Thickener composition for dysphagia patients
a dysphagia patient and thickener technology, applied in the field of dysphagia patients nutrition, can solve the problems of affecting the health of patients, affecting the quality of dysphagia patients, and a relatively long time to consume food, so as to improve the quality of fermented foods, and improve the effect of fermentation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
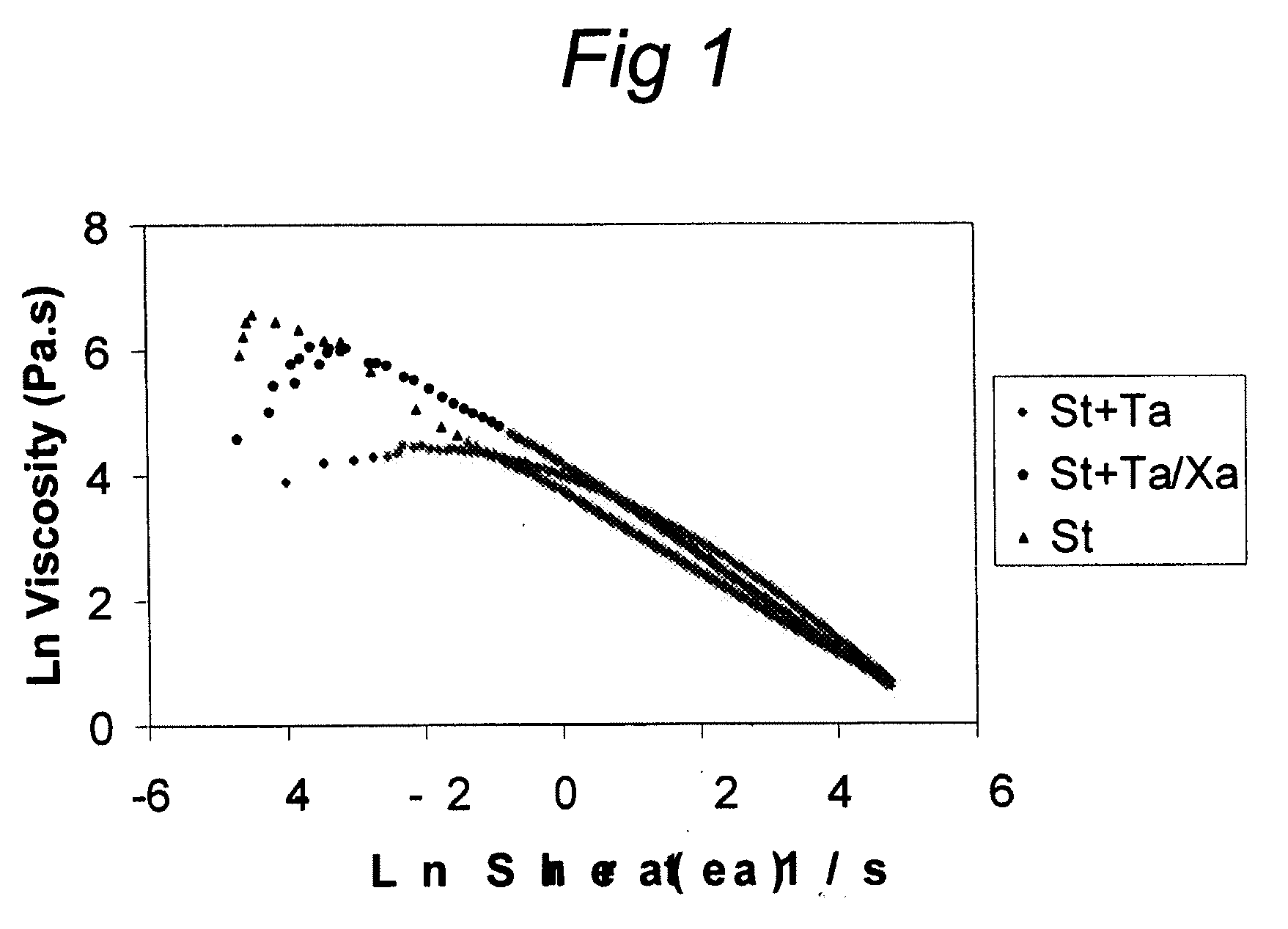
Viscosity Profile
[0033]During processing in the mouth and swallowing the viscosity of a food product changes due to shear forces. This change in viscosity can be analyzed in a laboratory mixing experiment of the food product. The force needed for mixing food product is a measure for the viscosity of this food product. As can be seen in FIG. 1, the viscosity decreases when the shear rate increases.
[0034]Consumers are accustomed to the ideal viscosity profile of a product entirely consisting of starch. This product is depicted as triangles (St) in FIG. 1. It was found that by combining tara gum, xanthan gum and starch a similar viscosity profile could be made depending on the quantity and ratios of these ingredients. Tara gum or xanthan gum alone were not able to mimic the viscosity profile. Tara gum and xanthan gum could be replaced or mixed with other polysaccharide gums of plant and microbial origin as there are locust bean gum, guar gum, fenugreek gum, tamarind gum, konjac mannan,...
example 2
[0037]Preparation of Dispersions
[0038]Dispersions were prepared by adding 12 gram of a thickener composition described in Example 4 to 200 gram of water in a 500 ml shaking beaker and shaking the mixture in the shaking beaker by hand until no powder particles could be observed anymore visually. Directly after preparation of the dispersion it was split in two and transferred to 100 ml cups. After preparation the dispersions were allowed to rest for 30 minutes at room temperature.
Freeze-Thaw-Heat Treatment
[0039]After preparation the dispersions were put in a freezer with a temperature of −18° C. and were left in the freezer overnight. Before a measurement dispersions were taken out of the freezer and heated up to 90° C. in a Micro-Wave. After heating the dispersions were allowed to rest and cool down for 30 minutes.
Treatment with Saliva
[0040]Fresh human saliva from one or more individual(s) was gathered and mixed carefully. Directly after fresh preparation of a dispers...
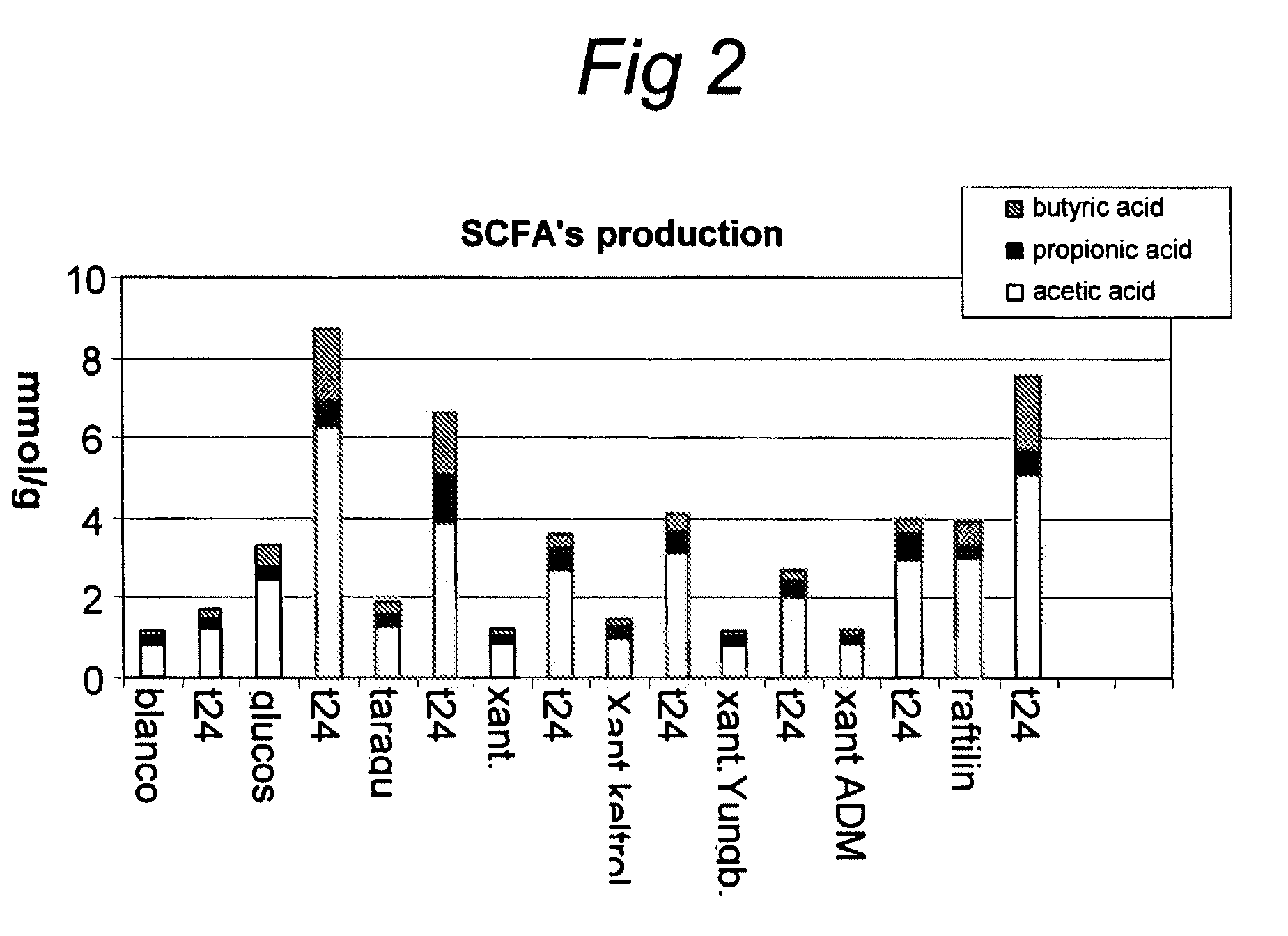
example 3
Fermentation of Gums
Microorganisms
[0042]Micro-organisms were obtained from fresh faeces from bottle fed babies. Fresh faecal material from babies ranging 1 to 4 month of age was pooled and put into preservative medium within 2 h.
Compositions / Substrate
[0043]As substrate either prebiotics (TOS; TOS and inulin HP mixture in a 9 / 1 (w / w) ratio; inulin HP; oligofructose and inulin HP mixture in a 1 / 1 (w / w) ratio, or none (blanc) was used.
Media
[0044]McBain & MacFarlane medium: Buffered peptone water 3.0 g / l, yeast extract 2.5 g / l. mucin (brush borders) 0.8 g / l, tryptone 3.0 g / l, L-Cysteine-HCl 0.4 g / l, bile salts 0.05 g / l, K2HPO4.3H2O 2.6 g / l, NaHCO3 0.2 g / l, NaCl 4.5 g / l, MgSO4.7H2O 0.5 g / l, CaCl2 0.228 g / l, FeSO4.7H2O 0.005 g / l. Fill 500 ml Scott bottles with the medium and sterilize 15 minutes at 121° C.
[0045]Buffered medium: K2HPO4.3H2) 2.6 g / l, NaHCO3 0.2 g / l, NaCl 4.5 g / l, MgSO4.7H2O, 0.5 g / l, CaCl2 0.228 g / l, FeSO4.7H2O 0.005 g / l. Adjust to pH 6.3±0.1 with K2HPO4 or NaHCO3. Fill 500...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| energy density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com