Asparaginase from basidiomycetes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
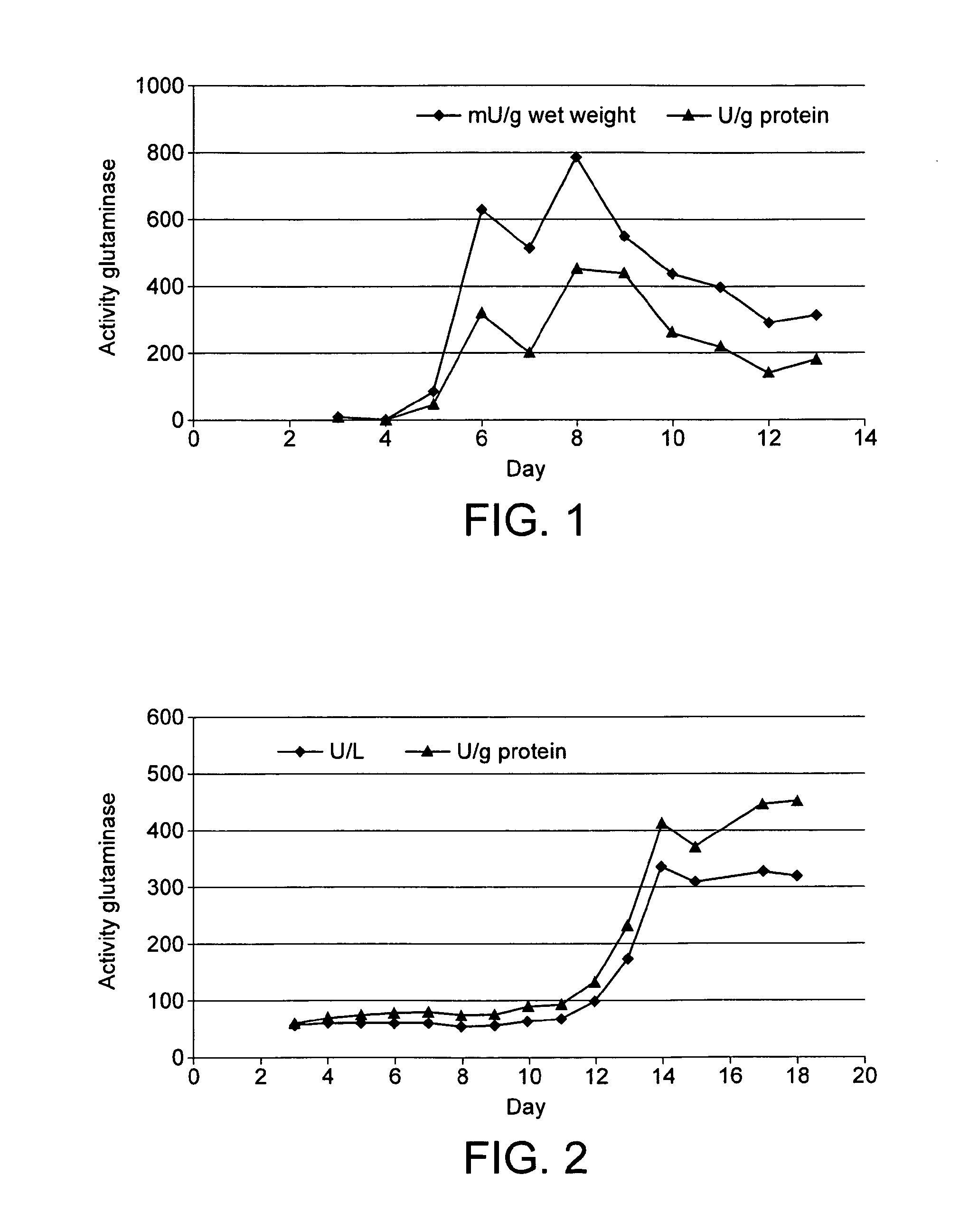
Cultivation of Flammulina velutipes
[0119]All media and equipment were autoclaved prior to use and standard sterile techniques were applied throughout the procedure. Flammulina velutipes was maintained on standard agar plates (30.0 g L−1 glucose-monohydrate; 4.5 g L−1 asparagine-monohydrate; 1.5 g L−1 KH2PO4; 0.5 g L−1 MgSO4; 3.0 g L−1 yeast extract; 15.0 g L−1 agar agar; 1.0 mL L−1 trace metal solution containing 0.005 g L1 CuSO4.5H2O, 0.08 g L−1 FeCl3.6H2O, 0.09 g L−1 ZnSO4.7H2O, 0.03 g L−1 MnSO4H2O and 0.4 g L−1 EDTA. The pH of the medium was adjusted to pH 6 with 1 M NaOH prior to sterilisation. Precultures were prepared by homogenisation of a 10×10 mm agar plug with mycelium of Flammulina velutipes in 100 mL of sterile standard nutrition solution using an Ultra Turrax (Miccra D-9, Art, Müllheim, Germany). Submerged cultures were maintained at 24° C. and 150 rpm. After cultivation for 5 days, 50 ml preculture were transferred into 250 ml main culture medium consisting of minimal...
example 2
Enzyme Preparation from Flammulina velutipes
[0120]After 18 days of cultivation, the culture was filtrated and the extracellular enzyme-containing supernatant (200 mL) was reverse-foamed, the asparaginase and another protein being the only proteins left in the supernatant. The remaining liquid was concentrated using ultra-filtration (MWCO 10,000), and both proteins were separated via size exclusion chromatography at a Superose 6.
[0121]Most of the hydrolytic activity originally present was recovered indicating that this protocol yielded a useful enzyme concentrate through two steps only.
example 3
Hydrolysis of L-Asparagine Using Native Enzyme
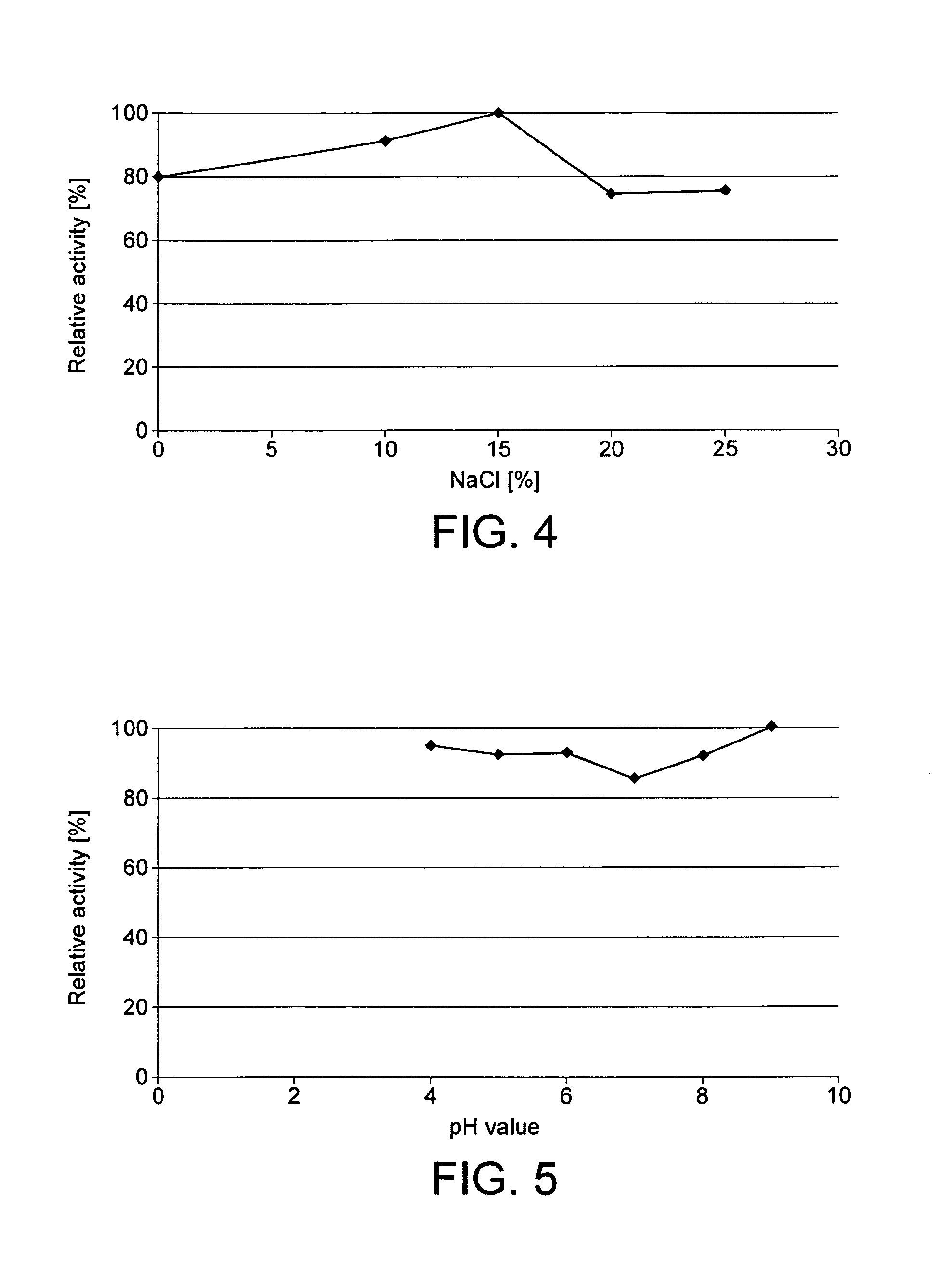
[0122]100 μL of 10 mM asparagine in 0.1 M K2HPO4 / KH2PO4 buffer (pH 7.0) were preheated at 37° C. for 5 min. The reaction was started with the addition of 50 μL enzyme solution. After an incubation time of 20 min at 37° C. and 400 rpm in a thermoshaker, the assay was stopped by the addition of 20 μL TCA. A control experiment was carried out without substrate. The contents of aspartic acid were quantitatively measured with the HPLC after OPA-derivatisation, and the difference between sample and control was used to calculate then enzyme's activity.
[0123]The analytical evidence indicates a fast enzymatic hydrolysis of the substrate L-asparagine.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com