Group III nitride semiconductor stacked structure
a stacked structure and nitride technology, applied in the direction of semiconductor devices, basic electric elements, electrical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of cumbersome process, complicated formation of insulating films or patterning processes such as photolithography and etching, etc., to enhance the peak inverse voltage, enhance light emission efficiency, and enhance light emission efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
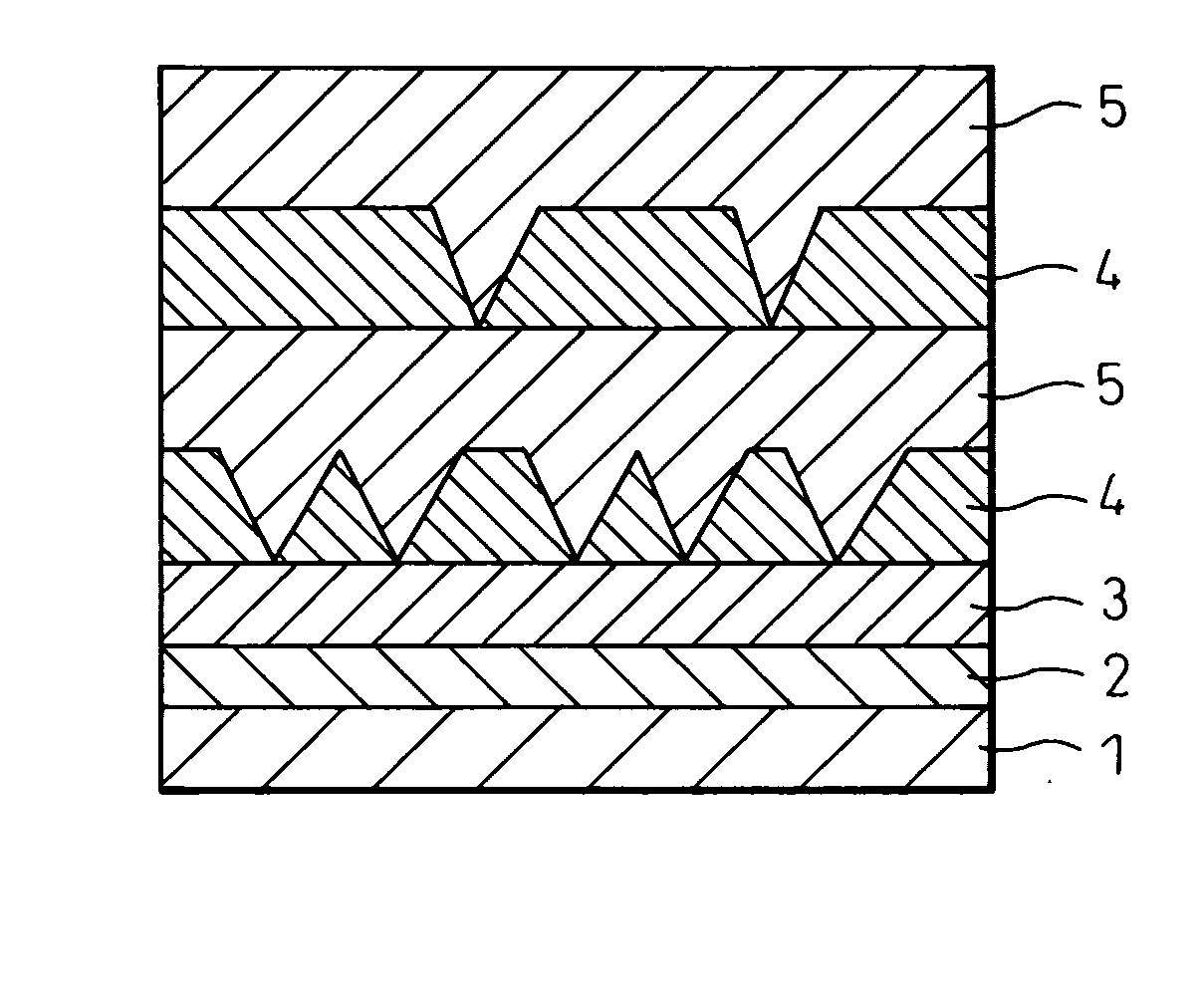
[0079]FIG. 1 is a view schematically showing the cross-sectional structure of the stacked structure for a Group III nitride semiconductor device, produced in this Example.
[0080] The structure where a Group III nitride semiconductor is stacked on a substrate comprising sapphire is formed through the following procedure by utilizing a general reduced-pressure MOCVD technique. First, a substrate 1 comprising (0001)-sapphire was placed on a susceptor made of a high-purity graphite for a semiconductor, which is heated to a film-forming temperature by a high frequency (RF) induction heating-type heater. Thereafter, a nitrogen gas was flowed into the stainless steel-made vapor phase growth reaction furnace to purge the inside of the furnace.
[0081] After flowing a nitrogen gas into the vapor phase growth reaction furnace over 8 minutes, the induction heating-type heater was actuated and the temperature of the substrate 1 was elevated from room temperature to 600° C. in 10 minutes. While k...
example 4
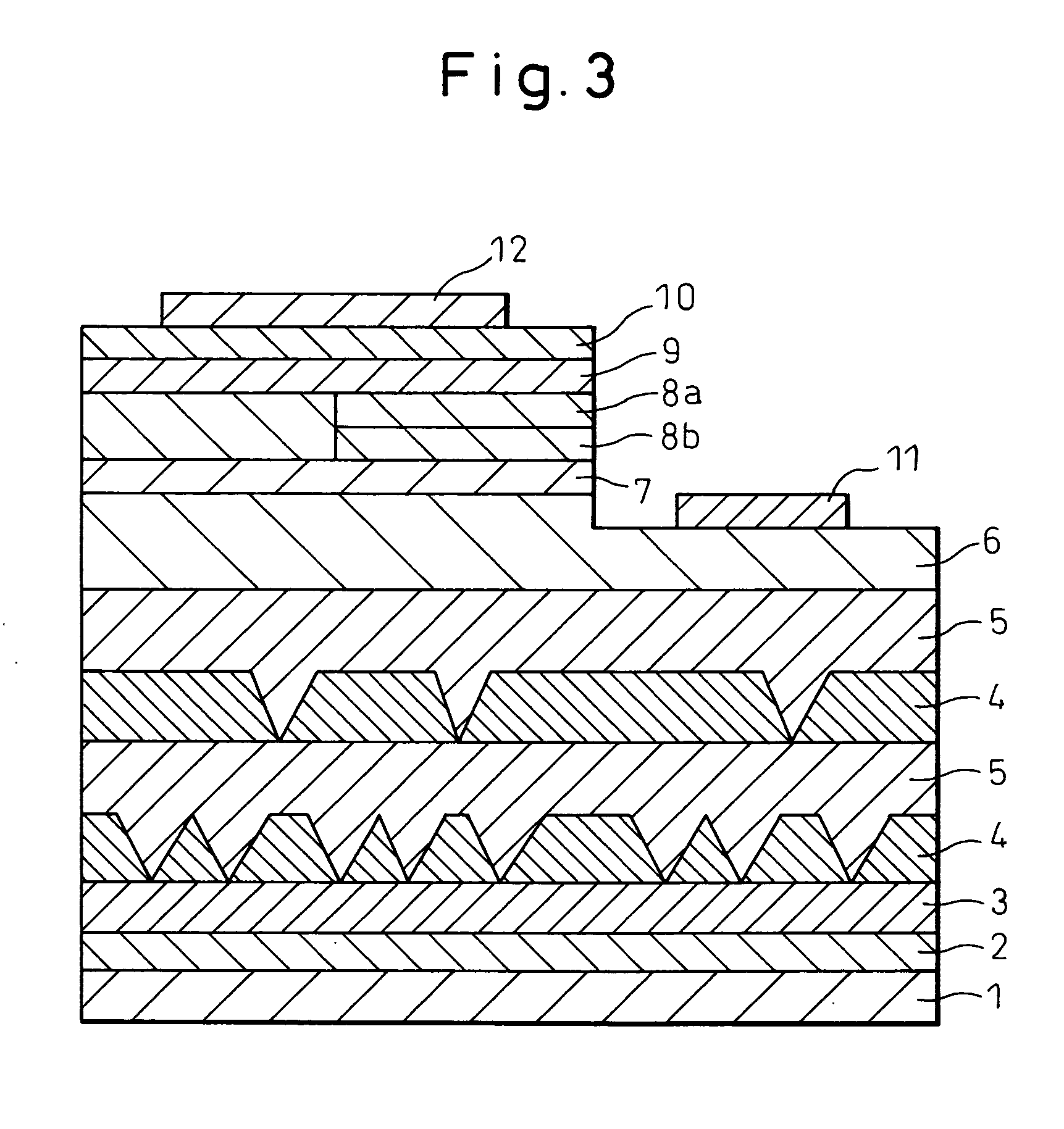
[0091] A Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device was produced by further stacking a Group III nitride semiconductor layer on the stacked structure produced in Example 1. FIG. 3 is a view schematically showing the cross-sectional structure of the Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device produced in this Example.
[0092] The procedure until the formation of the low-concentration impurity atom layer 5 was the same as that in Example 1. Thereafter, an n-contact layer 6 comprising Ge-doped GaN was stacked thereon at 1,120° C. and an n-clad layer 7 comprising undoped In0.03Ga0.97N was then stacked at 1,060° C. The thickness of the n-clad layer 7 was 12.5 nm. As for the n-contact layer 6 having a structure that a high-concentration Ge atom layer and a low-concentration Ge atom layer were alternately stacked in a repetition of 100 times, the total layer thickness was 2 μm.
[0093] Subsequently, the substrate 1 temperature was lowered to 730° C. and a multiple quantu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com