Plasma Etch Resistant, Highly Oriented Yttria Films, Coated Substrates and Related Methods
a technology of yttria film and substrate, applied in the direction of molten spray coating, vacuum evaporation coating, coating, etc., can solve the problems of increasing production cost, reducing the resistance of substrates to etching, so as to increase the plasma resistance of substrates and increase the resistance to degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
[0046]Two sets of yttrium oxide films were grown on fused quartz coupons (dimensions: 1 inch×1 inch; ⅛ inch thick) by electron beam evaporation. Each coupon was installed in the electron beam film chamber and the chamber was vacuum purged overnight. The film chamber vacuum level was maintained at 2.4×10−5 ton and preheated for 12 hours to ensure temperature equilibrium was reached.
[0047]High purity (>99.99%) Y2O3 target was evaporated by electron beam and each coupon was coated for 4 hours to reach target thickness of about 4 microns. During the film process, temperature of the substrate was maintained between about 150° C. to about 350° C.
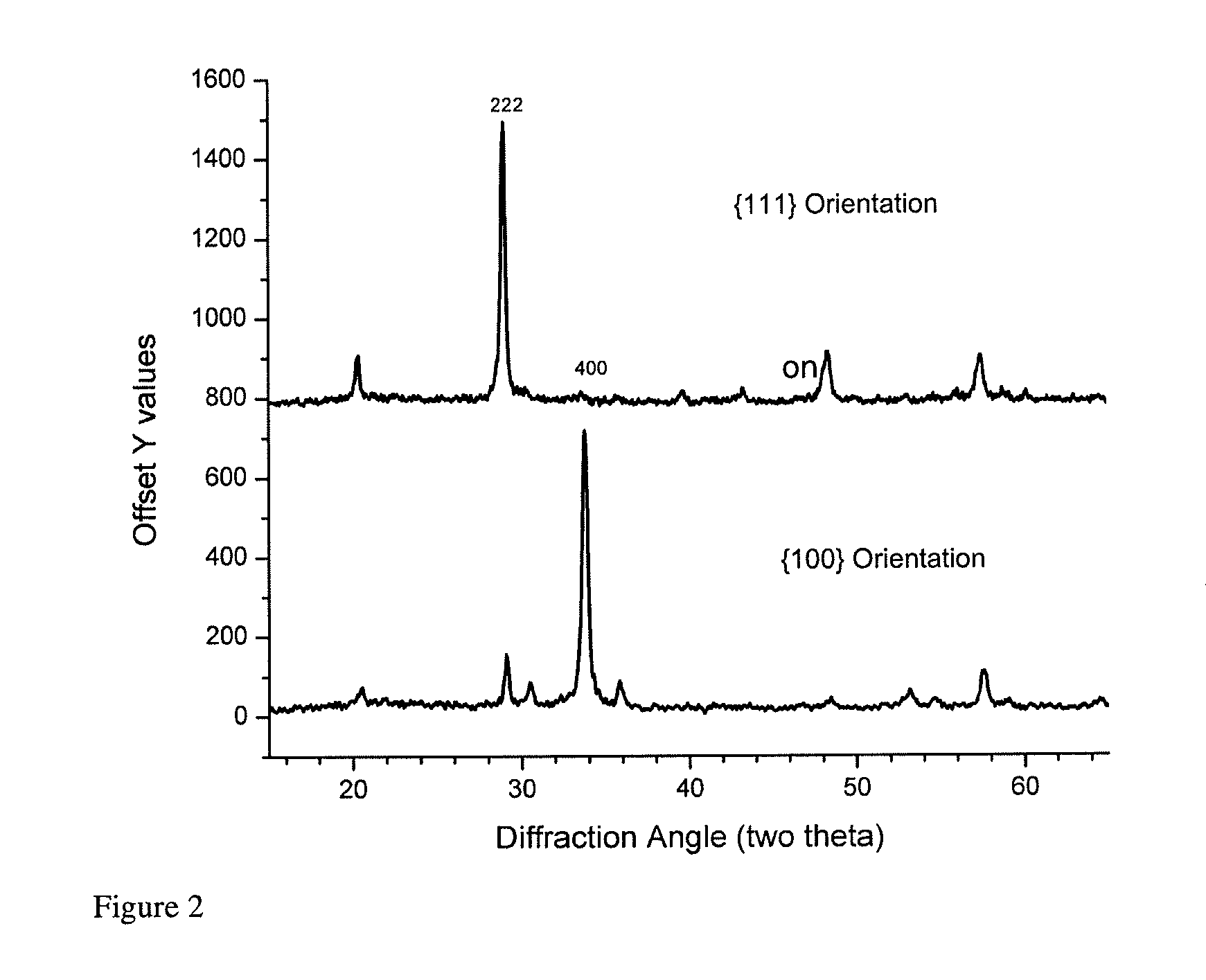
[0048]One set of films was grown to predominantly produce a crystalline structure having an orientation described by Miller Index notation {100}. The second set was grown to produce predominantly a crystalline structure having an orientation described by Miller Index notation {111}.
[0049]FIG. 2 shows x-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements of the two...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com