Osteogenic Composite Matrix, Method for the Production Thereof and Implant and Scaffold for Tissue Engineering Provided with a Coating Formed by Said Osteogenic Composite matrix
a composite matrix and osteogenic technology, applied in the field of osteogenic composite matrix, to achieve the effect of promoting and accelerating bone accumulation and bone growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
working example 1
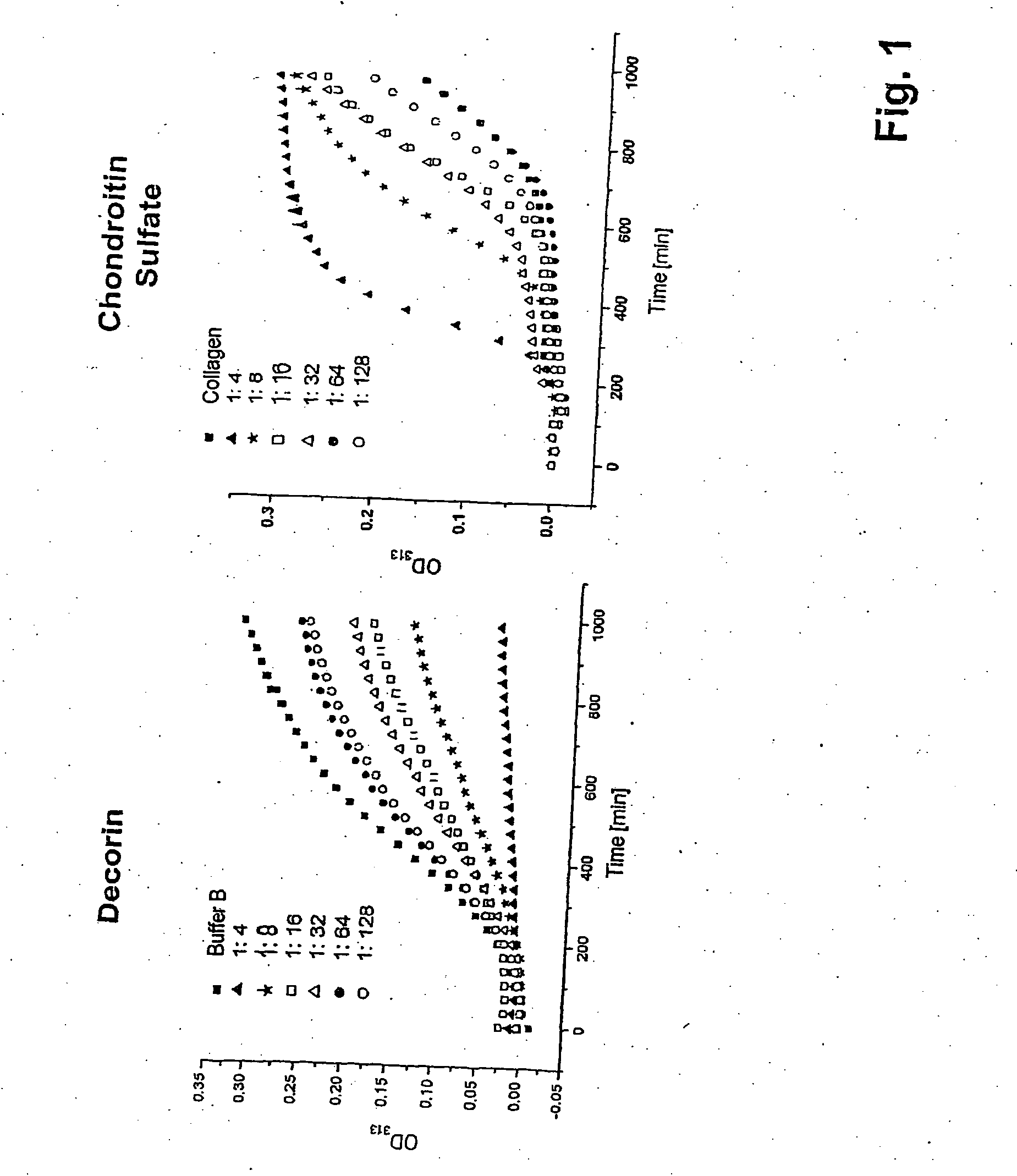
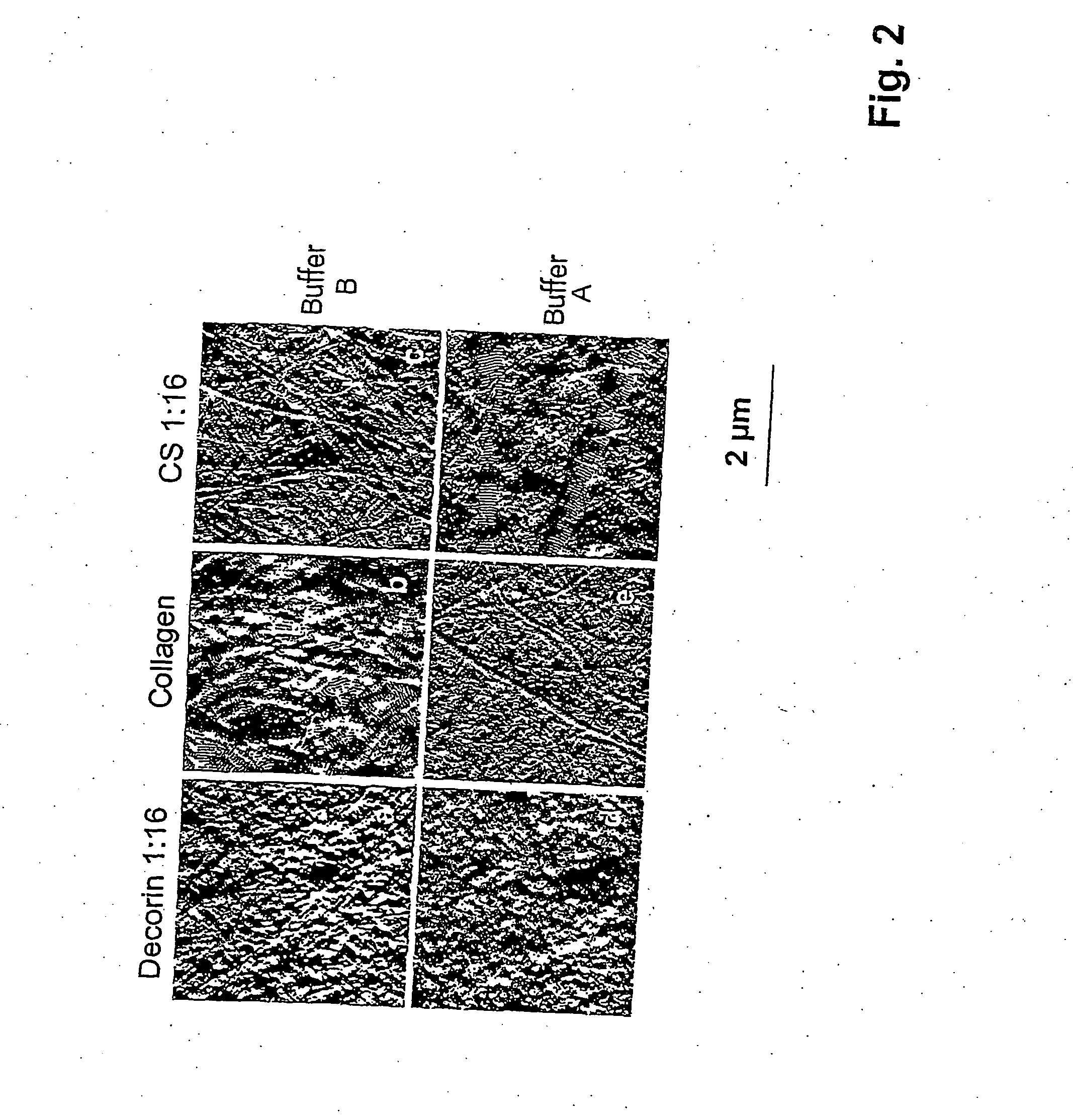
Fibril Structure after Fibrillogenesis under Various Conditions
[0055] For the generation of the osteogenic matrix composite, a solution of collagen monomers in 0.01 M acetic acid is prepared by stirring for 24 hours at 4° C. The collagen fibrils are subsequently formed in the presence of the noncollagenic components by a process of self-aggregation (fibrillogenesis) in aqueous phosphate buffer solutions at neutral pH and a temperature of 37° C.
[0056] The range for the formation of the fibrils is between 0.5 and 5 mg of collagen / ml and 0.1 to 5 mg of glycosaminoglycan / ml, 1 mg / ml of collagen and 0.2 mg / ml of GAG and 30 μg / ml of proteoglycan being the preferred conditions. The preferred fibrillogenesis parameters were a 30 mmol / l phosphate buffer pH 7.0, either with 135 mmol / l of NaCl or without NaCl addition.
[0057] Glycosaminoglycans or other matrix components are added to the collagen monomers before fibrillogenesis and thereby integrated at least partially into the resulting fib...
working example 2
Incorporation of Noncollagenic Components into Collagen Fibrils
[0061] For generation of the osteogenic matrix composite, a solution of collagen monomers in 0.01 M acetic acid is prepared by stirring at 4° C. for 24 hours. The collagen fibrils are subsequently formed by a process of self-aggregation (fibrillogenesis) in aqueous phosphate buffer solutions at neutral pH in the presence of the noncollagenic components. Formation conditions: 250 μg / ml of collagen, 37° C., 30 mmol / l of phosphate buffer pH 7.4 (buffer A) or 30 mmol / l of phosphate buffer pH 7.4 containing 135 mmol / l of NaCl (buffer B) with different chondroitin sulfate and decorin concentrations.
[0062] After washing and hydrolysis of the fibrils in 500 μl of 6 M HCl at 105° C. for 6 hours, decorin and chondroitin sulfate integrated into the fibrils was determined according to the method of Pieper et al. [Pieper J S, Hafmans T, Veerkamp J H, van Kuppevelt T H. Development of tailor-made collagen-glycosaminoglycan matrices:...
working example 3
Recruitment of Growth Factors by an Implant Coated with an Osteogenic Matrix Composite
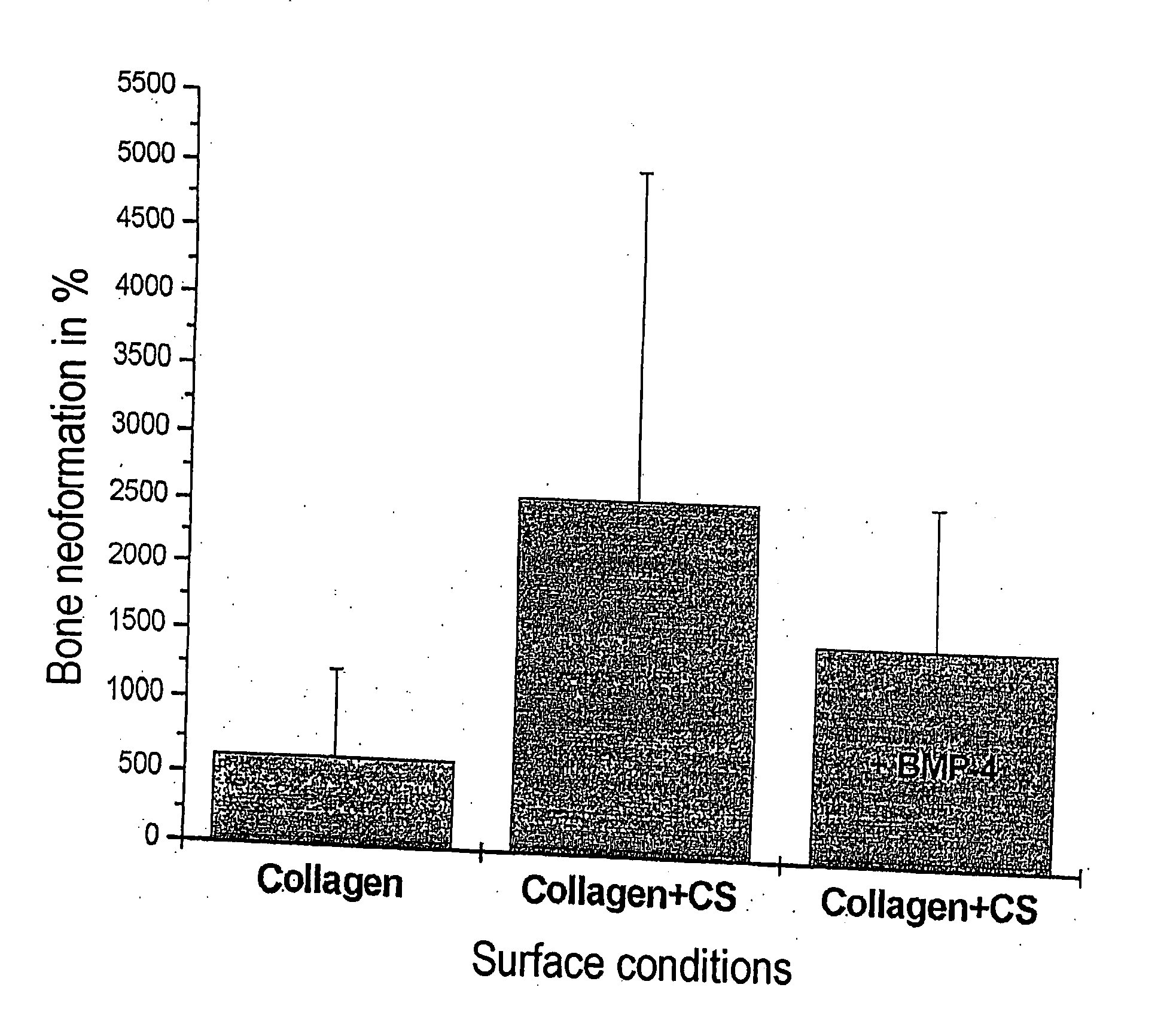
[0065] Matrices composed and produced according to the invention can accelerate and improve bone formation and accumulation without the use of recombinant growth factors by the recruitment of endogenous growth factors. In the experiment, such a binding behavior can only be demonstrated using recombinant growth factors.
[0066] A sandblasted, cylindrical sample of TiAl6V4 having a diameter of 10 mm is cleaned with ethanol, acetone and water.
[0067] A solution of 1 mg / ml of bovine collagen type I in 0.01 M acetic acid is produced by stirring overnight at 4° C. Noncollagenic ECM components (glycosaminoglycan 30 μg / ml, proteoglycans 15 μg / ml) are added to this solution. The mixtures are treated with fibrillogenesis buffer (60 mmol / l of phosphate, 270 mmol / l of NaCl, pH 7.4) on ice and incubated at 37° C. for 18 h. The resulting fibrils are centrifuged off, washed, homogenized and resuspended to give a ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com