Use of RNA for reprogramming somatic cells
a somatic cell and rna technology, applied in the field of rna for reprogramming somatic cells, can solve the problems of limited number of types, restricted differentiation potential, poor growth, etc., and achieve the effect of facilitating reprogramming of somatic cells, controlling the amount of rna, and relatively high transfection ra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
n of IVT RNA
[0206]The first step in the production of IVT RNA comprises linearization of a plasmid containing the coding sequence for a particular factor and having an SP6 promoter or T7 promoter before the start codon, starting from which an in vitro transcription is possible. To this end, restriction enzymes are used, for example. Following linearization, the enzyme is inactivated by phenol-chloroform precipitation and removed. For this, an isovolume of a mixture of phenol and chloroform is added and mixed thoroughly.
[0207]Brief centrifugation at 10 000×g provides separation into a lower organic phase and an upper aqueous phase, which contains the DNA. The latter is transferred to a new reaction vessel. Then the aqueous phase is mixed with an isovolume of pure chloroform, to remove any phenol residues. After centrifugation, the aqueous phase is removed and precipitated for 2 h by adding two isovolumes of ethanol and 10% v / v 3M sodium acetate pH 4.5 at −20° C. The DNA is sedimented...
example 2
ration of Cells
[0211]The principle of electroporation is based on disturbing the transmembrane potential of the cells by a brief current pulse. The alteration of the transmembrane potential by an external stimulus is described by the following equation:
ΔVm=fEextr cos φ
[0212]Vm is the transmembrane potential and f is a form factor, which describes the influence of the cell on the extracellular field distribution. fEext describes the applied electric field, r the cell radius and φ the angle to the externally applied electric field. Factor f is often given as 1.5, though it depends on many other factors. The electroporation of the cells is successful if the applied electric field exceeds the capacity of the cell membrane, i.e. ΔVm is greater than a threshold value ΔVs, given as 1V (Kinosita, K., Jr. and Tsong, T. Y. (1977) Nature 268, 438-441). Since construction of the cell membrane as a bilayer is a feature that is common to eukaryotic cells, this value shows little variation for dif...
example 3
of Proteins Expressed by Transfected RNA
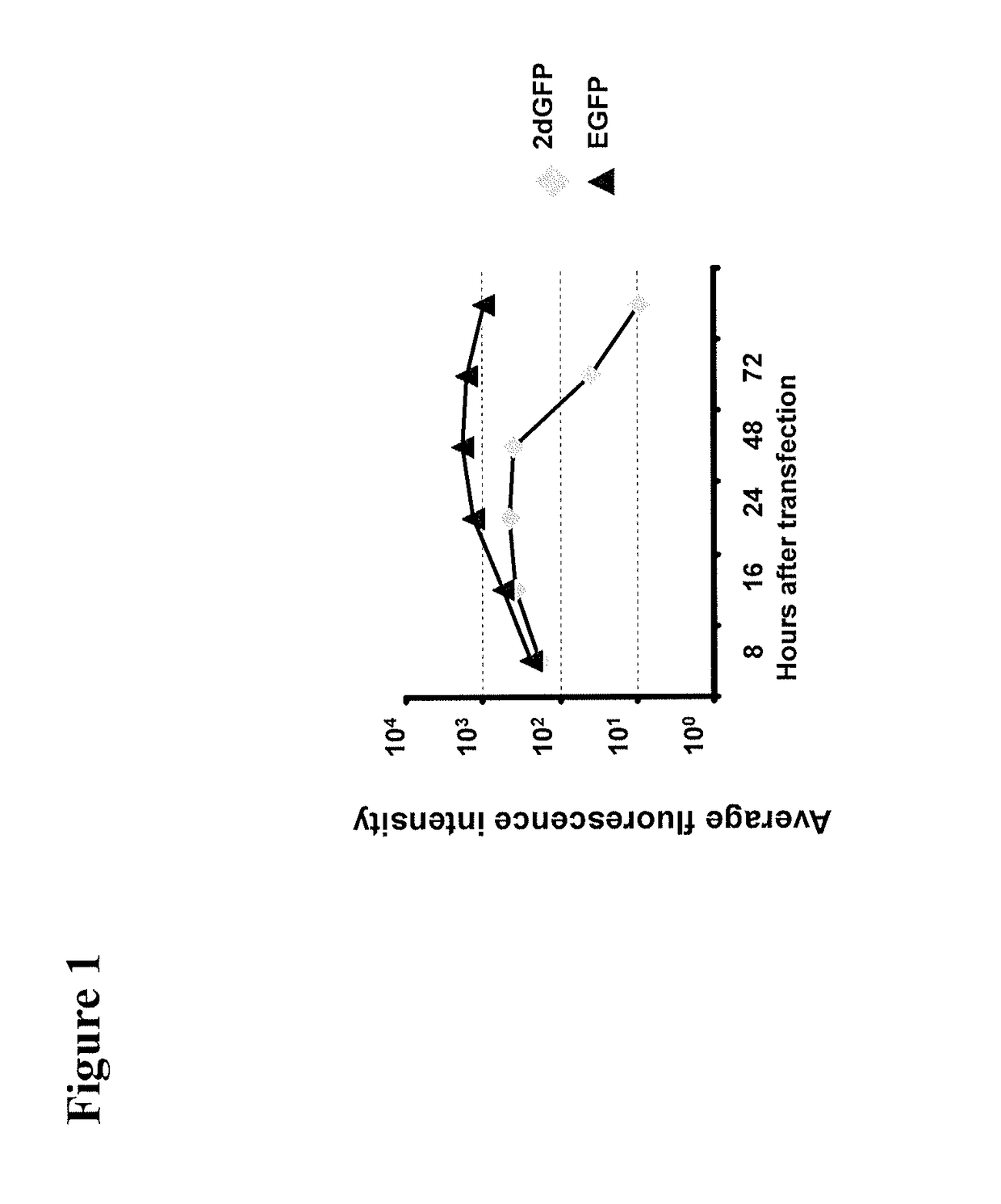
[0220]We next examined for how long proteins with different halftimes following transfer of IVT RNA can be stably detected in cells. 786-0 cells were transfected with 20 μg eGFP IVT RNA and 2dGFP IVT RNA, respectively, and the fluorescence intensity was measured in the time course of 3 h to 120 h. The eGFP protein has a halftime of 16 h, while the halftime of the destabilized variant 2dGFP due to the integration of a PEST amino acid sequence effecting protein degradation is reduced to 2 h (Clontech, 1998). The experiment showed that already after 4 h a substantial amount of translated protein was detectable which further increased until 24 h after transfection. The amount of eGFP protein remains relatively constant for more than 120 h. Even the destabilized 2dGFP shows stable protein expression for 48 h (FIG. 1). In order to induce protein expression of 2dGFP which is stable over a long period of time RNA can be transfected every 48 h.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com