Sorafenib hemi-p-tosylate monohydrate crystal and preparation process thereof
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
on of Sorafenib Hemi-p-Tosylate Monohydrate
[0041]At a room temperature, to a reaction tank were added anhydrous ethanol (85.6 kg) and purified water (11.9 kg), and then sorafenib (10.84 kg, 23.32 mol) were added under stirring. After stirring for 10 min, p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (2.38 kg, 12.51 mol) was added at one time. The resulting mixture was crystallized for 8 hours under stirring, and then filtrated under centrifugation. The resulting solid was dried for 10 hours at a temperature of 6035° C. under vacuum to obtain sorafenib hemi-p-tosylate monohydrate (11.48 kg, yield: 89.5% and purity: 99.96%).
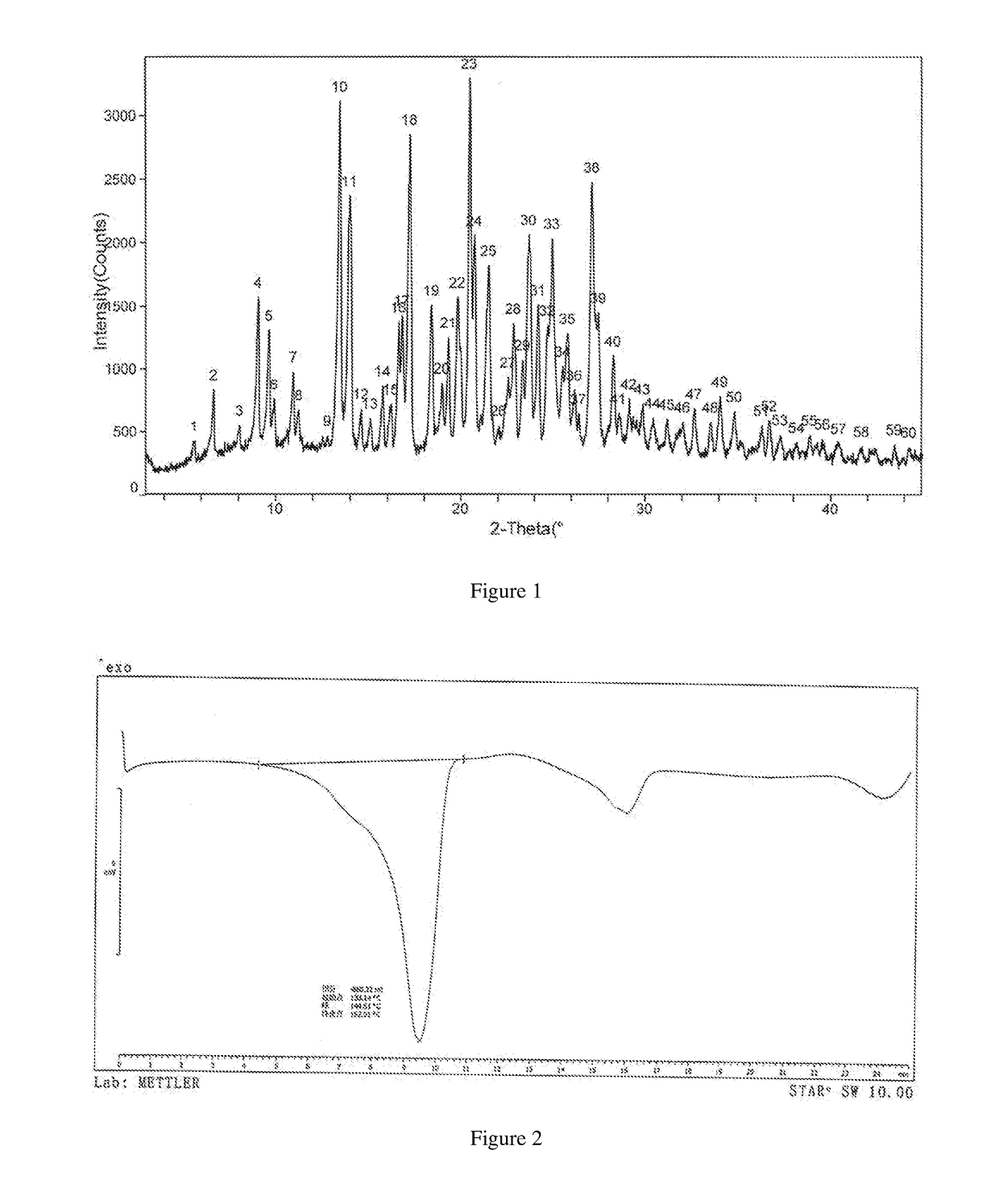
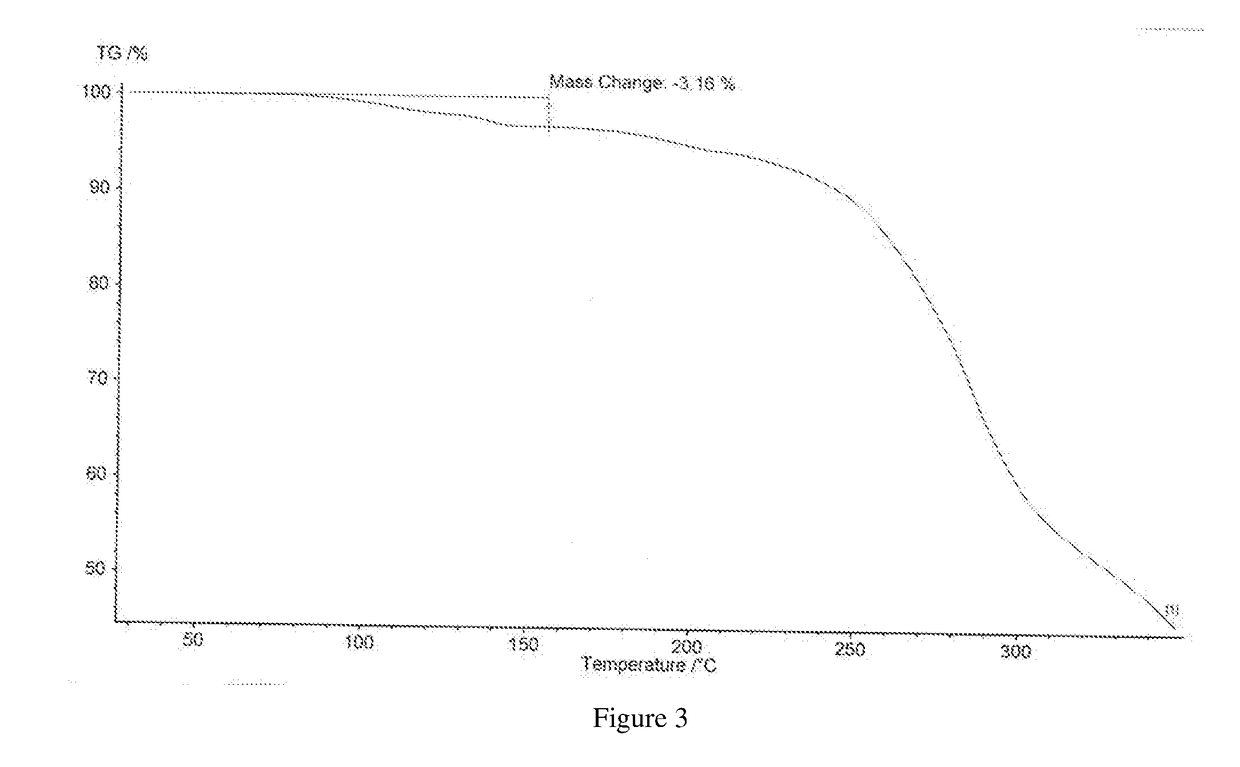
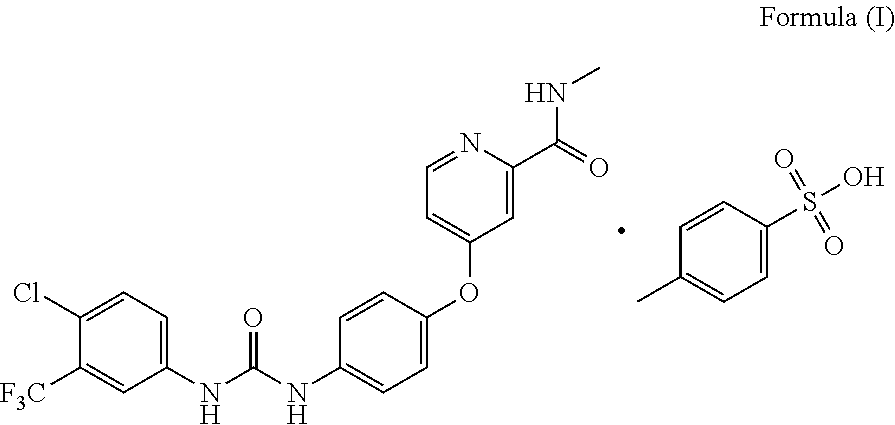
[0042]Its X-ray powder diffraction pattern using Cu Kα irradiation was shown in FIG. 1, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) pattern was shown in FIG. 2, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) pattern was shown in FIG. 3.
[0043]Element analysis: C: 51.64% (theoretical value: 51.72%), H: 3.98% (theoretical value: 3.90%), N: 9.83% (theoretical value: 9.85%), S: 2.85% (theoretic...
example 2
ase Condition for HPLC Analysis of Sorafenib Hemi-p-Tosylate Monohydrate
[0044]Chromatographic column: Agilent peptide map chromatographic column (3.0×150 mm, 2.7 μm)
[0045]Mobile phase A: phosphate buffer solution (monopotassium phosphate (0.79 g) was weighted and dissolved in water, then diluted to 1000 ml, and further adjusted to pH=2.4 with phosphoric acid)
[0046]Mobile phase B: ethanol-acetonitrile (40:60)
[0047]Detection wavelength: 235 nm for detection
[0048]Flow rate: 0.6 ml / min
[0049]Column temperature: 55° C.
[0050]Injection volume: 10 μl
[0051]Solvent: mobile phase A-mobile phase B (1:3)
[0052]Preparation of a solution of a test sample: an appropriate amount of the test sample was weighted and dissolved in the solvent [mobile phase A-mobile phase B (1:3)], then diluted to a solution which comprises about 0.16 mg of sorafenib per 1 ml as the solution of the test sample.
[0053]A linear gradient elution was performed according to the program as shown in Table 3:
TABLE 3Test condition f...
example 3
Test
[0054]The stability test for the sorafenib hemi-p-tosylate monohydrate crystal of the present invention was conducted according to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2010), Part 11, Appendix XIX C: Guideline for Stability Test of Bulk Drug and Pharmaceutical Preparation. The results were shown in Table 4.
TABLE 4Results of stability testExposure testto lightShading testStanding for 6StandingStandingStanding for 10(luminance:(luminance:months at 25° C. ±for 10for 10days at 25° C.6000 Lux),6000 Lux),2° C. anddays atdays atand humidity ofstanding forstanding forhumidity ofDay 040° C.60° C.92.5% ± 5%10 days10 days60% ± 5%Purity99.96%99.96%99.95%99.96%99.97%99.96%99.96%
[0055]The results in the above table showed that the sorafenib hemi-p-tosylate monohydrate of the present invention is highly stable, and therefore particularly suitable for a pharmaceutical preparation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com