Method of increasing enzyme stability and activity for pulp and paper production
a technology of enzyme stability and activity, applied in the field of managing wood pitch, can solve the problems of reducing paper quality, affecting the physical properties of the pulp, and impairing the bonding of fibers to fibers, and achieves the effects of stabilizing the enzyme formulation, speeding up the enzymatic reaction, and enhancing the effect of enzyme formulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Increased Triglyceride Conversion Kinetics in TMP Pulp
[0044]Materials and Methods
[0045]A newsprint mill TMP pulp stock, collected from secondary refiner accept with no alum addition, was collected. Prior to lab tests, it was mixed well to ensure uniformity of the stock. The stock consistency was determined. Based on the consistency, the stock was diluted to 1.0% consistency, and the pH was adjusted to 5.0-5.2. 100 grams of the 1.0% stock was transferred into each of a series of flasks. The flasks containing stock were conditioned in a water bath at the required temperature for 30 minutes with continuous mixing. Alum solution was added to the stock and mixed for 30 seconds and then enzyme solutions were added to the stock. Pulp samples were collected at reaction time of 20 min to 1.5 hours for testing.
[0046]Results
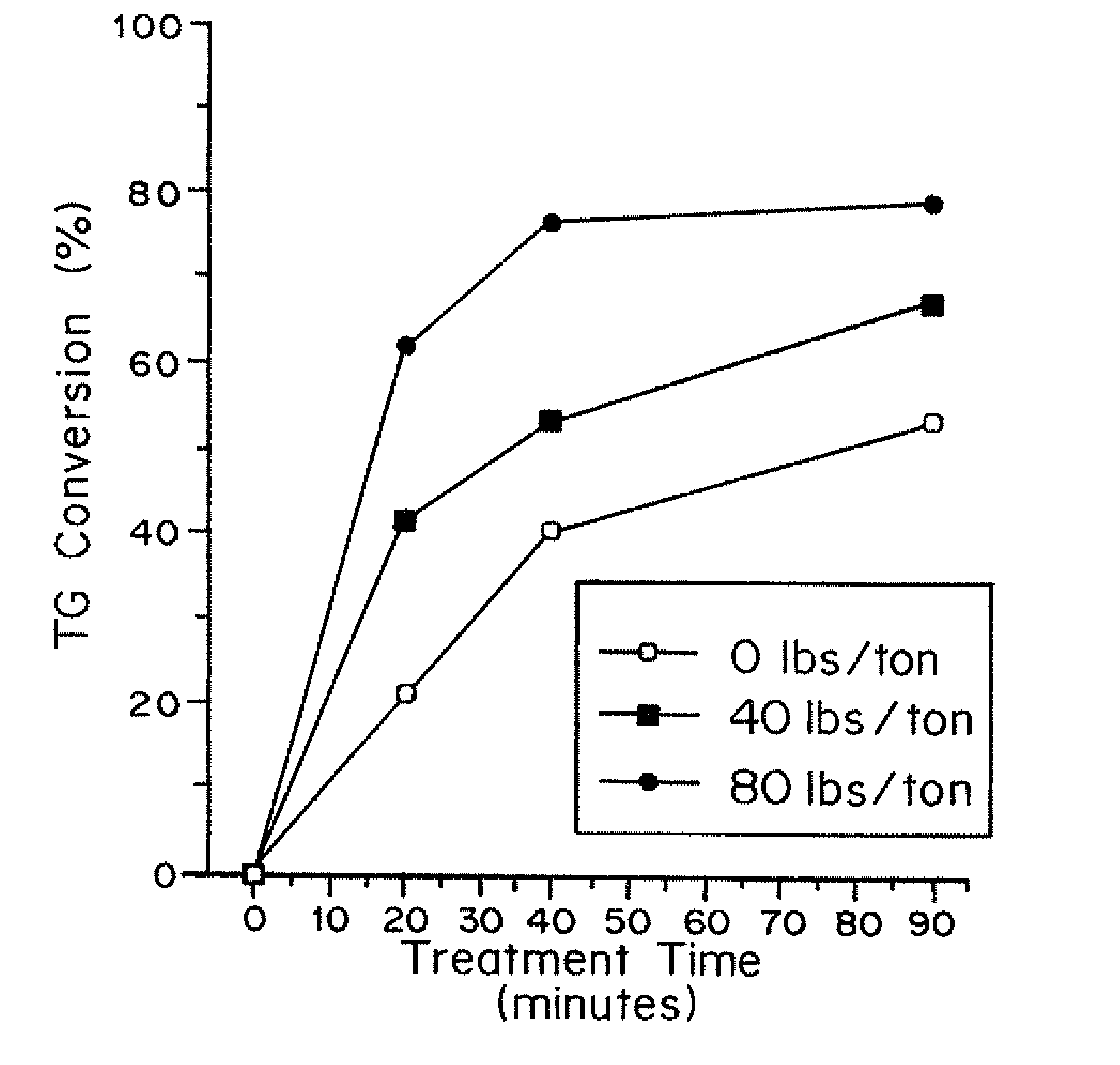
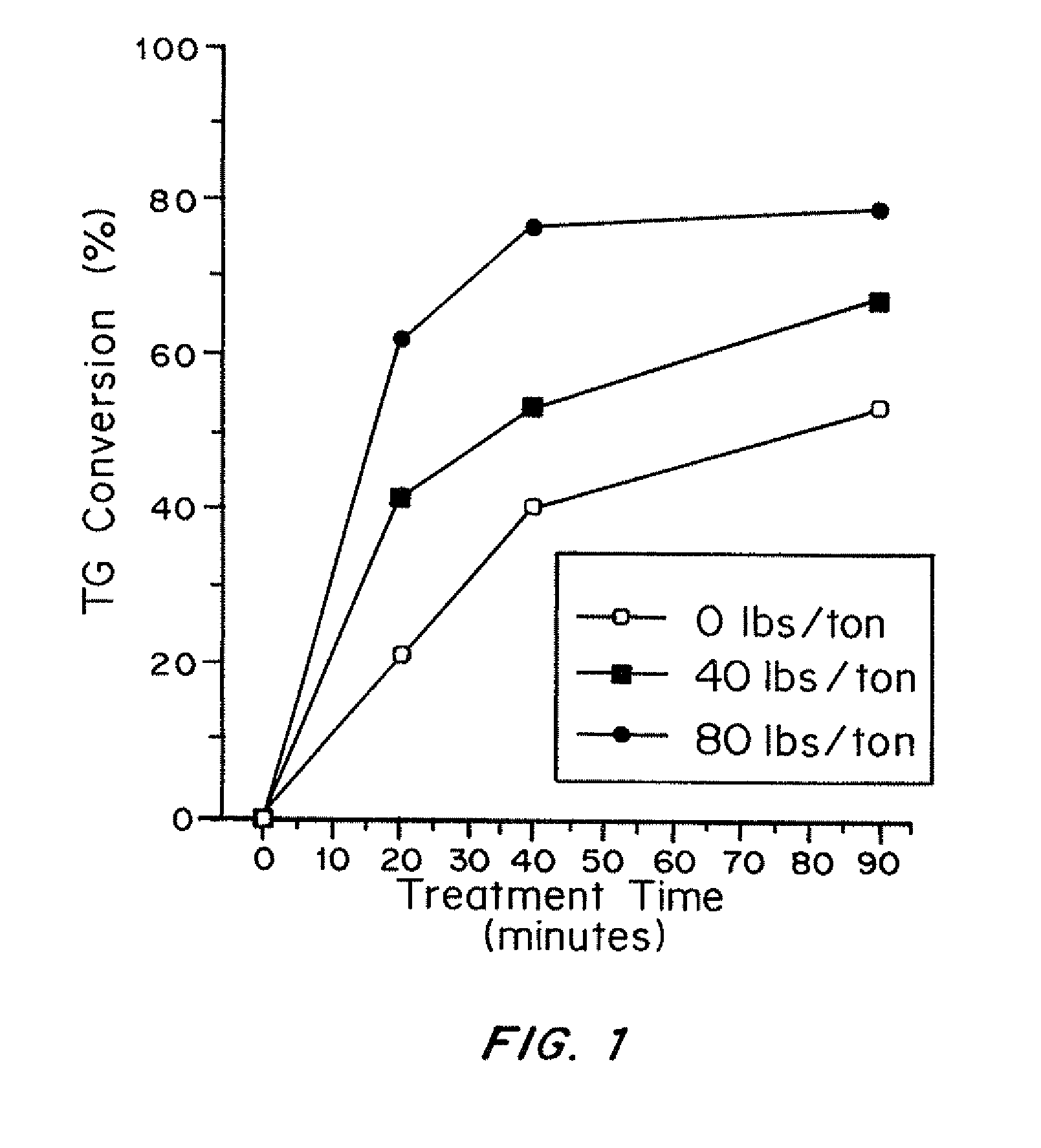
[0047]FIG. 1 shows the TG conversion results without and with 40# / ton and 80# / ton alum using 0.04% EnzOx® A at 65° C. Total TG conversion as well as the rate of conversion ...
example 2
Increased TG Conversion at a Broader pH Range by Aluminum Addition
[0048]Materials and Methods
[0049]The stock preparation procedure is the same as in Example 1. Two sets of diluted stocks were prepared and pH values were adjusted to pH4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0 and 10.0, respectively. One set had no alum, while the other set of was treated with 40 lbs / ton of alum. These stocks were then treated with 0.04% of EnzOx® A for 3 hours. The TG content was measured for pulp samples after the treatment.
[0050]Results
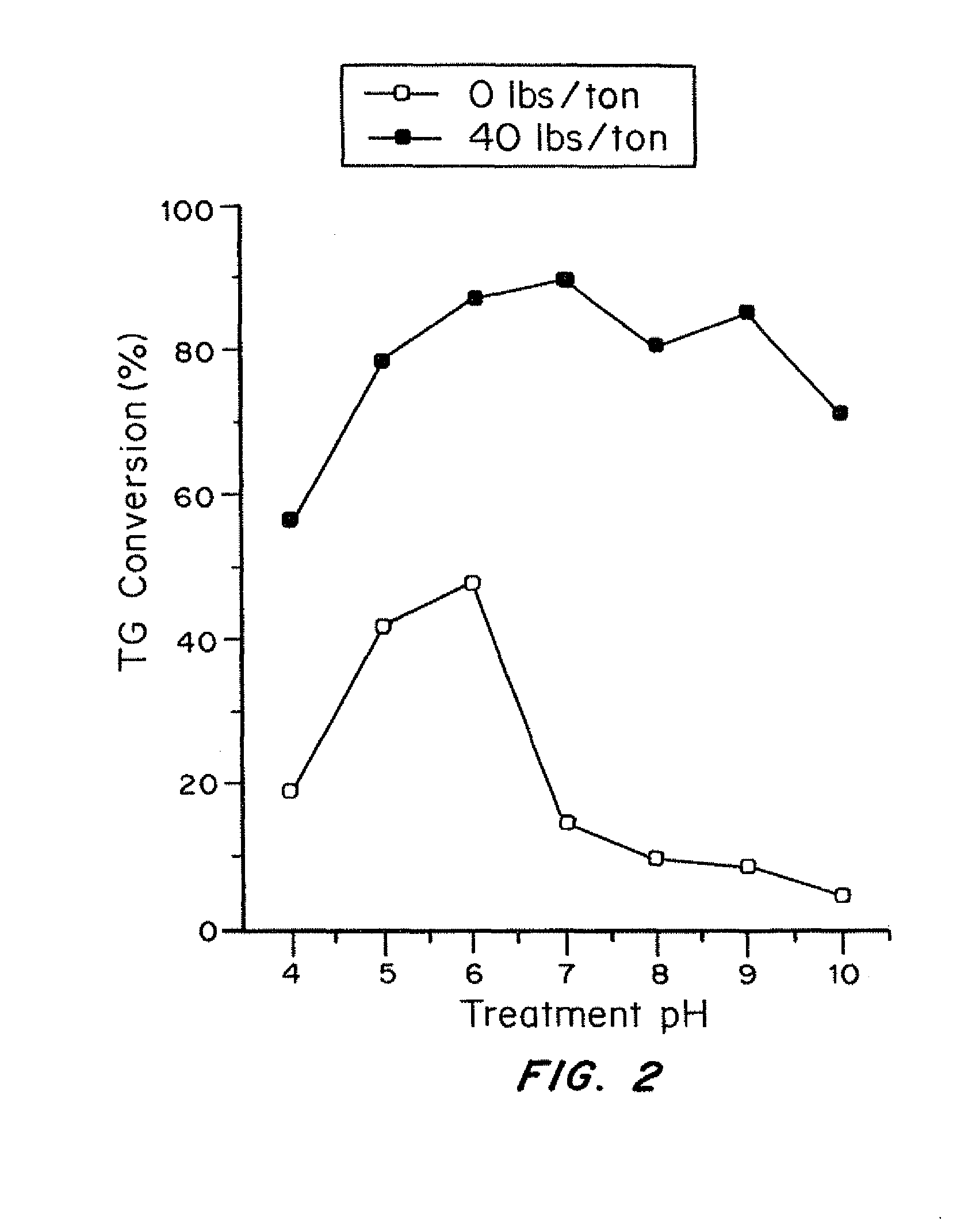
[0051]The results are given in FIG. 2. The alum treatment clearly increased the TG conversion by EnzOx® A treatment over the entire pH range tested (4-10). Without alum, only moderate TG conversion was obtained in a narrow range of pH 5-6. Above pH=7, there was essentially no apparent enzyme conversion of TG. With 40# / ton alum addition, the TG conversion was increased to 70-80% with alum treatment. This example demonstrated that aluminum ions could stabilize the lipase enzyme act...
example 3
Increased TG Conversion with Alum Treatment at a Higher Temperature Range with EnzOx® A
[0052]Materials and Methods
[0053]The pulp stock preparation procedure is the same as in Example 1. Two sets of stocks, one with no alum and the other with 30 lbs / ton alum, were prepared. The stocks were then treated with EnzOx® A at 0.04% based on O.D. fibers at different temperatures from 65 to 85° C. for three hours.
[0054]Results
[0055]The results are shown in FIG. 3. Without alum addition, there was no significant TG conversion at above temperature 75° C., indicating that the enzymes were mostly thermally deactivated. In the presence of alum, TG conversion was significantly increased. For instance, at 75° C. TG conversion increased from about 18% without alum to about 82% with 30# / ton alum. It is very obvious that the presence of alum stabilized and protected the enzymes from heat deactivation. The alum addition increased the effective working temperatures for EnzOx® A by about 10° C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com