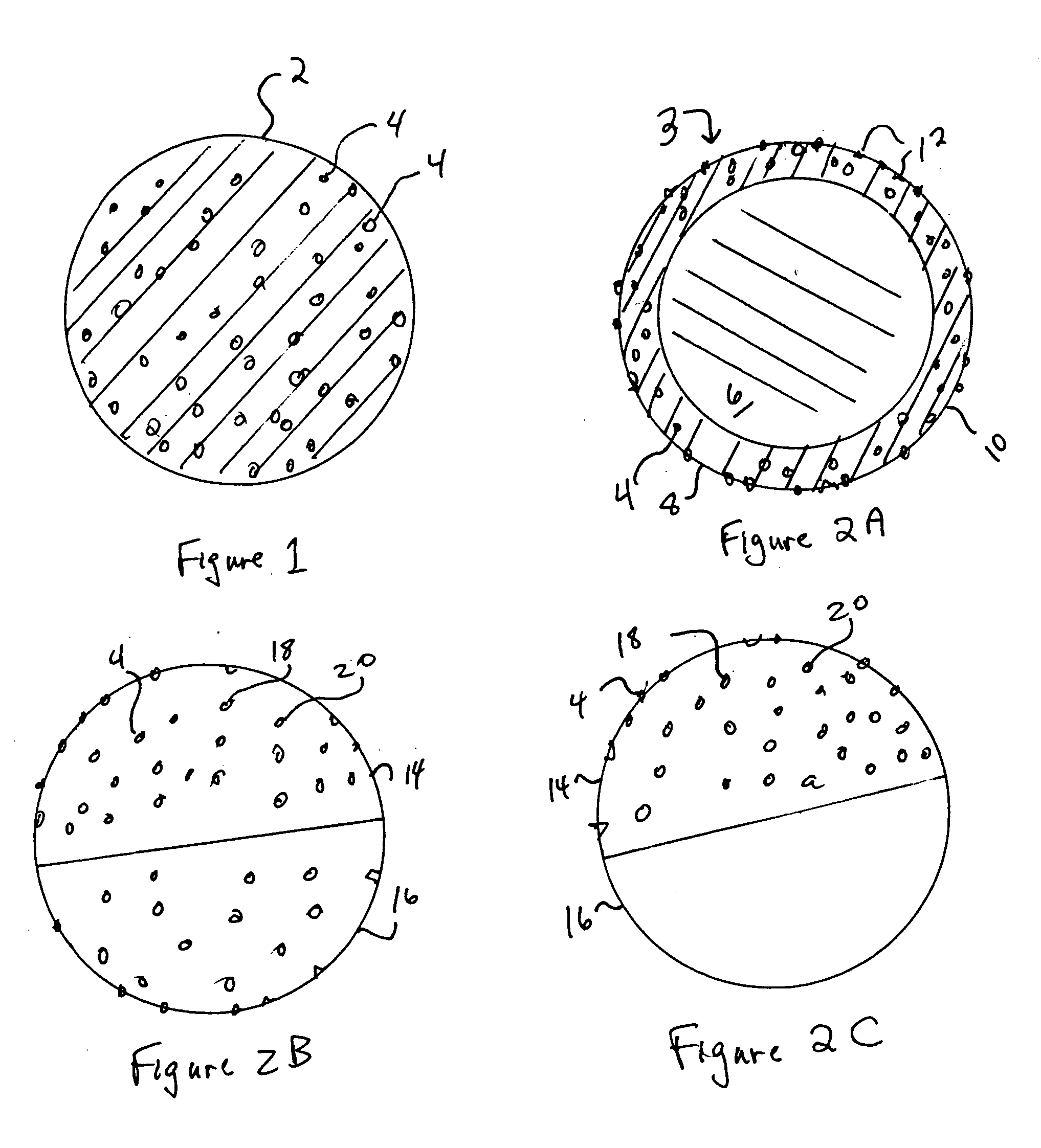
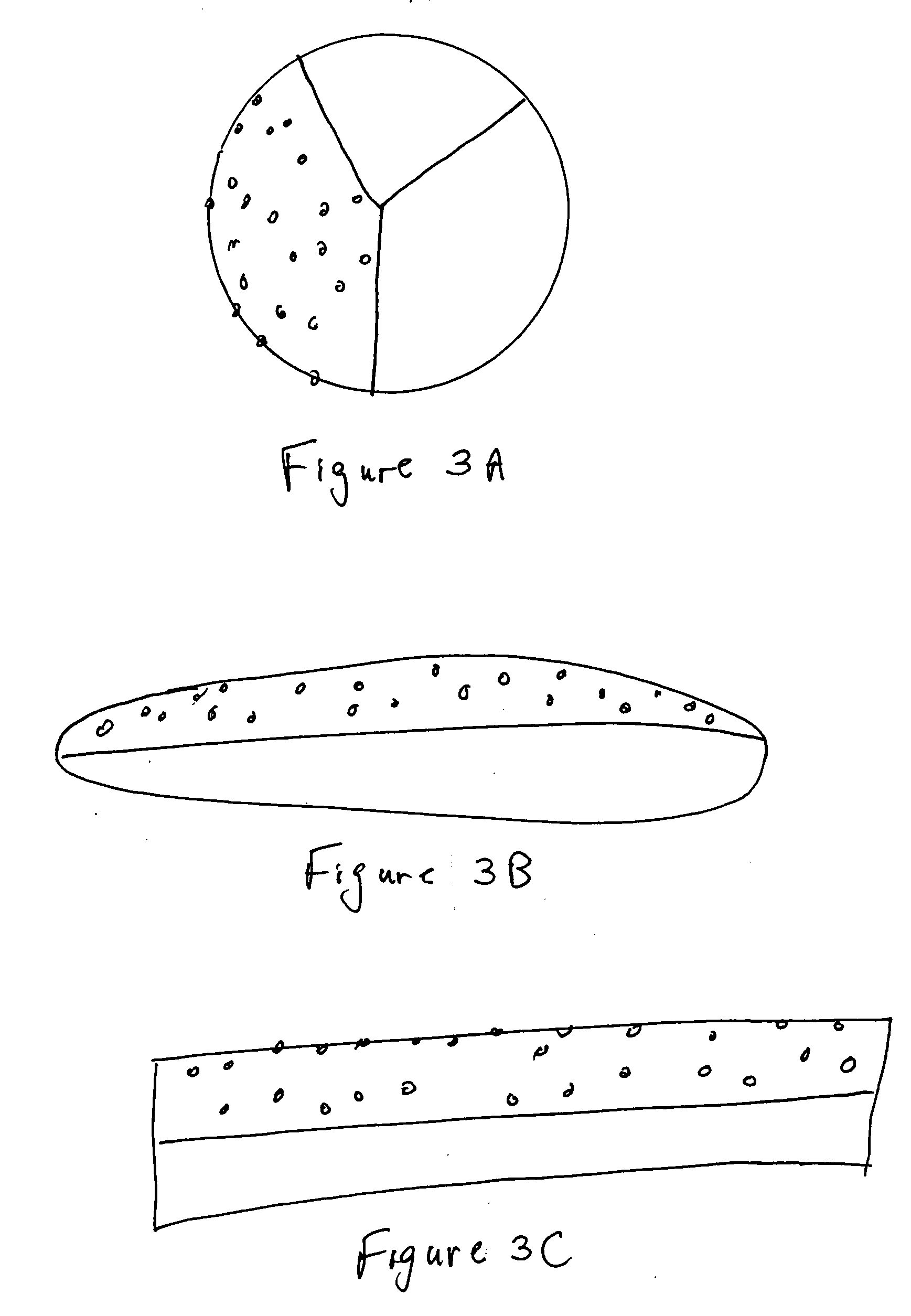
[0012] The present invention provides synthetic fibers enhanced with PTFE and fabrics made from same, as well a methods for producing the enhanced fibers.
[0013] By adding fine particles of PTFE to a polymer such as, for example, polyesters (e.g., PET), polyolefins (e.g. polypropylene), nylon and acrylics during a melt stage of an extrusion or other melt stage, or by other means without melting, UV resistance and other properties of the fiber can be improved significantly. Selecting for introduction into the polymer PTFE particles in a range of size such that the particle size is in the range of the wavelength of the UV light to be resisted enhances the fiber's ability to withstand UV-induced degradation.
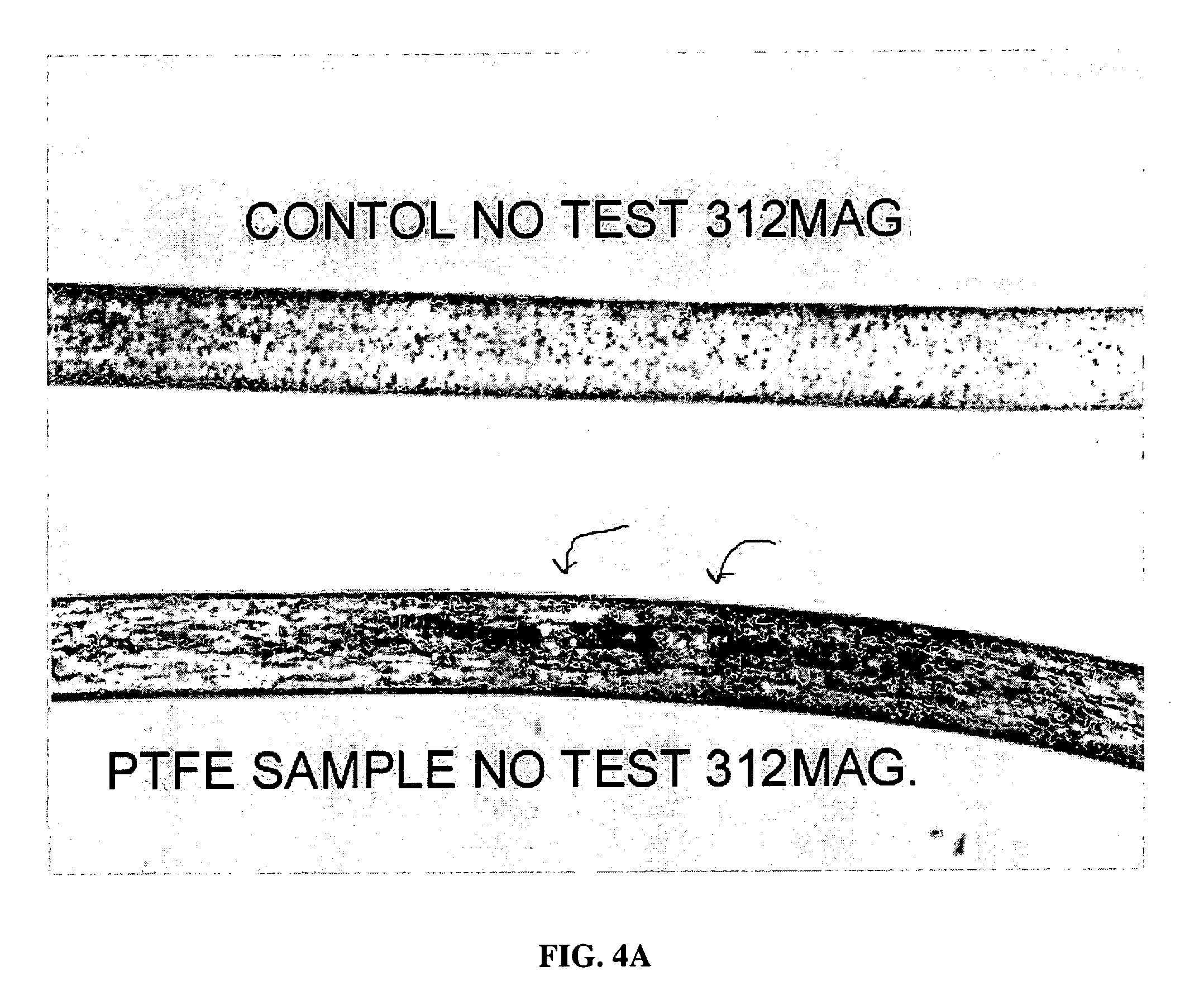
[0014] Experiments were conducted to demonstrate this enhanced resistance to UV. Typical PET starts to degrade at 250 kilojoules (kJ) of exposure. PTFE particles in the range of 0.2 to 0.5 μm (microns) were added to the PET in the range from about 0.8 to about 2.5% by weight. At 2 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com