Mesoporous fcc catalysts with excellent attrition resistance
a technology of mesoporous fcc and cracking catalyst, which is applied in the field of new fluid catalytic cracking catalysts, can solve the problems of increasing the cost of catalyst to the refiner, physical breaking down of catalyst into even smaller particles called “fines”, and achieving high overall pore volume, improved attrition resistance, and improved attrition resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
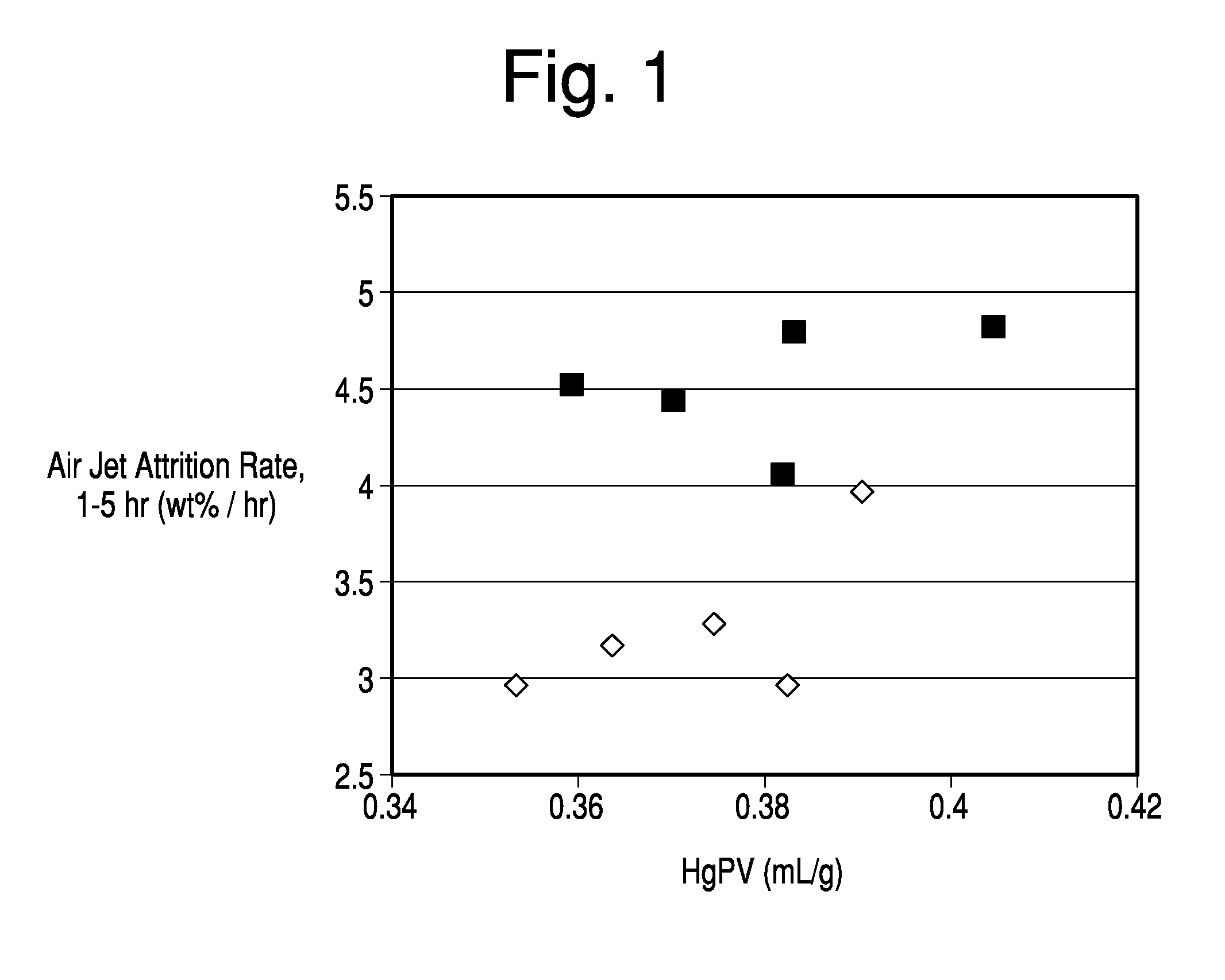
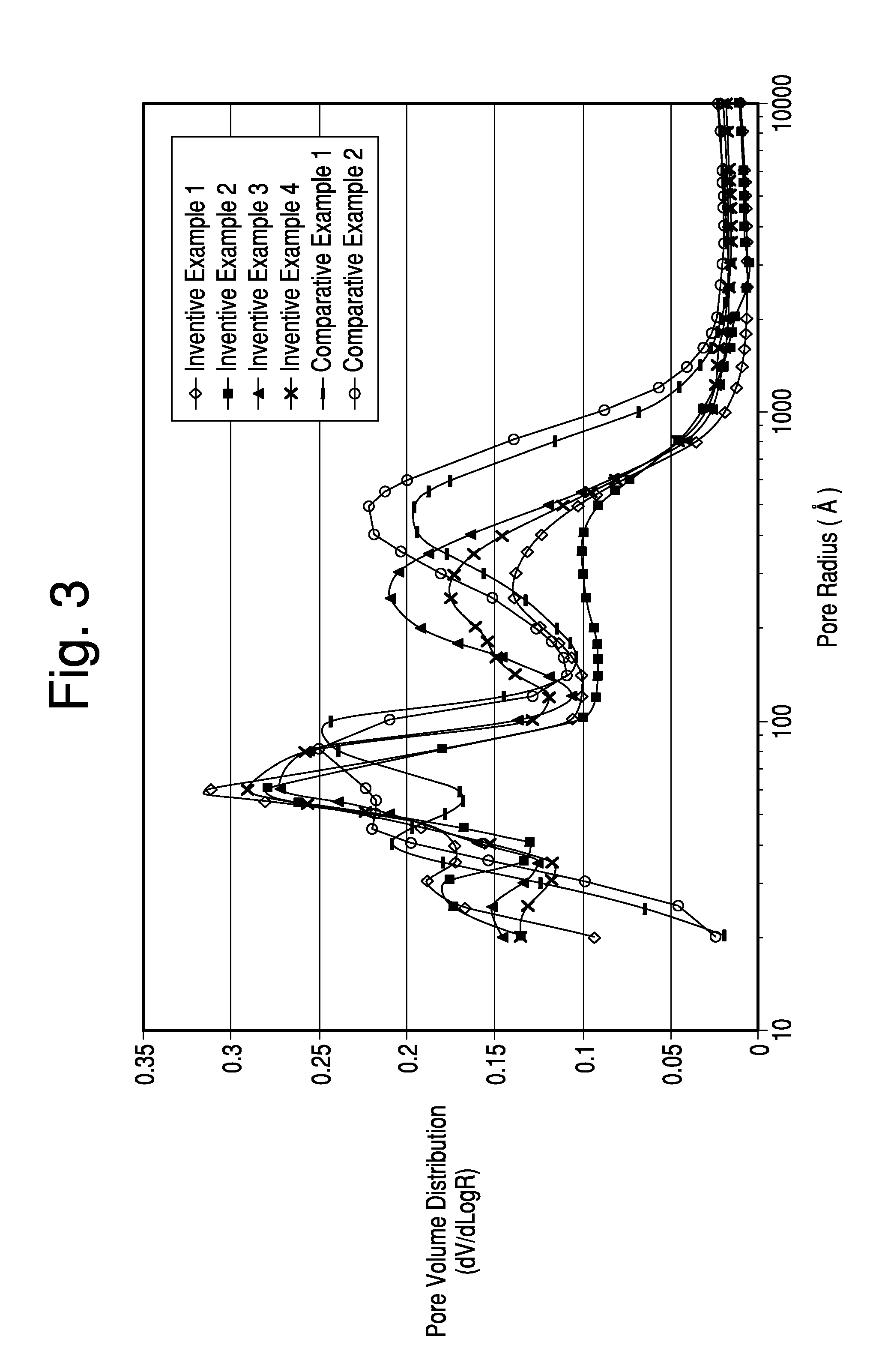
[0064]This example and corresponding data were produced and described in the commonly assigned U.S. application Ser. No. 13 / 042,790. The procedure and results are mentioned here for comparative purposes. Hydrous kaolin slurry consisting of particles with greater than 70% having an equivalent spherical diameter less than 2 μm as measured by Sedigraph 5200 and less than 0.5% particles captured on a 325-mesh screen was utilized. The hydrous kaolin in the amount of 37.5 dry wt. % was mixed with calcined kaolin in the amount of 62.5 dry wt. % to produce five inventive samples, each of which had a total slurry solids level of ˜50% by weight. The physical properties of the kaolins are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
[0065]The incorporated calcined kaolin consisted of material that was heated beyond the characteristic exothermic transition at ˜950° C. to form spinel, mullite or a combination of spinel and mullite. The Mullite index (MI) is the ratio of the mullite peak in the kaolin sample to a 100...
example 2
[0073]Hydrous kaolin slurry consisting of particles with greater than 70% having an equivalent spherical diameter less than 2 μm as measured by Sedigraph 5200 and less than 0.5% particles captured on a 325 mesh screen was utilized. The hydrous kaolin in the amount of 46 to 52 dry wt. % was mixed with calcined kaolin in the amount of 48 to 54 dry wt. % to produce six inventive samples, each of which had a total slurry solids level of ˜50% by weight.
[0074]The calcined kaolin components for both the Inventive and Comparative samples were formed from the same hydrous kaolin slurry source. However, for the Inventive samples, a 37.0 wt % ammonium polyphosphate solution was added at 0.15 dry wt % as available phosphate to the hydrous kaolin slurry prior to calcination. For the Comparative samples the calcined kaolin was not pre-treated with phosphate. The physical properties of note related to the hydrous and calcined kaolin components are detailed in Table 1 of Example 1 and Table 7 below...
example 3
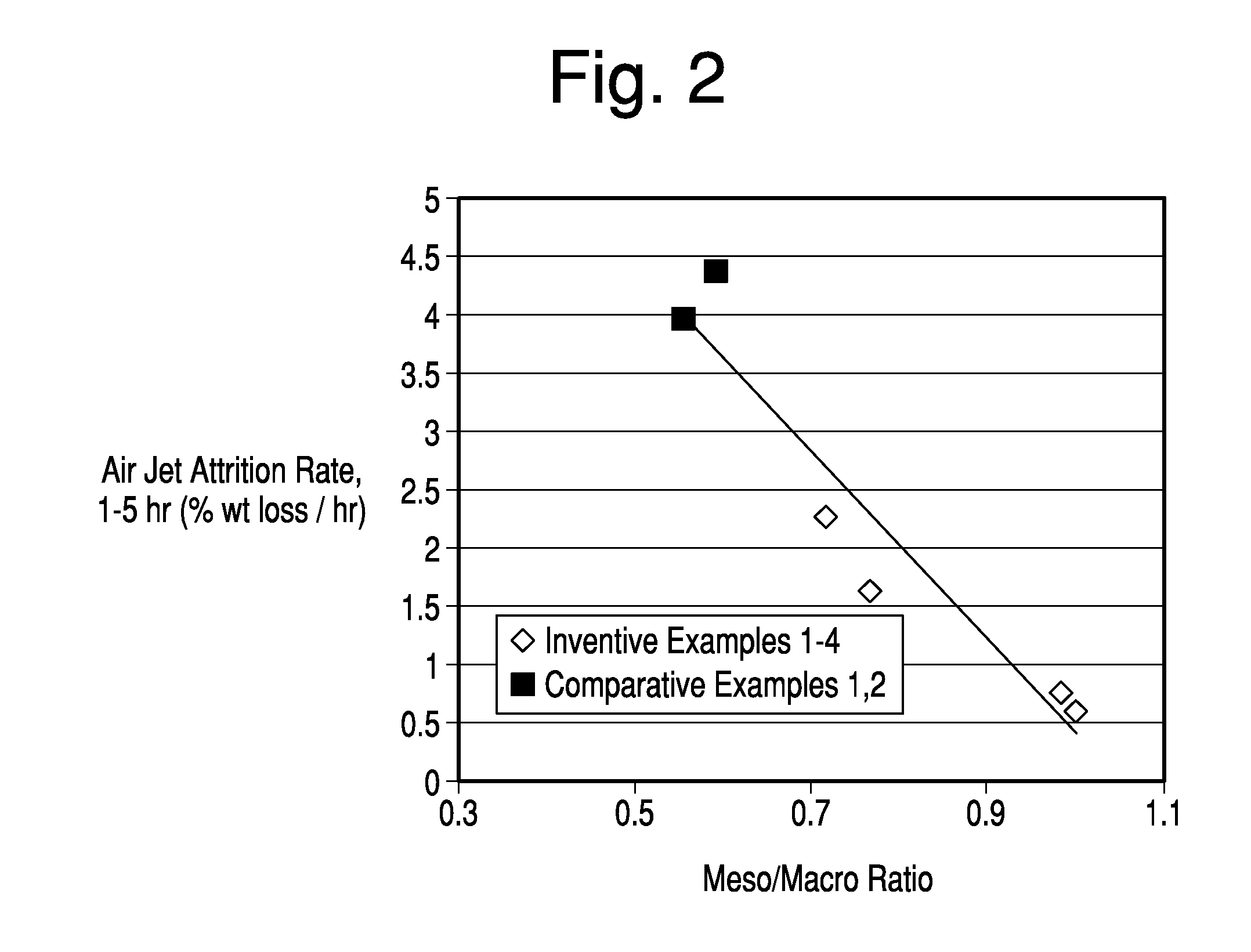
[0084]FIG. 4 compares the air jet attrition rates of Comparative FCC catalysts plotted as squares, including a commercial catalyst prepared in accordance with the teachings of U.S. Pat. No. 6,943,132, versus the Inventive samples noted by the data plotted as dots. The Comparative and Inventive samples demonstrated were prepared according to the procedures outlined in Example 2, but are not of the samples as described in Example 2. Specifically, in FIG. 4, for Inventive Samples, ammonium polyphosphate was added at a dosage of 0.15 wt % as available phosphate to the hydrous kaolin slurry prior to forming the calcined kaolin used in the subsequent blending step. Polyamine was added to the blend of hydrous and calcined kaolin at a dosage of 1 lb. / ton. In each Inventive example, the amount of polyamine treated kaolin in the microsphere equaled 48 to 52 wt. % and the polyphosphate treated kaolin equaled 52 to 48 wt. % of the total kaolin content of the microsphere. As shown in FIG. 4, the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt. % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com