Nitrogen oxide decomposing element and nitrogen oxide decomposing apparatus including the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
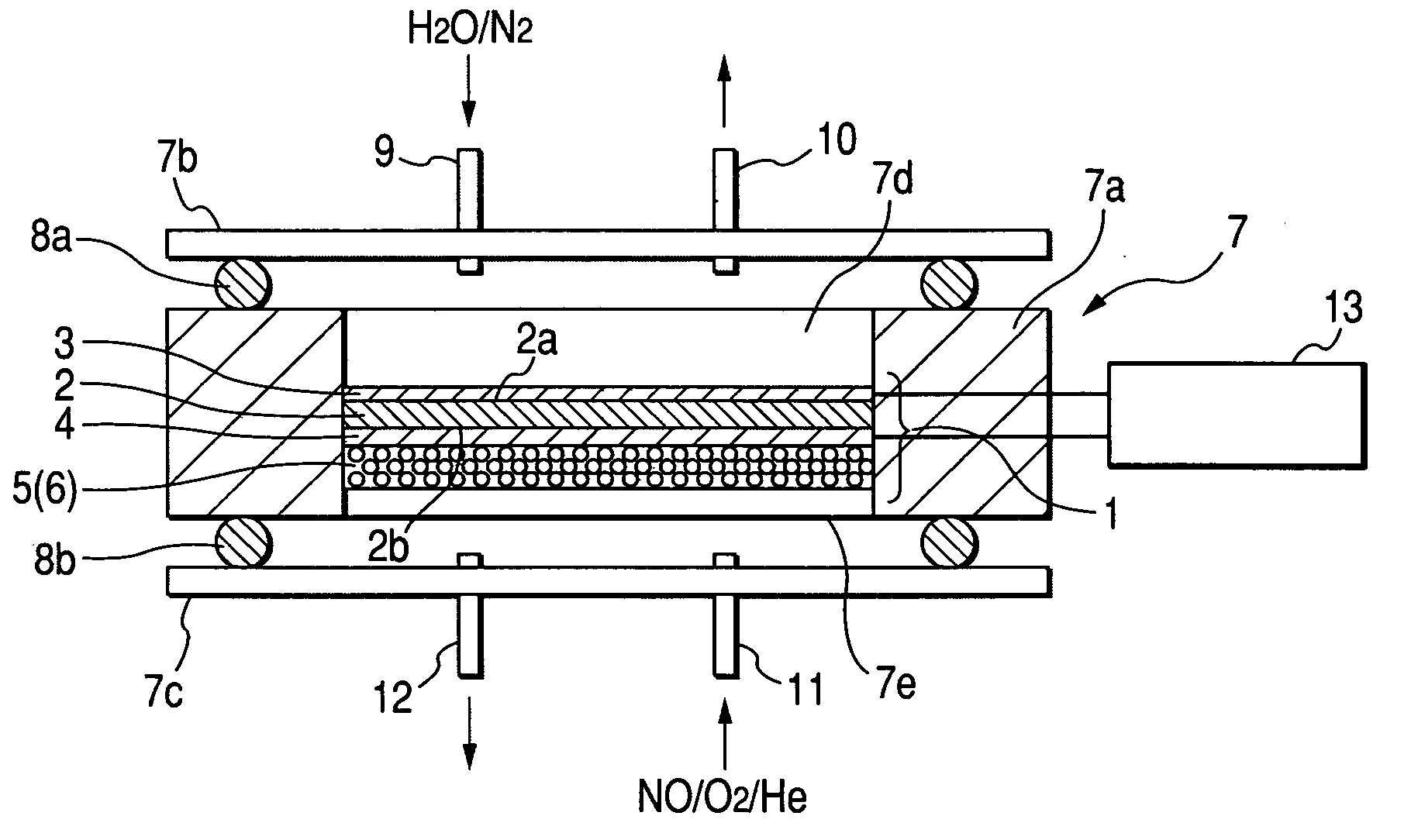
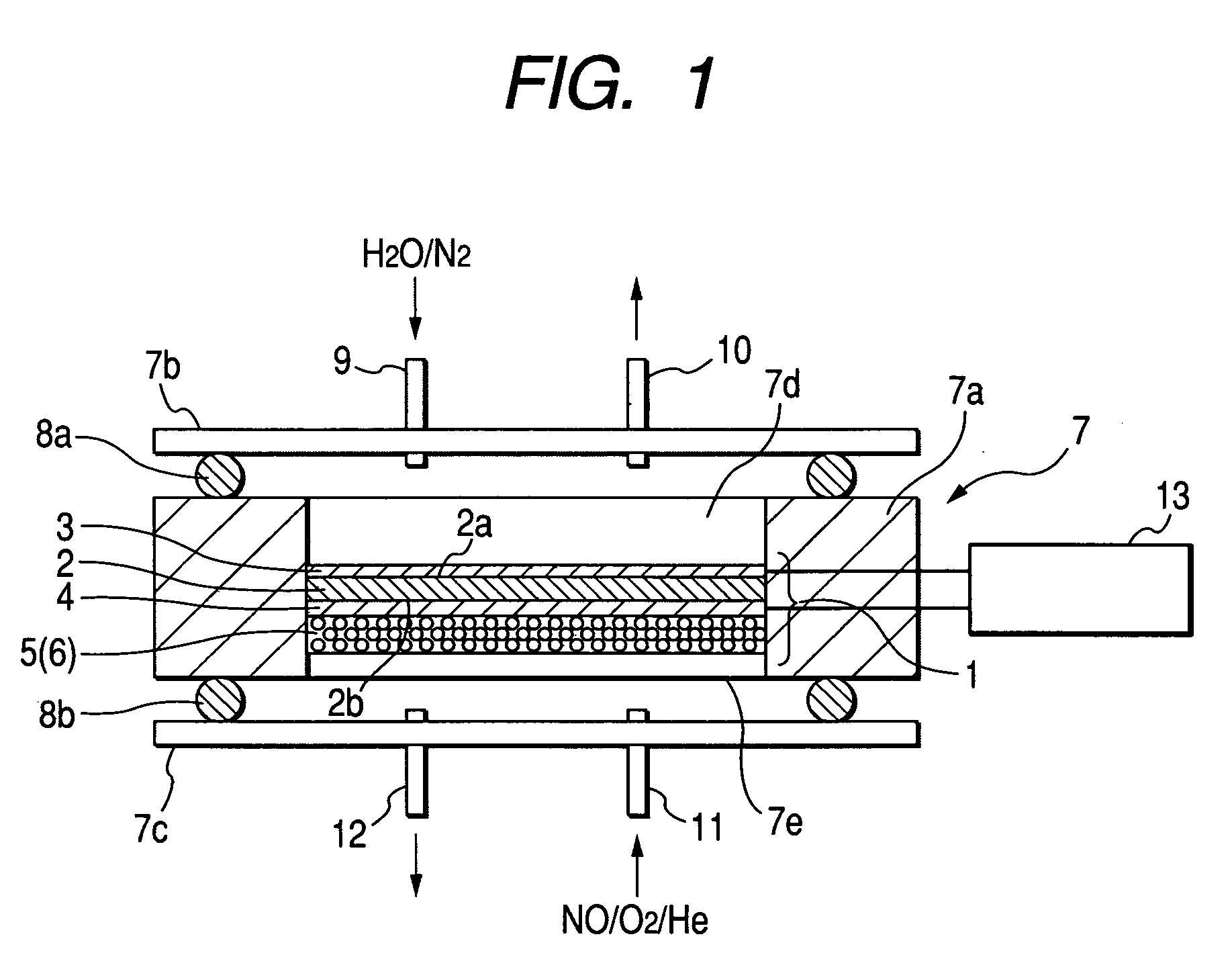
[0020]FIG. 1 is a schematic view showing a nitrogen oxide decomposing element of embodiment 1 of the invention and a structure of a nitrogen oxide decomposing apparatus.
[0021] The nitrogen oxide decomposing apparatus of embodiment 1 includes a nitrogen oxide decomposing element 1 and a frame 7 for housing it. The nitrogen oxide decomposing element 1 includes a conductive solid electrolyte film 2 for selectively allowing a hydrogen ion to pass through, a first electrode layer 3 made of an electronic conductivity base material disposed to be in contact with a part of a surface of the solid electrolyte film 2 and a catalyst (hereinafter referred to as an anodic catalyst) for accelerating anodic oxidation, a second electrode layer 4 made of an electronic conductivity base material disposed to be in contact with the other part of the surface of the solid electrolyte film 2 and a catalyst (hereinafter referred to as a cathodic catalyst) for accelerating cathodic oxidation, and a platinum...
embodiment 2
[0037] A nitrogen oxide decomposing element of embodiment 2 (not shown) is such that a mixed layer including an electronic conductivity base material, a solid electrolyte film, a platinum group catalyst and a cathodic catalyst is disposed between the solid electrolyte film 2 of the nitrogen oxide decomposing element 1 (see FIG. 1) of embodiment 1 and the second electrode 4 and is brought into close contact therewith. This mixed layer can be formed by dispersing aplatinum group catalyst, a cathodic catalyst, a fine-grained electronic conductivity base material, and a fine-grained solid electrolyte film into a solution, heating them to evaporate volatile components, and combining the fine grain components with each other.
[0038] Since the electrochemical reactions described in embodiment 1 occur at an interface between each electrode and the solid electrolyte film, the amount of reaction and the reaction speed are increased in proportion to the area of the interface. In embodiment 2, ...
embodiment 3
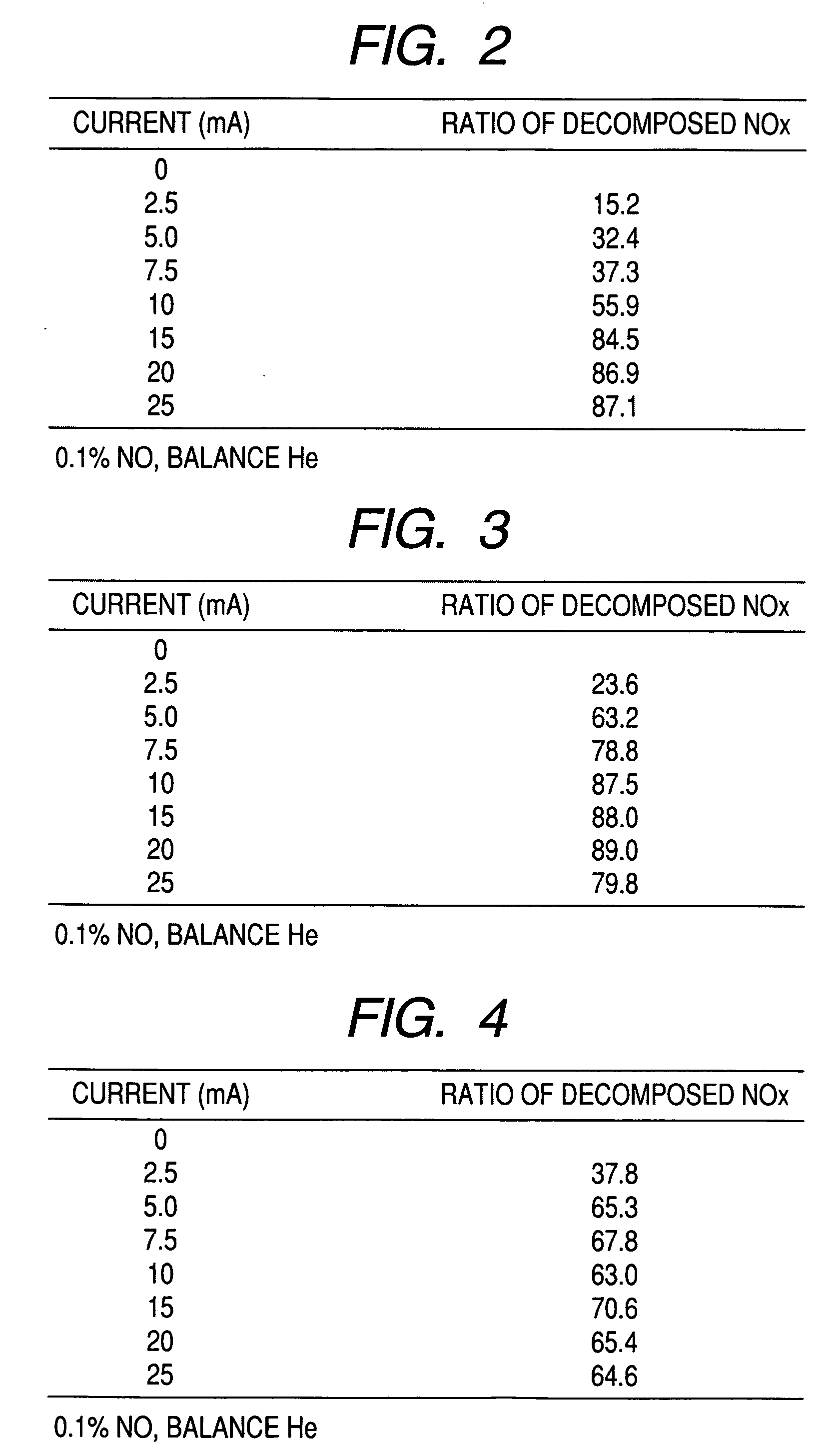
[0039]FIG. 6 is a schematic view showing a nitrogen oxide decomposing apparatus of embodiment 3. In the drawings, same or equivalent parts are denoted by the same reference numerals and their description will be omitted. The nitrogen oxide decomposing apparatus in this embodiment includes a nitrogen oxide sensor 14 for detecting the concentration of nitrogen oxide, and a power source / control device 15 for controlling the magnitude of a current flowing between a first and a second current layers 3 and 4 and an energization time in accordance with the concentration of the nitrogen oxide detected by the nitrogen oxide sensor 14. By this, it is possible to control the magnitude of the current flowing through the nitrogen oxide decomposing element 1 and the energization time in accordance with the concentration of the nitrogen oxide. Incidentally, it is desirable that the nitrogen oxide sensor 14 is disposed in the vicinity of a platinum group catalyst 6 supported by a metal oxide 5 at a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com