Methods and compositions comprising DNA damaging agents and p53
a technology of dna damaging agents and compositions, applied in the direction of dna/rna fragmentation, peptide/protein ingredients, viruses, etc., can solve the problems of cancer development, lung cancer mortality rate will remain high well into the 21st century, and current treatment methods for cancer, including radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, etc., to inhibit the tumorigenicity of h358 cells, great therapeutic
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of p53 Expression Vector
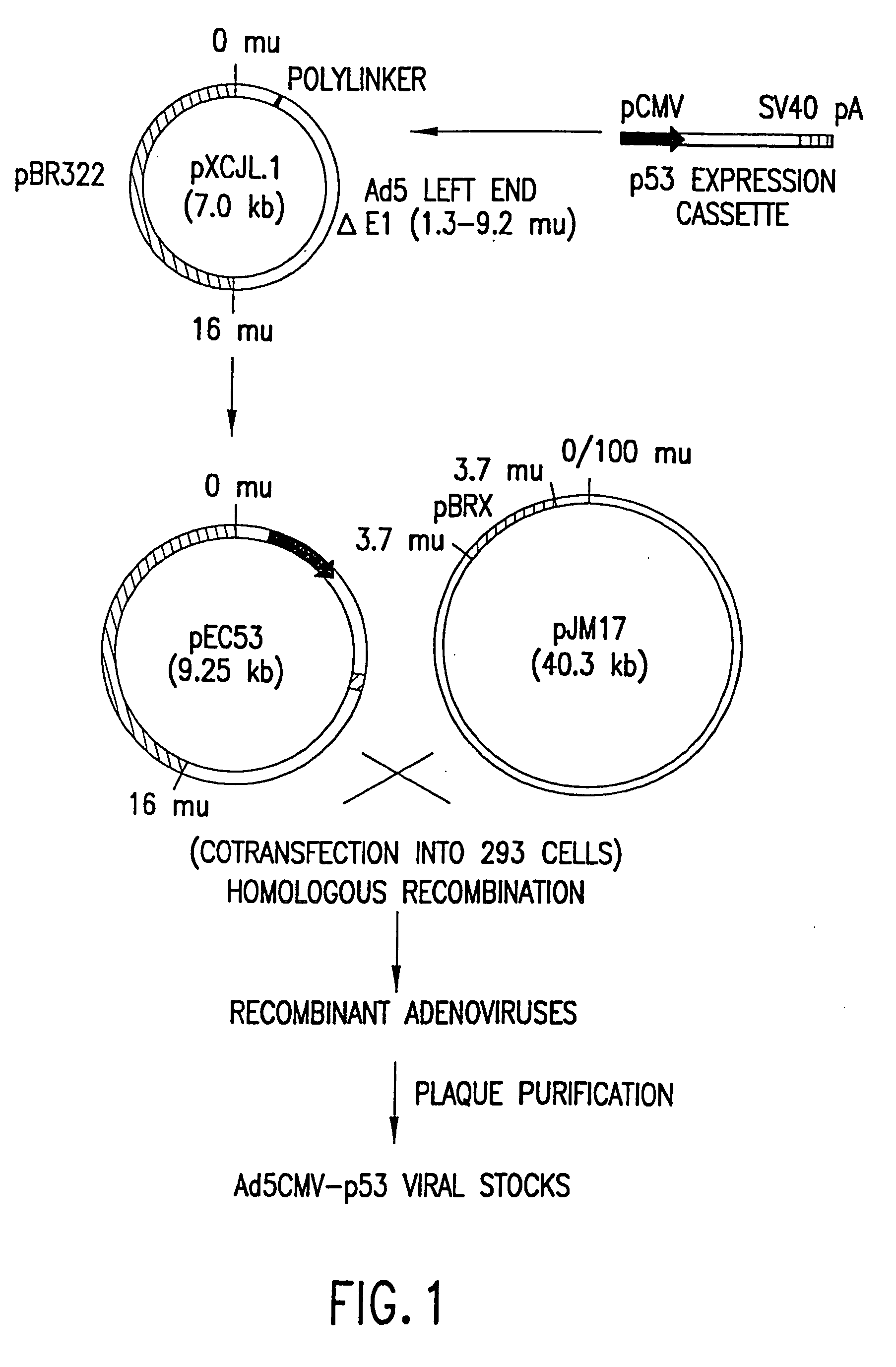
[0124] This example describes the construction of a p53 expression vector. This vector is constructed as indicated and is used to replace the E1 region (1.3-9.2 m.u.) of the Adenovirus strain Ad5 genome and employed to construct the Adenovirus virion described in Example 2.
[0125] The p53 expression cassette shown in FIG. 1, which contains human cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter (Boshart, et al., 1985), p53 cDNA, and SV40 early polyadenylation signal, was inserted between the Xba I and Cla I sites of pXCJL1 (provided by Dr. Frank L. Graham, McMaster University, Canada).
[0126] The genome size is about 35.4 kb, divided into 100 map units (1 m.u. 0.35 kb). The p53 expression cassette replaced the E1 region (1.3-9.2 m.u.) of the Ad5 genome.
[0127] Primer 1 has the sequence 5′-GGCCCACCCCCTTGGCTTC-3′ (SEQ ID NO:1) and is located in the first intron downstream of the human CMV major IE gene promoter (Boshart, et al., 1985). Primer 2 has the sequence 5′-T...
example 2
Generation and Propagation of Recombinant p53 Adenovirus
[0128] This example describes one method suitable for generating helper-independent recombinant adenoviruses expressing p53. The molecular strategy employed to produce recombinant adenovirus is based upon the fact that, due to the packaging limit of adenovirus, pJM17 cannot form virus on its own. Therefore, homologous recombination between the p53 expression vector plasmid and pJM17 within a transfected cell results in a viable virus that can be packaged only in cells which express the necessary adenoviral proteins.
[0129] The method of this example utilizes 293 cells as host cells to propagate viruses that contain substitutions of heterologous DNA expression cassettes at the E1 or E3 regions. This process requires cotransfection of DNA into 293 cells. The transfection largely determines efficiency of viral propagation. The method used for transfection of DNA into 293 cells prior to the present invention was usually calcium-ph...
example 3
Confirming the Identity of Recombinant Adenovirus
[0132] This example illustrates a new polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for confirming the identity of recombinant virions following cotransfection of the appropriate cell line.
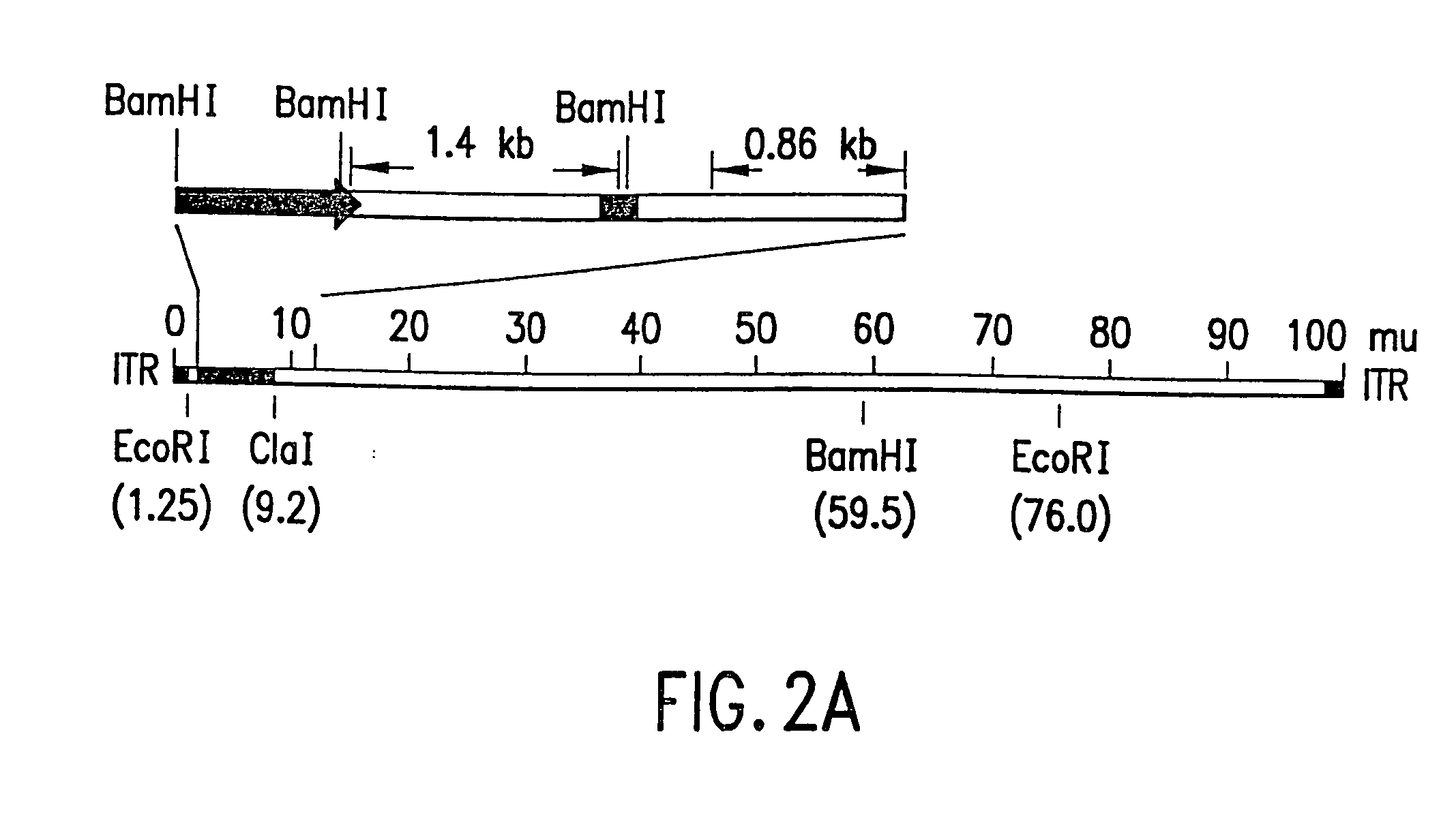
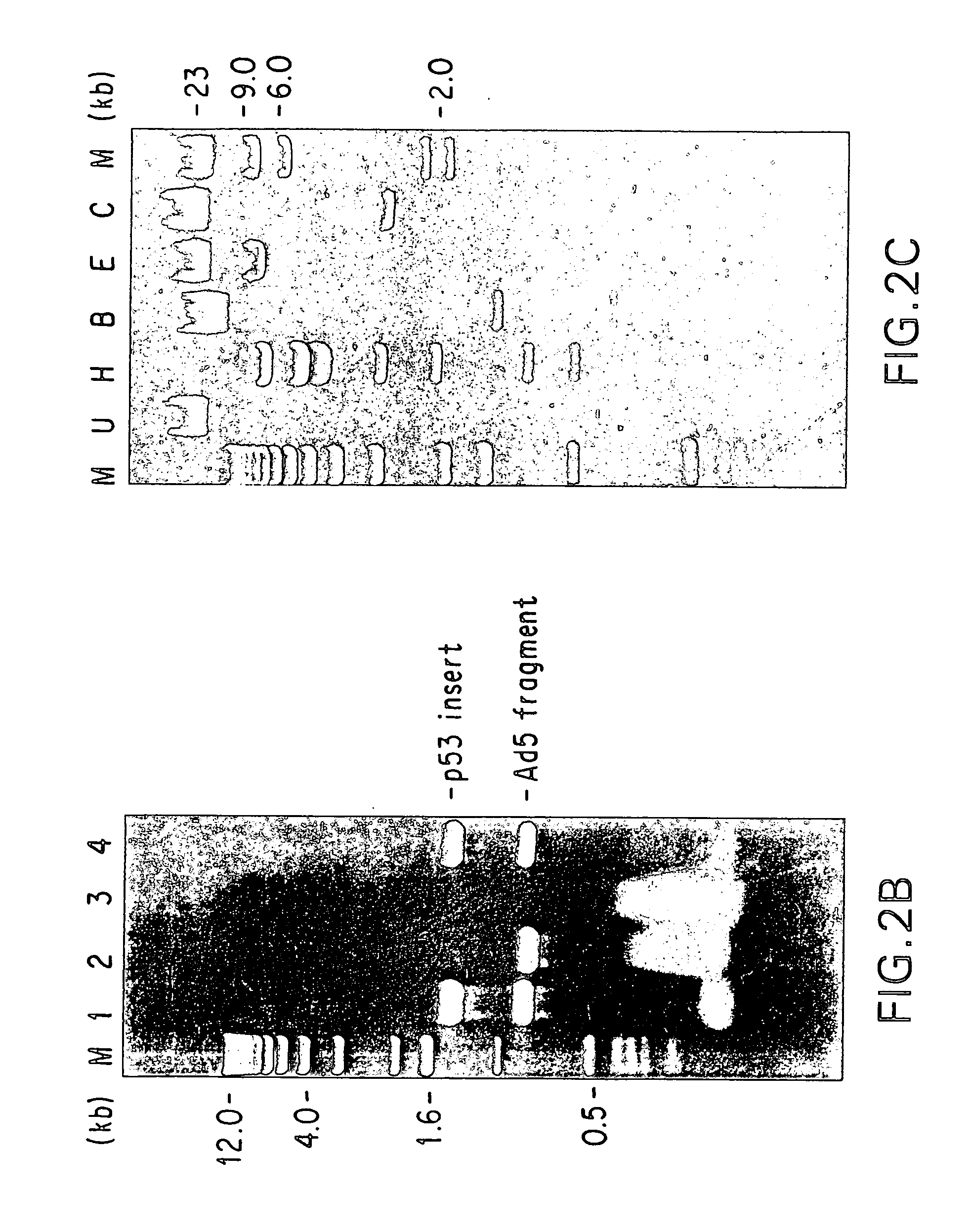
[0133] Aliquots of cell culture supernatants (50 to 370 μl) were collected from the test plates, treated with proteinase K (50 μg / ml with 0.5% SDS and 20 mM EDTA) at 56° C. for 1 hour, extracted with phenol-chloroform, and the nucleic acids were ethanol precipitated. The DNA pellets were resuspended in 20 μl dH2O and used as template for PCR amplification. The relative locations of the PCR primers and their sequences are depicted in FIG. 1 and are SEQ ID NOS:1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively. The cDNA insert-specific primers define a 1.4 kb PCR product and the viral genome-specific primers define a 0.86 kb PCR product. The PCR reactions were carried out in a 50 μl volume containing 4 mM MgCl2, 50 mM KCl, 0.1% triton X-100, 200 μM each of dTPs, 10 mM Tris-Cl (pH...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| delay time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| delay time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| delay time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com