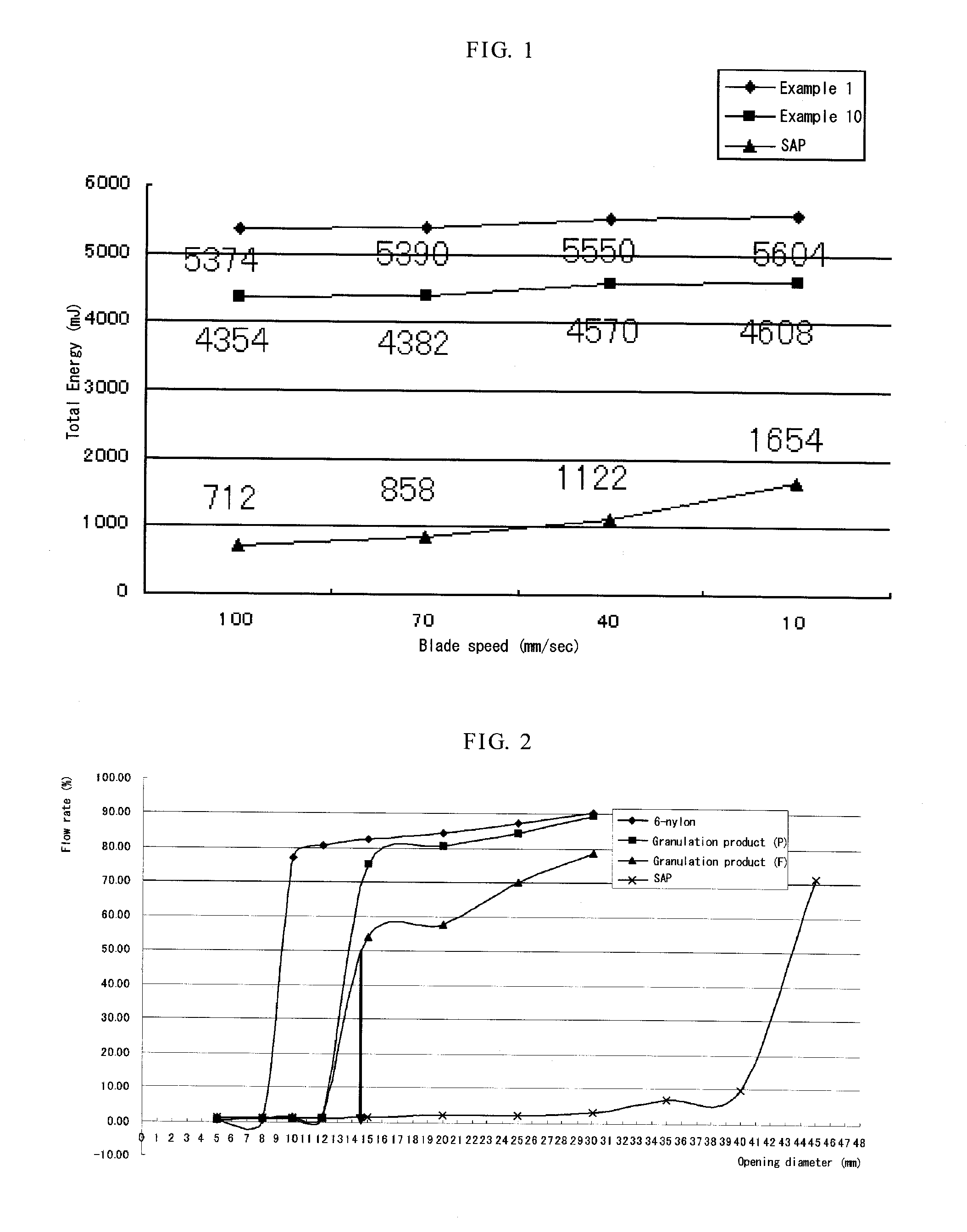
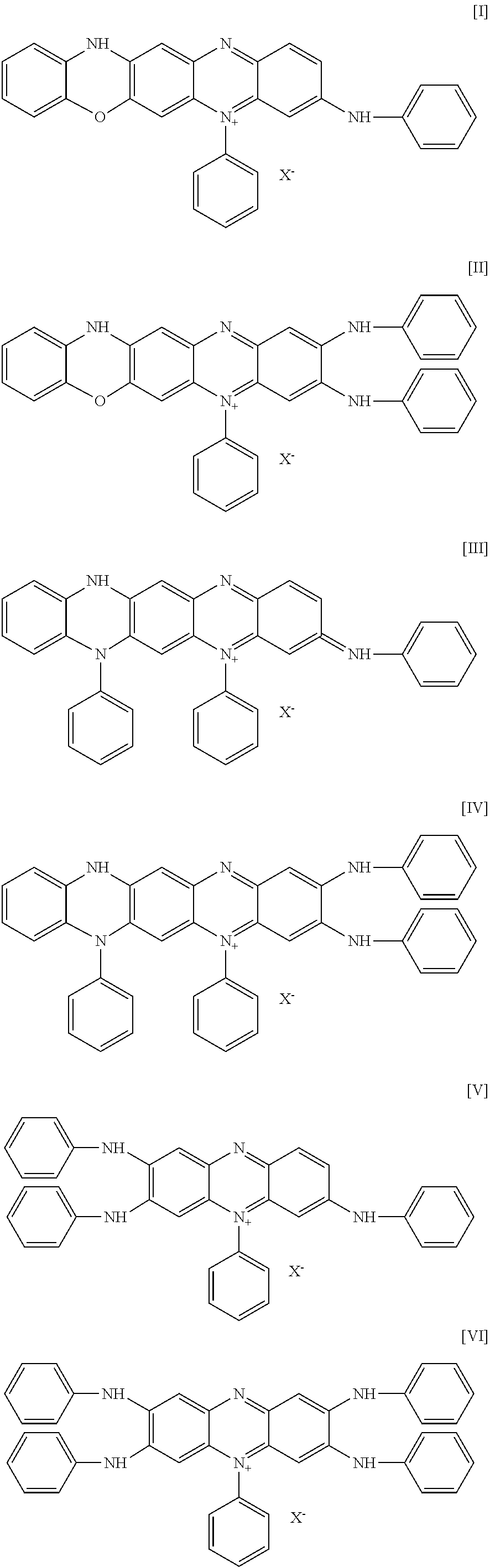
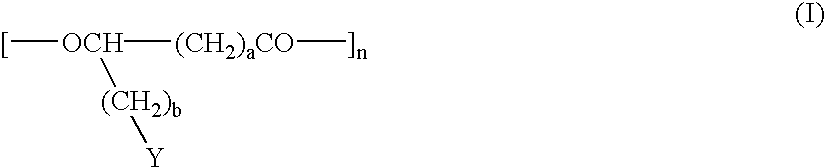Patents
Literature
55results about How to "Impact strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MBS impact modifiers
A process and composition for MBS modifiers having (A) a rubbery core, (B) an inner graft stage comprised mainly of a hard polymer, (C) an intermediate sealer stage comprised mainly of an alkyl acrylate monomer and / or a polyunsaturated crosslinker, and (D) an outer shell to provide compatibility of the core-shell polymer with the matrix polymer, is disclosed. A process for preparing MBS impact modifiers having suprisingly improved impact performance in matrix polymers is also disclosed. Articles prepared from blends of matrix polymers and the MBS core-shell polymers described herein are also disclosed.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Sacrificial Catalyst Polycrystalline Diamond Element
InactiveUS20110171414A1Reduce formationLow level of contaminationPigmenting treatmentDrill bitsMetallurgyPolycrystalline diamond
A superhard composite material comprising a polycrystalline diamond cutter (PDC) having a cutting surface and cutting edges having a polycrystalline diamond thickness of about 3 mm is integrally formed with a sacrificial catalyst source that is removed later in the processing of the of the cutter.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Novel Propylene Polymer Blends
InactiveUS20070299173A1Maintain good propertiesHigh transparencyGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSpecial tyresLinear low-density polyethyleneThermoforming
The invention relates to propylene polymer blends comprising 70-92 wt % of a propylene homopolymer, 5-15 wt % of an elastomeric ethylene-propylene copolymer, 3-15 wt % of a linear low density polyethylene and an a-nucleating agent. The propylene polymer blends have an excellent impact strength / stiffness balance and optical properties. They are especially suitable for thermoforming and extrusion blow moulding.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
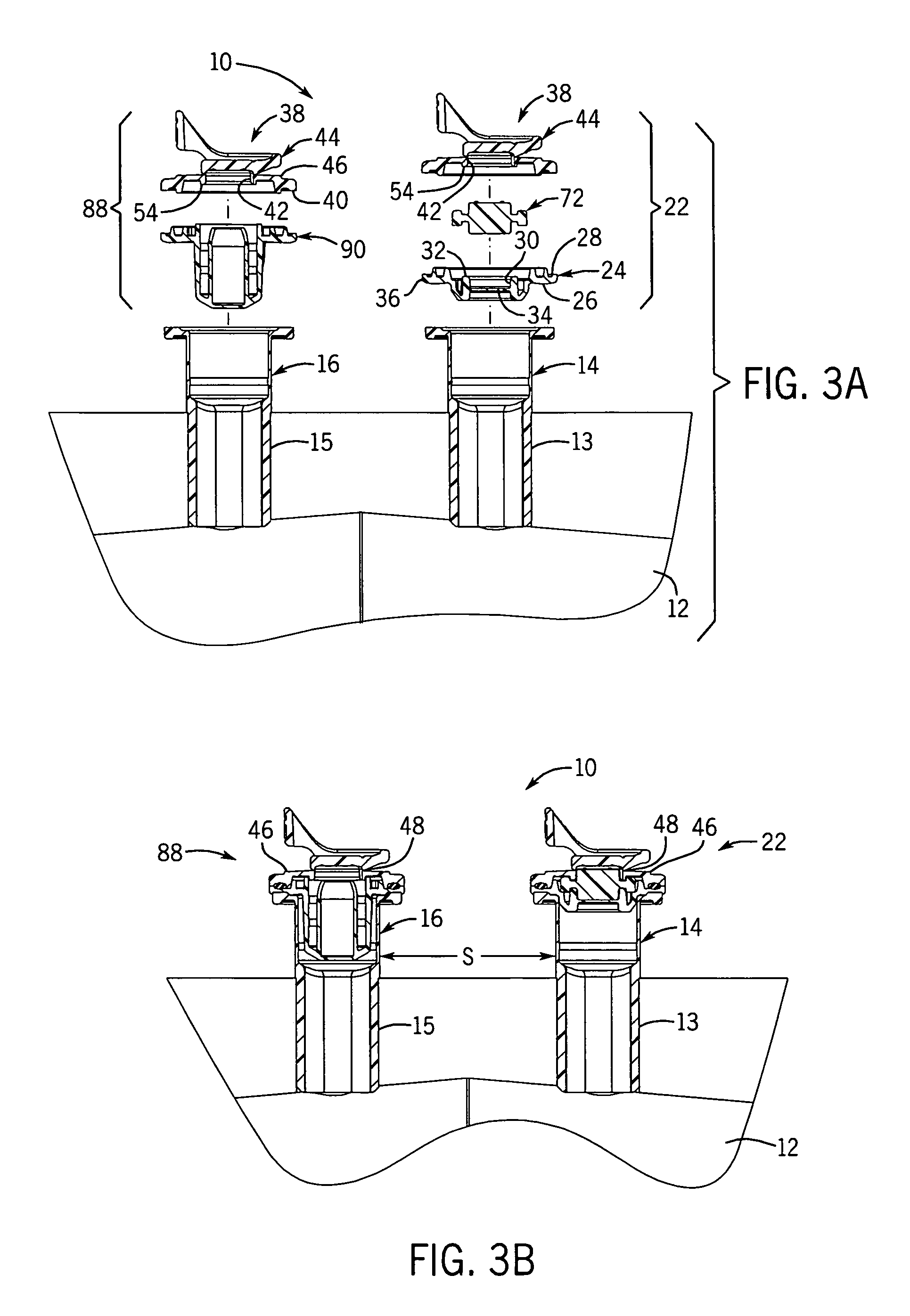
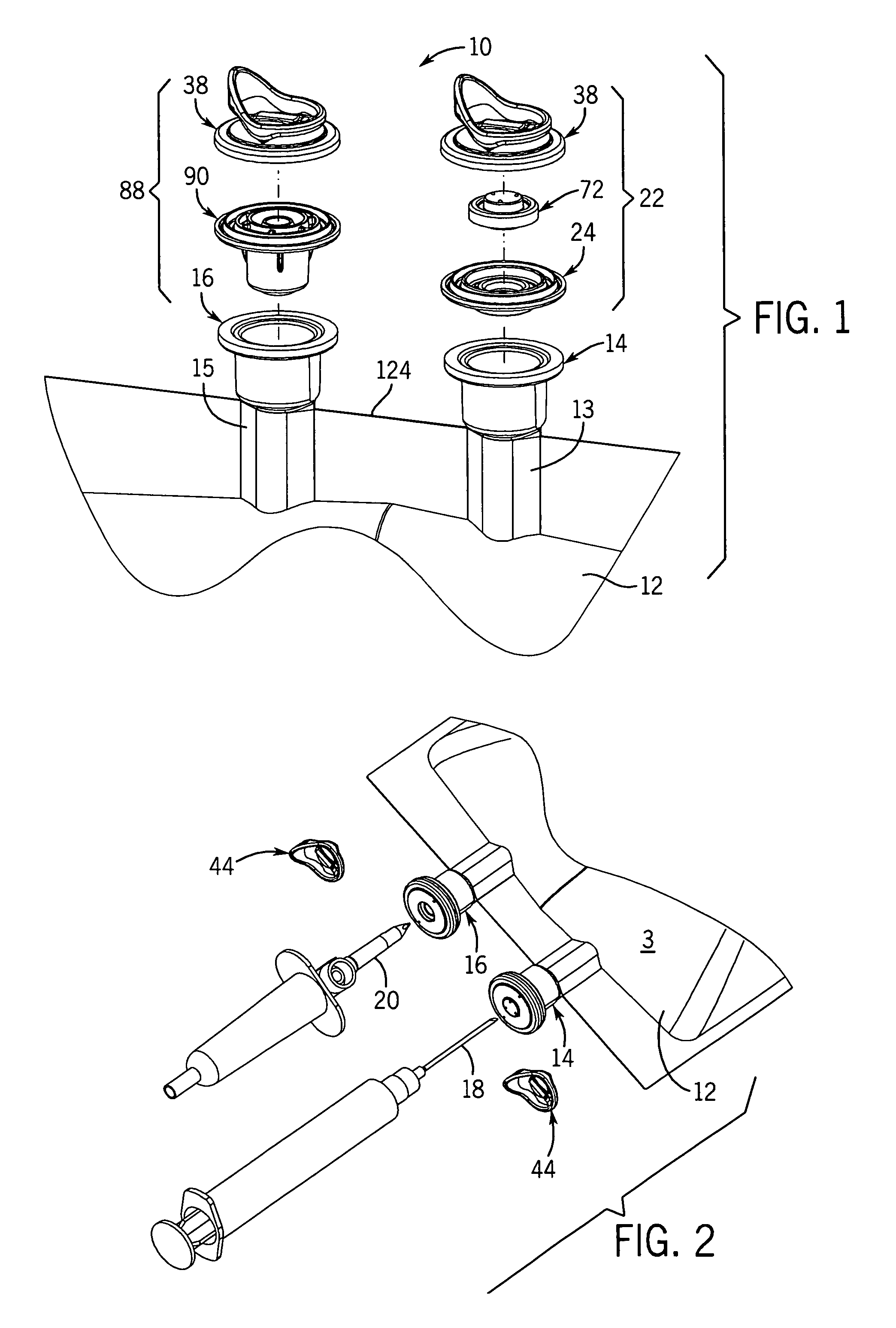
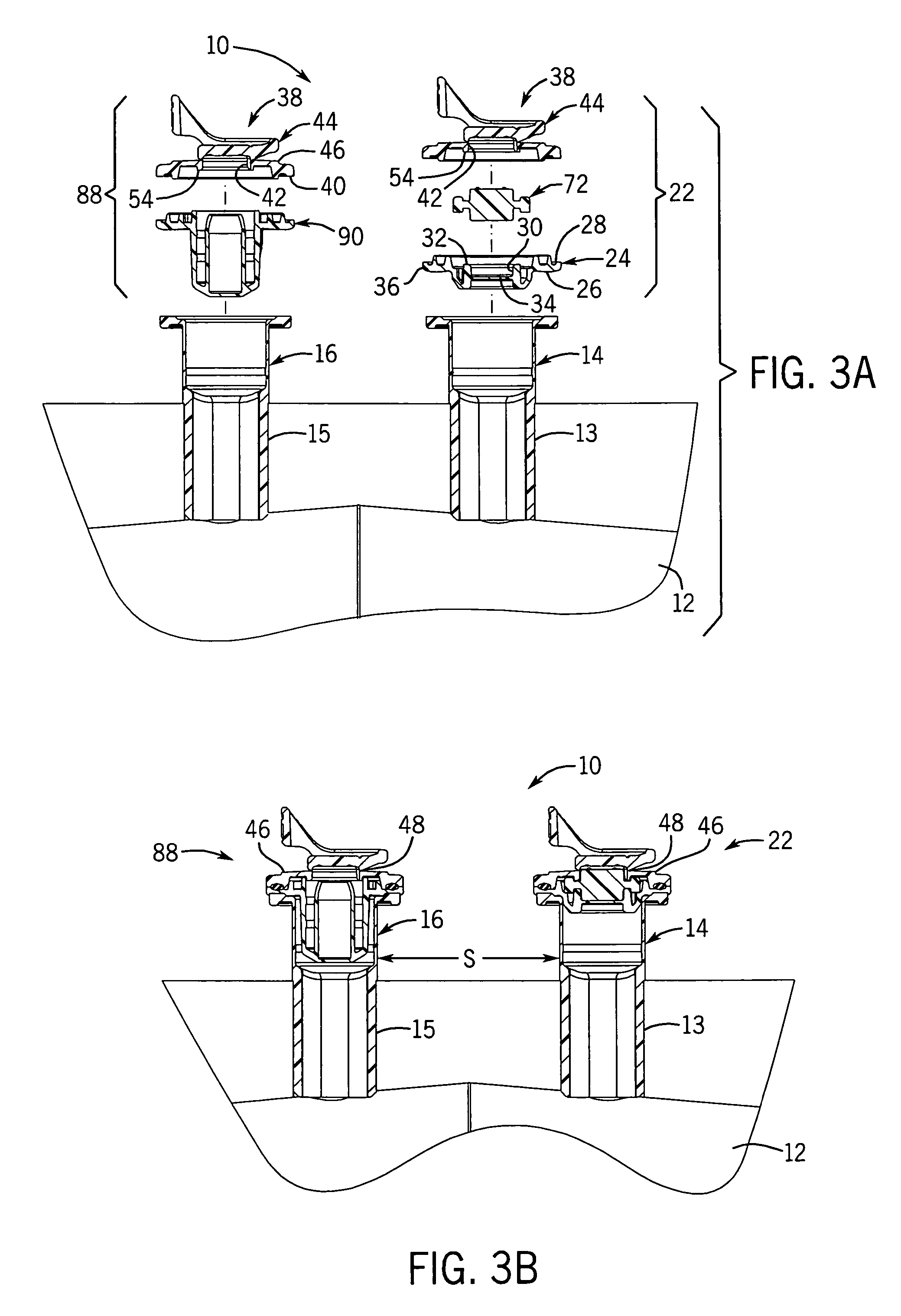
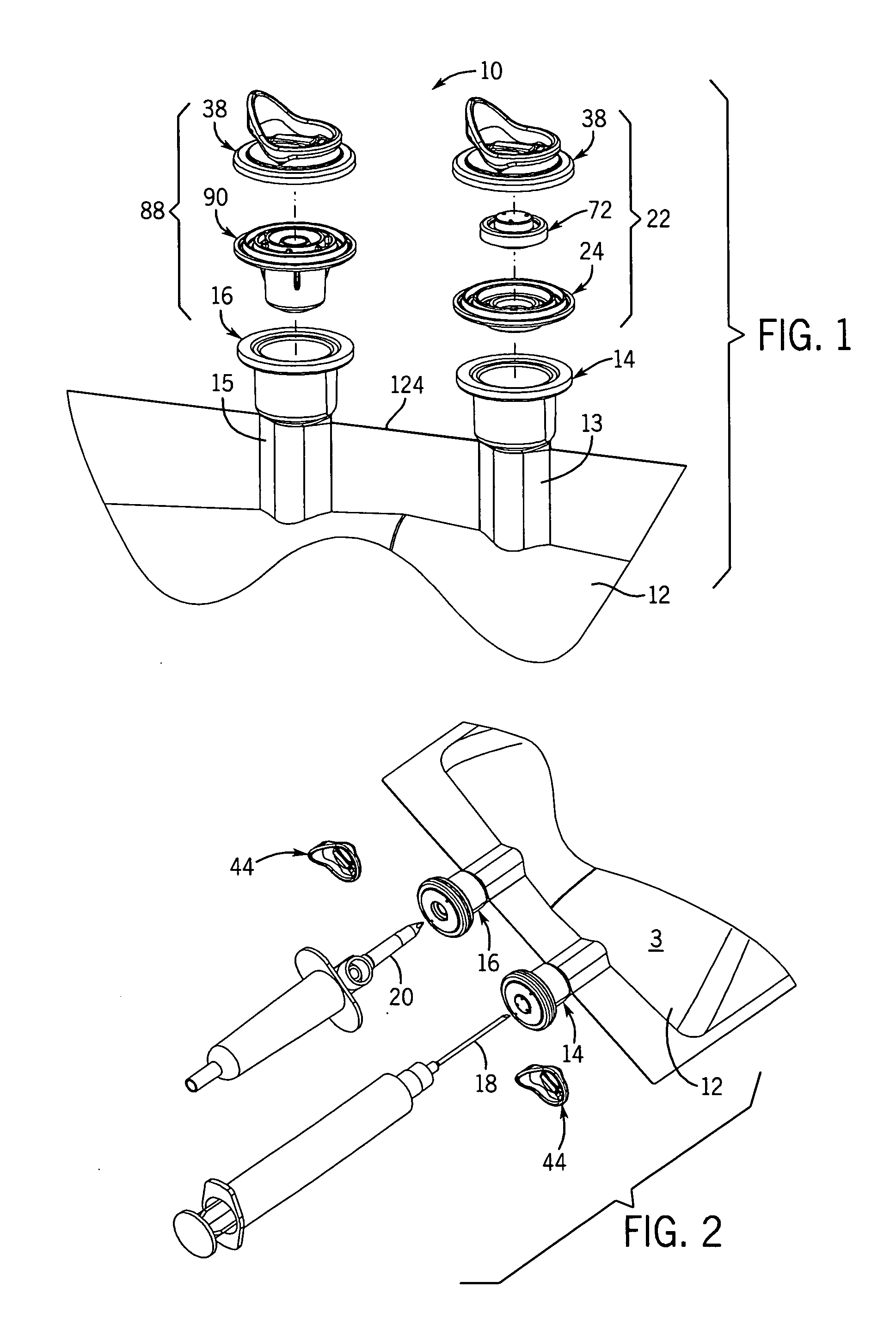
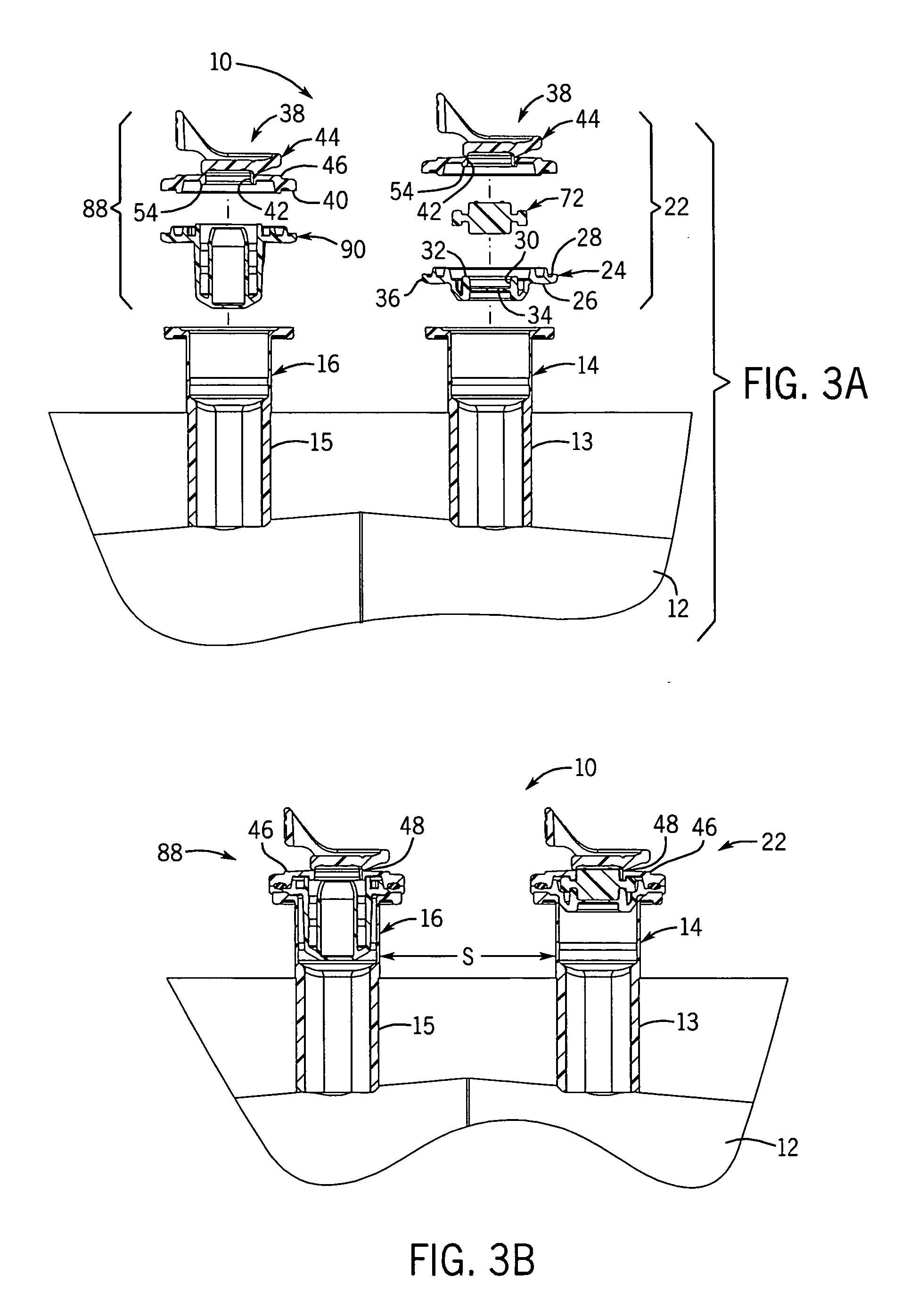
Medical fluid container
ActiveUS7527619B2Facilitate reliable fabrication and useLow moisture vapor transmission rateDiagnosticsSurgeryPolyolefinMoisture vapor transmission rate
A flexible non-PVC, non-DEHP container or bag for medical fluids has a container body formed of a multiple layer polyolefin film. The container has one or more ports equipped with a polyolefin fill tube and port closure assembly. The container has a low moisture vapor transmission rate.
Owner:HOSPIRA
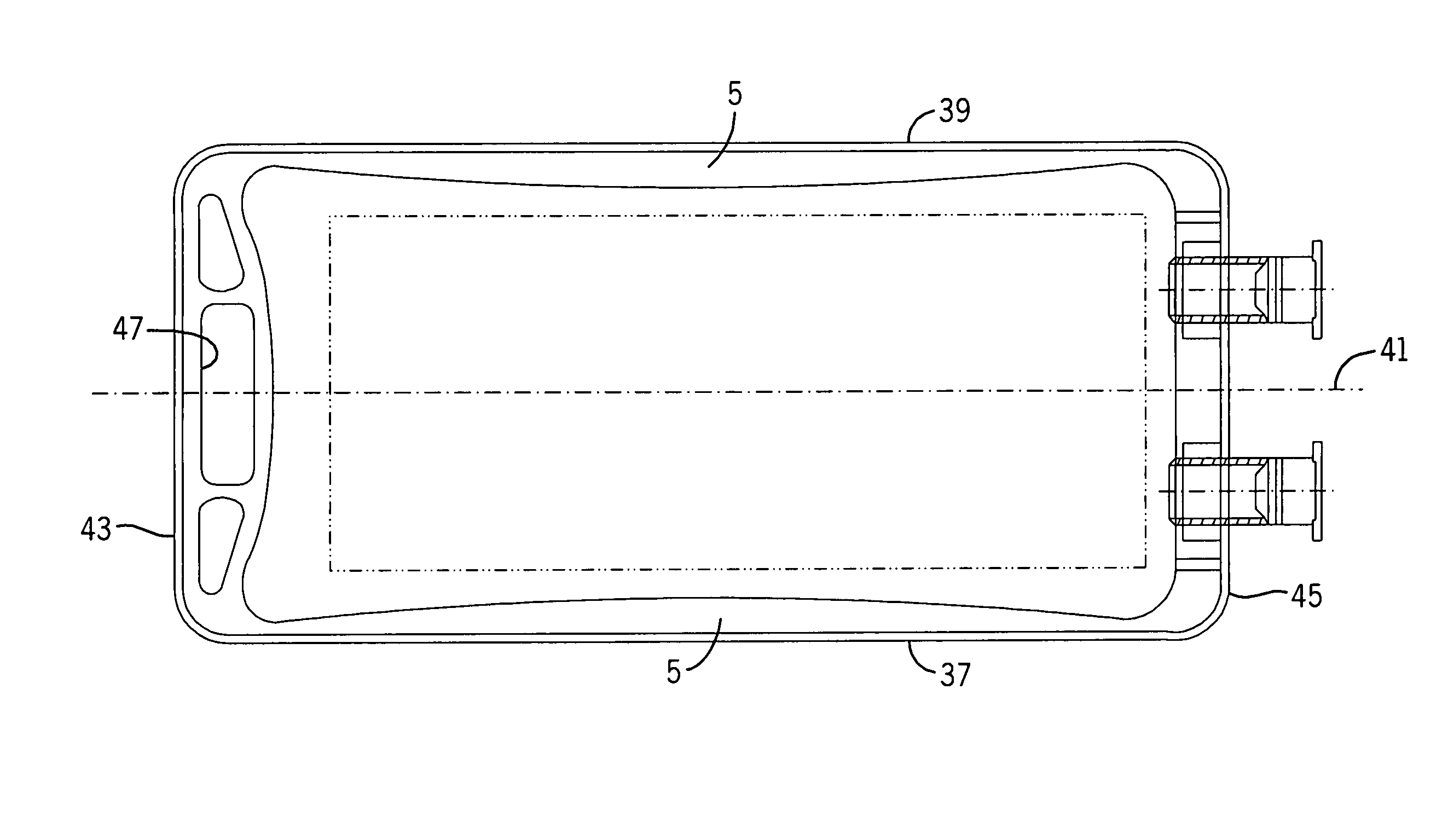
Medical fluid container with concave side weld
ActiveUS7717897B2Facilitate reliable fabrication and useLow moisture vapor transmission rateFlexible coversWrappersPolyolefinEngineering
A flexible non-PVC, non-DEHP polyolefin container or bag for medical fluids has an elongated container body formed of polyolefin film. The container has one or more ports equipped with a polyolefin fill tube and port closure assembly. The container includes a concave seam on at least one of its longitudinal sides.
Owner:HOSPIRA
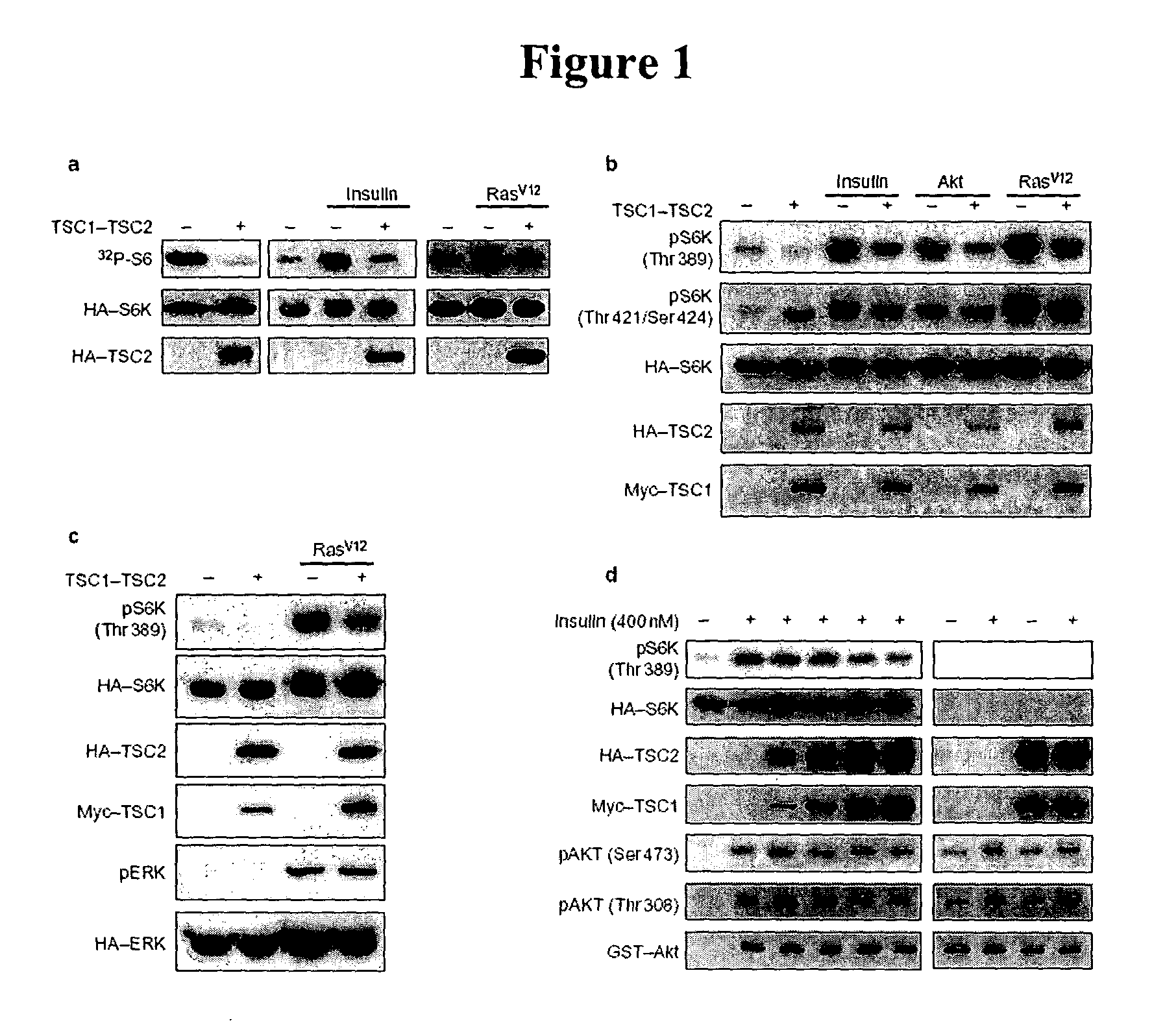
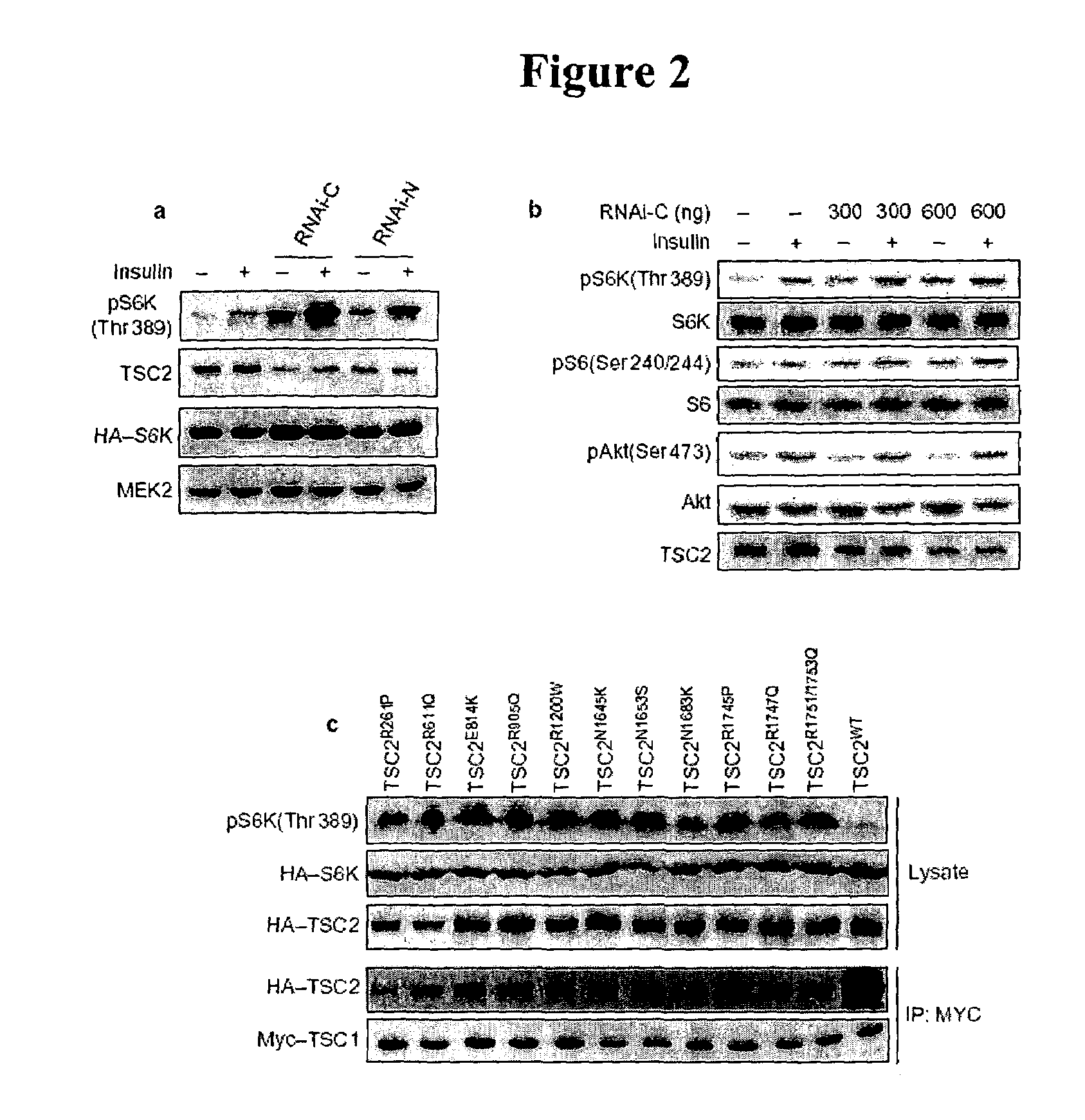
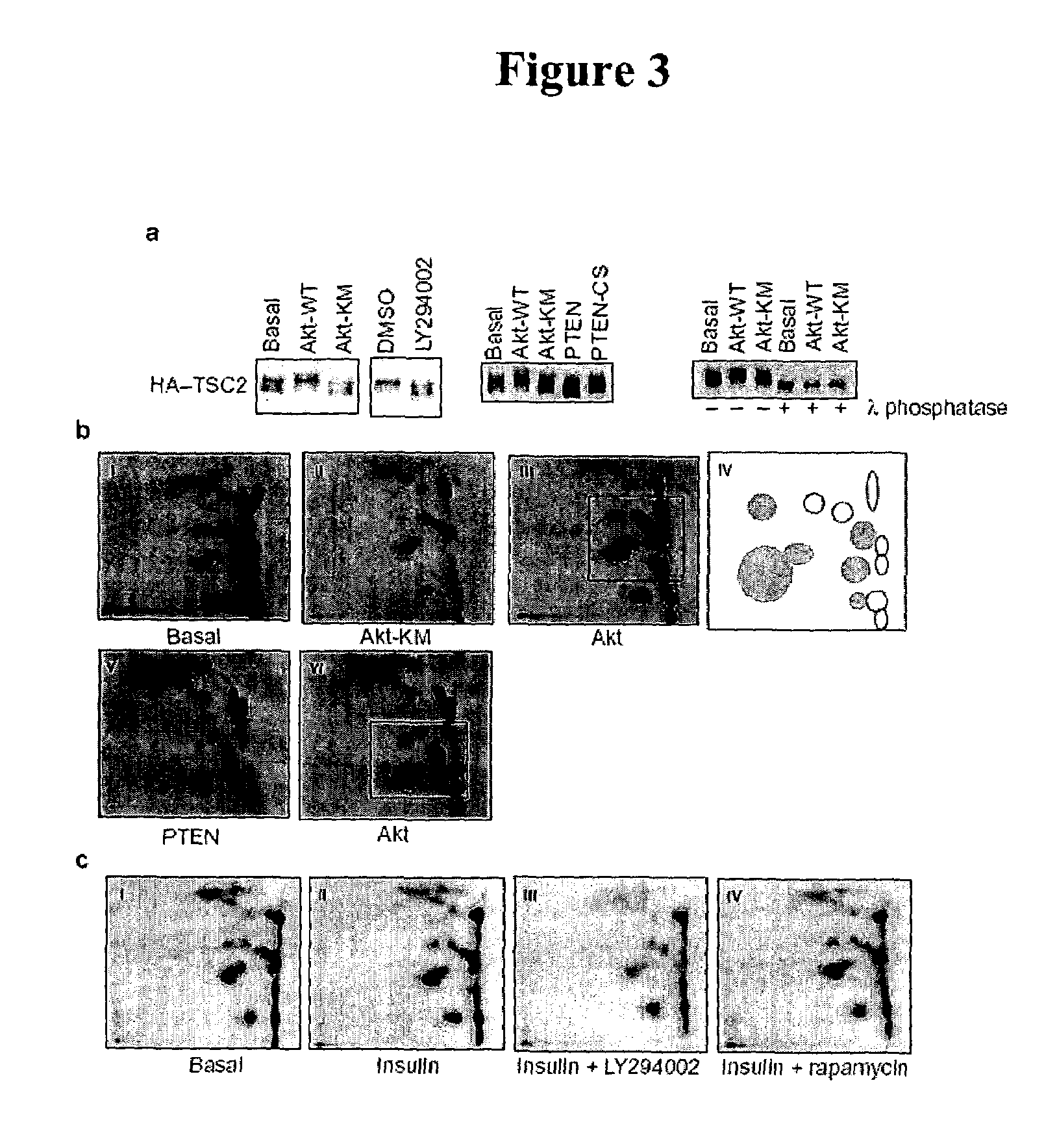
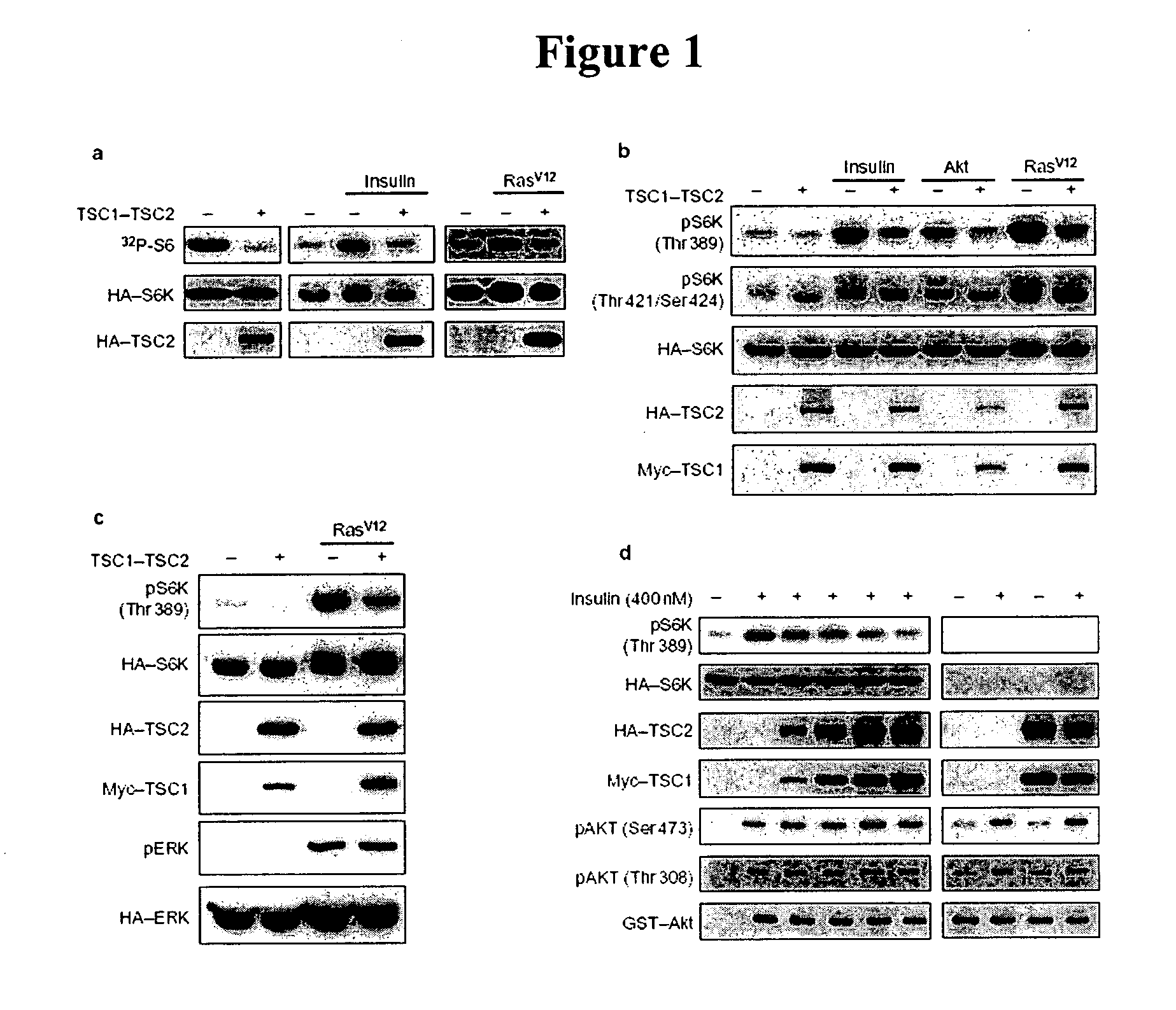
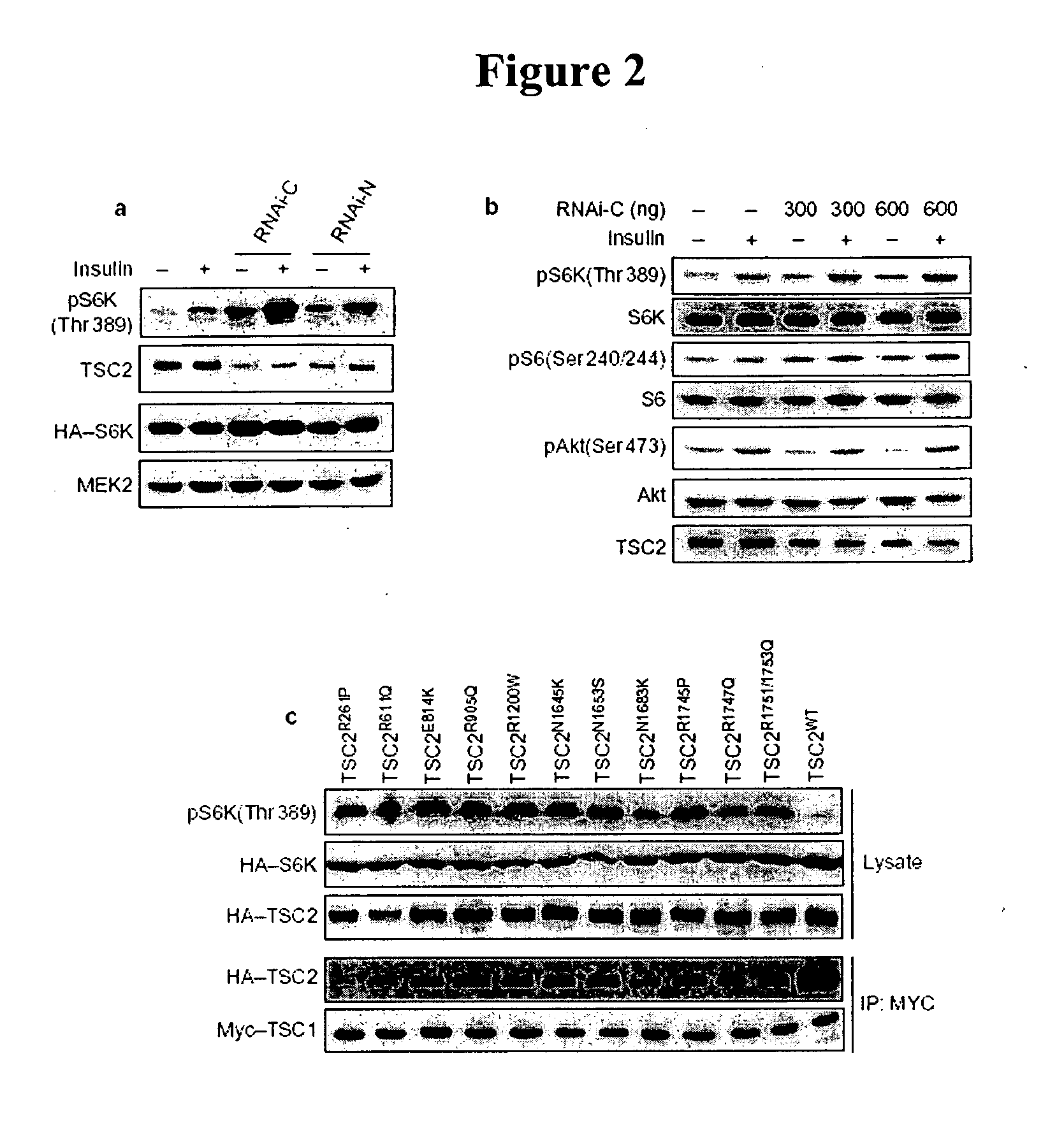
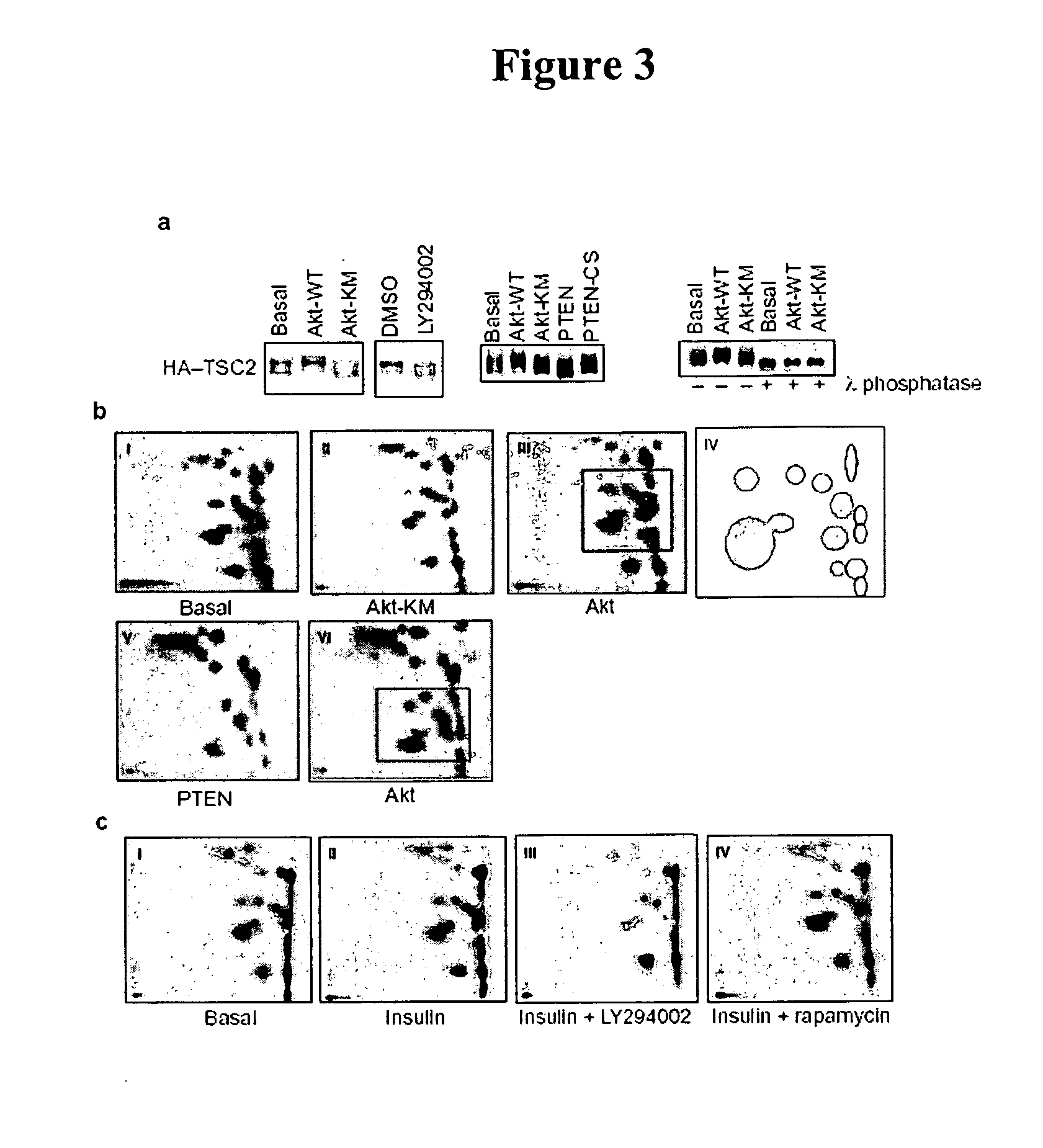
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases arising from defects in the tuberous sclerosis pathway
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for identifying abnormalities in TSC signaling pathways. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of diagnosing and treating disorders such as tuberous sclerosis, which are caused by mutations in the TSC genes. The present invention further relates to methods and compositions for treating cancers mediated by TSC signaling disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Medical fluid container
ActiveUS20060282061A1Facilitate reliable fabrication and useLow moisture vapor transmission rateDiagnosticsSurgeryPolyolefinMoisture vapor transmission rate
A flexible non-PVC, non-DEHP container or bag for medical fluids has a container body formed of a multiple layer polyolefin film. The container has one or more ports equipped with a polyolefin fill tube and port closure assembly. The container has a low moisture vapor transmission rate.
Owner:HOSPIRA
Thermoplastic Resin Composition and Molded Product
The present invention provides a thermoplastic resin composition comprising 100 mass parts of a polycarbonate resin composition comprising 50 to 95 mass % of (A) a polycarbonate resin and 50 to 5 mass % of (B) a polylactic acid based resin and 5 to 65 mass parts of (C) a vinyl based graft copolymer. The above thermoplastic resin composition comprising the polycarbonate resin and the lactic acid based resin and endowed with a mechanical characteristic of polycarbonate and an excellent fluidity of polylactic acid in combination is improved in a hydrolysis resistance and provides a molded article further improved in an impact resistance and a thin-walled falling weight impact strength. A rise in the above characteristics makes it possible to use the plastic molded articles over a long period of time, and not only the thin-walled molding property and the portability are improved, but also the thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention can industrially advantageously be used as well for large-sized molded articles. In the thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention use of the polycarbonate-polyorganosiloxane copolymer as the polycarbonate resin component makes it possible to improve as well the flame retardancy and advantageously use the thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention for office automation equipments, information and communication equipments, car parts, building components, home electric appliances and the like.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases arising from defects in the tuberous sclerosis pathway
InactiveUS20050070567A1Impact strengthBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementNodular sclerosisSignal pathway
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for identifying abnormalities in TSC signaling pathways. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of diagnosing and treating disorders such as tuberous sclerosis, which are caused by mutations in the TSC genes. The present invention further relates to methods and compositions for treating cancers mediated by TSC signaling disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
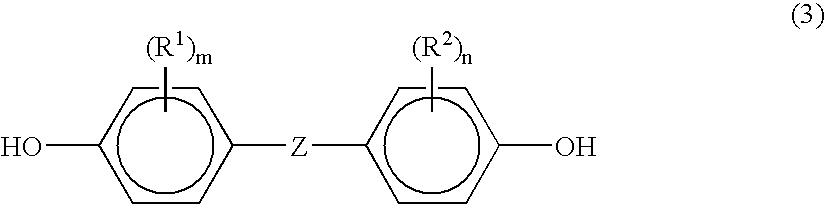
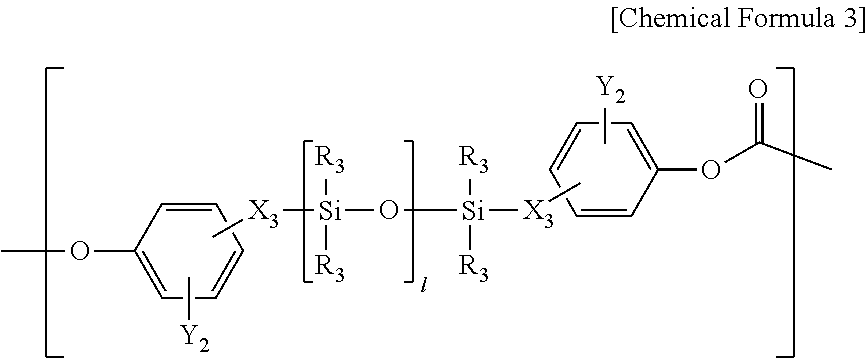
Copolycarbonate and composition comprising the same
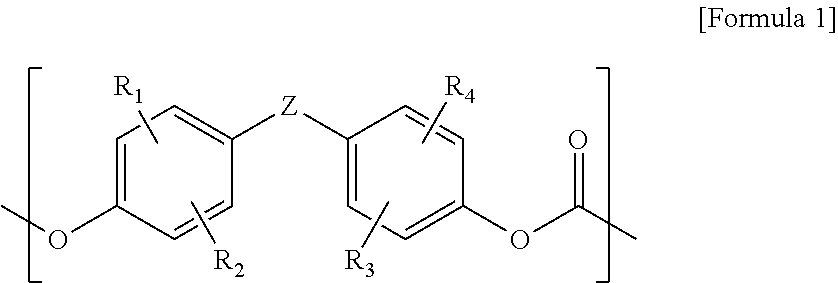
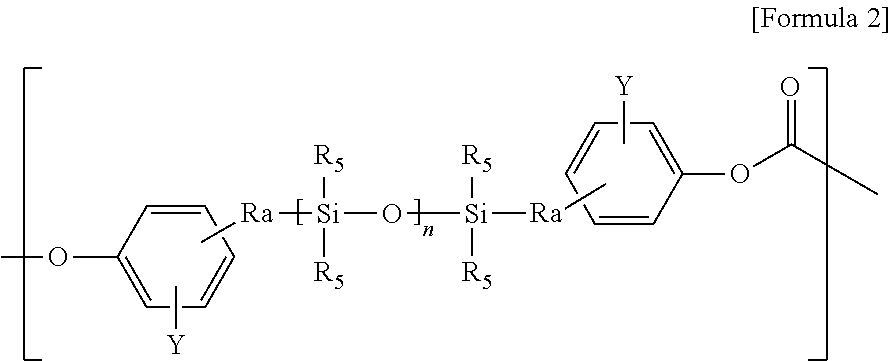
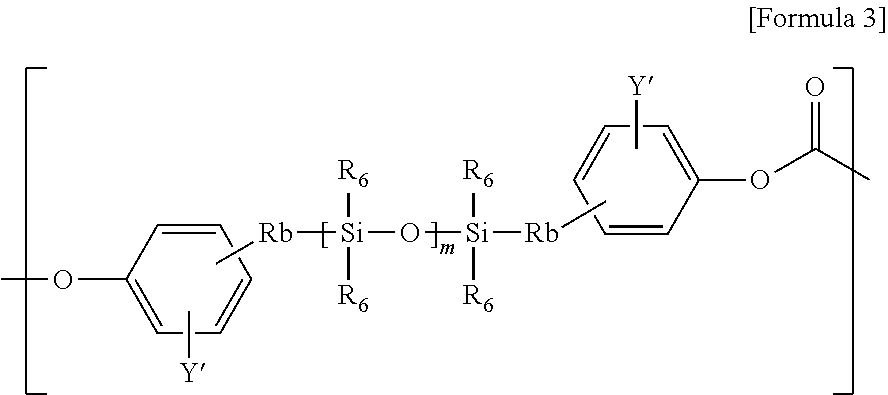
The present invention relates to copolycarbonates and a composition comprising the same. The copolycarbonate according to the present invention has a structure in which specific siloxane compounds are introduced in the main chain of polycarbonate and thus exhibits the effects of improving impact strength at room temperature, impact strength at low-temperature and melt index.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Medical fluid container with concave side weld
ActiveUS20070027437A1Increase container sealing reliabilityEase and efficiency of manufactureFlexible coversWrappersPolyolefinEngineering
A flexible non-PVC, non-DEHP polyolefin container or bag for medical fluids has an elongated container body formed of polyolefin film. The container has one or more ports equipped with a polyolefin fill tube and port closure assembly. The container includes a concave seam on at least one of its longitudinal sides.
Owner:HOSPIRA
Copolycarbonate and composition comprising the same
The present invention relates to a copolycarbonate and a molded article comprising the same. The copolycarbonates according to the present invention has a structure in which a specific siloxane compound is introduced in a main chain of the polycarbonate, and has effects of improving impact strength at room temperature, impact strength at low temperature, and melt index properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Medical fluid container
InactiveUS20060276769A1Increase container sealing reliabilityEase and efficiency of manufactureDiagnosticsInfusion devicesPolyolefinEngineering
A flexible non-PVC, non-DEHP container or bag for medical fluids has a container body formed of a multiple layer polyolefin film. The container has one or more ports equipped with a polyolefin fill tube and port closure assembly. The container has a low moisture vapor transmission rate.
Owner:HOSPIRA
Novel propylene polymer blends
InactiveUS20110196078A1Maintain good propertiesHigh transparencyImpression capsMixingLow-density polyethyleneLinear low-density polyethylene
Owner:BOREALIS TECH OY
Reactive polyamide resins and polyamide resin compositions
Provided is a polyamide resin composition comprising an elastomer etc, and a reactive polyamide resin excellent in reactivity. The polyamide resin composition comprises 0.5 to 100 parts by mass of an elastomer per 100 parts by mass of a reactive polyamide resin, wherein the reactive polyamide resin obtained by polycondensing a diamine (A) containing 70 mol % or more of a diamine structural unit derived from xylylenediamine and a dicarboxylic acid (B) containing 50 mol % or more of a dicarboxylic acid structural unit derived from sebacic acid, and has a concentration of reactive functional groups of 100 μeq / g or more and a molar ratio of reacted diamine to reacted dicarboxylic acid (the number of moles of reacted diamine / the number of moles of reacted dicarboxylic acid) of 1.0 or more.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
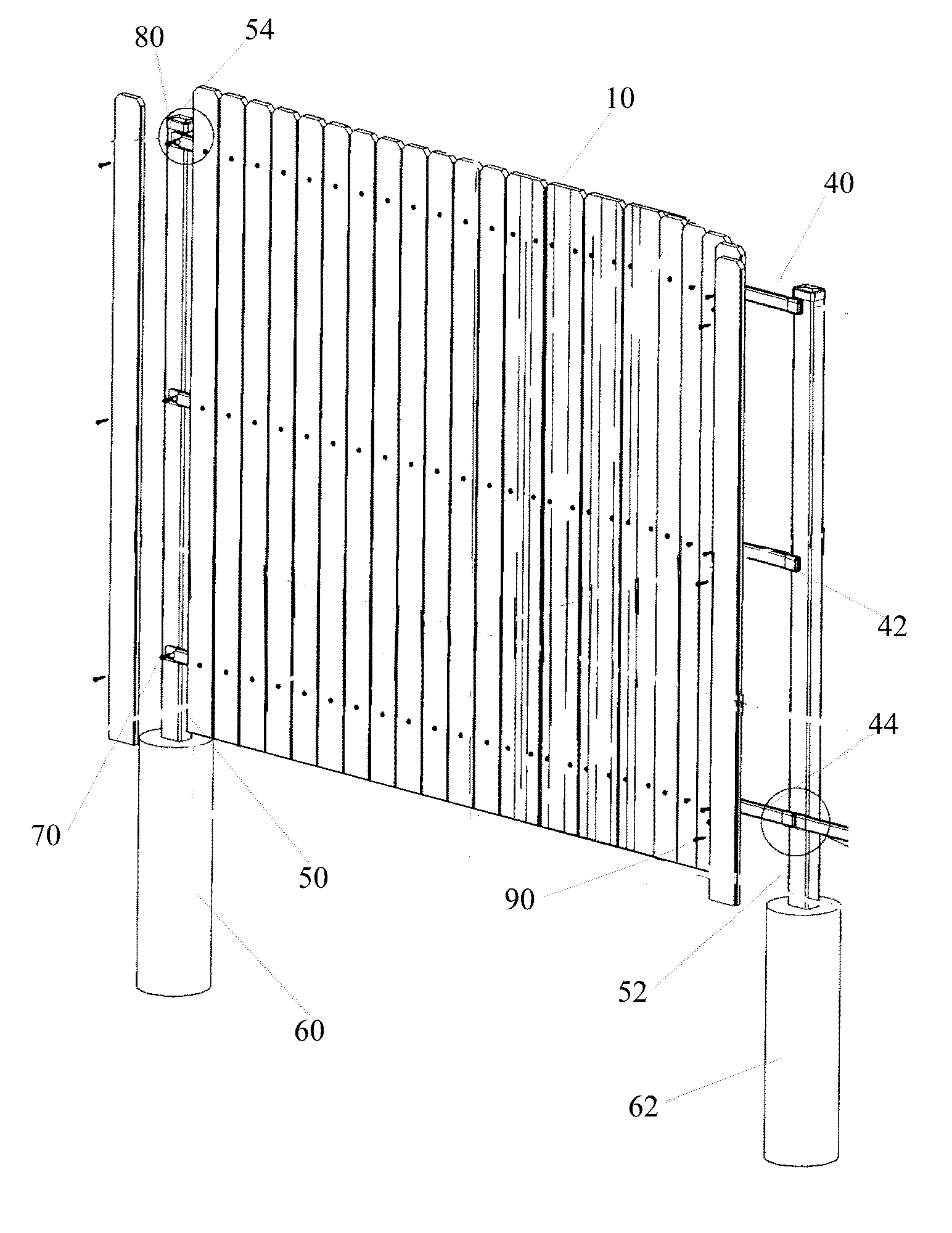
Plastic building material components
A plastic extruded building material component such as picket fence or skirting component. The building material component is profile extruded to have texturing and color streaking to simulate a wood building material. A unique mechanism for dispersing and melting the streaking and texturing agents is provided for extruding the product.
Owner:GIACCHINO KEITH
Method for forming flexible composites using polymer coating materials
ActiveUS7470453B1High tear strengthSmall particle sizeConveyorsPretreated surfacesThermoplasticFluoropolymer
A method for forming a flexible composite useful for forming belts that are processed into pressure sensitive tapes or converted into rolled goods. The method impregnates a flexible substrate with a polymer coating that includes a thermoplastic or thermoset resin that is not a fluoropolymer. The impregnating coating layer may also include a fluoropolymer. Additional fluoropolymer polymer overcoating layers are applied to the impregnating layer to form the flexible composite. The coating layers are applied as a liquid and dried.
Owner:ADVANCED FLEXIBLE COMPOSITES
Shock-absorbing member
InactiveUS20140124315A1Heavy loadEfficient receptionElastic dampersBumpersLoad resistanceMechanical engineering
A shock-absorbing member may include a cylindrical member configured to receive an impact load applied axially and capable of being axially compressed by the impact load, a wood member received within the cylindrical member without contacting each other and having an impact load-resistance strength greater than the cylindrical member, and a foam material capable of positioning the wood member with respect to the cylindrical member and filled in a clearance formed between an outer surface of the wood member and an inner wall surface of the cylindrical member partially or over the entirety thereof by foaming. The foamed foam material has a strength that does not prevent the cylindrical member from radially inwardly deforming when the cylindrical member is axially compressed with the wood member by the impact load.
Owner:TOYOTA SHATAI KK
Bracket for Protecting Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) of Portable Display Device
InactiveUS20130165576A1High modulusLow moisture absorptionSpecial tyresCeramic shaping apparatusFiberLiquid-crystal display
A bracket for protecting the liquid crystal display (LCD) of a portable display device comprises (A) a polyamide resin, and (B) a carbon fiber, wherein the ratio of (A):(B) of the (A) polyamide resin and the (B) carbon fiber is about 20 to about 40 wt %: about 60 to about 80 wt %, and the (A) polyamide resin comprises (a1) an aromatic polyamide and (a2) an aliphatic polyamide including a C10 to C20 aliphatic group.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Laser welding of overlapping metal workpieces assisted by oscillating laser beam focal position
InactiveUS20190224781A1Maintain good propertiesHigh strengthVehicle componentsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOptoelectronicsFocal position
A method of laser welding a workpiece stack-up (10, 10′) that includes at least two overlapping metal workpieces (12, 150, 14) comprises advancing a beam spot (44) of a laser beam (24) relative to a top surface (20) of the workpiece stack-up (10, 10′) and along a beam travel pattern (66) to form a laser weld joint (64) that fusion welds the metal workpieces (12, 150, 14) together. While the beam spot (44) is being advanced between a first point (76) and a second point (78) of one or more weld paths (74) of the beam travel pattern (66), the position of a focal point (52) of the laser beam (24) is oscillated relative to the top surface (20) of the workpiece N stack-up (10, 10′) along a dimension (68) oriented transverse to the top surface (20).
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Granulated colorant and related art
InactiveUS20070149658A1Reduce anisotropyHigh dimensional accuracyOrganic chemistryBenzene azine dyesHigh concentrationThermoplastic elastomer
A granulated colorant as a granulation product of a powdery nigrosine dye, that has a bulk density of 0.4 to 0.7 g / ml and a hardness of 1 to 20 N. A high-concentration master batch obtained by blending a granulated colorant and a thermoplastic resin, which comprises 25 to 100 parts by weight of a nigrosine dye in the granulated colorant per 100 parts by weight of the thermoplastic resin. A colored composition comprising a granulated colorant or high-concentration master batch and a thermoplastic resin or thermoplastic elastomer.
Owner:ORIENT CHEM INDS
Polypropylene Resin Composition With Good Transparence And Good Impact Strength
ActiveUS20100144975A1High impact strengthTransparence be improvedThin material handlingFlexural modulusAlpha-olefin
Provided is a polypropylene resin composition having excellent impact resistance, impact strength at low temperature and transparence comprising ethylene-alpha olefin copolymer (c) to a polypropylene resin composition in which the ratio of viscosity is regulated by adjusting molecular weight of propylene-alpha olefin random copolymer (a) and propylene-alpha olefin elastic copolymer (b), thereby regulating impact resistance and flexural modulus of the polypropylene resin composition and improving transparence; therefore, applying as various products including cold-storage containers for freezer and refrigerator, food packaging container, extrusion blow molding material, film, sheet and bottle cap, etc.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Copolycarbonate and composition comprising the same
The present invention relates to a copolycarbonate and a molded article comprising the same. The copolycarbonates according to the present invention has a structure in which a specific siloxane compound is introduced in a main chain of the polycarbonate, and has effects of improving impact strength at room temperature, impact strength at low temperature, and melt index properties.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Golf ball
Owner:BRIDGESTONE SPORTS
Polyolefin compatibilizer composition for compounding to improve stiffness and impact balance
This disclosure provides for compatibilizer compositions that are useful in compounding polypropylenes and ethylene elastomeric copolymers for injection molding applications. The compatibilizer includes a combination of: Component A of polypropylene homopolymers or polypropylene copolymers containing small amounts of ethylene; and Component B of propylene bipolymers with ethylene and / or other α-olefin comonomers, the bipolymer having a relatively high proportion of propylene moieties, for example, 50-75% propylene. Compared to known or conventional compatibilizer formulations, the bipolymer Component B is relatively propylene rich and generally can be used in the injection molding composition in lower concentrations.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Articulating dunnage and method of use
InactiveUS20070214750A1Effective and efficient polymeric dunnageImprove protectionUsing shock-absorbing mediaLiquid materialDunnageEngineering
Articulated dunnage having at least two corner support portions joined along a hinge. The dunnage is movable between an open orientation and a folded configuration. The dunnage may be formed in the open configuration so that the dunnage is biased in the open orientation by the shape memory of the polymeric material. The dunnage is configured to be fitted around a portion of the article and to extend between adjacent corners of the container when in the folded configuration. The present invention also provides a method for packaging using articulating dunnage including the general steps of (a) placing the dunnage in the open configuration on the container over the opening, (b) moving the article into engagement with the dunnage, and (c) inserting the article and dunnage into the container through the opening, the action of inserting the article and dunnage into the container causing the dunnage to move from the open configuration to the closed configuration.
Owner:DISPLAY PACK
Body for a writing, tracing, drawing or coloring pencil
PendingUS20220048312A1Improve mechanical propertiesImpact strengthNon-propelling pencilsPolymer sciencePoly(butylene succinate)
A body for a writing, tracing, drawing or coloring pencil has a composition that includes, by weight, with respect to the total weight of the body between 50% and 95% of a mixture of polylactic acid and of polybutylene succinate in a polylactic acid / polybutylene succinate ratio by weight of between 90 / 10 and 60 / 40 and between 5% and 50% of filler that can have shellfish shells and / or calcium carbonate. A writing, tracing, drawing or coloring pencil has such a body.
Owner:SOC DITE SOC BIC
Polymer blends containing polyhydroxyalkanoates and compositions with good retention of elongation
Biodegradable polymer blend compositions are provided which contain oligomeric esters. The oligoester compound can compatibilize blends of two or more biodegradable polymers resulting in excellent ductility and reduced tendency to embrittlement of products produced from therefrom. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the blend composition comprises a PHA, polycaprolactone (PCL) and one or more oligomeric esters. In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the blend composition comprises a PHA, polybutylenesuccinate-adipate (PBSUA), and one or more oligomeric esters.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Polylactic acid composites
InactiveUS8143340B2Excellent mechanical properties and heat resistanceImpact strengthSpecial tyresHeat resistanceMaterials science
The present invention features polylactic acid composite compositions, more particularly a composite composition. The provided polylactic acid composite composition preferably includes the biomaterial polylactic acid resin and, accordingly, it is capable of effectively reducing carbon dioxide emission. Hence, it goes along with the low-carbon, green growth initiative. Further, with improved mechanical strength and heat resistance, it is usefully applicable to automotive interiors / exteriors, construction interiors, etc.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Granulated colorant and related art
ActiveUS20110065844A1Easy to transportGood dispersionOrganic chemistryBenzene azine dyesHigh concentrationThermoplastic elastomer
A granulated colorant as a granulation product of a powdery nigrosine dye, that has a bulk density of 0.4 to 0.7 g / ml and a hardness of 1 to 20 N. A high-concentration master batch obtained by blending a granulated colorant and a thermoplastic resin, which comprises 25 to 100 parts by weight of a nigrosine dye in the granulated colorant per 100 parts by weight of the thermoplastic resin. A colored composition comprising a granulated colorant or high-concentration master batch and a thermoplastic resin or thermoplastic elastomer.
Owner:ORIENT CHEM INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com