Method for improved pulping using an environmentally friendly pulping aid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
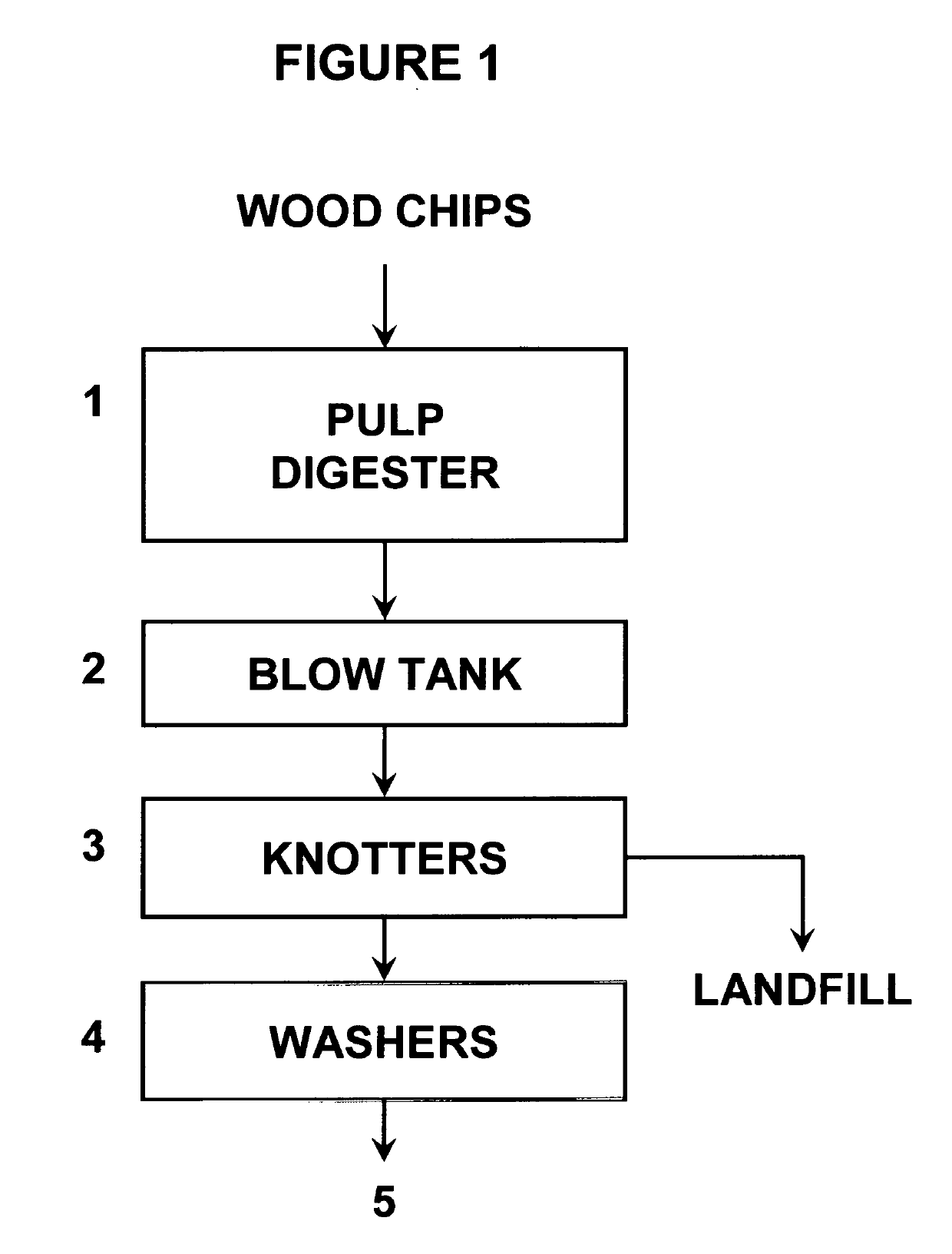
Image
Examples
example 1
[0025]A multi-day trial was used to determine the impact of the pulping aid of this invention on mill pulp production. Hardwood chips comprising a majority of maple wood chips were contacted with between 0.2 lbs and 4.0 lbs of pulping aid per ton of dry pulp, the pulping aid being a mixture of 60% terpenes and 40% of a dispersant blend. As summarized in Table 1, at a constant addition level of 2.5 lbs per dry ton of pulp, the H-factor was unchanged. However, rejects were reduced by 45% and the pulp extractives content was reduced by 57.3%. The incremental fiber production realized from the lower rejects level was about 14.4 dry tons per day. Furthermore, the use of a surfactant-based pitch control chemical was eliminated and the use of defoamers was reduced by about 20%.
example 2
[0026]A multi-day trial was used to determine the impact of the pulping aid of this invention on mill pulp production. Hardwood chips comprising a majority of aspen wood chips were contacted with between 0.2 lbs and 4.0 lbs of pulping aid per ton of dry pulp, the pulping aid being a mixture of 60% terpenes and 40% of a dispersant blend. As summarized in Table 1, at a constant addition level of 2.5 lbs per dry ton of pulp, the H-factor was reduced by 8.0%; rejects were reduced by 53% and the pulp extractives content was reduced by 27.3%. In addition, the pulp production rate of the mill was increased by 4.4% from the base rate. The incremental fiber production realized from the lower rejects level was 7.5 dry tons per day. Furthermore, the use of a surfactant-based pitch control chemical was eliminated and the use of defoamers was reduced by about 20%.
example 3
[0027]A relatively long (multi-week) trial was used to determine the robustness of the method of this invention on mill pulp production. Hardwood chips comprising a blend of aspen and maple wood chips were contacted with 0.2 lbs and 4.0 lbs of pulping aid per ton of dry pulp, the pulping aid being a mixture of 60% terpenes and 40% of a dispersant blend. As summarized in Table 1, at a constant addition level of 0.5 lbs per dry ton of pulp the H-factor was reduced by 6.7%; alkalinity was reduced by 4.3% from 23.0 g / L; rejects were reduced by 47% and the pulp extractives content was reduced by 36.1%. Further, the pulp production rate of mill was increased by 4.8% from the base rate. The incremental pulp fiber production realized from the lower rejects level was 5.5 dry tons per day. Furthermore, the use of a surfactant-based pitch control chemical was eliminated and the use of defoamers was reduced by about 20%.
TABLE 1H-FactorExtractives (g / L)RejectsPercentPercentIncremental TonsExampl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com