Gastro-retentive drug delivery system
a drug delivery system and gastro-retentive technology, applied in the field of gastro-retentive drug delivery systems, can solve the problems of insufficient gastric residence time and the general recognition of the vulnerability of floating drug delivery systems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
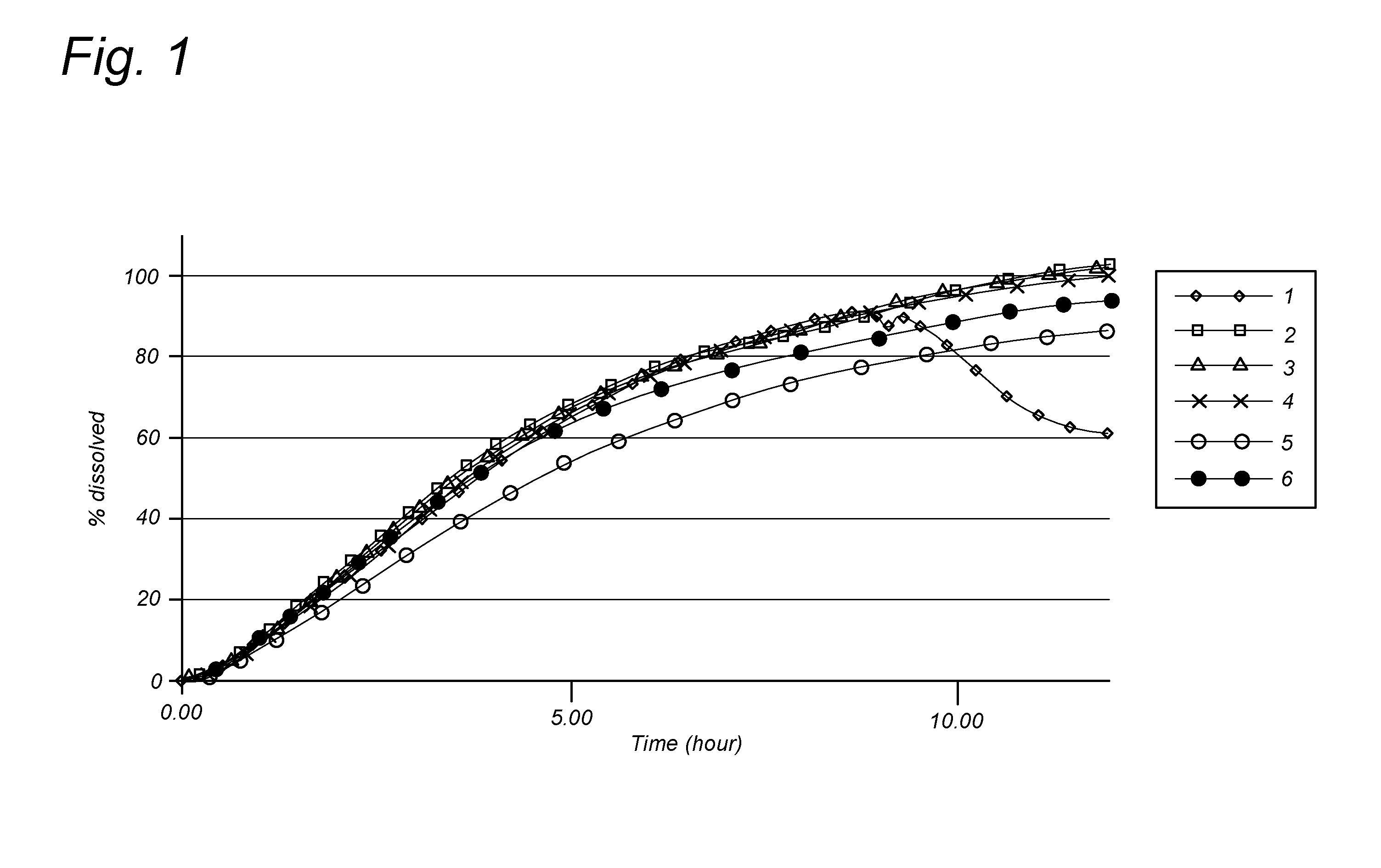
[0080]A typical example of a gastro-retentive system can be obtained by coating of an empty gelatine capsule with coating comprising at least one pharmacologically active ingredient.
[0081]In a specific embodiment the gelatine capsule is coated with a suspension containing:[0082]drug (e.g. nicotinamide): 1 to 95% of the solids in the suspension;[0083]polymers and release controlling agents: 5 to 99% of the solids in the suspension.
[0084]The amount of drug that will be sprayed onto the capsule is determined by the desired dose of the drug and the concentration of the drug in the coating. The composition of the drug containing coating layer is determined by the desired release profile. Typical polymers like Hypromellosum 4000 mPa·s., viscosity 2% m / V or Eudragit RL PO can be used whereas plasticizers such as Polyethylenglycolum 6000 or dibutyl phthalate can be used. Other excipients that can be used in the coating suspension are magnesium stearate, talc or mannitol. The coating suspens...
example 2
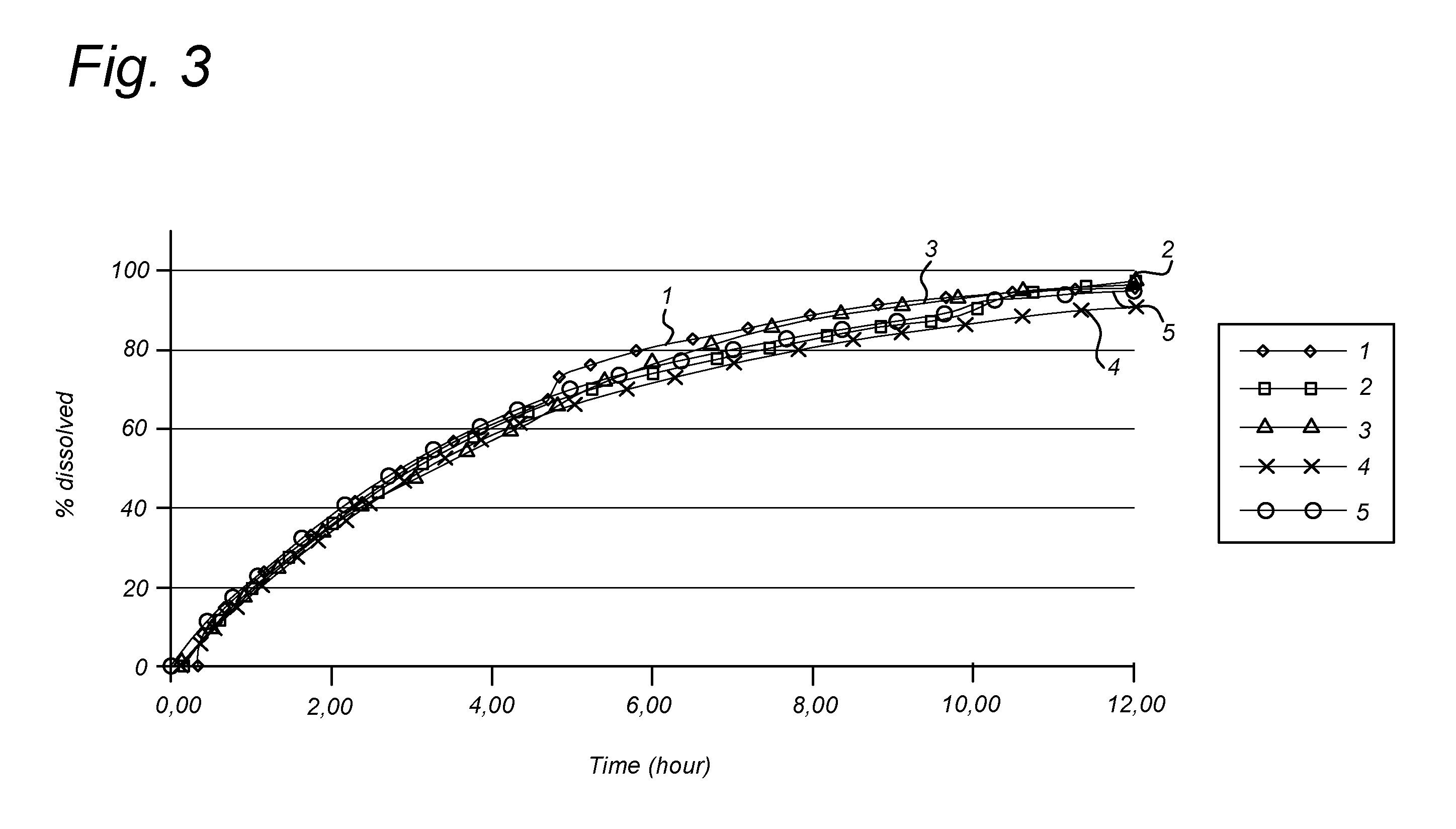
Dissolution of Nicotinamide from FDDS
Materials
[0088]HPMC (Hypromellosum 4000 mPa·s., viscosity 2% m / V) was obtained from Bufa BV, Uitgeest, The Netherlands. Macrogol 6000 (Polyethylenglycolum 6000) was obtained from Fagron, The Netherlands. Eudragit RL PO (Pharma Polymere, Röhm GmbH) was obtained from Chemische Fabric, Kirschenallee, Darmstadt, Germany. Nicotinamide Ph.Eur.quality was used.
Methods
[0089]A number of different coating dispersions (also referred herein as “suspensions”) were prepared (see Table 1). The required amount of HPMC was weighted to a beaker and then mixed with Ethanol (100 ml). Subsequently, the nicotinamide was added in the amounts indicated below. In parallel, in another beaker Macrogol 6000 was prepared by melting at a temperature not higher than 80° C., after melting, ethanol (50 ml) was added and subsequently the required amount of Eudragit RL PO was added. The cooled solution was mixed with the contents of the first beaker to provide a coating dispersion...
example 3
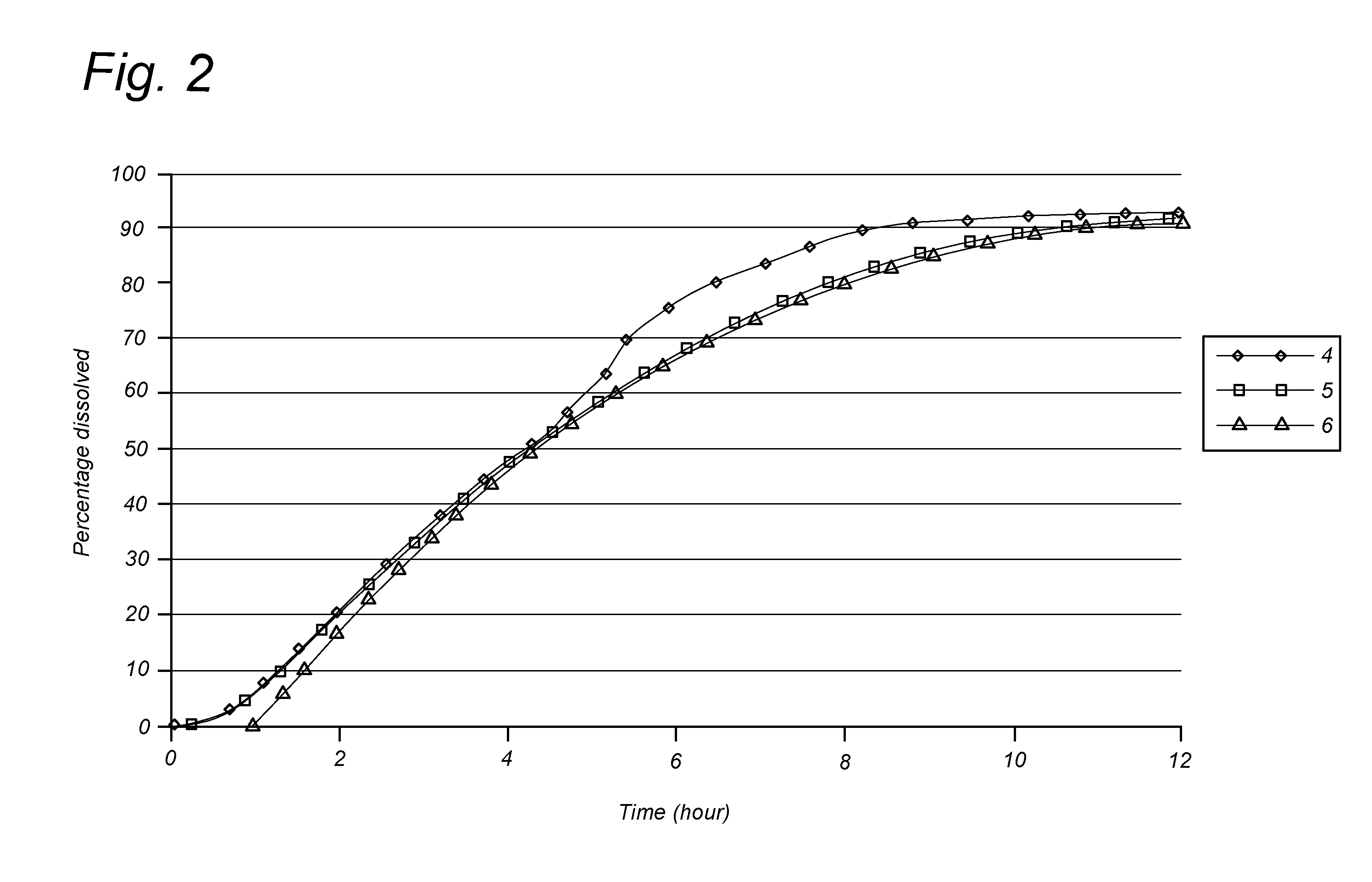
Development of a 300 mg and a 600 mg Nicotinamide Gradient FDDS
Background
[0096]The concept of an FDDS comprising several layers of distinct composition and distinct amounts of nicotinamide was tested. Also the concept of an FDDs comprising an outer coating layer comprising no nicotinamide was tested.
[0097]The aim of the experiment was to optimize the formulation, especially to prevent an initial release burst and to prolong the period of constant nicotinamide release, preferably over the entire residence time of the FDDS in the stomach. This involved testing of formulations containing outer coatings containing a high percentage of hypromellose and outer coatings containing no nicotinamide as well as formulations containing an inner layer with a high percentage of starch.
Materials & Methods
[0098]Nicotinamide was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, hypromellose 400 mPa·s from Bufa, Starch 1500 from Colorcon and magnesium stearate from Genfarma by. In all experiments demineralized water was ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| residence time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com