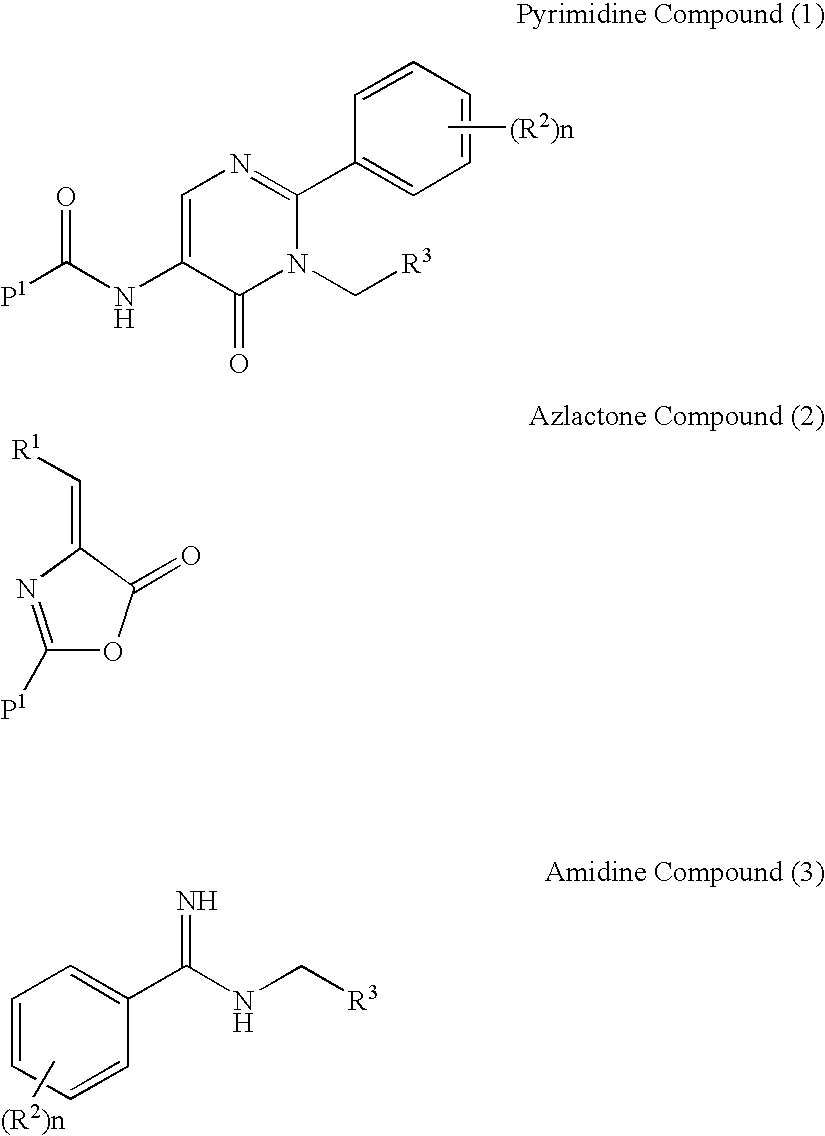
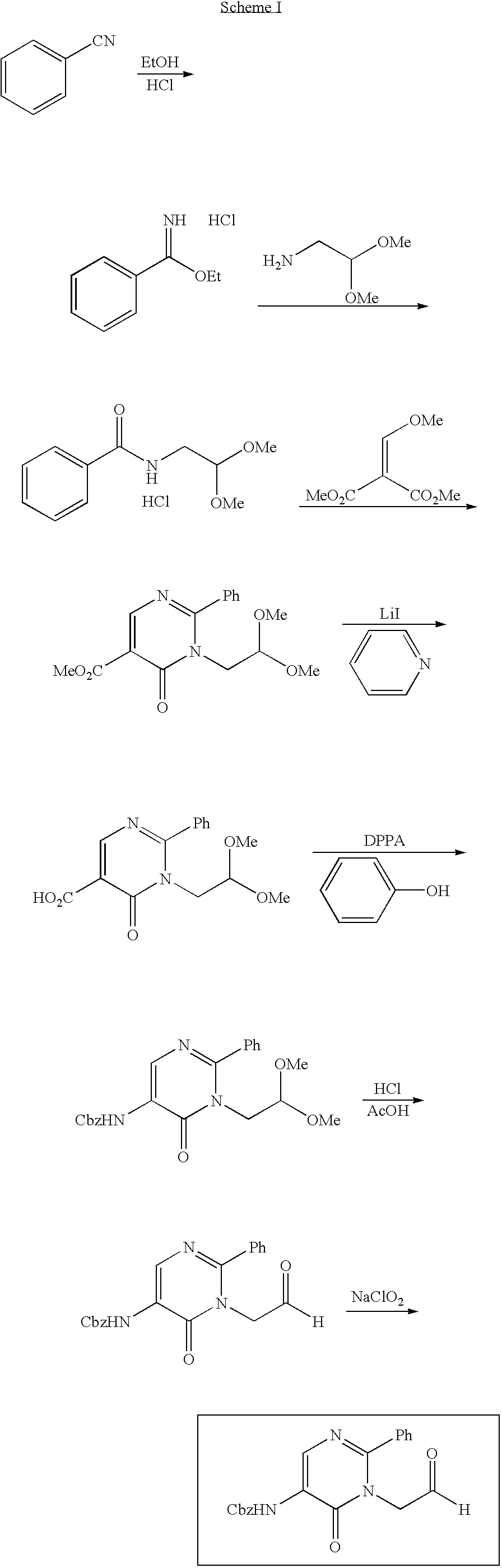
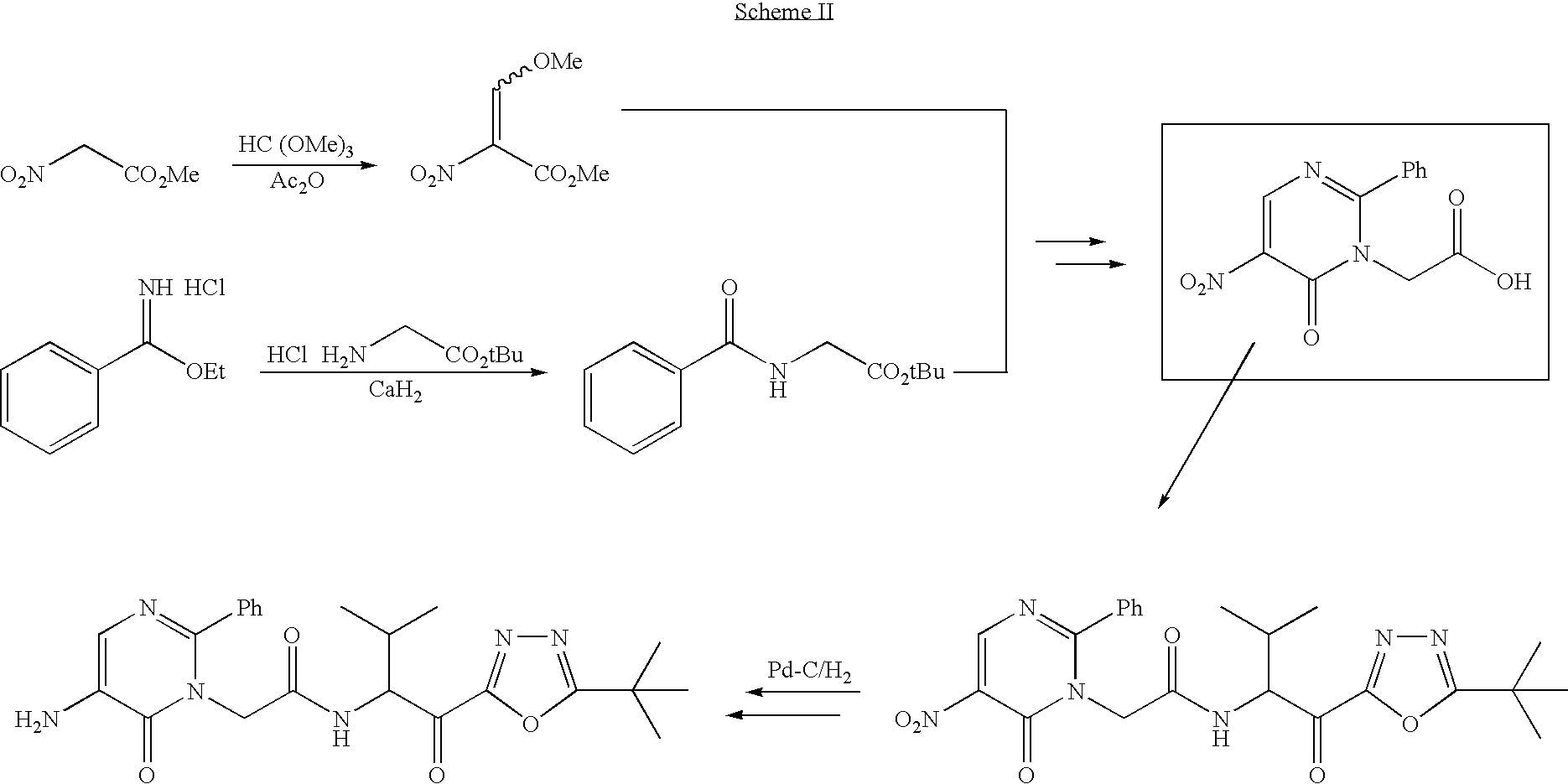
Process for preparing pyrimidine compound
a technology of pyrimidine and compound, applied in the field of compound, can solve the problems of inability to be said to be always industrially suitable, and conventional methods of preparing compounds used as enzyme inhibitor intermediates, etc., to achieve safe preparation, low cost, and good yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0144] Hippuric acid (5.0 g, 27.9 mmol), triethyl ortho-formate (5.4 g, 36.3 mmol), and acetic anhydride (8.6 g, 83.7 mmol) were stirred, and refluxed for 3 hours. Subsequently, the mixture was cooled, toluene (50 ml) and ethanol (4 ml) were added, and the mixture was concentrated. Further, toluene (30 ml) was added and the mixture was concentrated under reduced pressure, after which hexane (10 ml) was added, and the residue was crystallized under ice cooling. The precipitate was filtered and washed with hexane, and the mother liquor was concentrated, after which hexane (2 ml) was added, and the residue was crystallized in the same manner to yield a second batch of crystals. The obtained crystals were combined and dried under reduced pressure to yield a 4-ethoxymethylene-2-phenyl-5-azlactone crystal (4.24 g, 19.5 mmol).
[0145]1H-NMR(CDCl3)δppm: 1.48-1.51 (3H,t,J=7.1 Hz), 4.42-4.47(2H,q,J=7.1 Hz), 7.35(1H, s), 7.45-7.56(3H,m), 8.06-8.09(2H,m).
example 2
[0146] N-(tert-butoxycarbonylmethyl)phenylamidine hydrochloride (4.2 g, 15.6 mmol) was stirred in toluene (6 ml), and water (6 ml), and sodium carbonate (7 g) was added. After the organic layer was separated, the water layer was extracted by the addition of toluene (5 ml), and the organic layers were combined, washed with saline, and dried with sodium sulfate. To the solution, a solution of 4-ethoxymethylene-2-phenyl-5-azlactone (2.60 g, 12.0 mmol) in acetonitrile (4 ml) was added drop by drop over 30 minutes, and this mixed solution was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour and at 80° C. overnight. Subsequently, the mixed solution was washed with 1N aqueous hydrochloric acid, saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate, and saline, the organic layer was concentrated, hexane (12 ml) was added, and the residue was crystallized. After stirring at room temperature, the crystals were collected by filtration and dried to yield 1-(tert-butoxycarbonylmethyl)-6-oxo-2-phenyl-5-benzoylamino-1,6-dih...
example 3
[0149] To acetylglycine (0.2 g, 1.7 mmol), triethyl ortho-formate (0.76 g), acetic anhydride (1.74 g), and ethyl acetate (1.5 ml) were added, and the mixture was stirred at 95° C. overnight, after which the reaction solution was washed with saline, and the organic layer was concentrated, after which toluene (3 ml) was added, and the mixture was concentrated to dryness. N-(tert-butoxycarbonylmethyl)phenylamidine hydrochloride (2.22 mmol) was stirred in toluene (6 ml) and water, and sodium carbonate (1.6 g) was added. After the organic layer was separated, the water layer was extracted by the addition of toluene (3 ml), and the organic layers were combined, washed with saline, and dried with sodium sulfate. To the obtained solution, the previously obtained dry solid was added, and the mixture was stirred at 60° C. overnight and 80° C. overnight. The reaction solution was washed with 1N hydrochloric acid, saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate, and saturated saline, and the organi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com