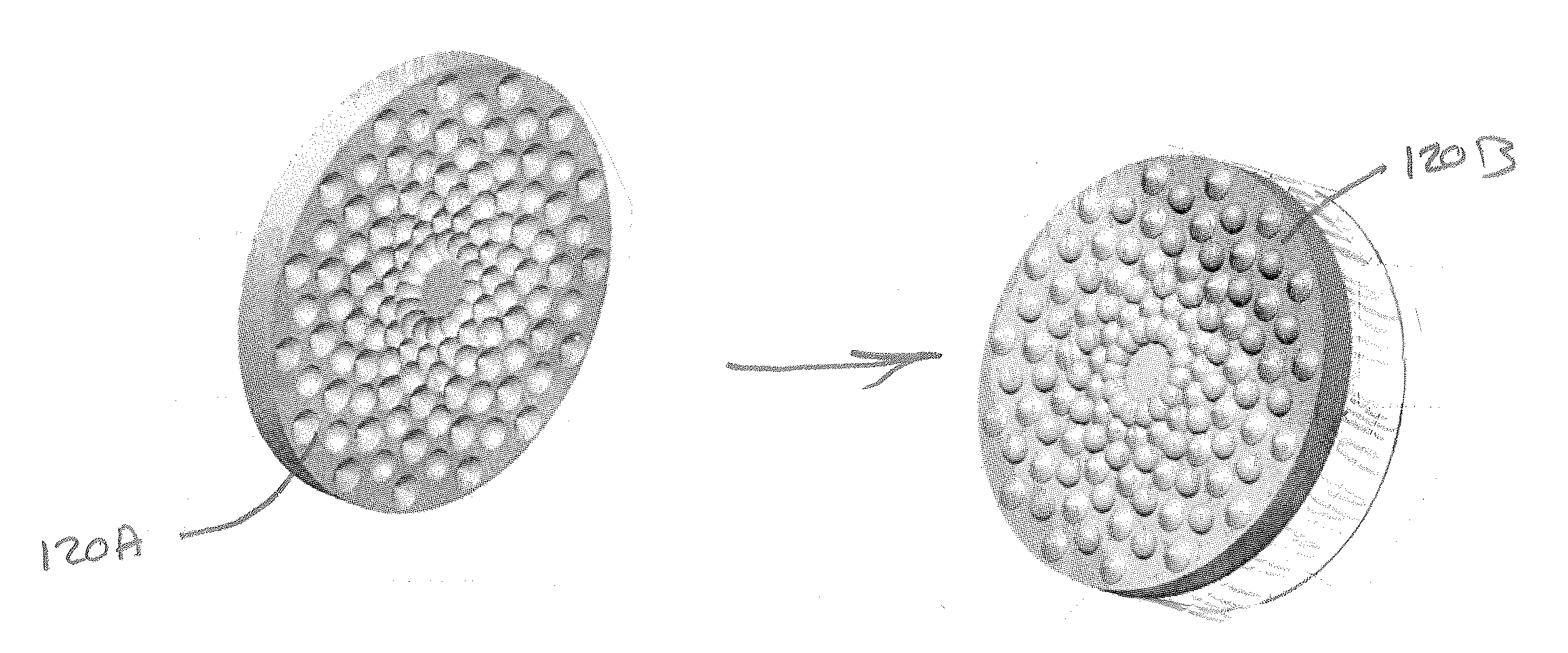
Sacrificial Catalyst Polycrystalline Diamond Element
a technology of polycrystalline diamond and catalyst, which is applied in the direction of cellulosic plastic layered products, instruments, other chemical processes, etc., can solve the problems of assembly being subjected to very high temperature and pressure, surface texture and geometry, and impose a limit on the maximum useful operating temperature of the element, etc., to achieve low contamination level of pcd working surface, aggressive cutting of formation, and optimized for wear and impact strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
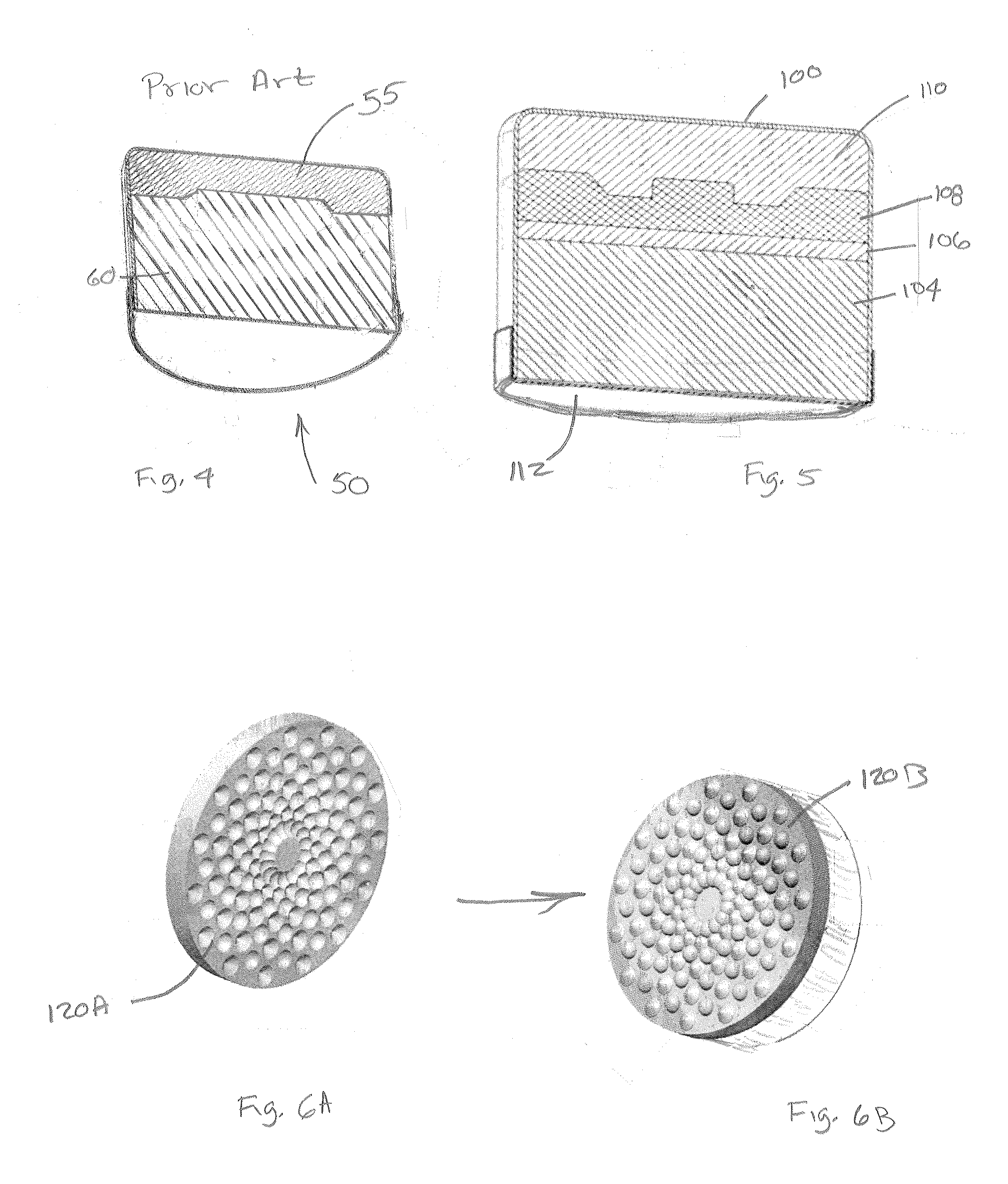
[0034]In the following description, it is understood that the composite described hereafter as formed of polycrystalline diamond, PCD, or sintered diamond as the material is often referred to in the industry, but can also be any of the super hard abrasive materials, including, but not limited to, synthetic or natural diamond, cubic boron nitride, and related materials.
[0035]Polycrystalline diamond cutters are well known and used as cutting elements in drilling bits used to form boreholes into the earth, and are primarily used for, but not limited to, drilling tools for exploration and production of hydrocarbon minerals from the earth.
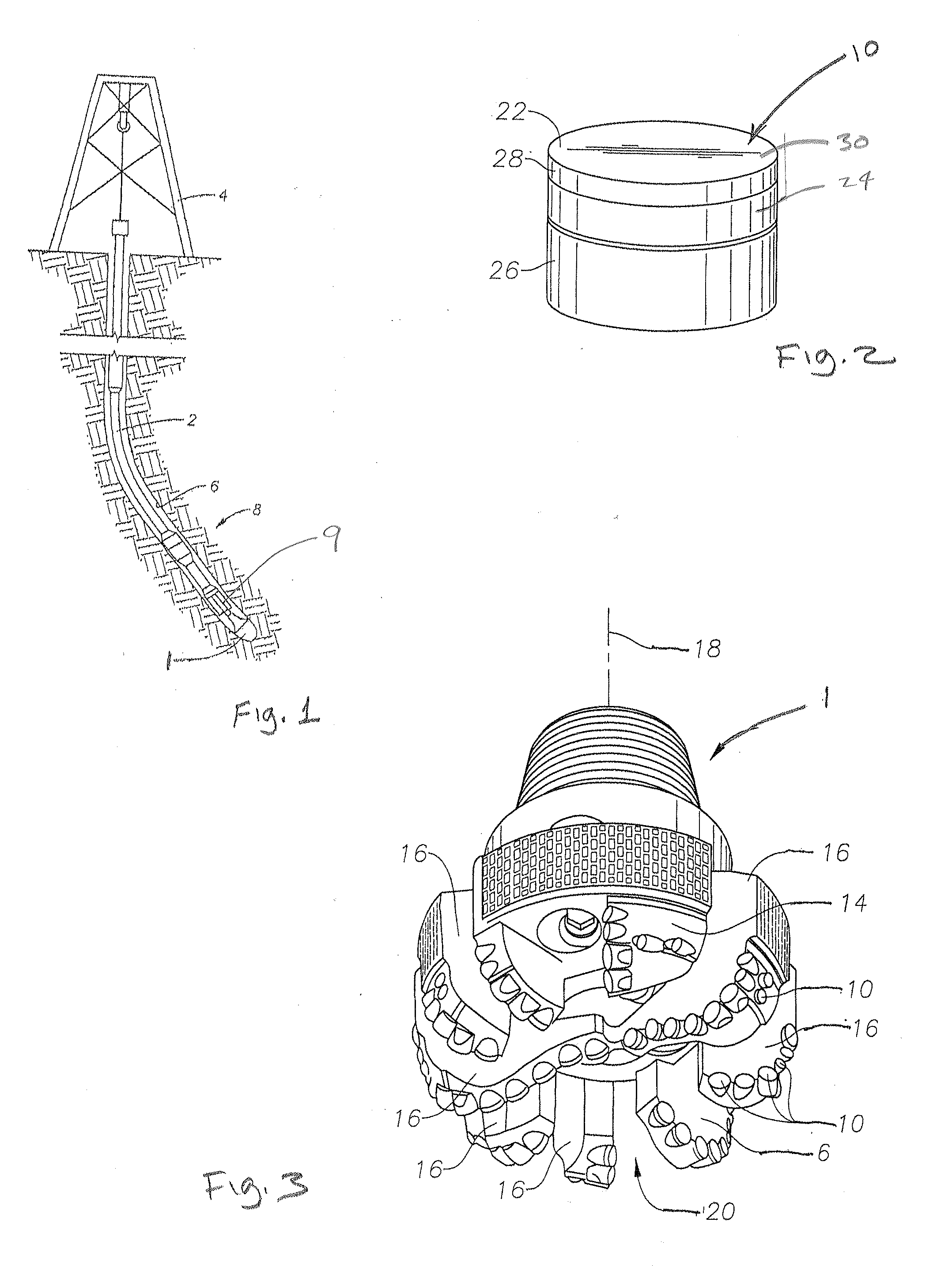
[0036]For illustrative purposes only, a typical drilling operation is shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 1 shows in schematic form a representation of a drill string 2 suspended by a derrick 4 for drilling a borehole 6 into the earth for minerals exploration and recovery, and in particular petroleum. A bottom-hole assembly (BHA) 8 is located at the bottom of the bor...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com