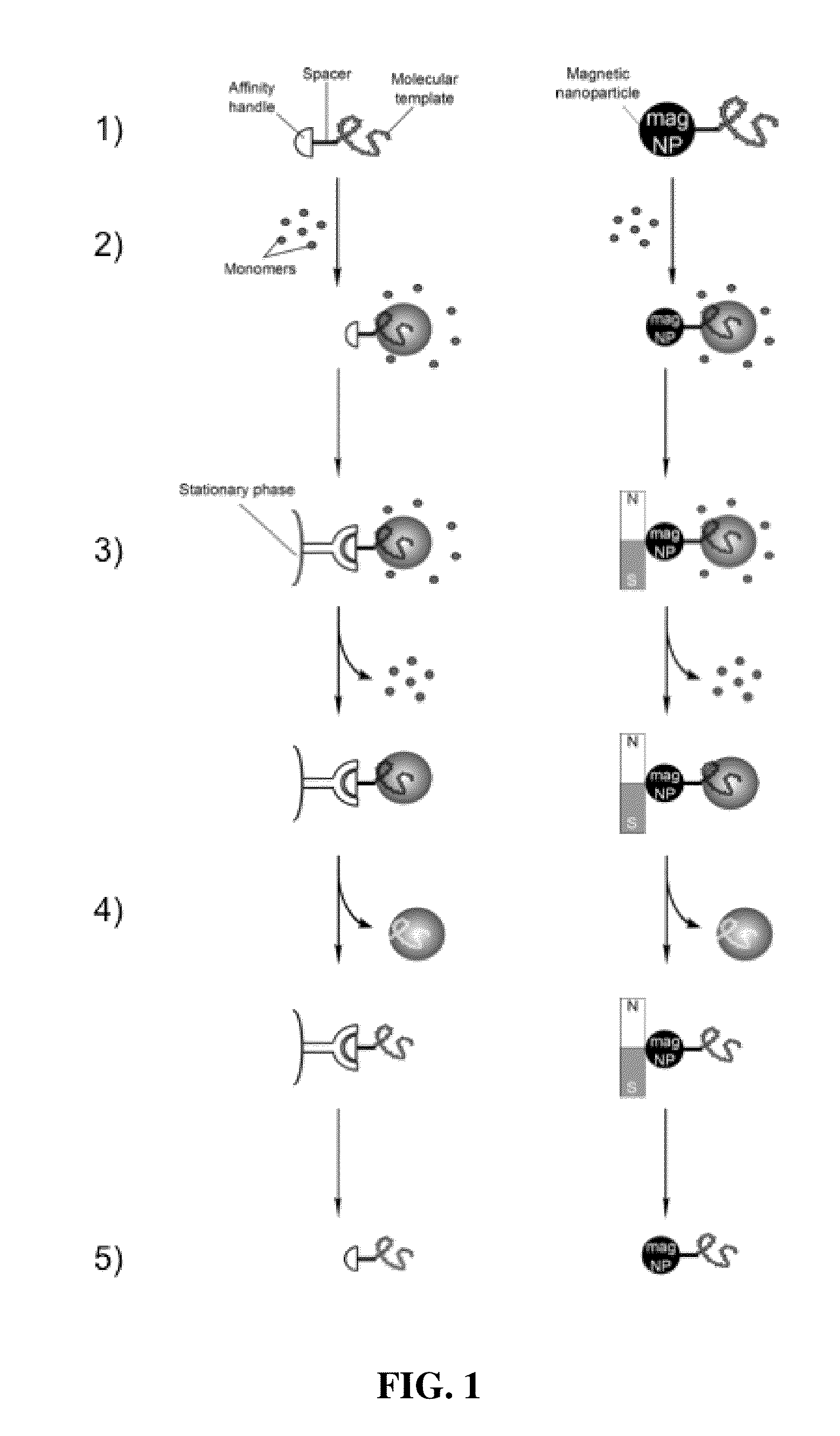
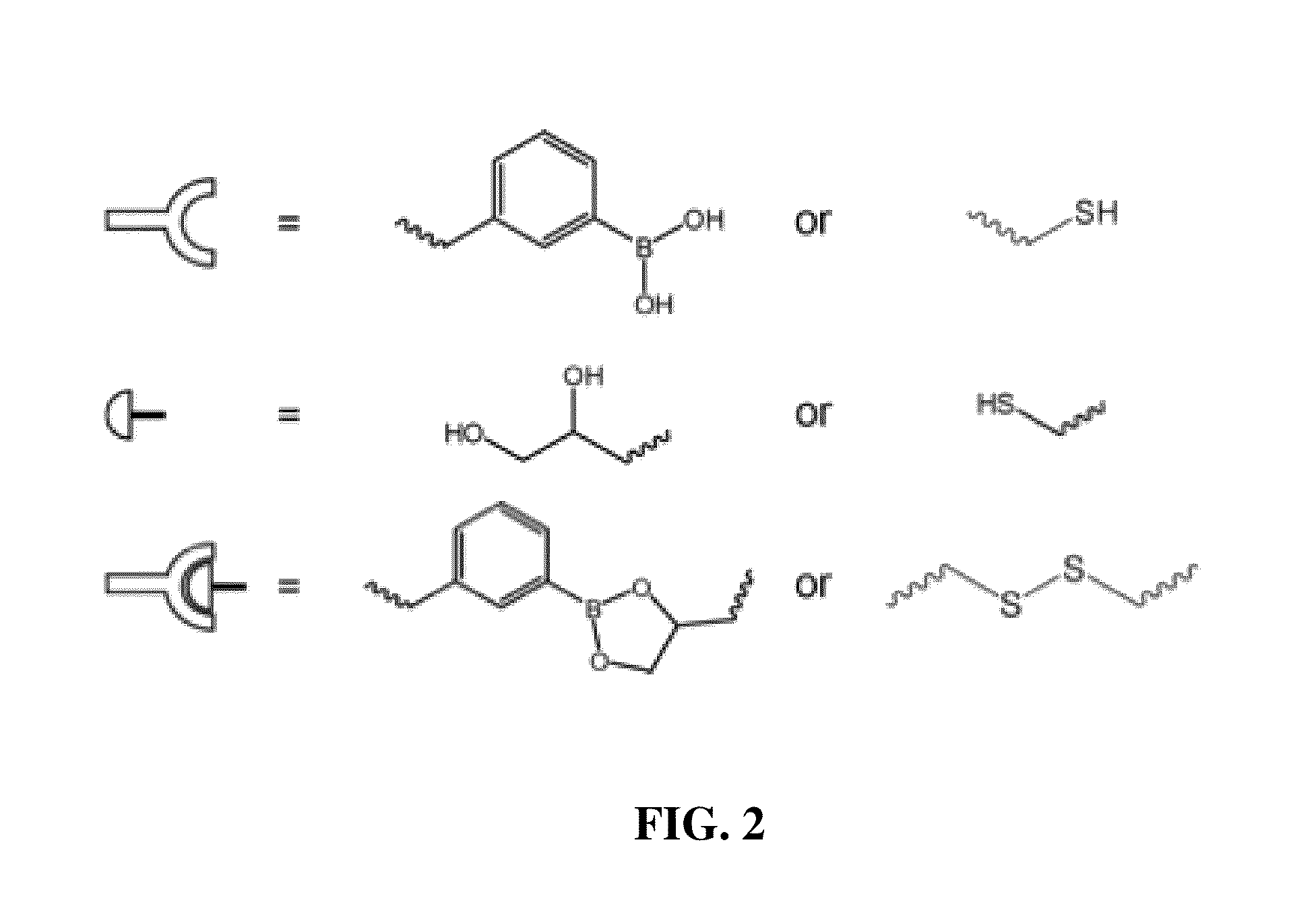
Polymers prepared using smart templates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of a Magnetic Core Silica Shell Nanoparticles (magNP@SiO2)
[0095]Synthesis of magnetic core particles: 6 g FeSO4.7H2O and 7 g anhydrous FeCl3. were dissolved in 200 ml millipore water under N2 with vigorous stirring at 85° C. 15 mL of 25% ammonia (aq) were added quickly into the solution. The solution turned from orange to black due to the precipitation of the magnetite nano-particles. The solution was stirred for 30 min at elevated temperature and then allowed to cool down to RT. Afterwards, the magnetic particles were collected using a magnet and washed with 3×50 mL water and finally with 50 mL 0.2M NaCl solution. The particles were dried at 80° C. under vacuum.
[0096]Synthesis of magnetic core silica shell particles (magNP@SiO2): 2 g of dry magNP were dispersed in 50 mL water by sonication. Then they were collected by a magnet and the supernatant was removed. Then, a 10% (v / v)TEOS-solution (230 mL) was added followed by 200 mL glycerol. The pH was adjusted to 4.6 with g...
example 2
Functionalization of the Magnetic Silica Core-Shell Beads with Glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane (GPTMS) to Give magNPepoxy
[0097]3,25 g magNP@SiO2 were dispersed in 50 mL dry toluene under N2-atmosphere by sonication. 1 mL GPTMS was added to the solution and the mixture was heated to reflux under positive nitrogen pressure and stirred using an overhead-stirrer for 30 h. Then, the particles were collected using a magnetic separator and washed with 3 times with 50 mL toluene and 3 time with 50 mL acetone and dried under vacuum at 40° C.
example 3
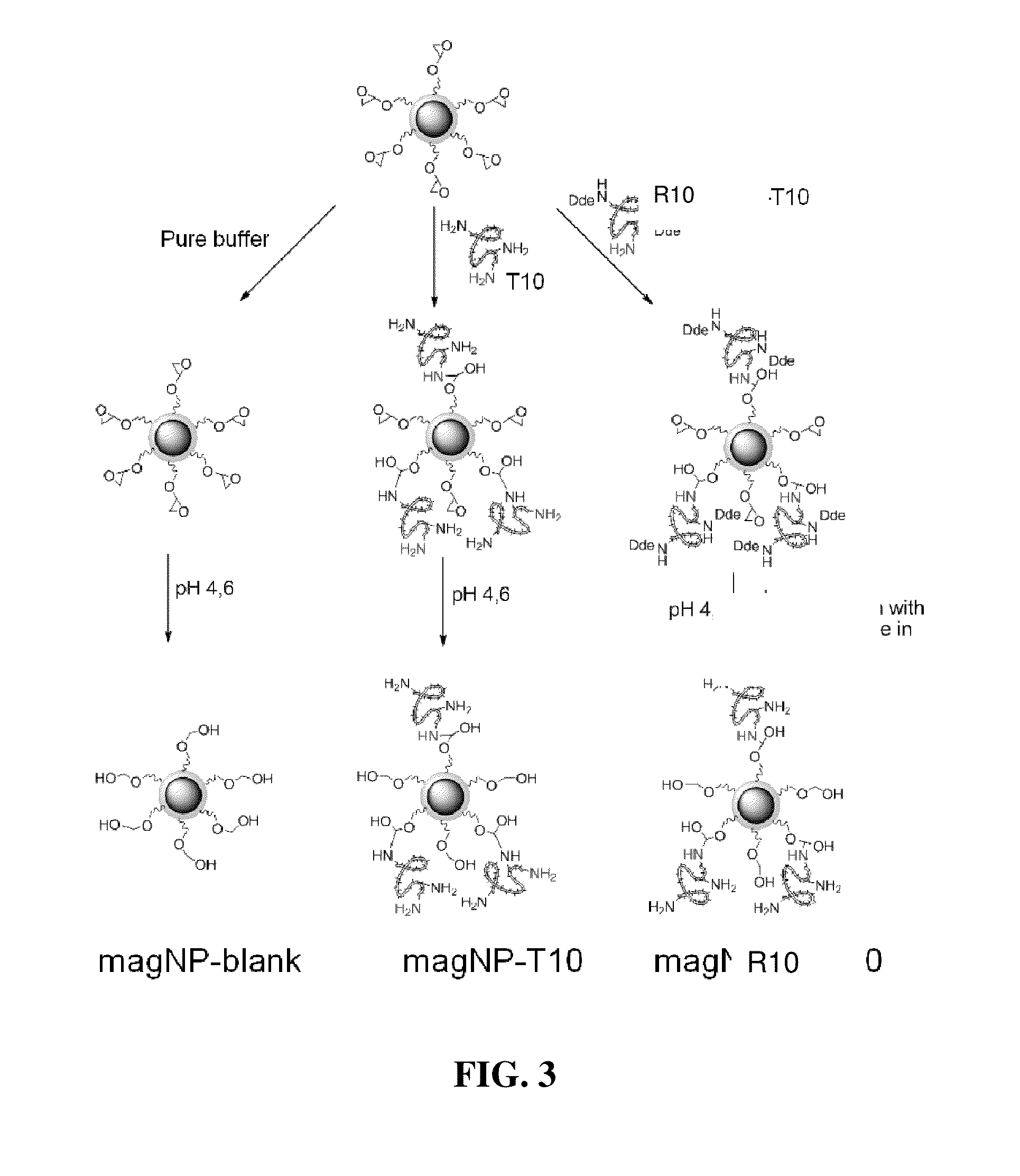
Immobilization of the Decapeptides NH2—O—K—S-L-S-L-S—P-G-K—COOH (T10) and NH2—O-L-S—K—S—K—S—P-G-L-COOH (R10) on the magnetic nanoparticles to give magNP-T10 and magNP-R10 (FIG. 3).
[0098]1 g of epoxy-functionalized magnetic particles were dispersed In buffer (phosphate buffer, pH 7.4)(5 mL) by sonication. They were separated using a magnet and the supernatant was discarded. Then, a solution of 5.3 mg T10 or R10 in 5mL of the same buffer was added to the magnetic particles. Also a blank sample was prepared by adding 5mL pure buffer. The three samples were incubated over night at RT on a shaker. MALDI TOF analysis of the nanoparticle samples with reference to free peptide demonstrated the successful immobilization (FIG. 4).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Magnetic field | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com