Patents
Literature
83results about "Synchronised browsing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
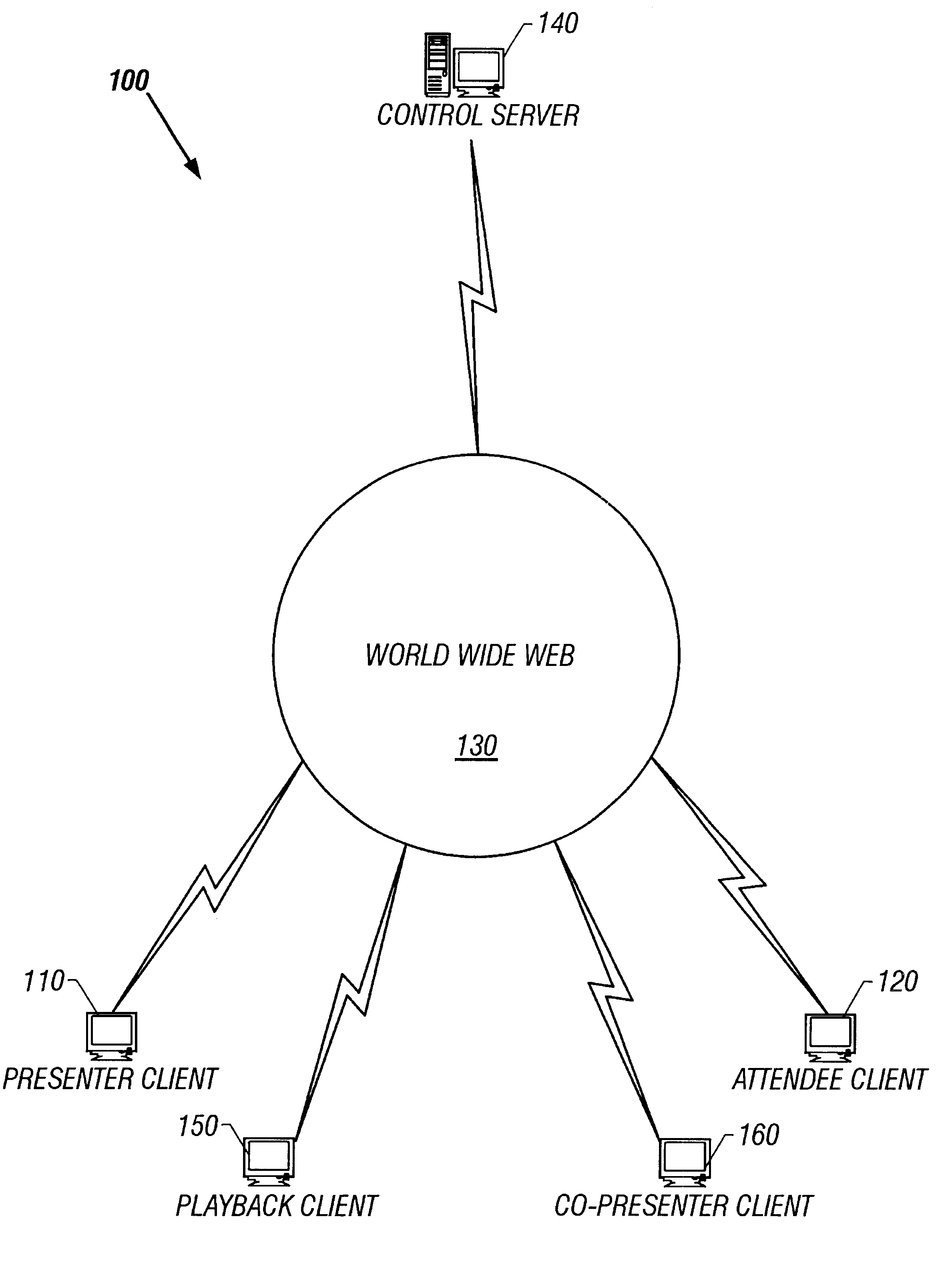
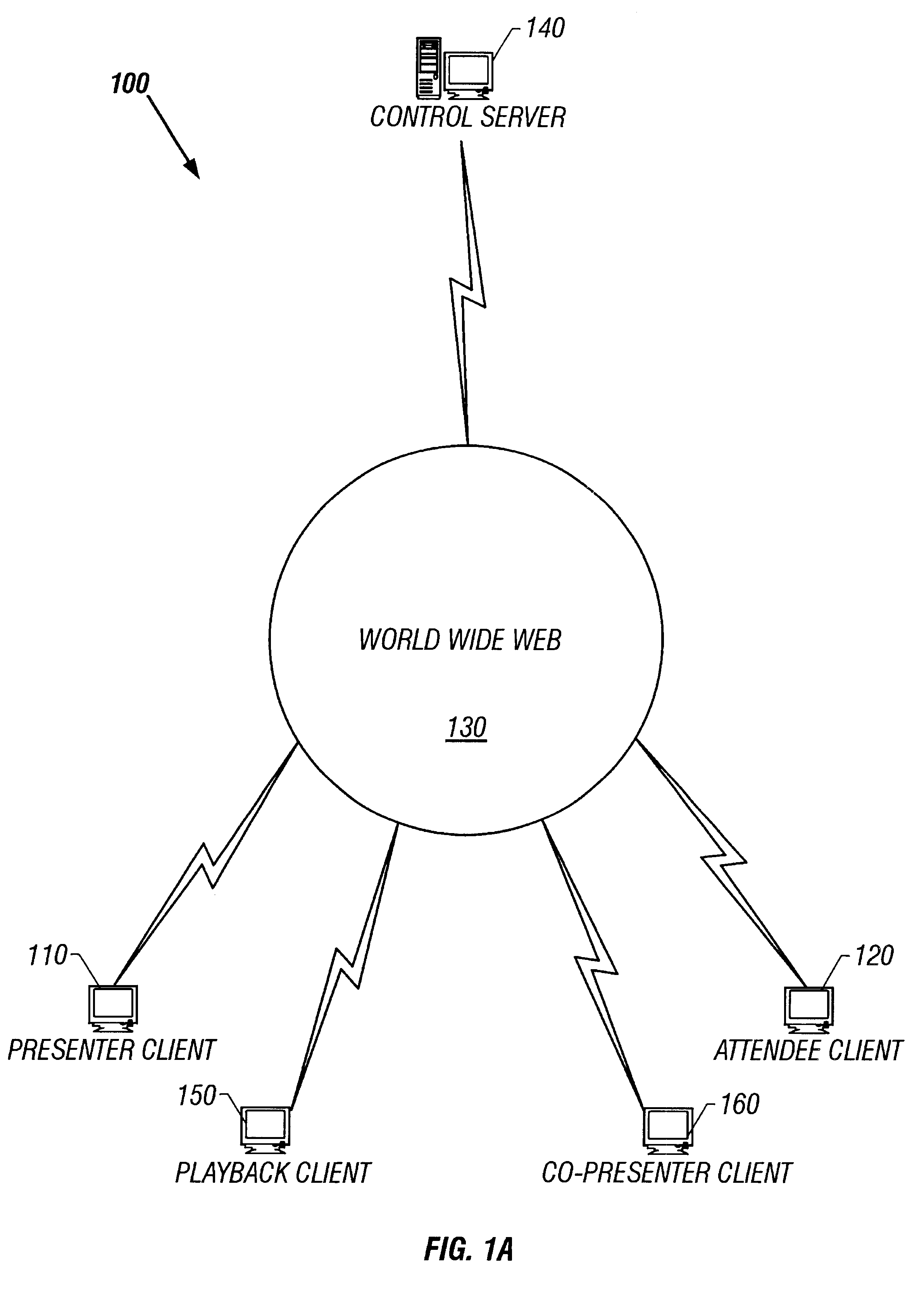
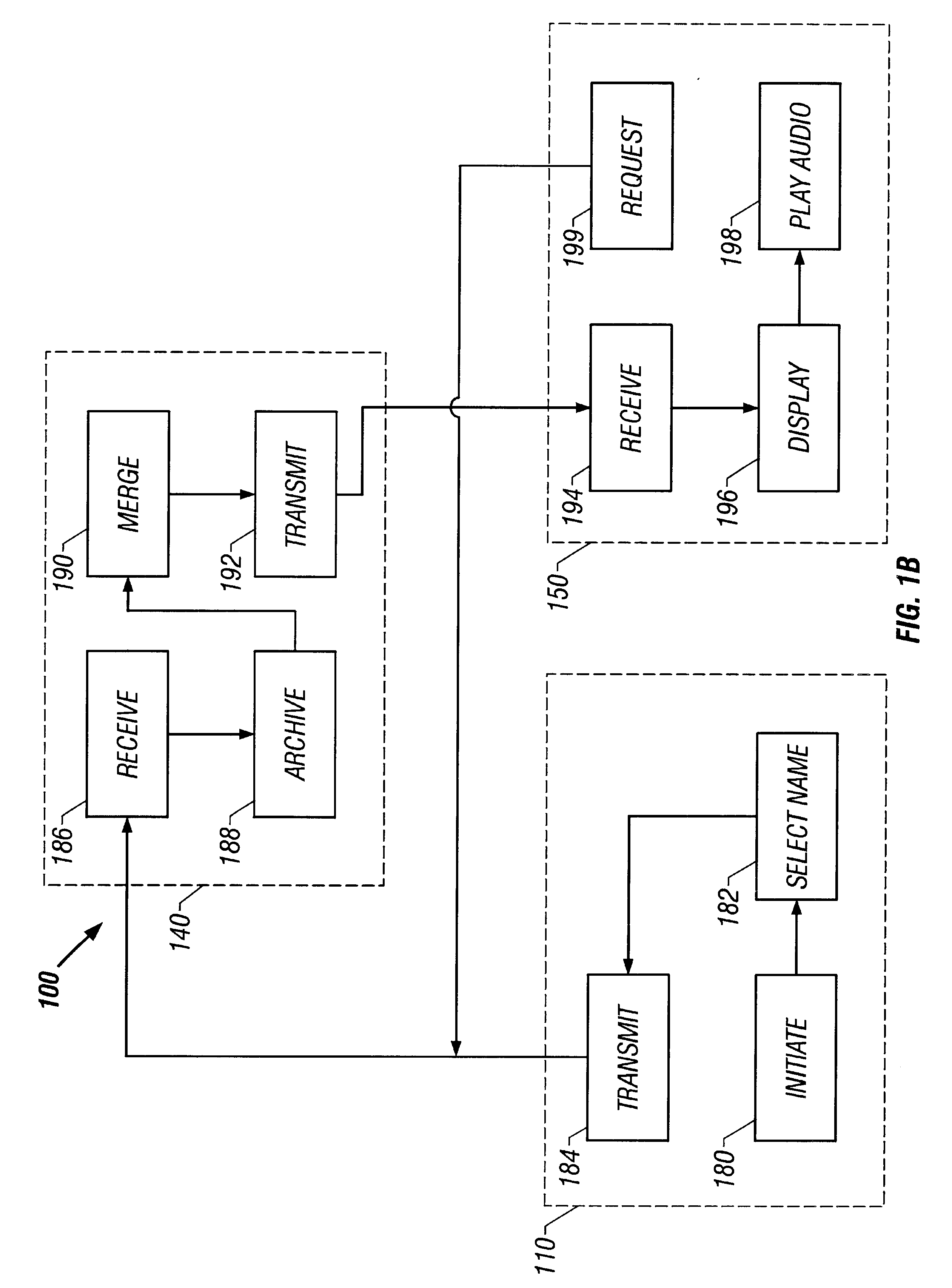
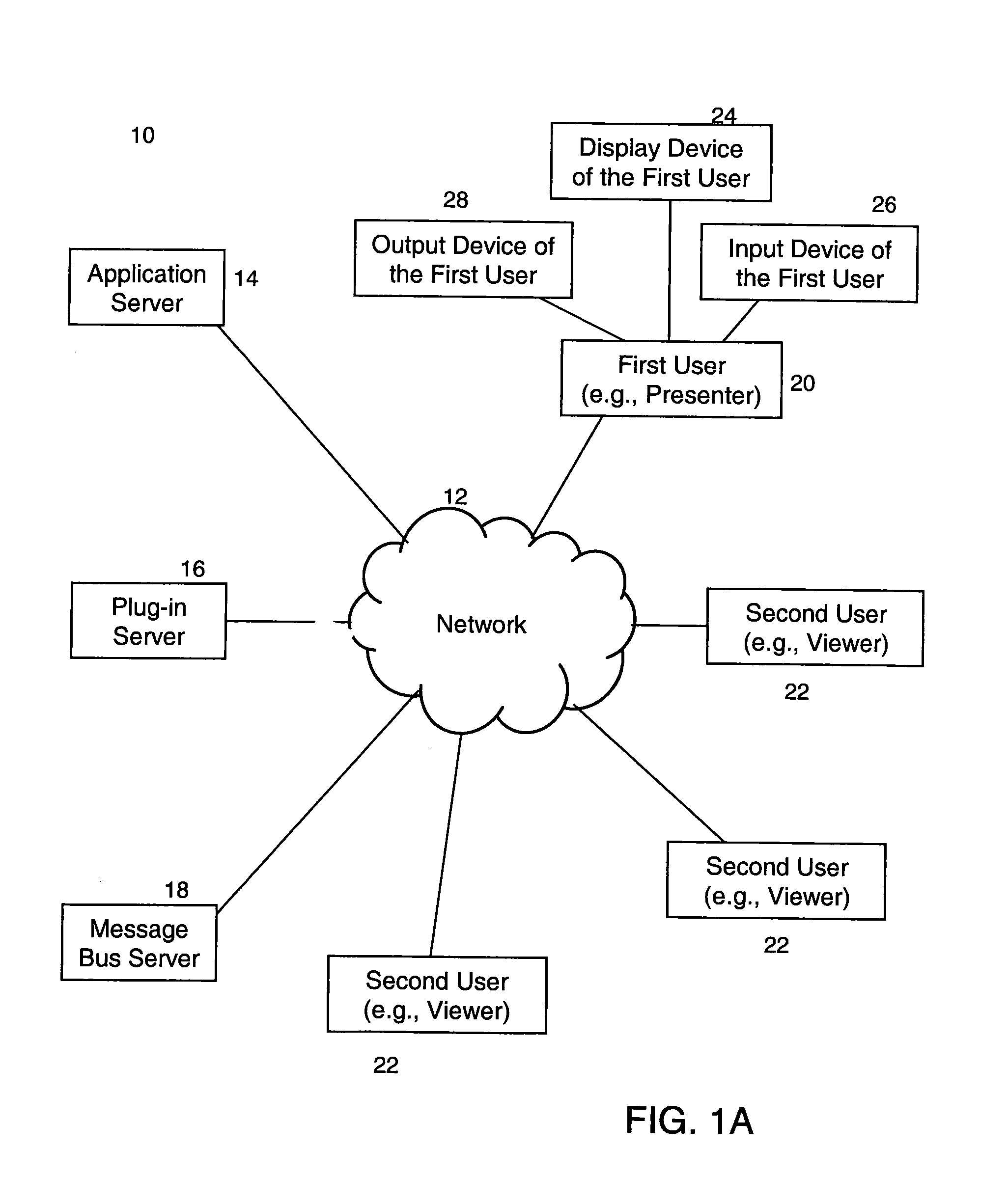
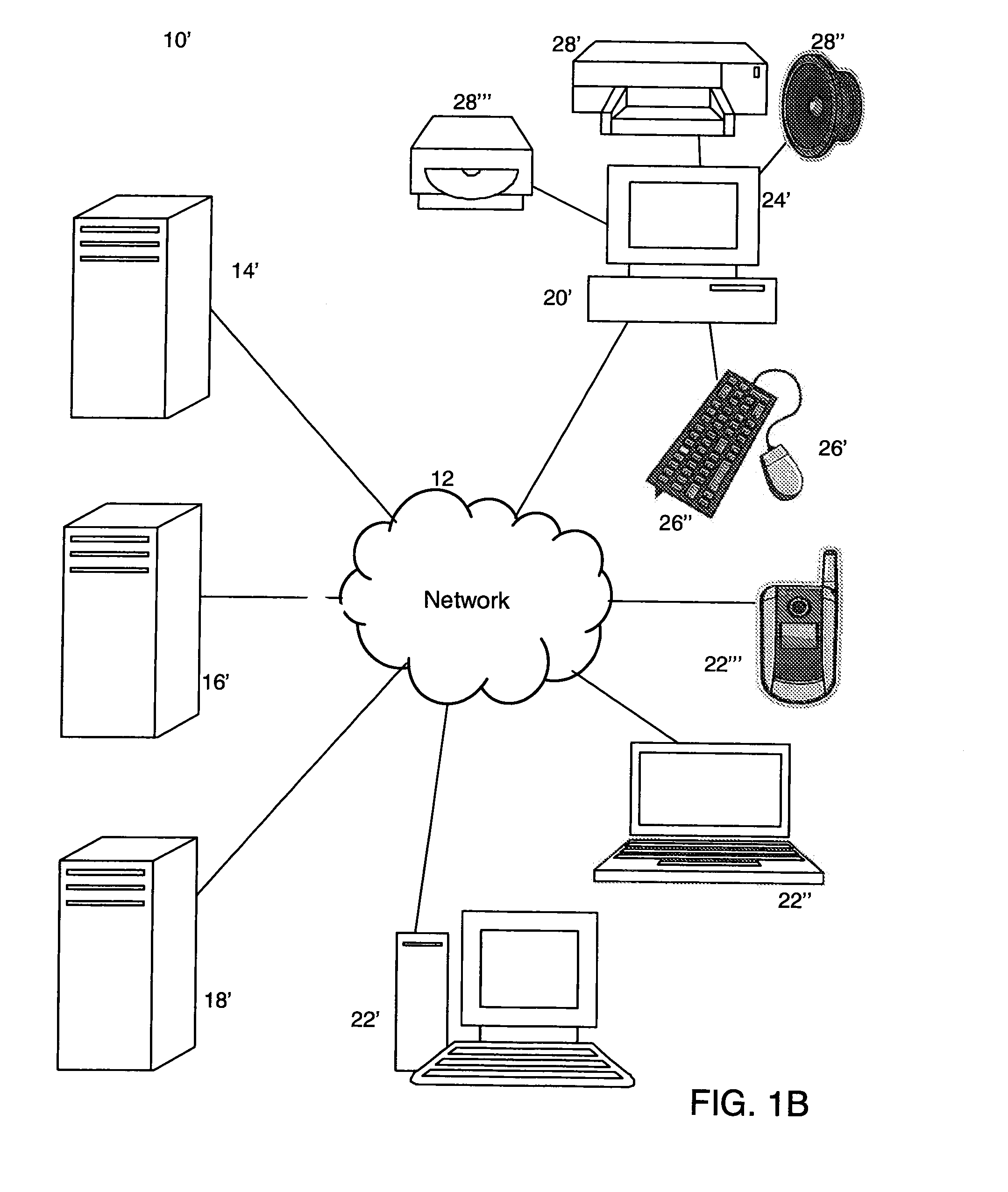
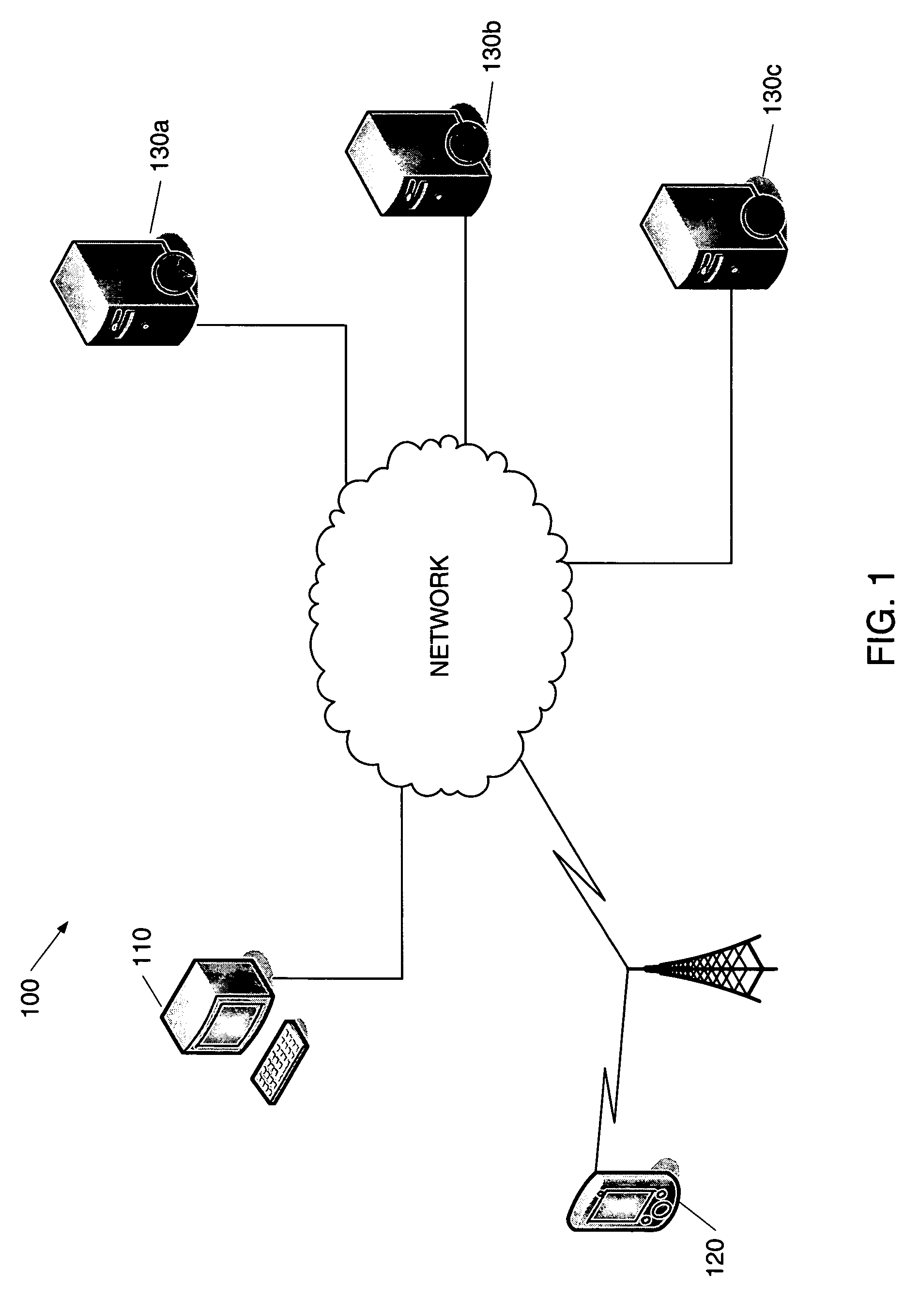
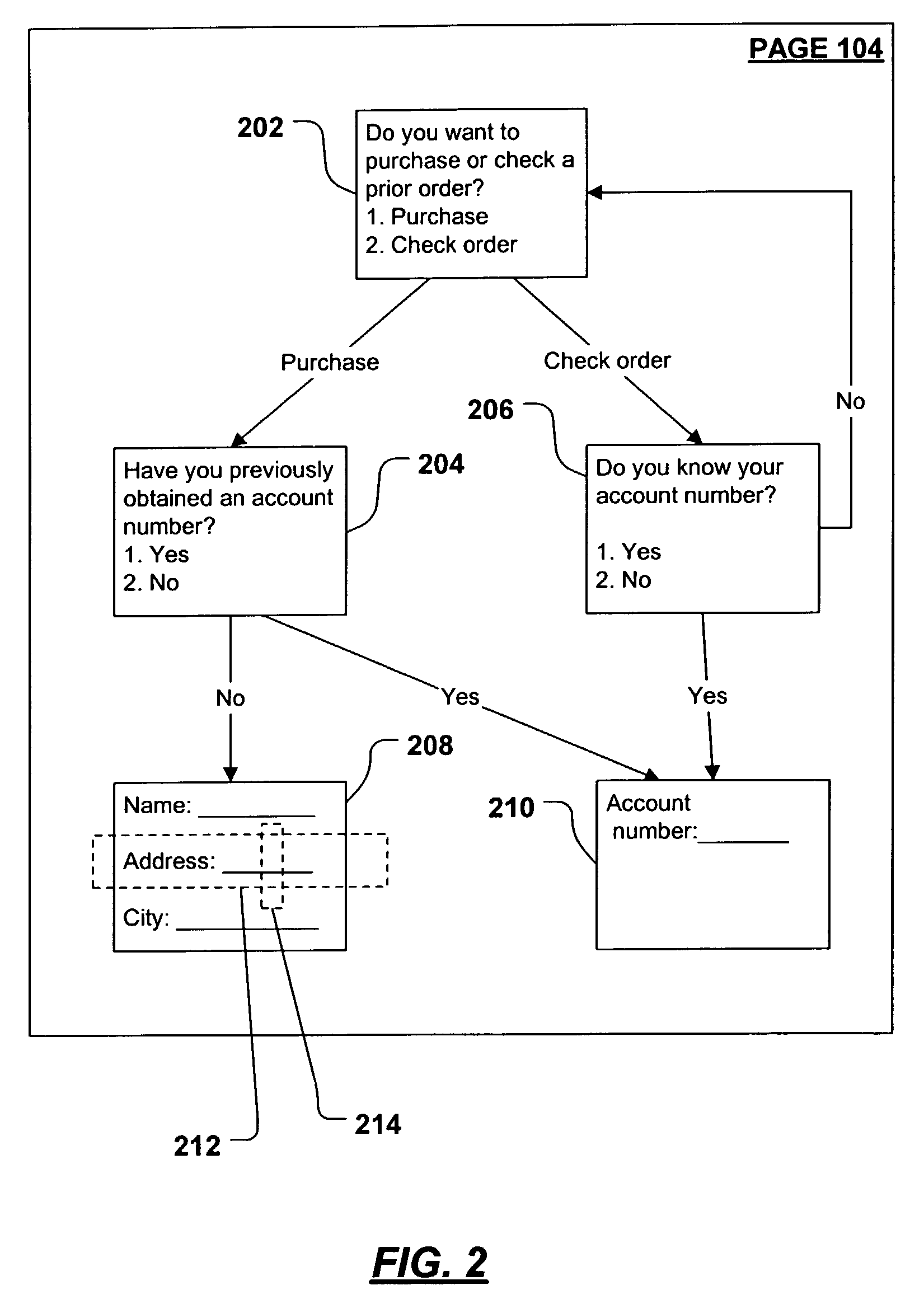
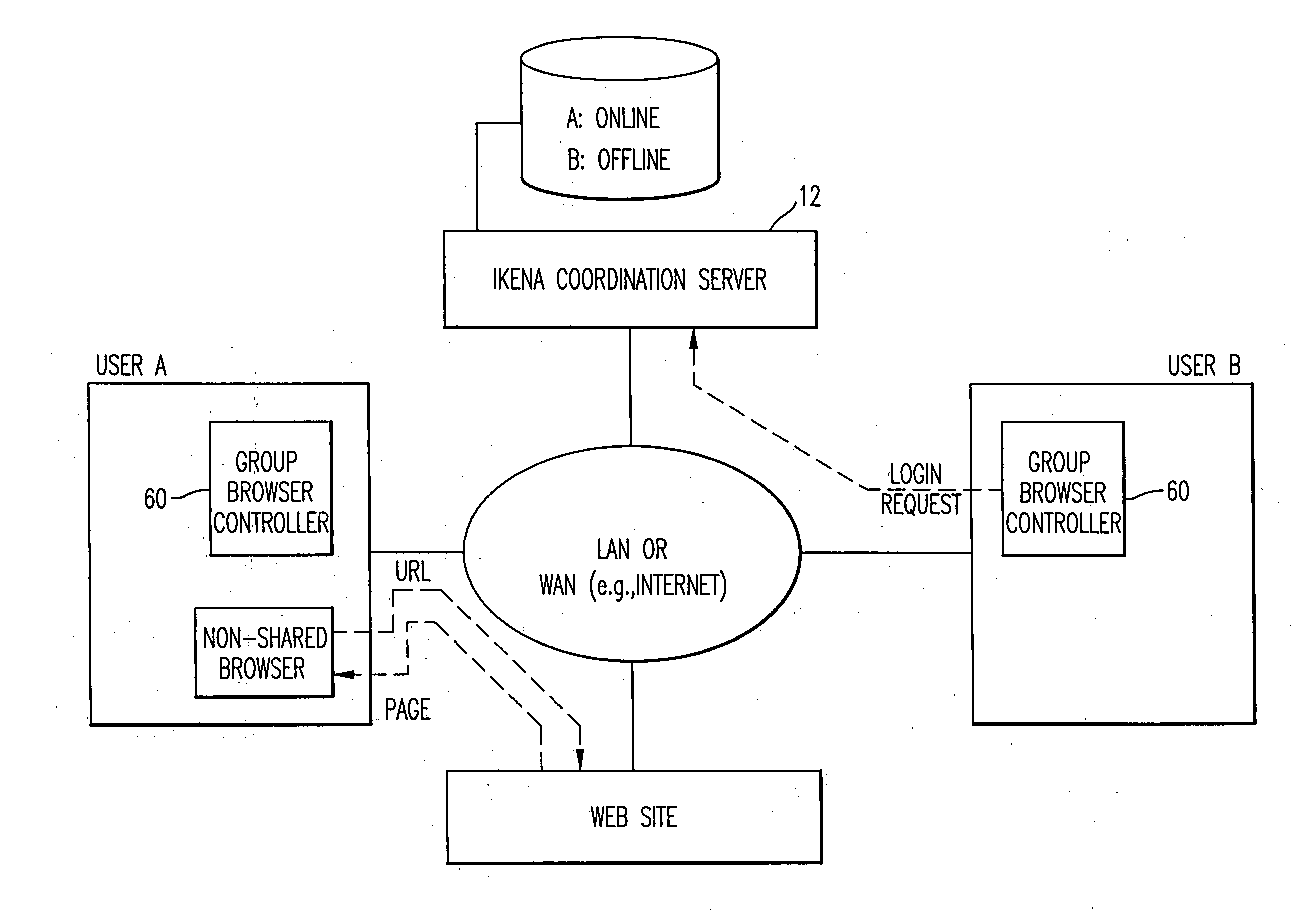
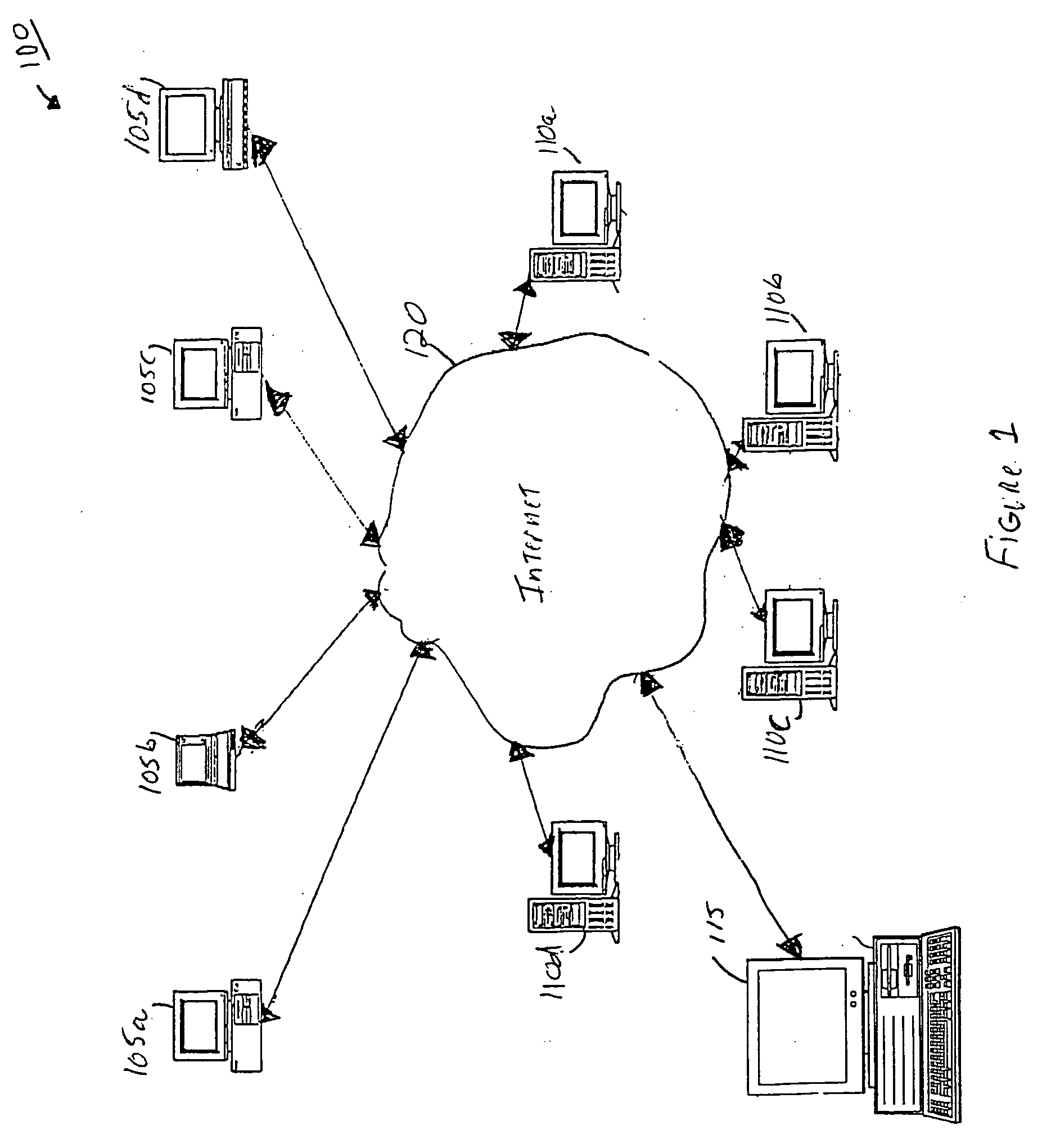
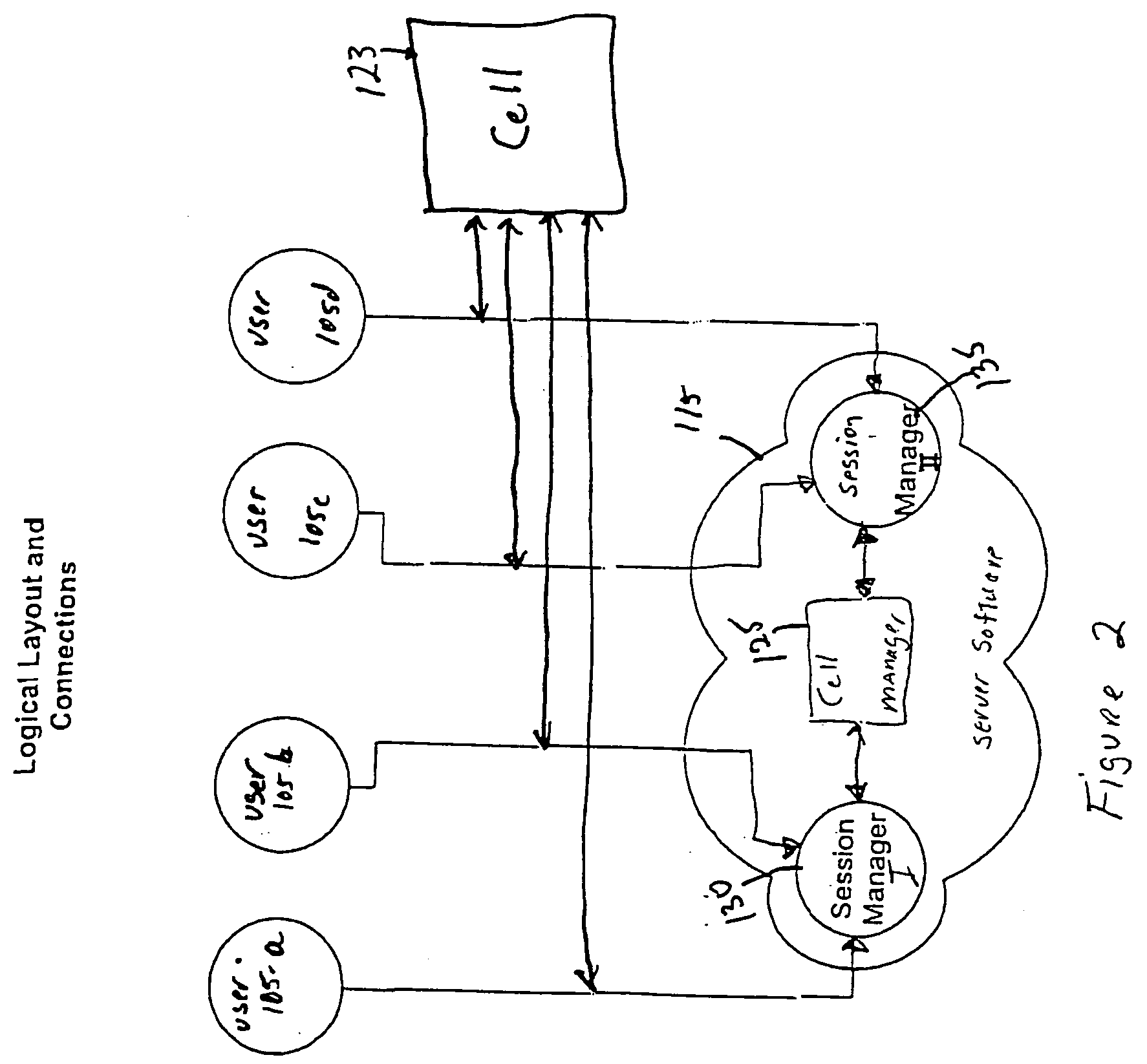
System and method for record and playback of collaborative Web browsing session
InactiveUS6535909B1Cost-effectiveSynchronised browsingWeb data retrievalNetwork connectionWorld Wide Web
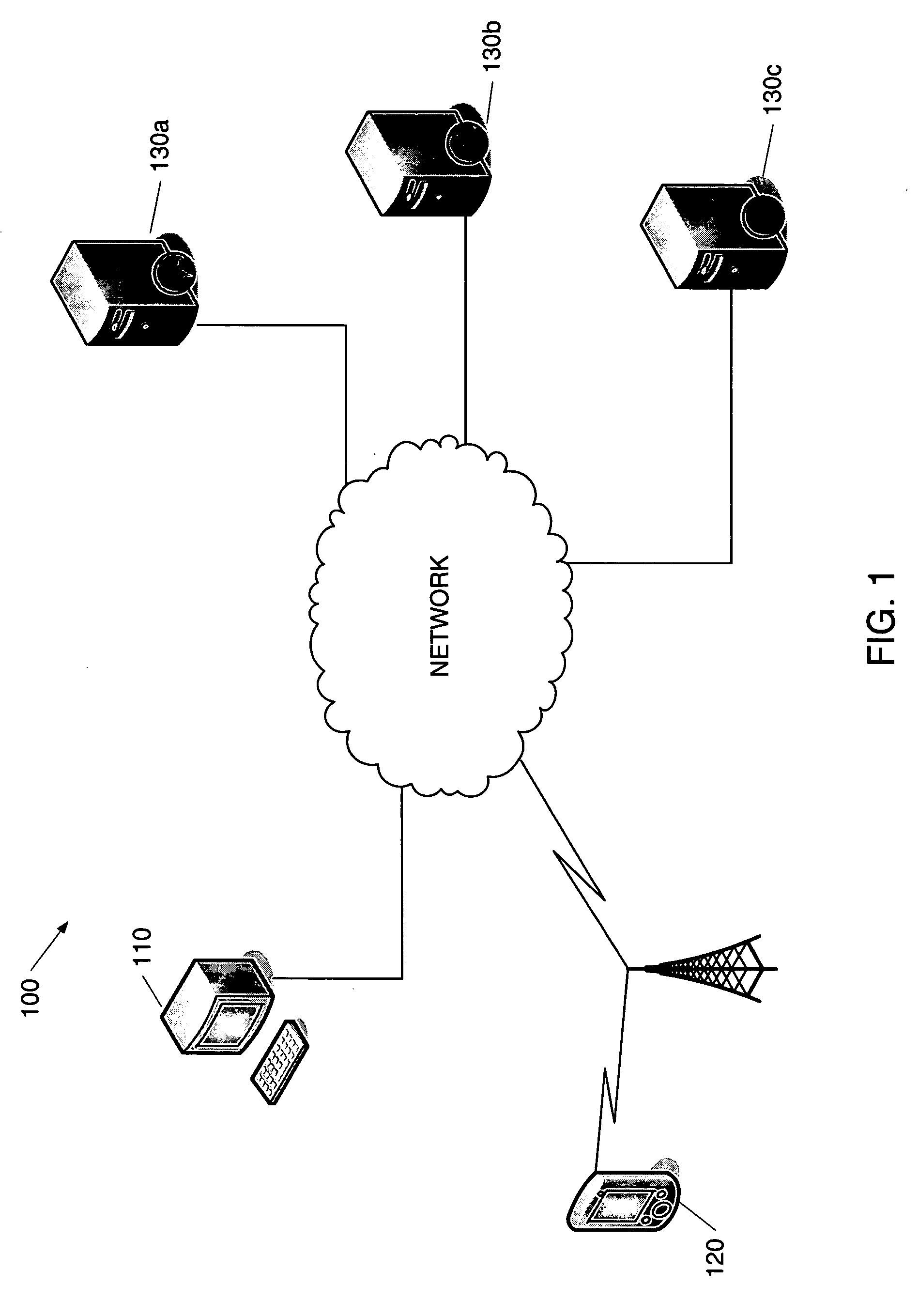
A collaborative Web browsing session may take place over a network, allowing the presenter on a first computer to direct the audio and visual components of a browser on one or more second computers. The second computer is instructed to log into a control site that downloads an active control, such as an applet, to the second computer. The present invention allows a collaborative Web browsing session ("session"), as created by the presenter and witnessed by one or more users on second computers, to be recorded and archived by the control site. When a user of a computer is connected to the control site through a communication network such as the World Wide Web, that user may log into the control site and request to view an archived session. The session will then be replayed by the control site on the user's computer, directing the audio and visual components of the browser on the user's computer as if the user was attending the live session. The recorded session replays the events of the live session in real time such that the playback experience contains the same audio and visual events that took place when the session was originally being recorded.
Owner:RED HAT +1
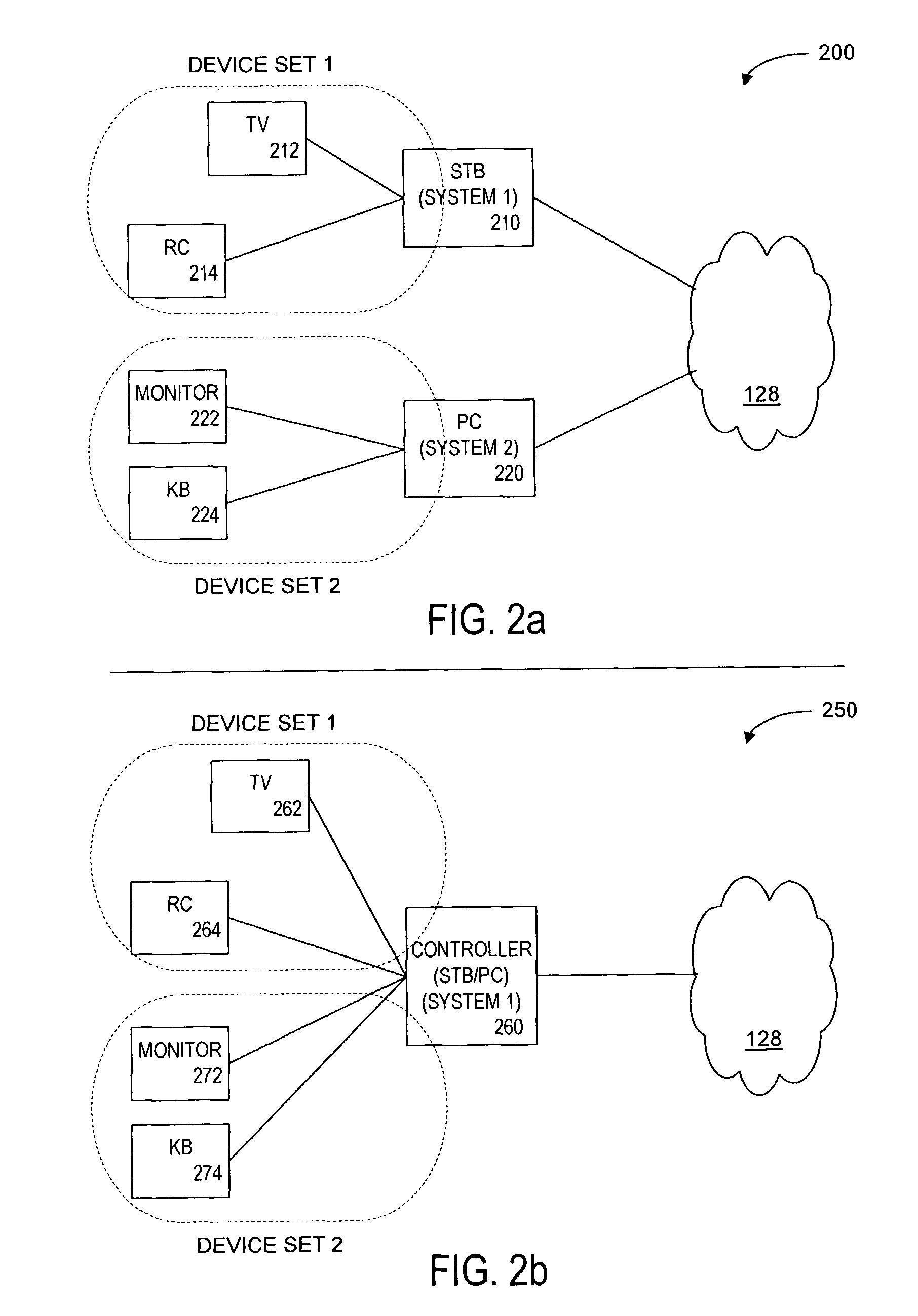
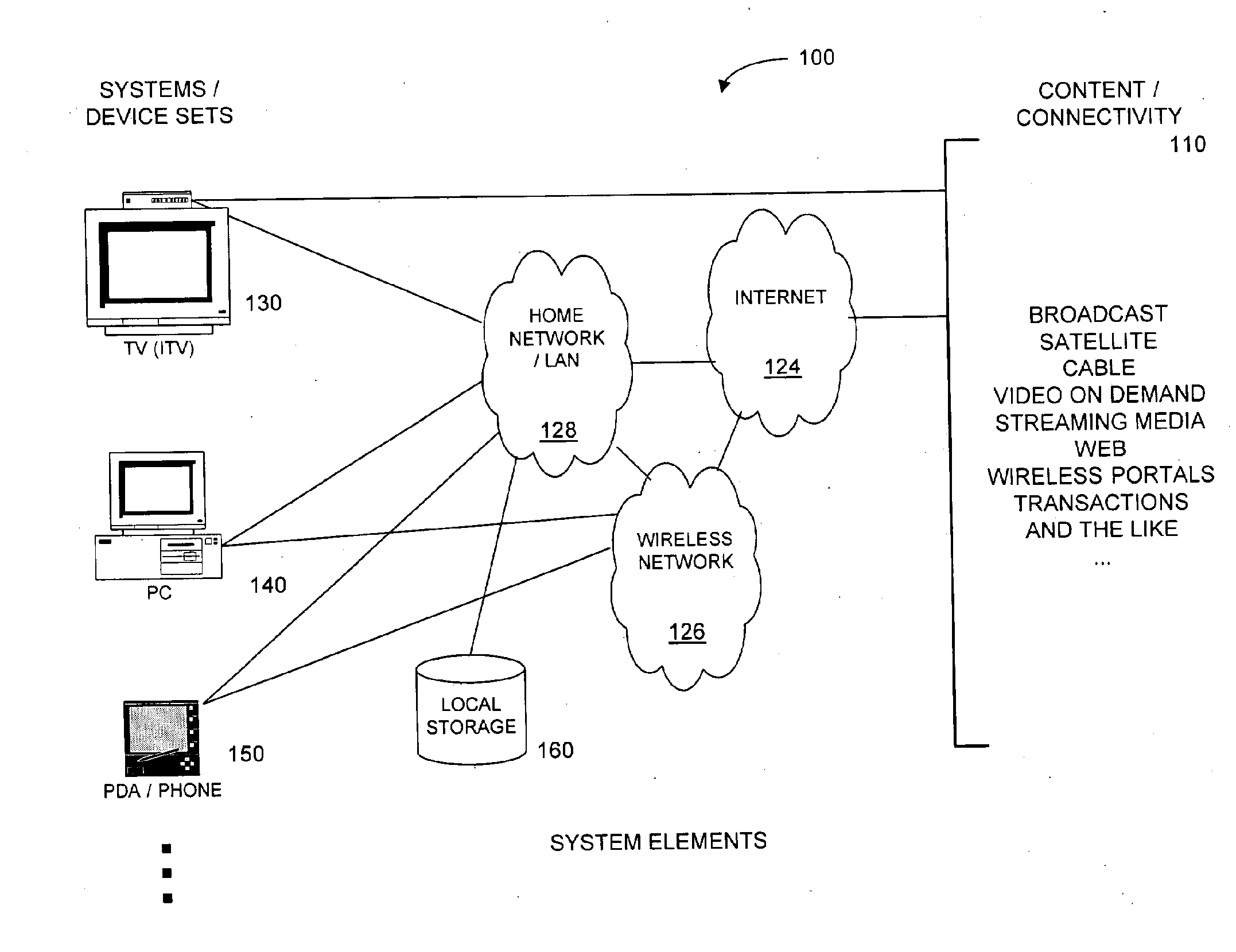
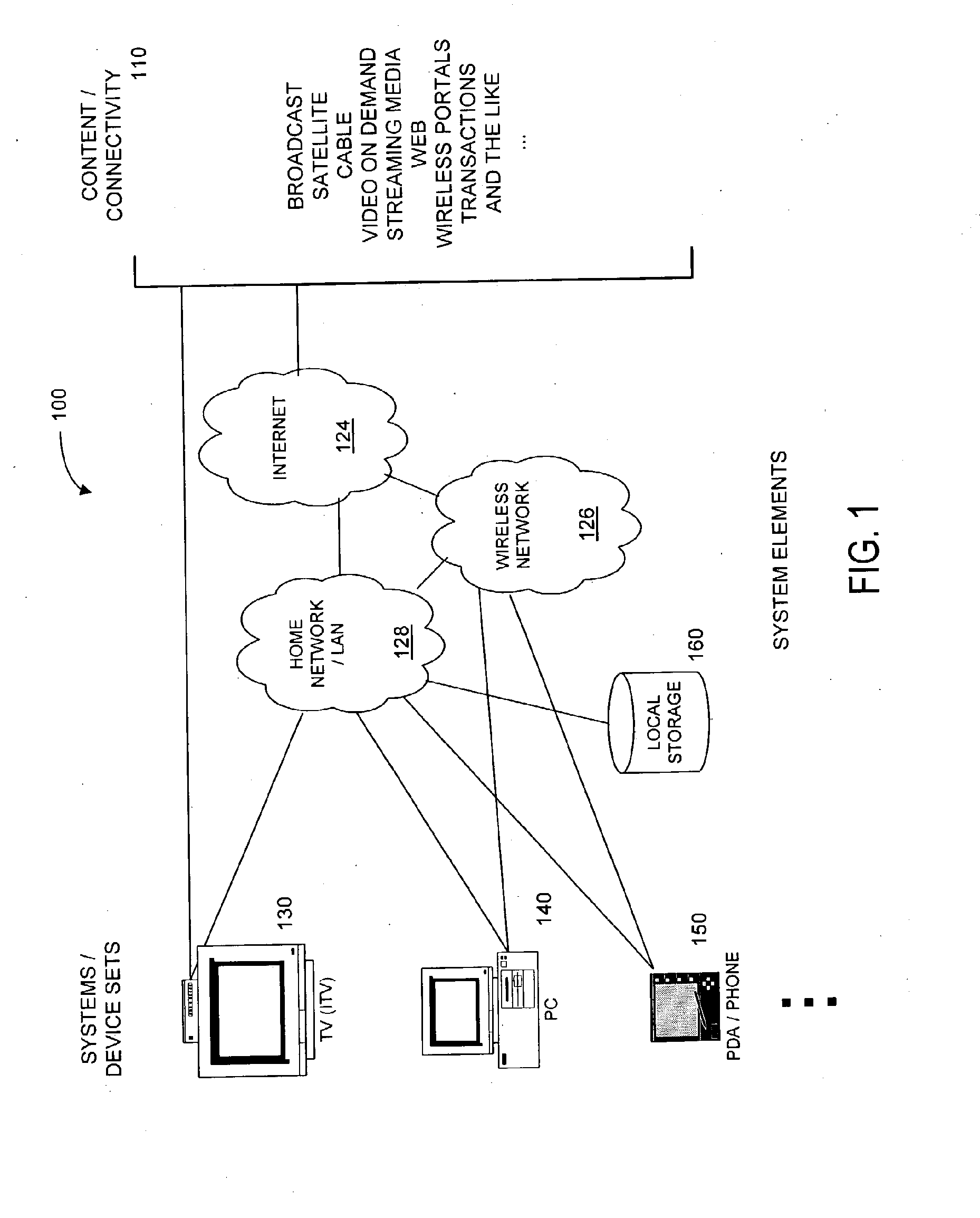
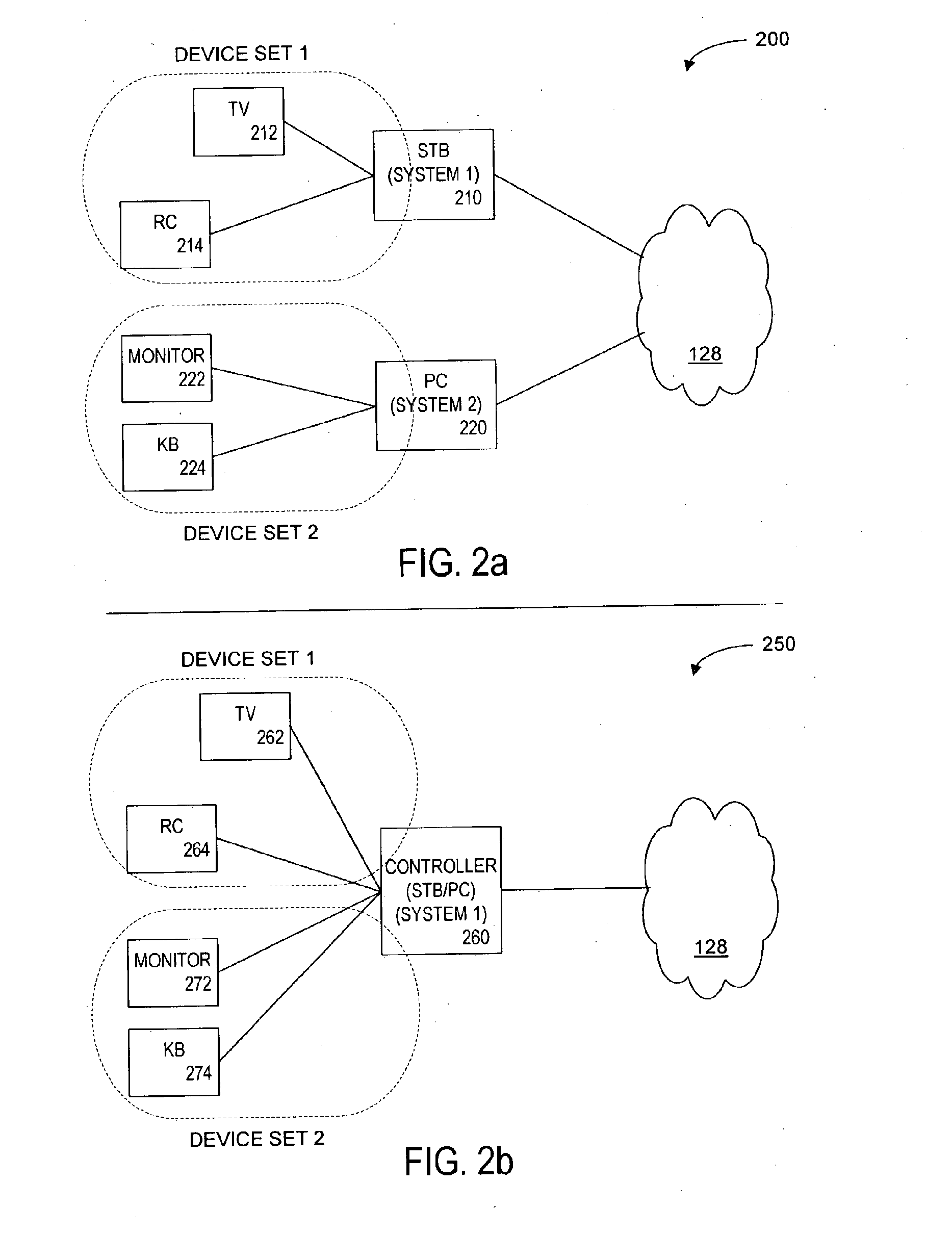
Method and Apparatus for Browsing Using Multiple Coordinated Device Sets
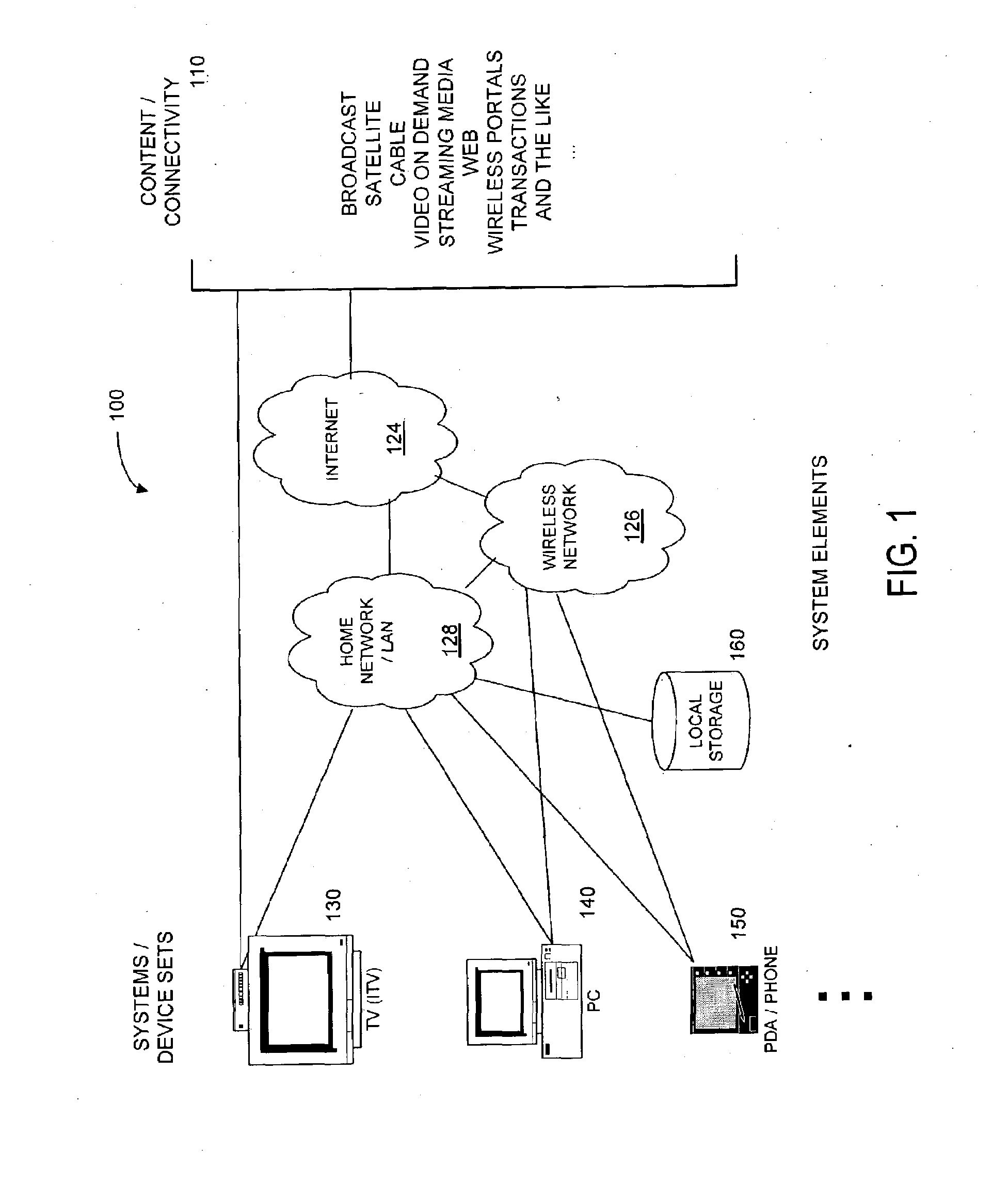
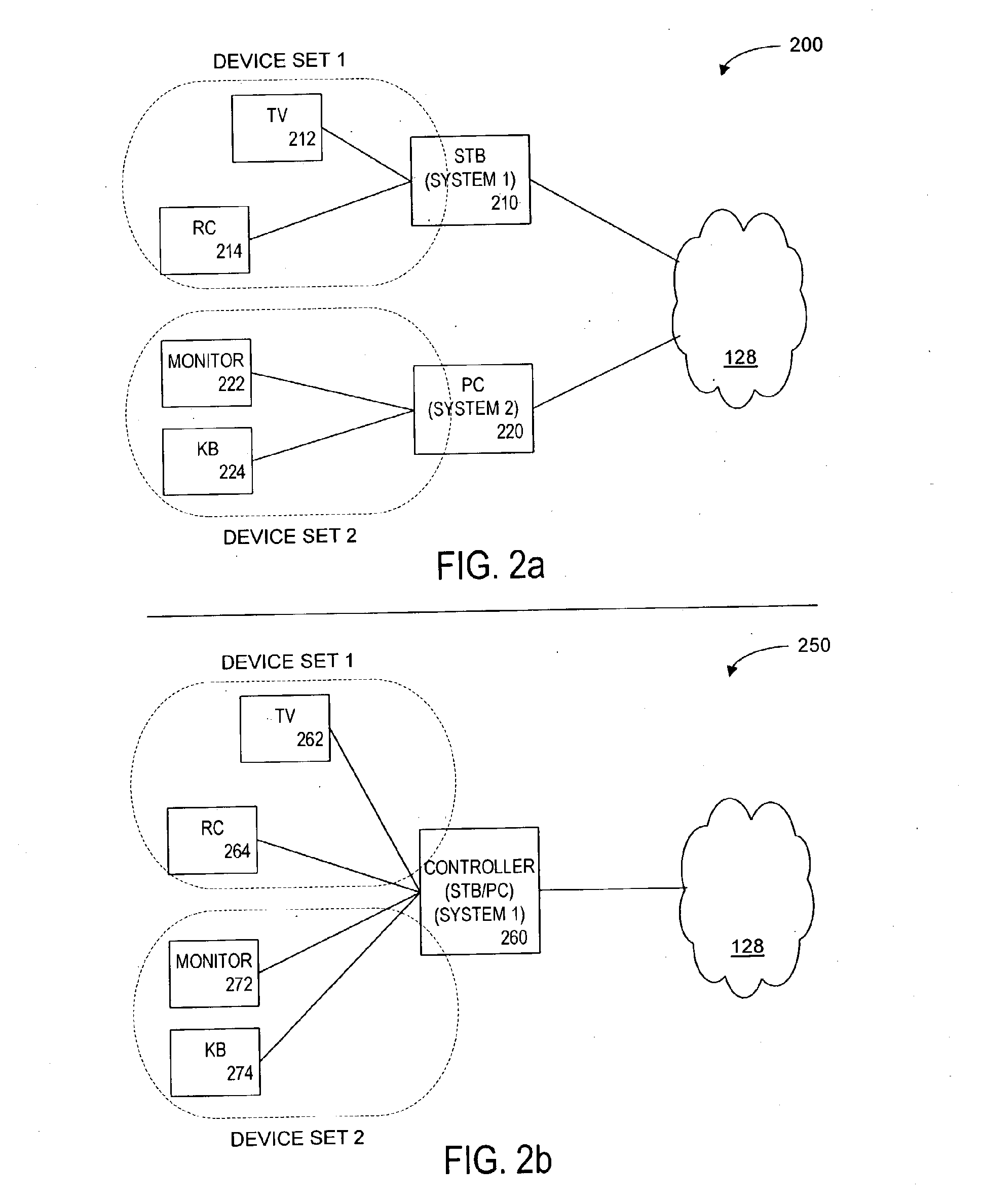
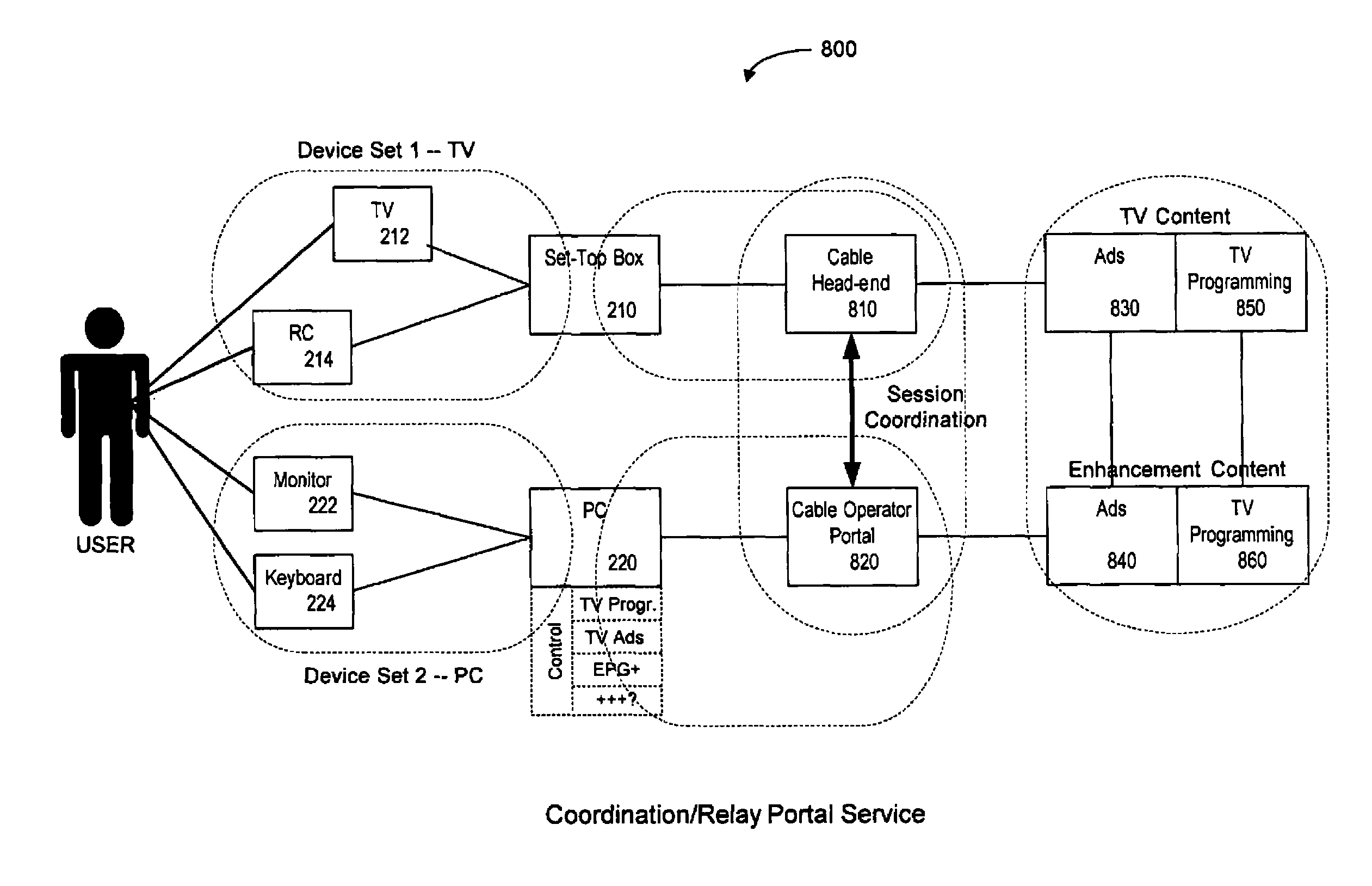
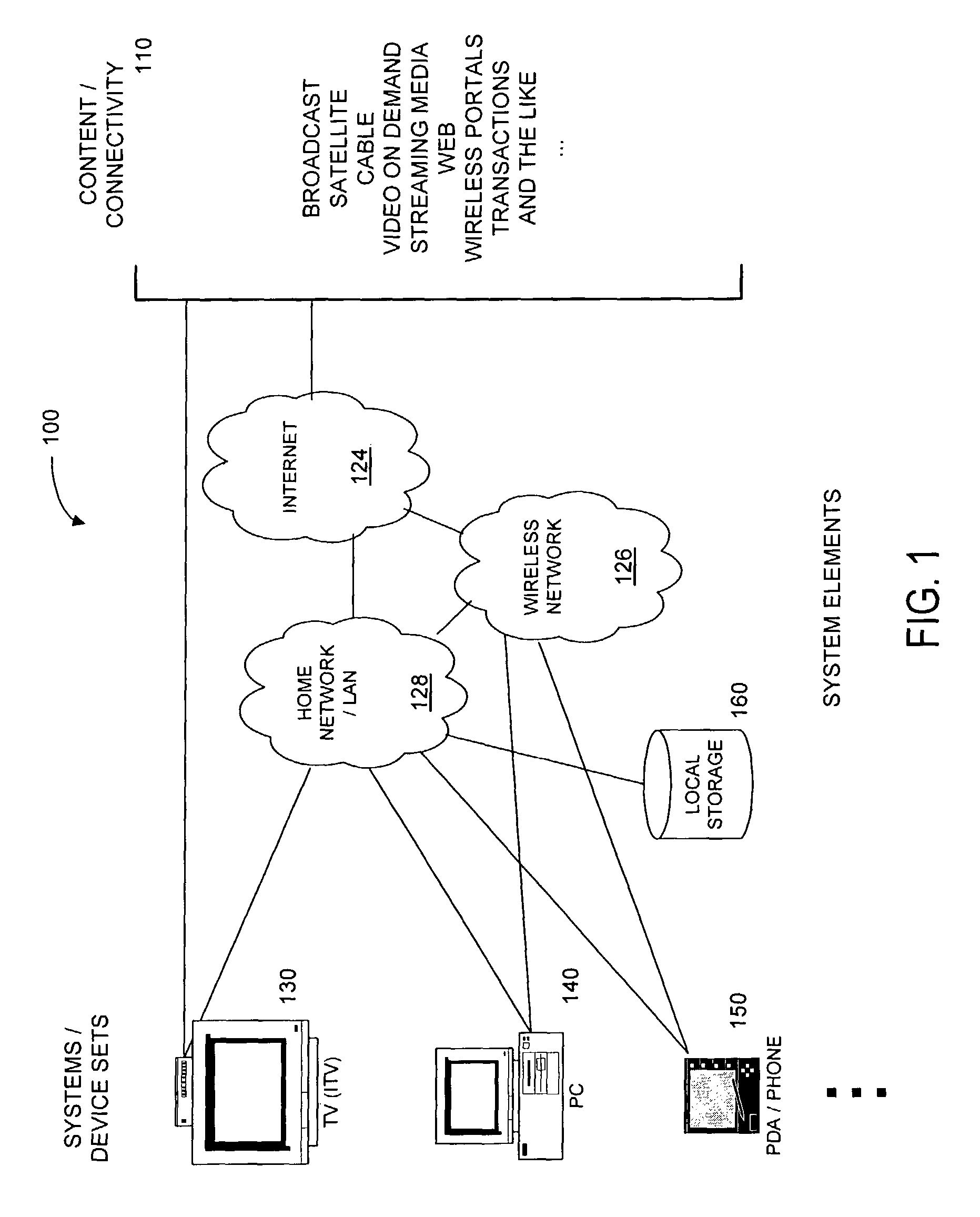
Systems and methods for navigating hypermedia using multiple coordinated input / output device sets. Disclosed systems and methods allow a user and / or an author to control what resources are presented on which device sets (whether they are integrated or not), and provide for coordinating browsing activities to enable such a user interface to be employed across multiple independent systems. Disclosed systems and methods also support new and enriched aspects and applications of hypermedia browsing and related business activities.
Owner:CONVERGENT MEDIA SOLUTIONS
Method and apparatus for browsing using multiple coordinated device sets
InactiveUS7899915B2Synchronised browsingBroadcast information characterisationOutput deviceBusiness activities
Owner:CONVERGENT MEDIA SOLUTIONS
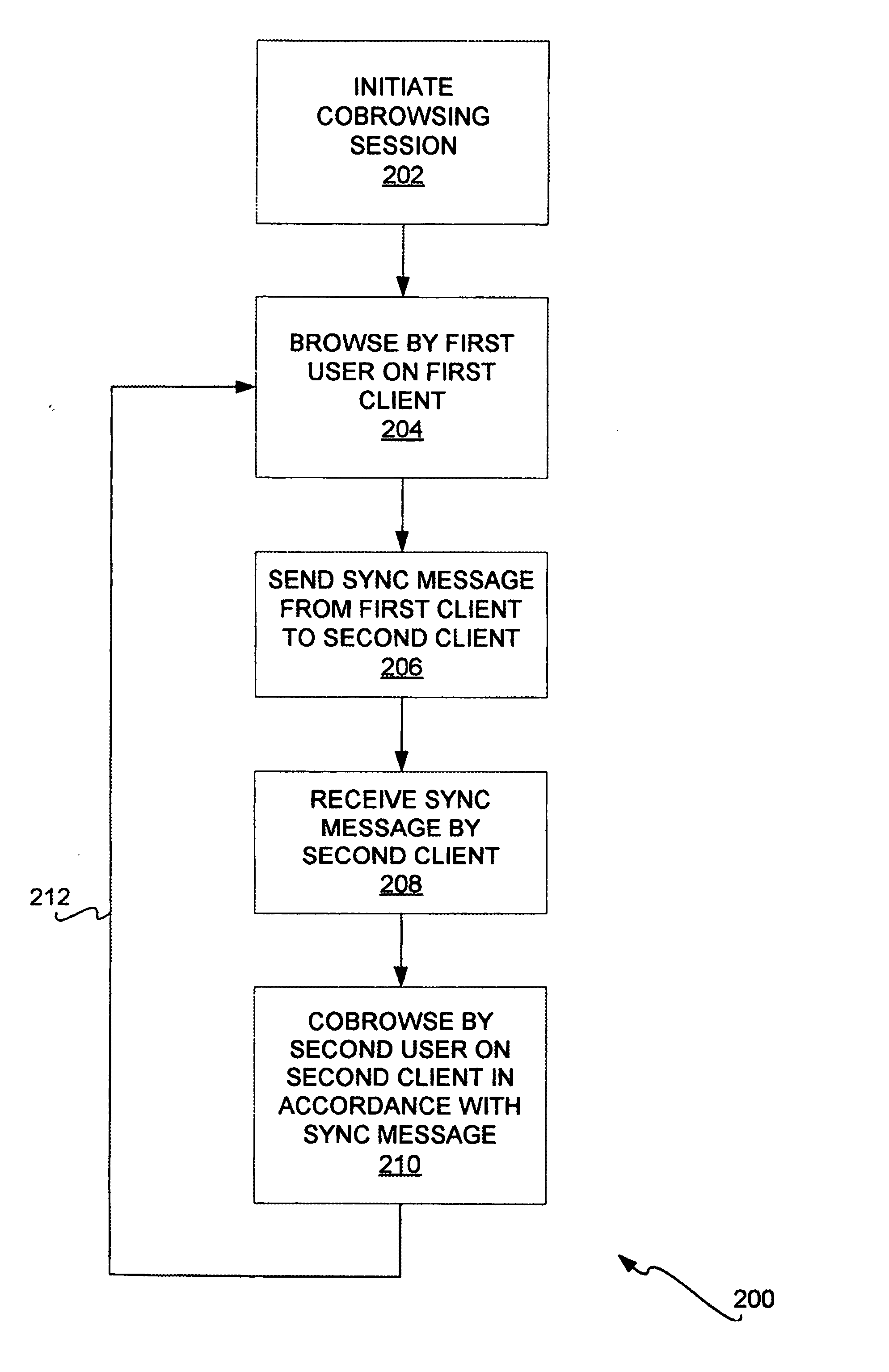
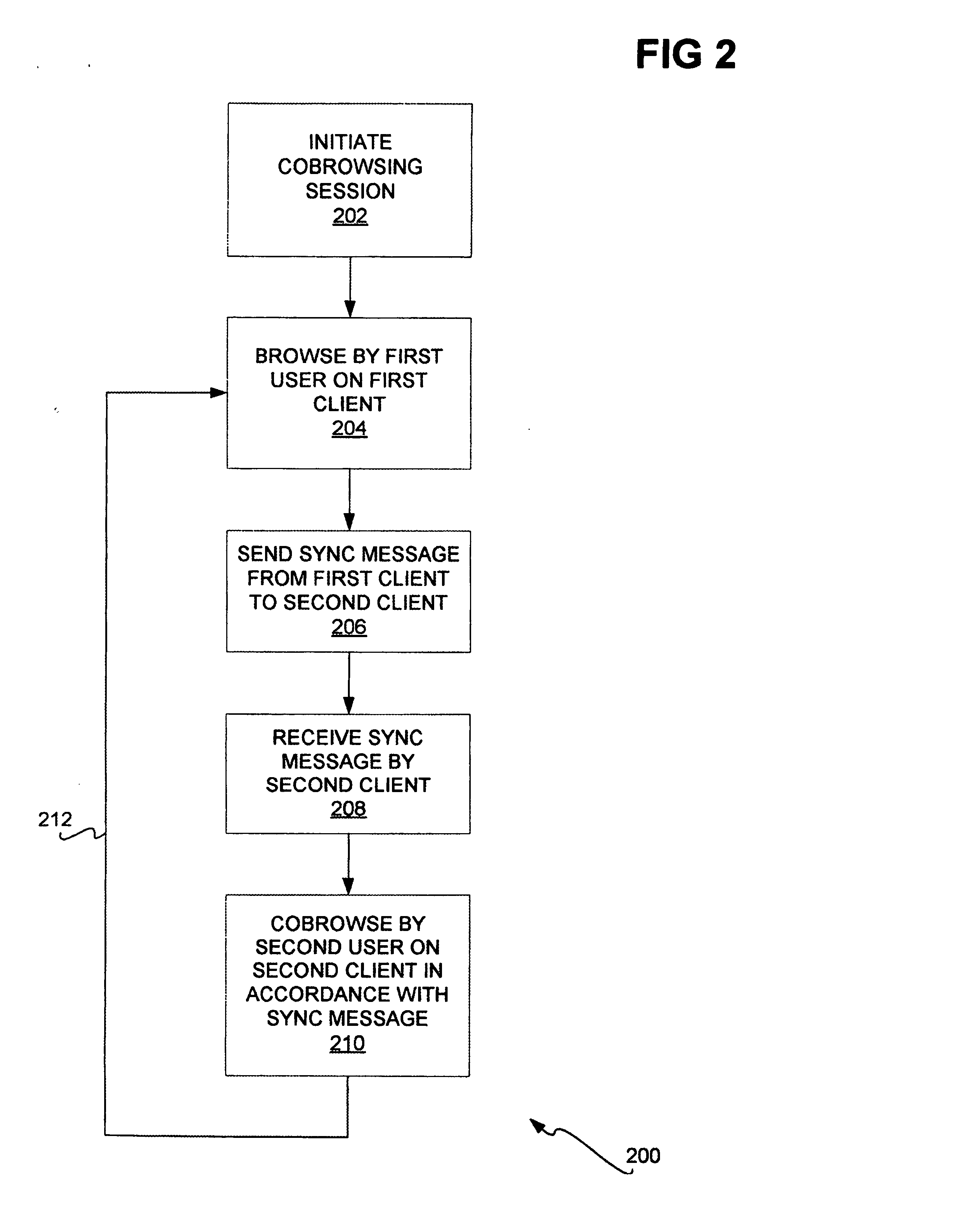
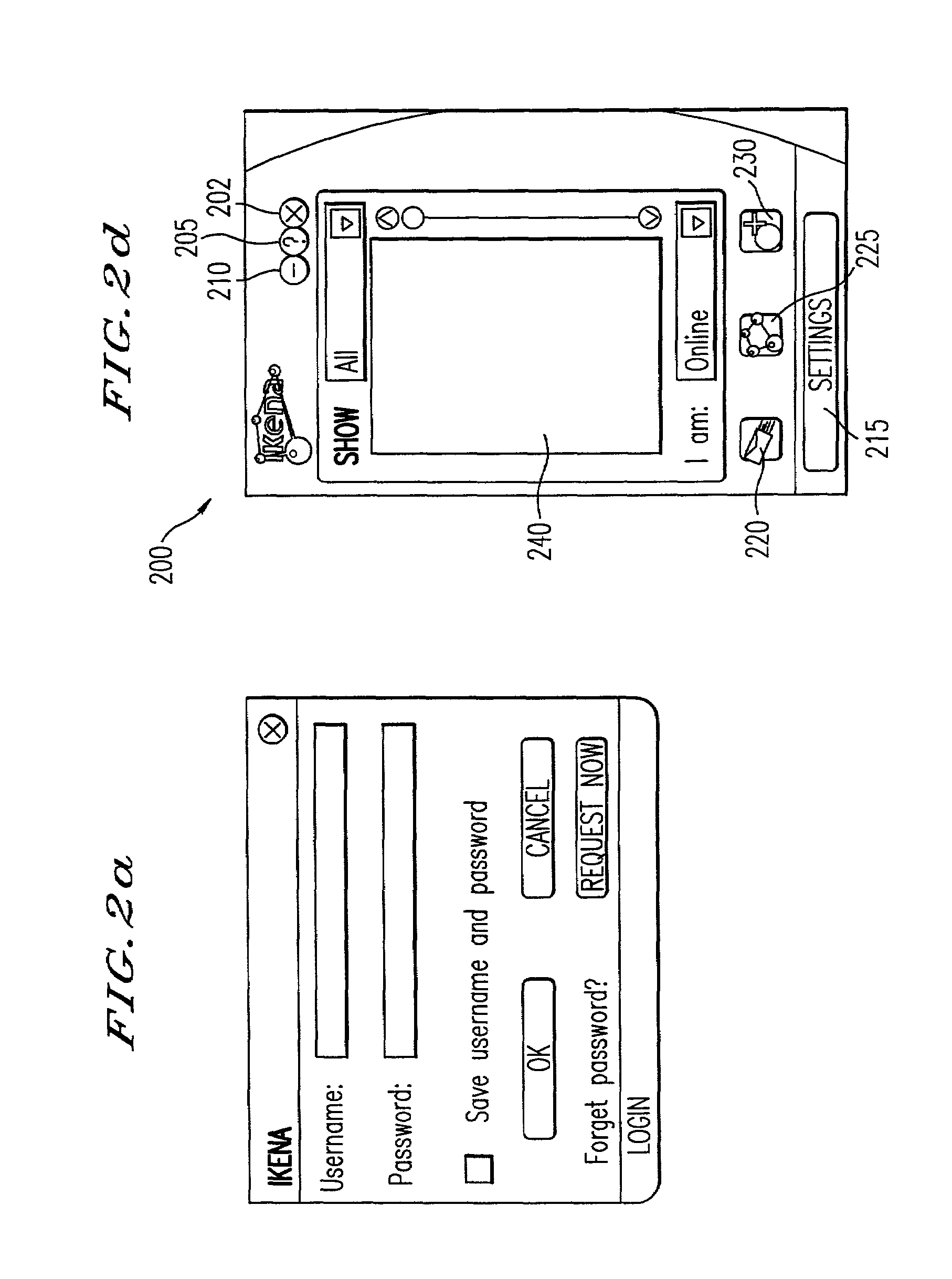
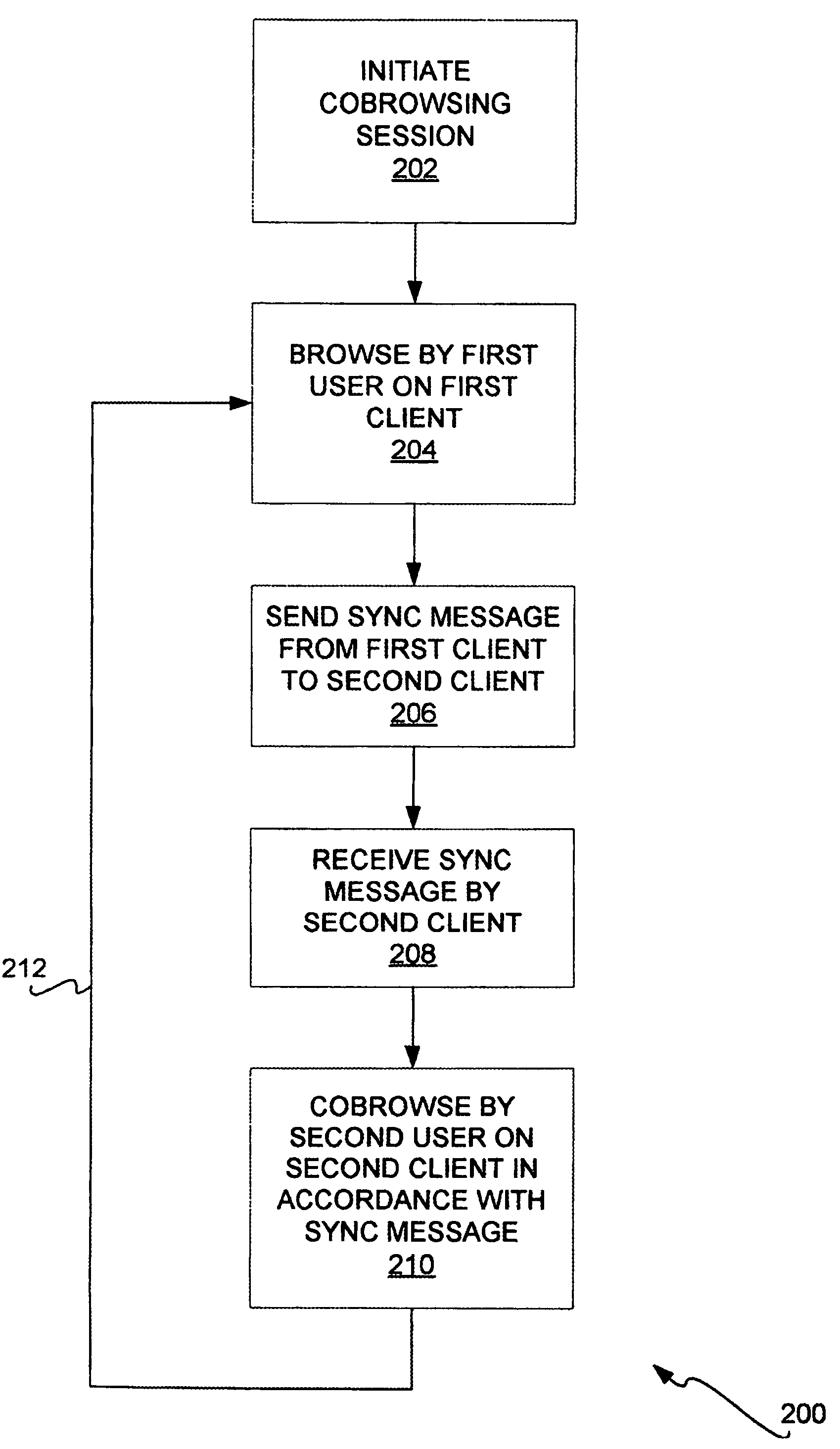
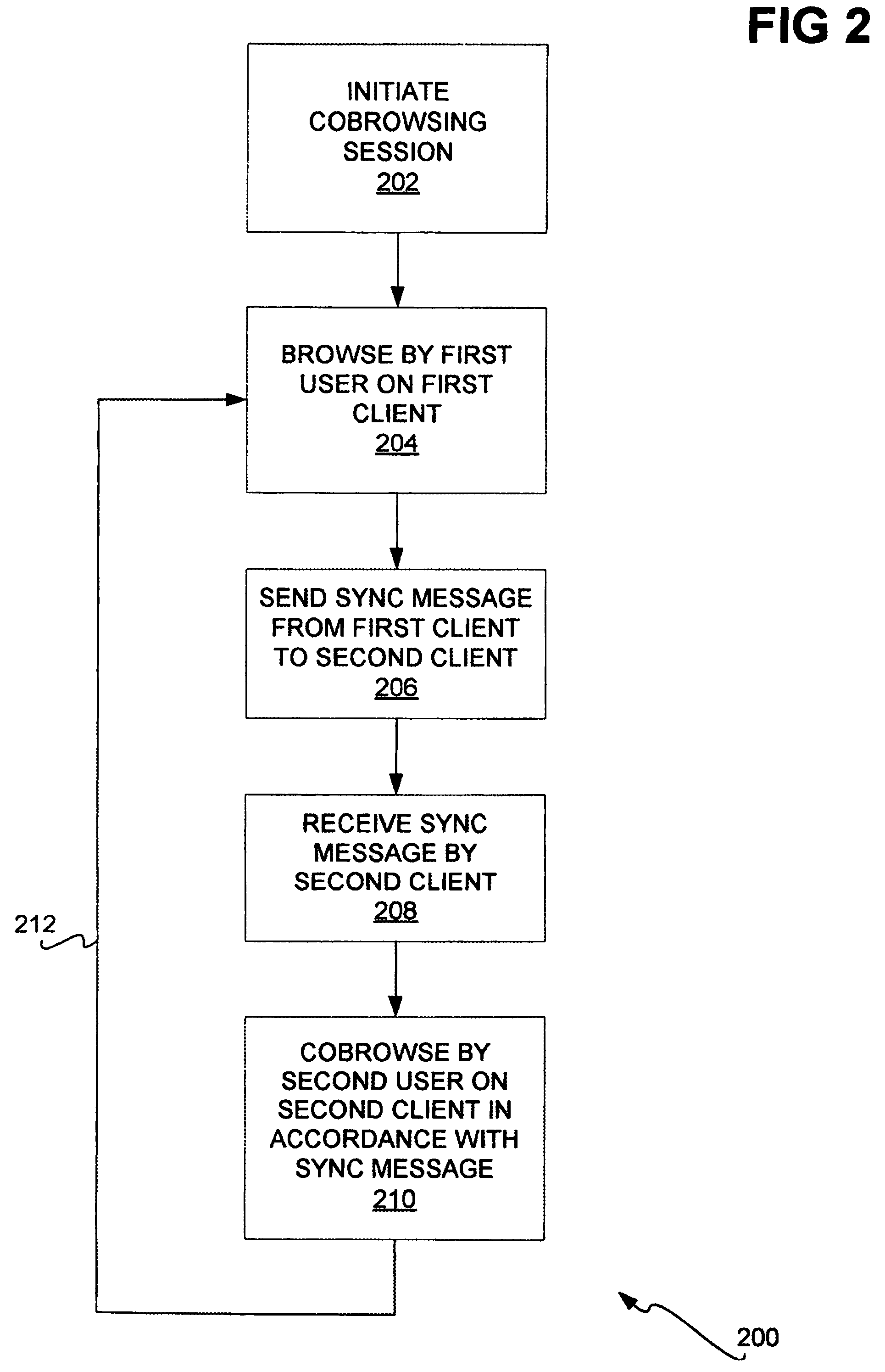
Web site cobrowsing
InactiveUS20050091572A1Synchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb siteGranularity
Cobrowsing web sites by two or more users is disclosed. For a cobrowsing session between a first client of a first user and a second client of a second user, the cobrowsing session is first initiated. The first user browses a web site on the first client. The first client sends to the second client a synchronization message. The synchronization message indicates one or more commands reflecting the browsing performed by the first user. The second client receives the synchronization message, and cobrowses the web site in accordance with the message and its included commands. Cobrowsing continues until the cobrowsing session is terminated. The commands of the synchronization message allow for fine granularity of cobrowsing.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
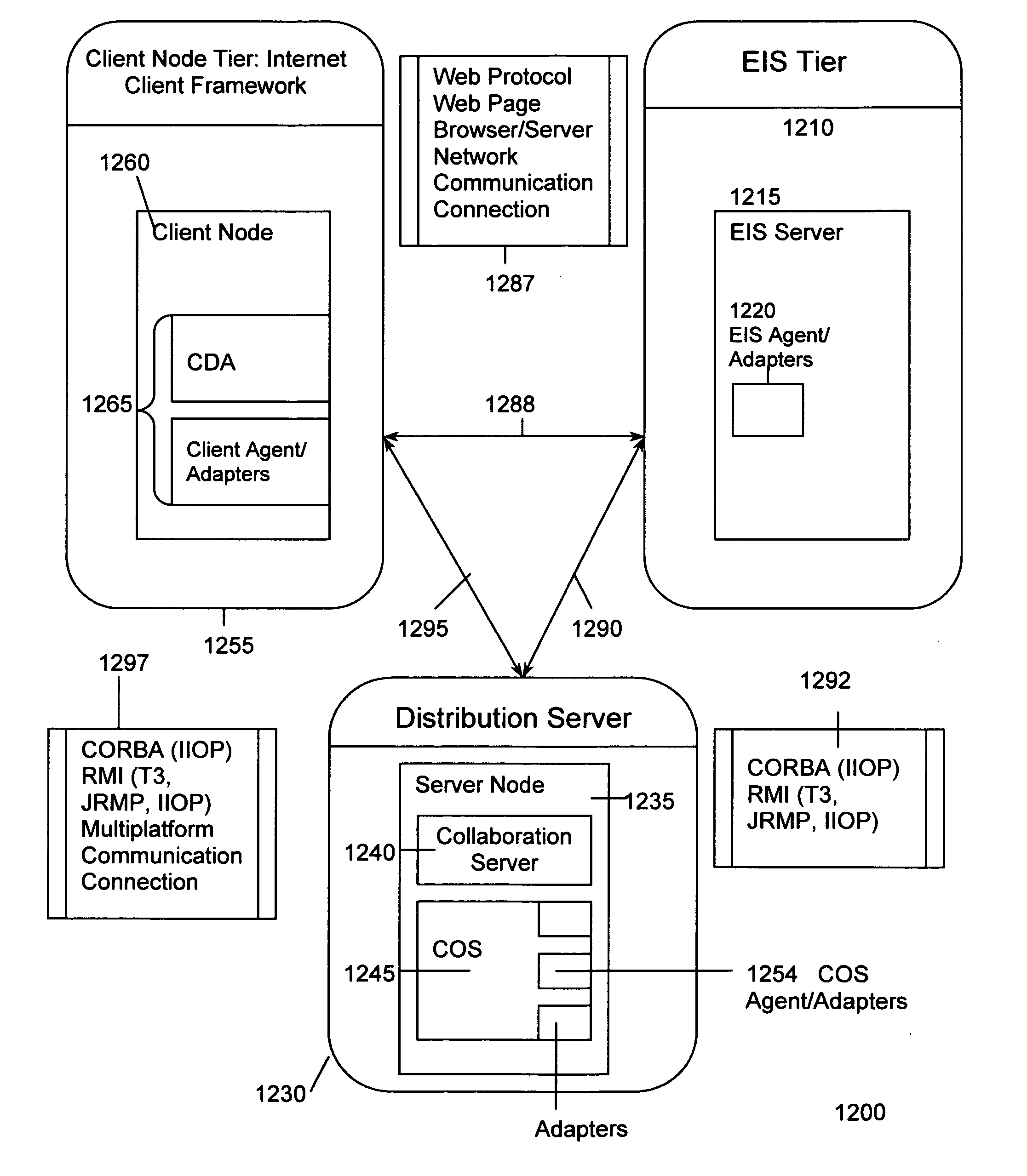
Method and system for deploying an asset over a multi-tiered network
ActiveUS7150015B2Synchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsApplication softwareMulti layer network
A method and system for deploying assets to multi-tiered network nodes. An asset may represent network and / or application components (e.g., data, objects, applications, program modules, etc.) that may be distributed among the various resources of the network. In one embodiment, a target node's environment may be adjusted before an asset is deployed to that target node. In an alternative embodiment, a target deployment adapter, associated with the asset, may be selected and deployed with the asset in order to allow the asset to operate in the target node environment. An implementation class, associated with the asset, may be inserted into the target node environment. An altered target deployment descriptor may also be inserted into the target node environment.
Owner:OP40 HLDG
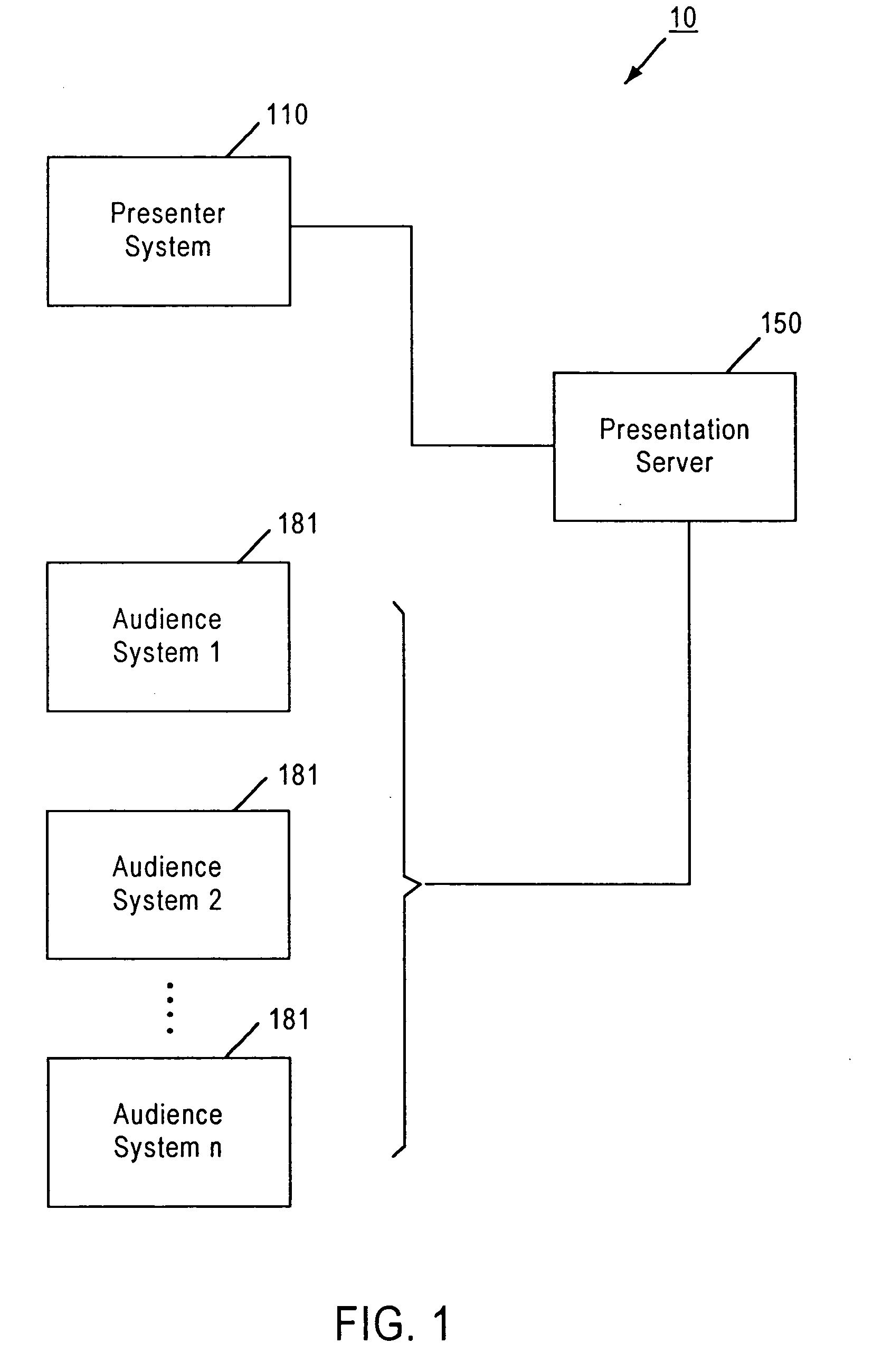
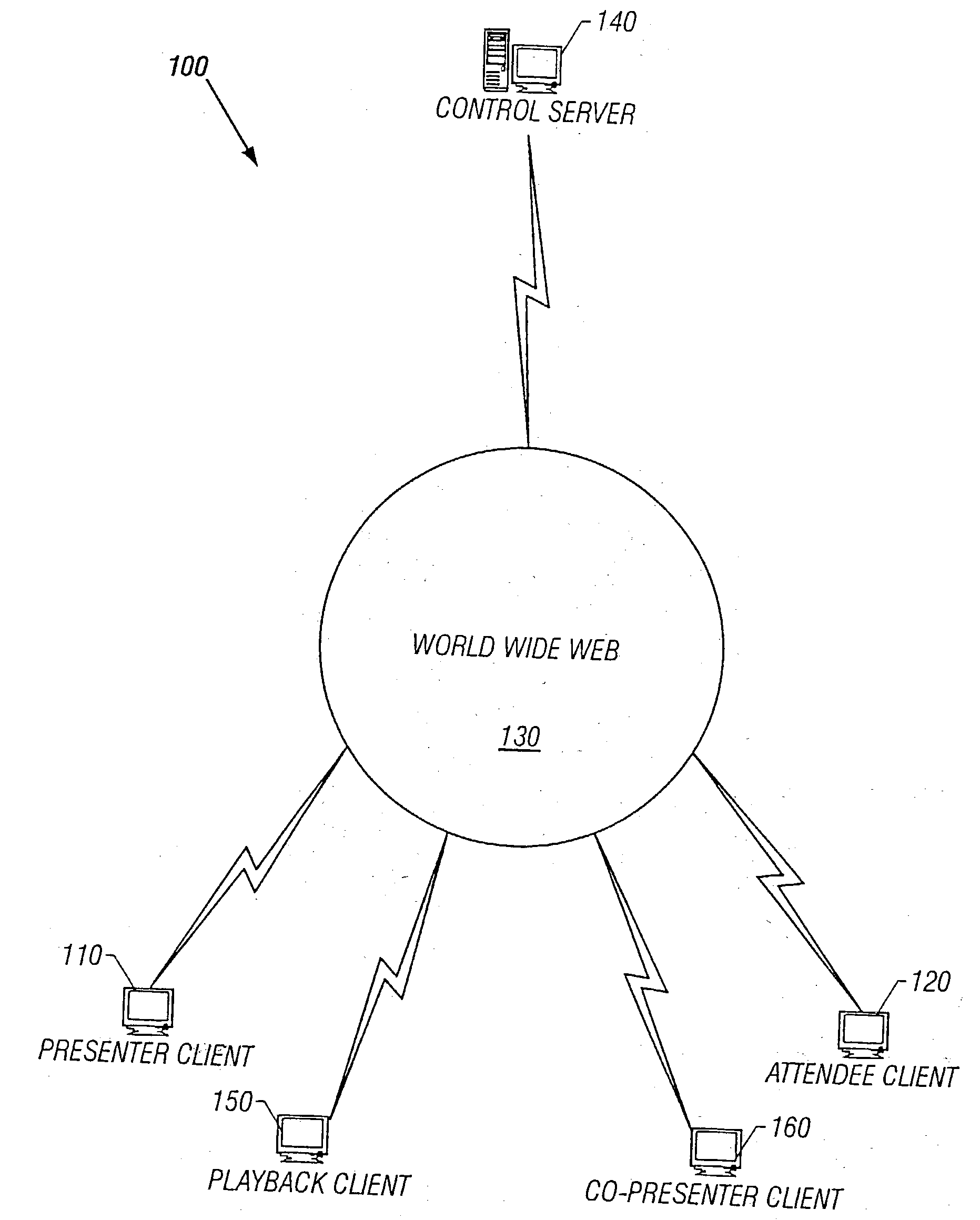
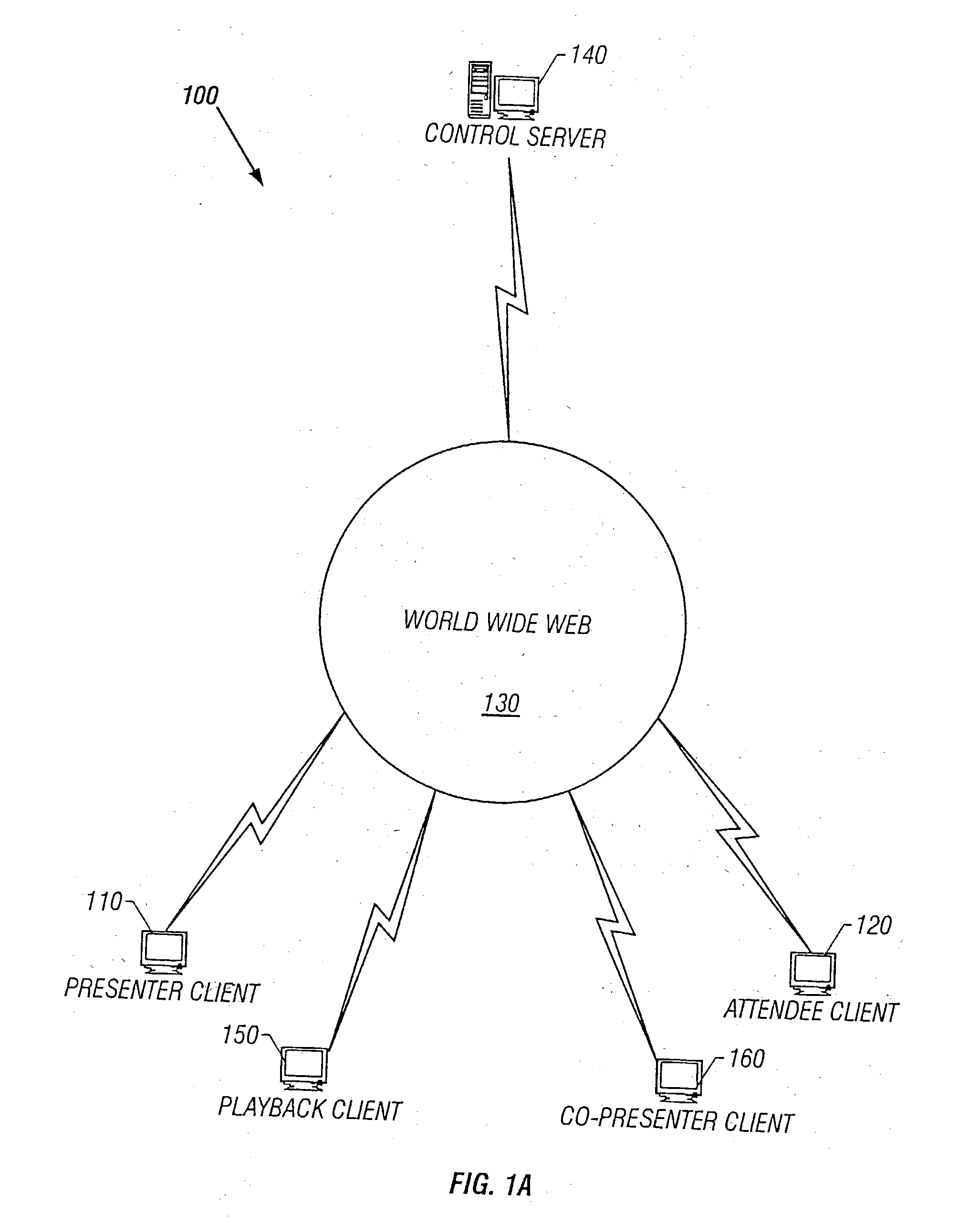
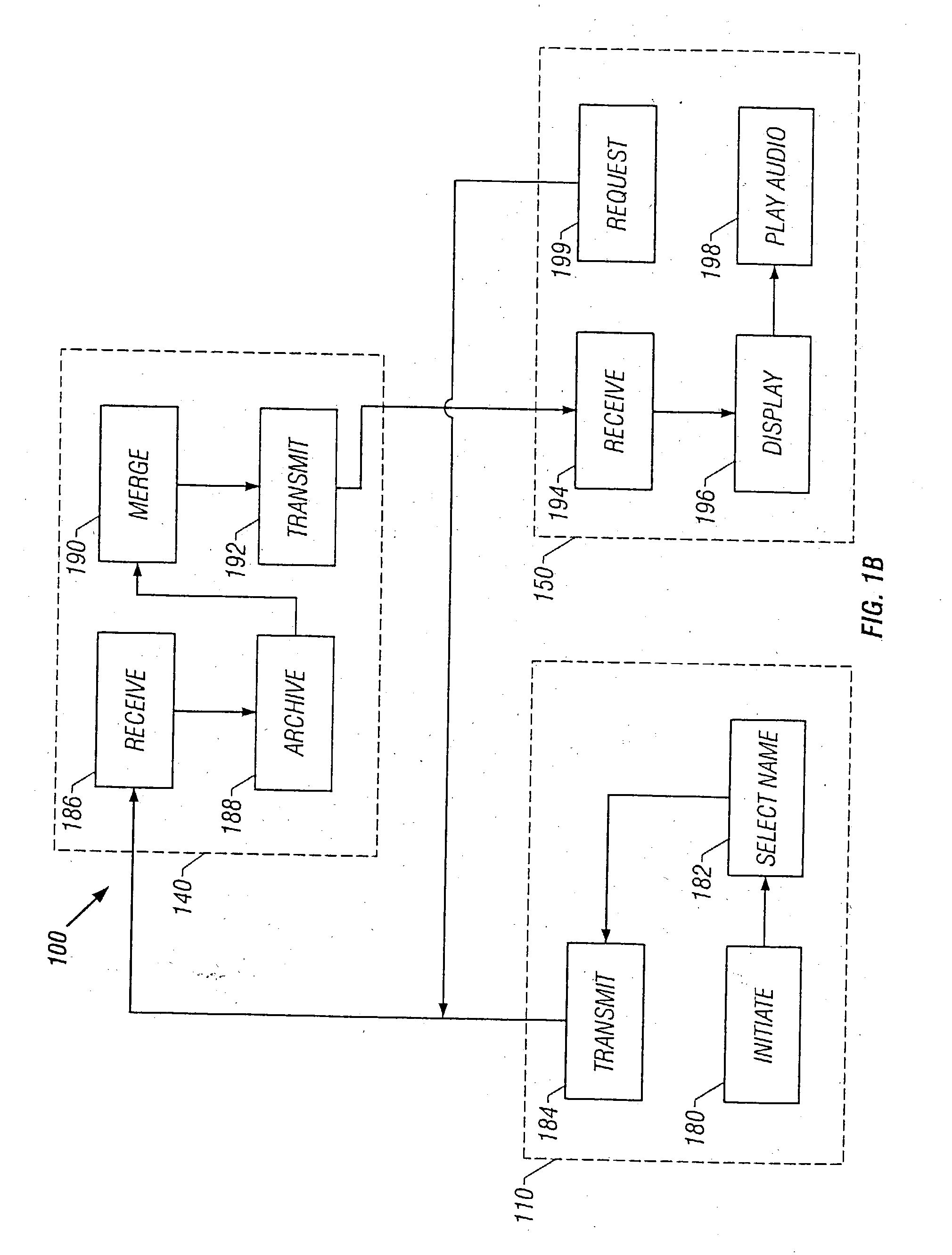
Networked presentation system
InactiveUS20040255232A1Synchronised browsingDigital computer detailsSystems managementData transmission
A networked presentation system manages transmission of presentation units to the audience, and ensures that the presentation units are displayed to, or accessible by, the audience in the same sequence as the presenter intends. The networked presentation system includes a presenter system, a presentation server and at least one audience system that connect to each other using a data transmission network. The networked presentation system controls to deliver the active presentation unit to the audience systems such that whenever the presenter renders one presentation unit active, the networked presentation system makes the active presentation unit available to the audience system. The networked presentation system allows users of the audience system to configure the way the presentation units are displayed on the audience system, and to attach notes to the presentation units. In addition, the networked presentation system may obtain feedback from the audience with respect to a specific presentation unit and calculate various indices representing the audience's responses based on the feedback. The networked presentation system may allow the presenter to access notes taken by the audience during the presentation in connection with a specific presentation unit. The networked presentation system may allow users to share notes with other people.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
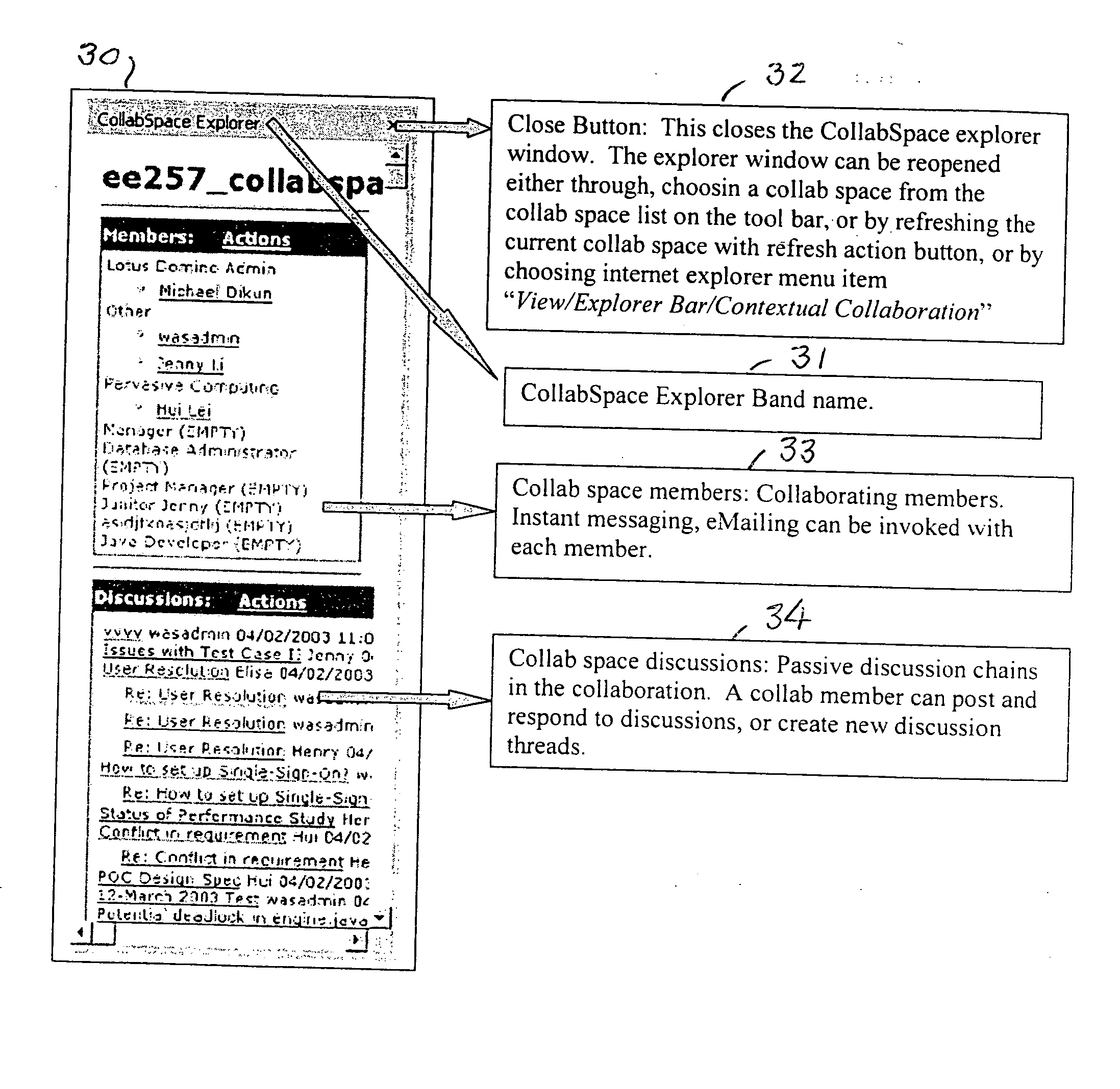
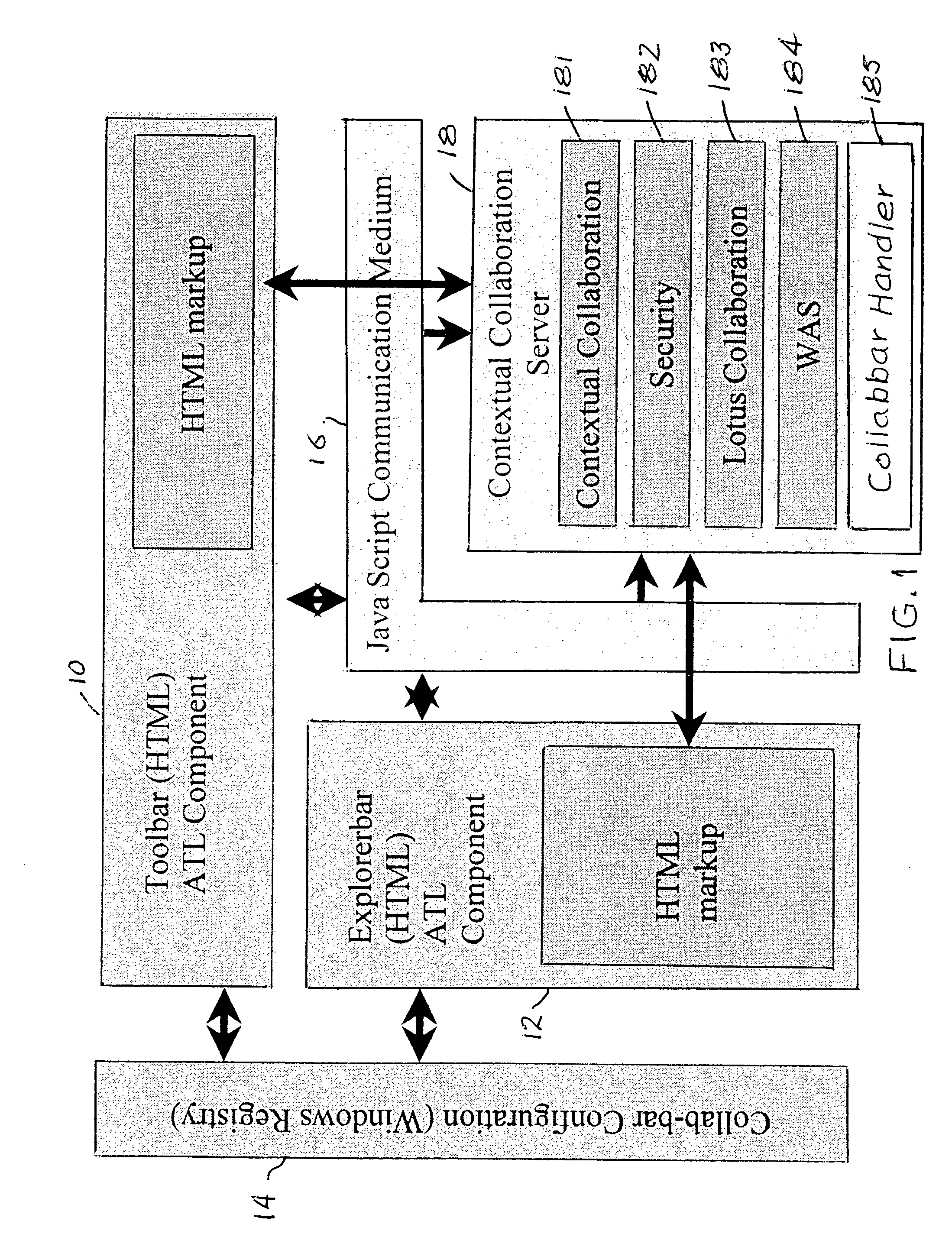
Method and system for collaborative web browsing
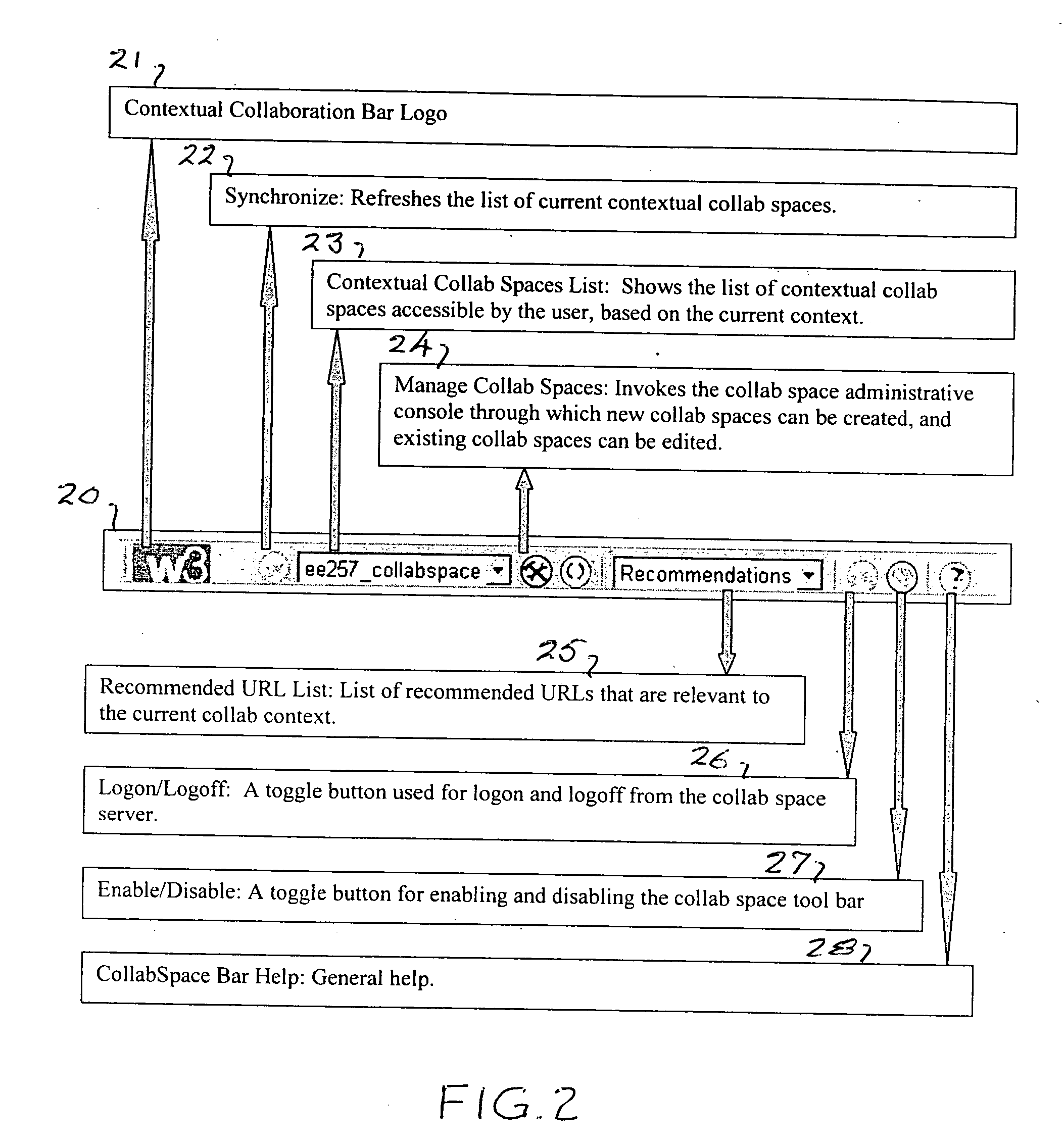
ActiveUS20050114789A1Increase heightImprove experienceSynchronised browsingWeb data navigationWeb browserPaper document
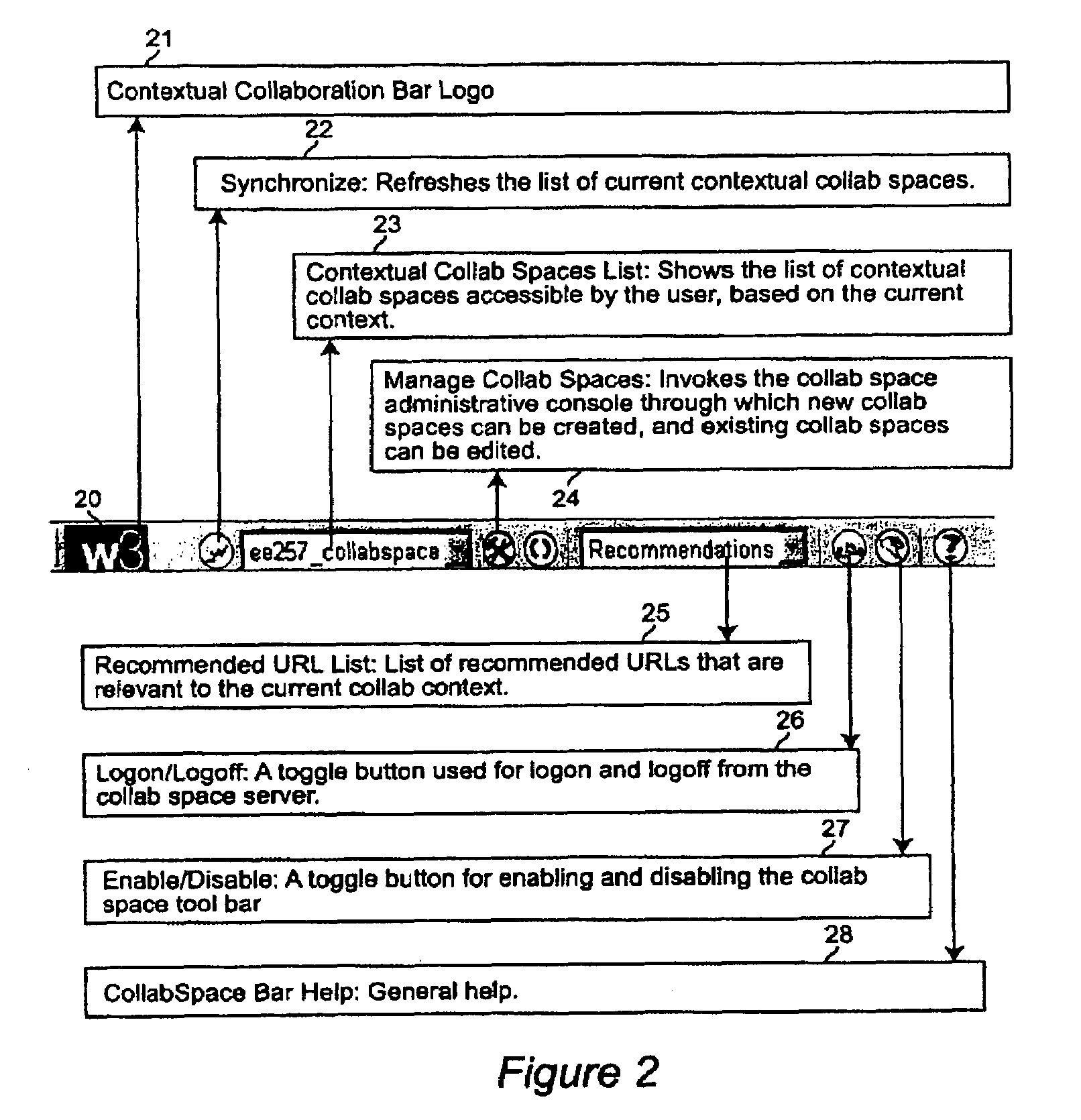
A Web browser is augmented with collaborative features to support community aware browsing sessions. The augmentation provided includes a data mining plug-in for the browser to establish collaborative context based on Uniform Resource Locator (URL) meta data keywords, or mined topics, and a collaboration co-browser (explorer bar) which displays a collaboration space, called CollabSpace, corresponding to the document that is displayed in the main browser. With this augmented browser, a user can perform various collaboration functions from the collaboration explorer bar, including viewing the online status of members of the CollabSpace, communicate with members of the CollabSpace via electronic mail (e-mail), instant messaging or discussion threads, and register as a member of the CollabSpace. CollabSpaces can be established and associated with one or more Web documents, meta data keywords or topics.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
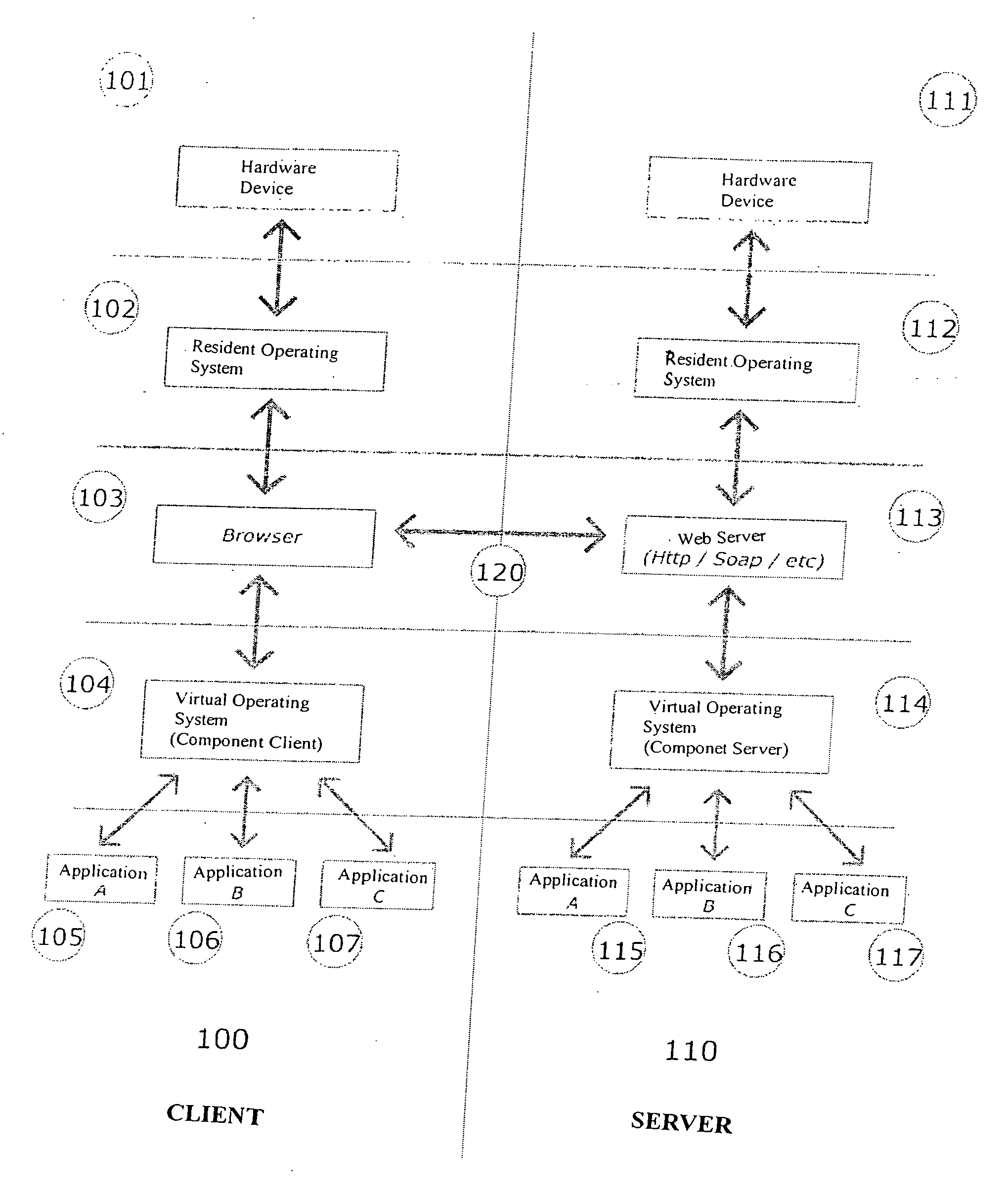
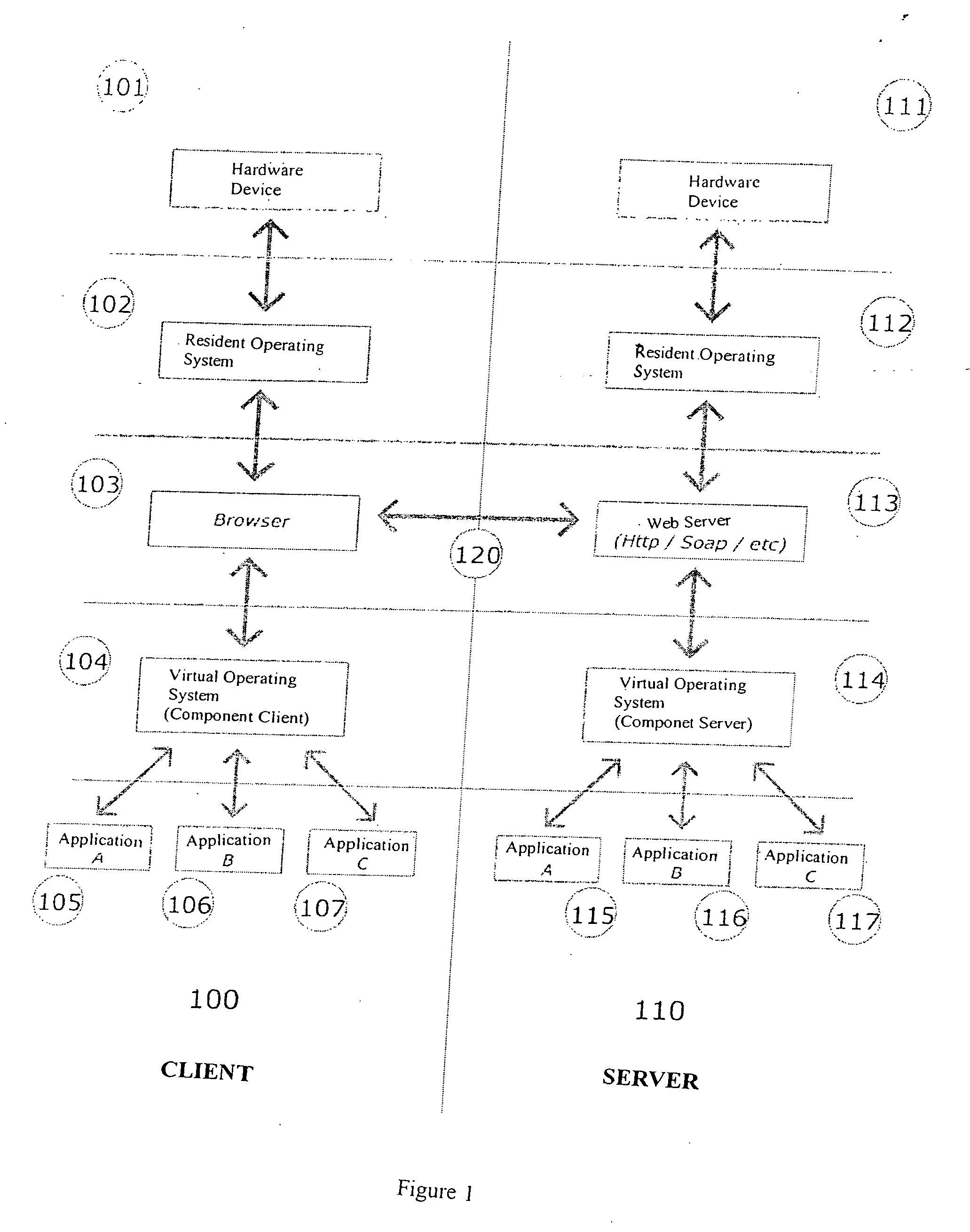
System for management of interactions between users and software applications in a web environment
ActiveUS7721303B2Improve interactivitySynchronised browsingWeb data retrievalEmbodied agentApplication software
There is disclosed a system for management of interactions between users and software applications in a web environment, related to an operating environment which functional devices are in charge of providing methods allowing maximum interactivity between the end user and the application. The operating environment also includes a set of applications available to end users, administrators and developers. The applications for end users are intended to provide interactivity, storage, data organization, publication and search. For the administrators, the applications allow full configuration of the behavior of the system and of the agents included within its scope. And for the developers, the system provides configuration kits that enable interfacing between the objects included in its operating context.
Owner:EMBRIA INFORMATICA
Method and apparatus for browsing using alternative linkbases
InactiveUS20150135206A1Synchronised browsingBroadcast information characterisationBusiness activitiesHuman–computer interaction
Systems and methods for navigating hypermedia using multiple coordinated input / output device sets. Disclosed systems and methods allow a user and / or an author to control what resources are presented on which device sets (whether they are integrated or not), and provide for coordinating browsing activities to enable such a user interface to be employed across multiple independent systems. Disclosed systems and methods also support new and enriched aspects and applications of hypermedia browsing and related business activities.
Owner:CONVERGENT MEDIA SOLUTIONS
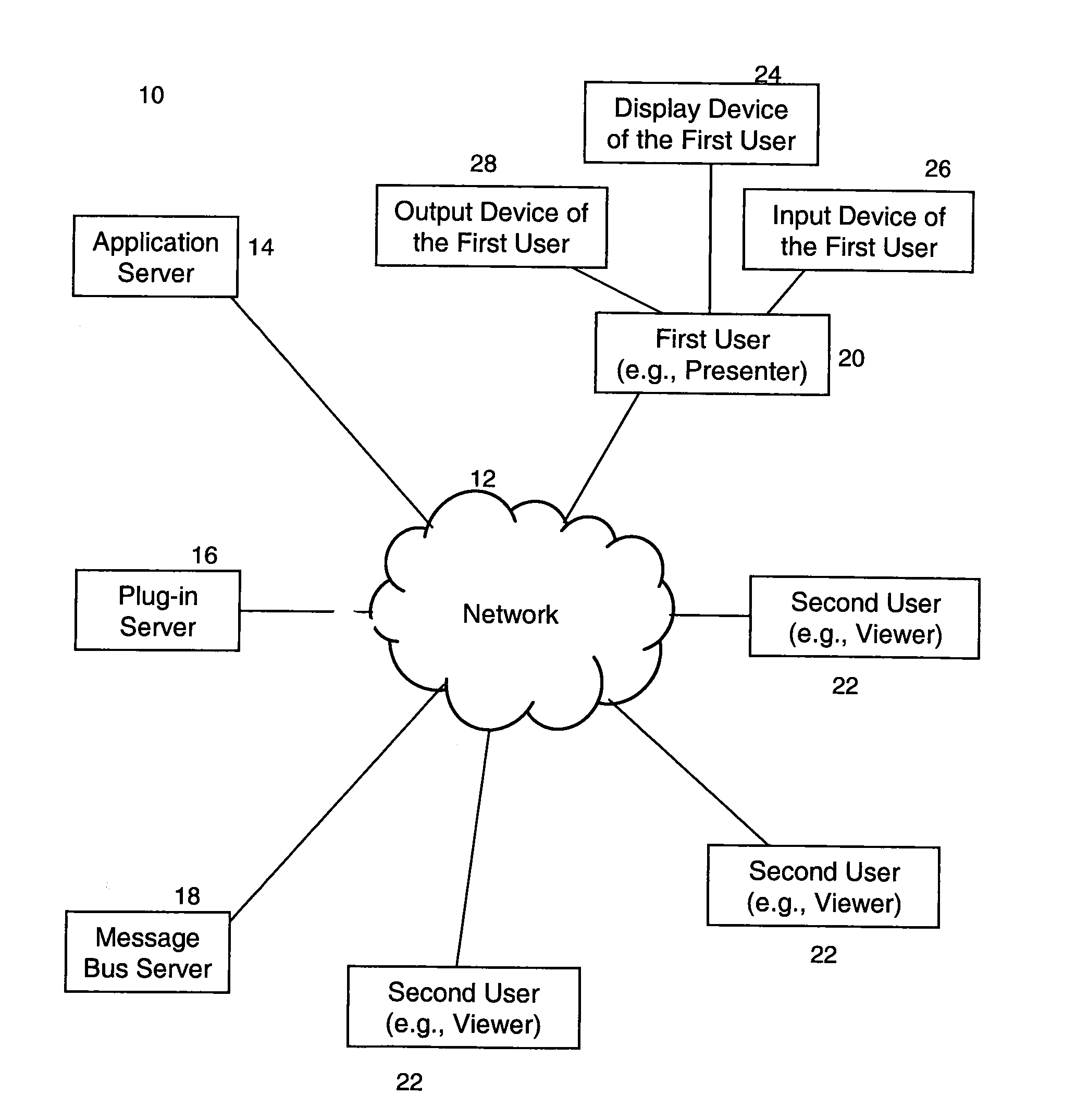
System and method for synchronizing collaborative web applications
InactiveUS20100257451A1Synchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb applicationApplication software
A system and method for synchronizing collaborative web applications including using a message bus server and HTTP protocol.
Owner:HBR LABS
System for management of interactions between users and software applications in a web environment
ActiveUS20060080592A1Improve interactivitySynchronised browsingWeb data retrievalUser managementManagement environment
There is disclosed a system for management of interactions between users and software applications in a web environment, related to an operating environment which functional devices are in charge of providing methods allowing maximum interactivity between the end user and the application. The operating environment also includes a set of applications available to end users, administrators and developers. The applications for end users are intended to provide interactivity, storage, data organization, publication and search. For the administrators, the applications allow full configuration of the behavior of the system and of the agents included within its scope. And for the developers, the system provides configuration kits that enable interfacing between the objects included in its operating context.
Owner:EMBRIA INFORMATICA
Systems and methods for webpage creation and updating
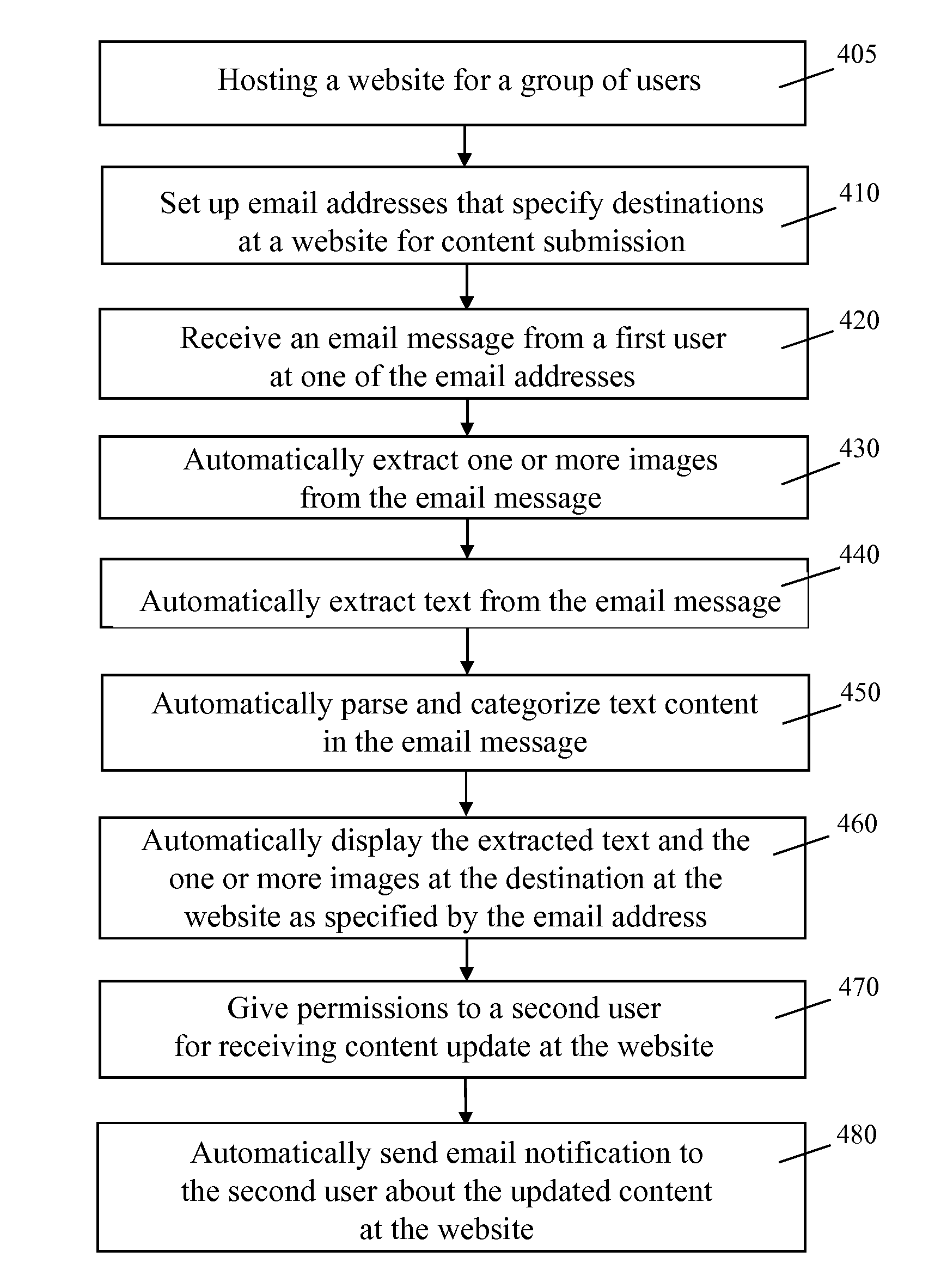
ActiveUS20140304622A1Effectively integrated with contentIncrease flexibilitySpecial service provision for substationSynchronised browsingWeb siteEmail address
A computer network system for posting content at a web site includes computer servers configured to host a web site for a group of users, and a data storage configured to store an email address in association with a destination at the website. The computer servers can receive an electronic message at the email address by the computer servers from a user. A computer processor can automatically extract content from the electronic message. The computer servers can automatically post the content extracted from the electronic message at the destination at the website.
Owner:SHUTTERFLY LLC
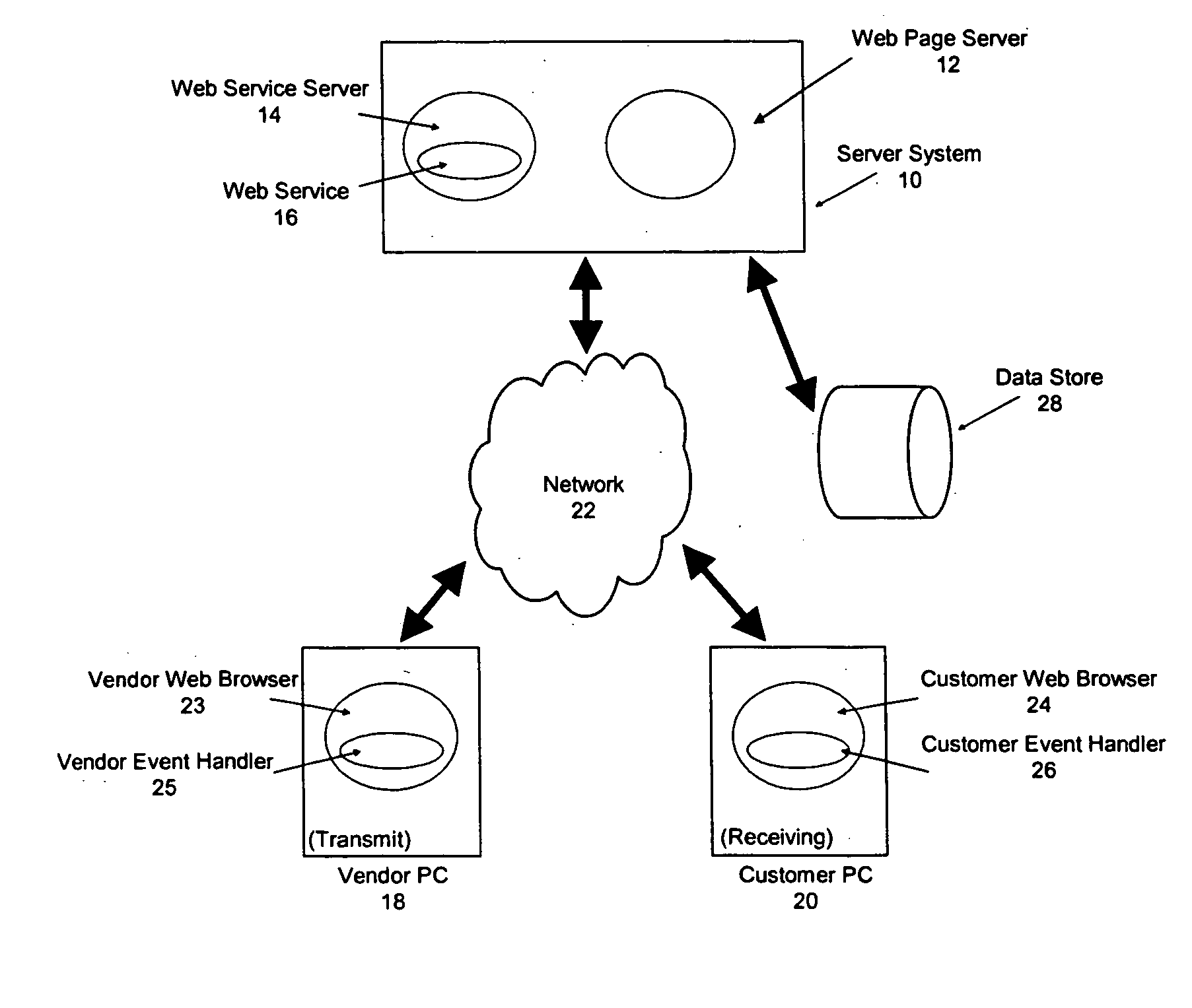
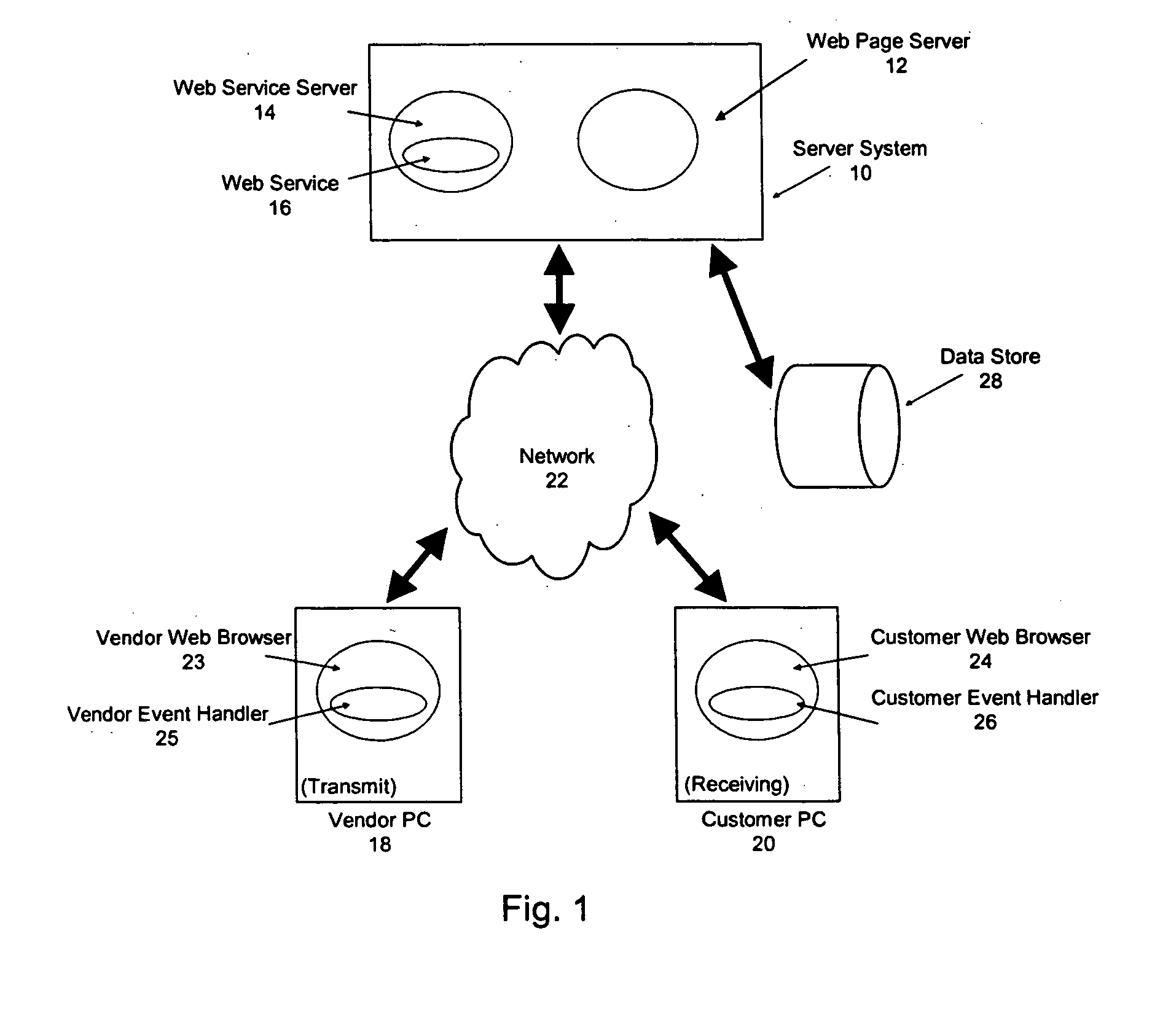
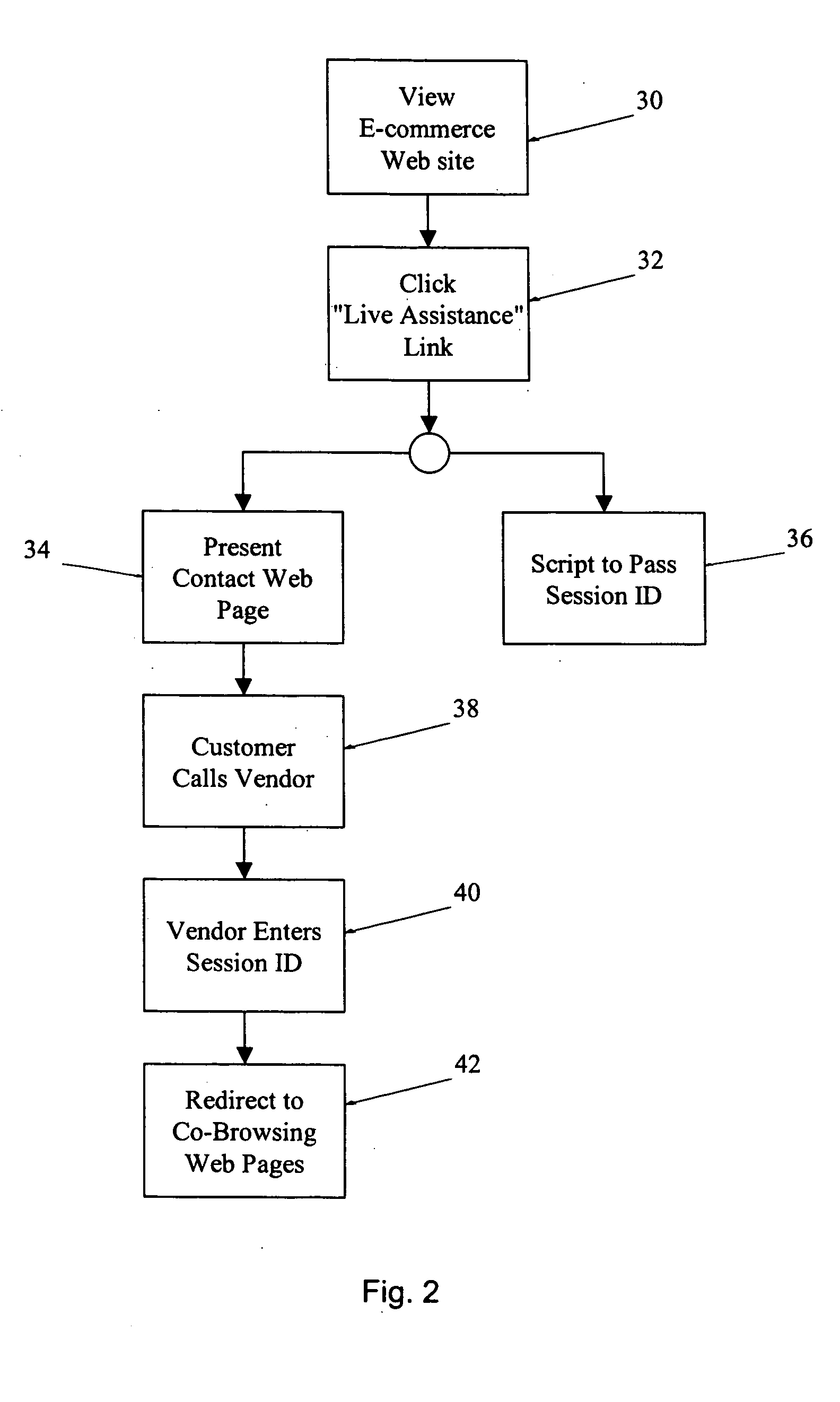
Apparatus and method for remotely sharing information and providing remote interactive assistance via a communications network
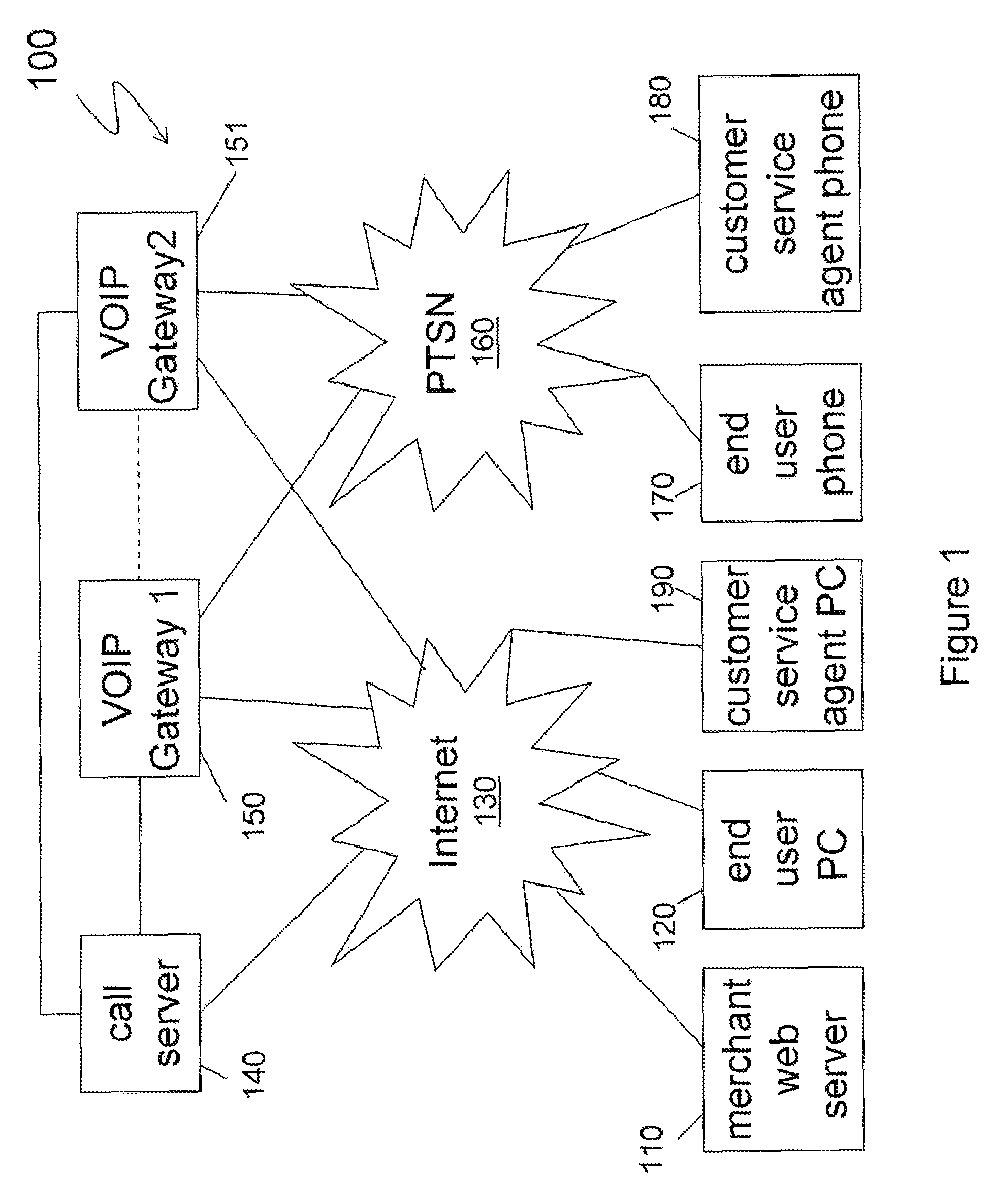
InactiveUS20050097159A1Easily initiate co-browsing sessionImprove scalabilitySynchronised browsingMultiprogramming arrangementsSoftwareWeb site
A system for providing collaborative browsing of information and interactive communications on the worldwide web. A customer may use the system for a co-browsing session with a customer assistance representative by simply providing an access number from an accessed web site to the customer service representative. The customer is transparently switched from a normal web site to a co-browsing web site merely by clicking on a button to request assistance. The co-browsing site includes software to periodically poll a server for synchronization purposes.
Owner:BENEFITS TECH
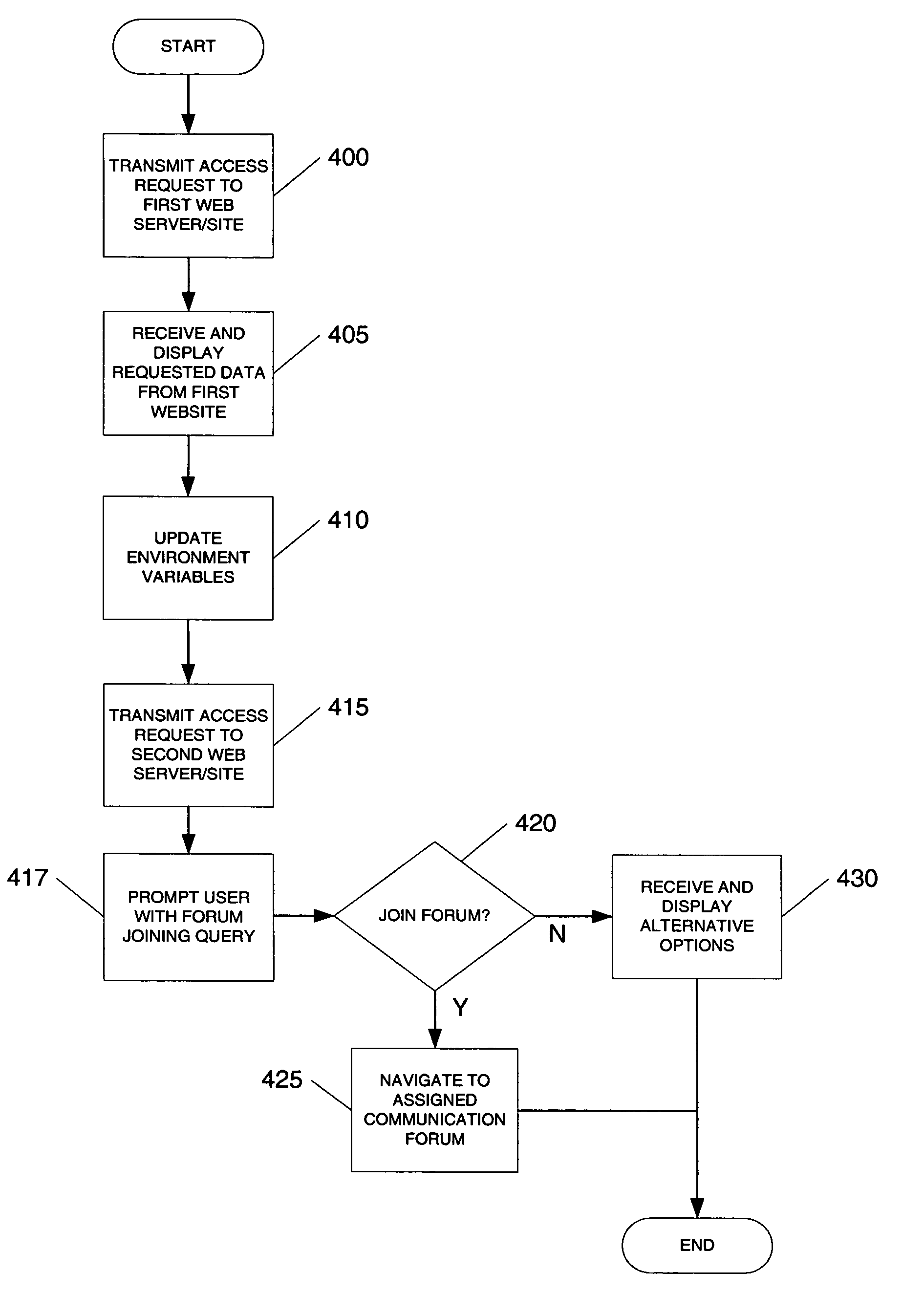
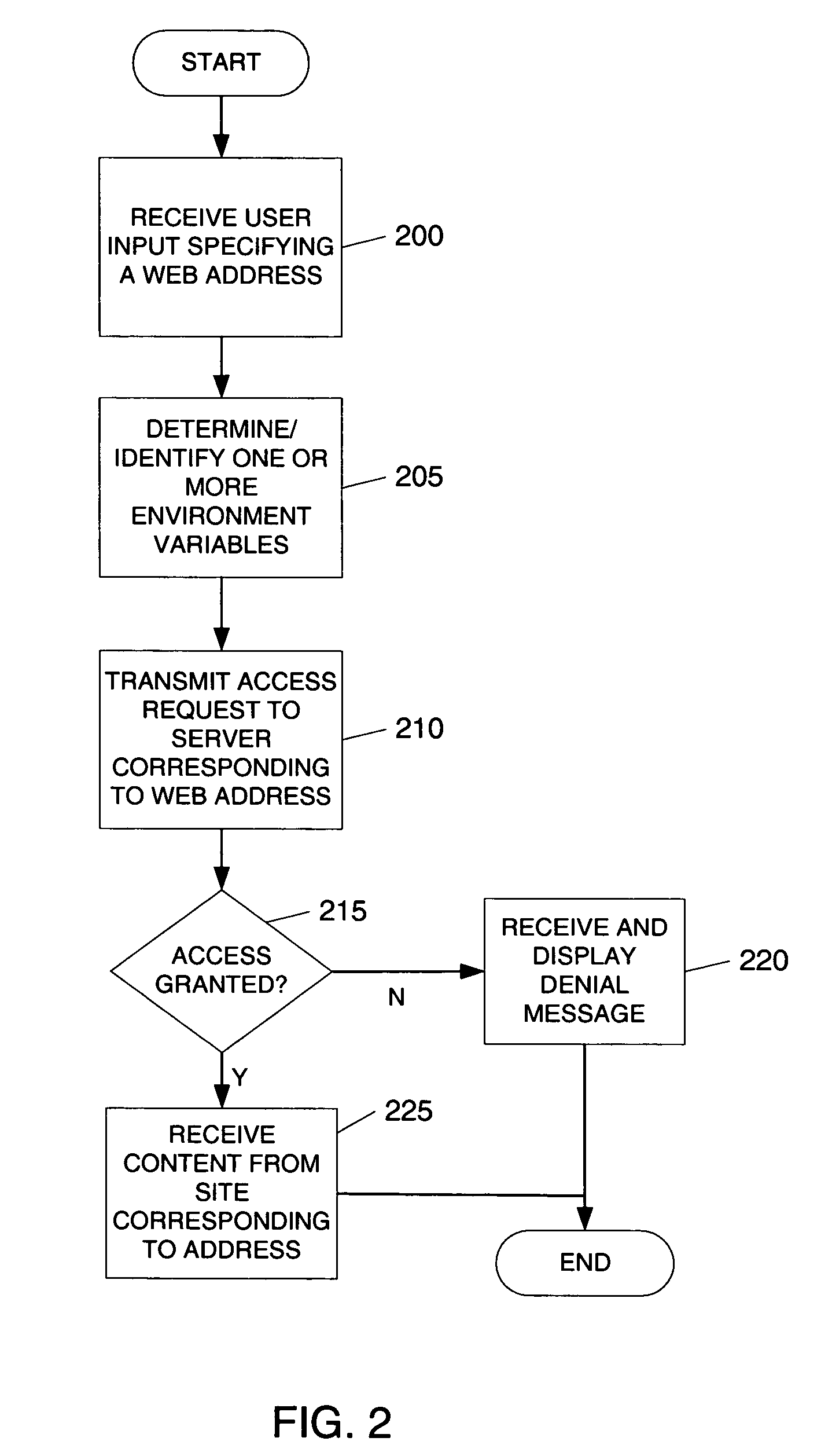
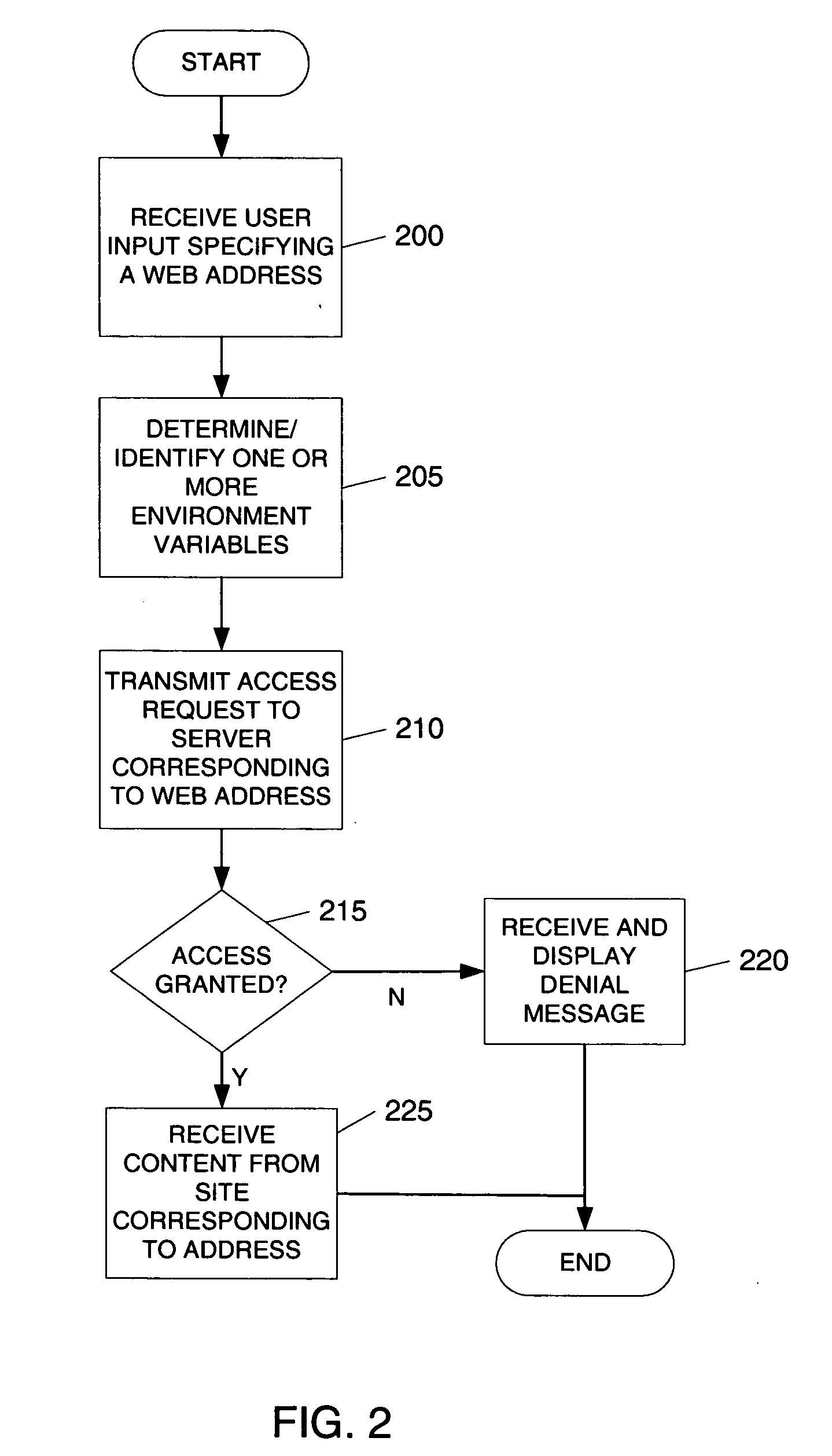
Facilitating interaction between web browsers
Users browsing the same website may join in a single communication forum by navigating to a predefined communication web server or website. Navigating to the predefined communication web server includes transmitting an access request to the web server. The access request includes various information including identification information associated with the referring website. Based on the identity of the referring website, the web server joins users into an appropriate communication forum. If a pre-existing communication forum corresponding to the referring website is unavailable, a new communication forum corresponding to the referring website may be created. The communication forum allows users viewing the same referring website to interact and communicate in a variety of ways.
Owner:GLOBAL INFORMATION SOLUTIONS
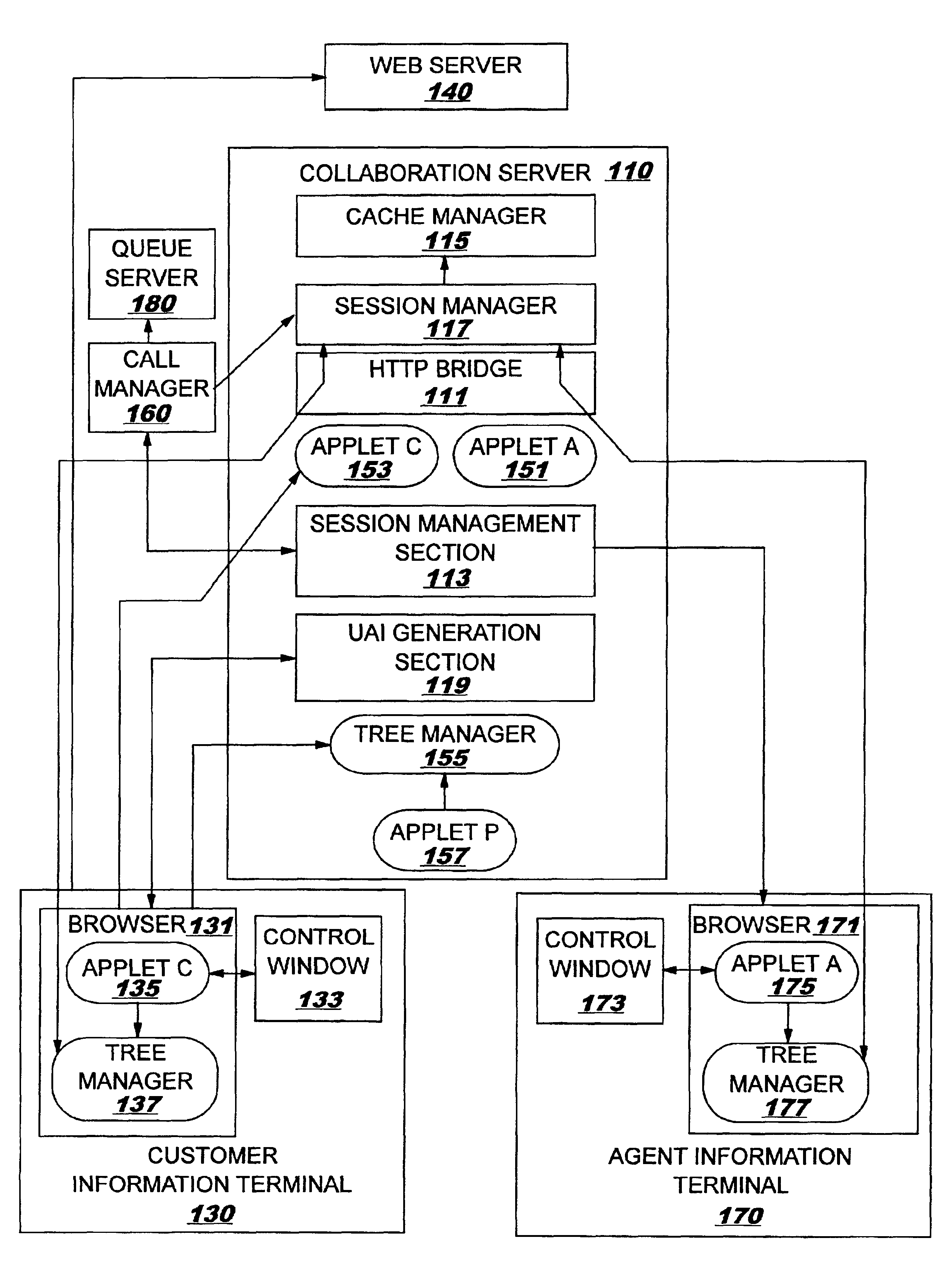
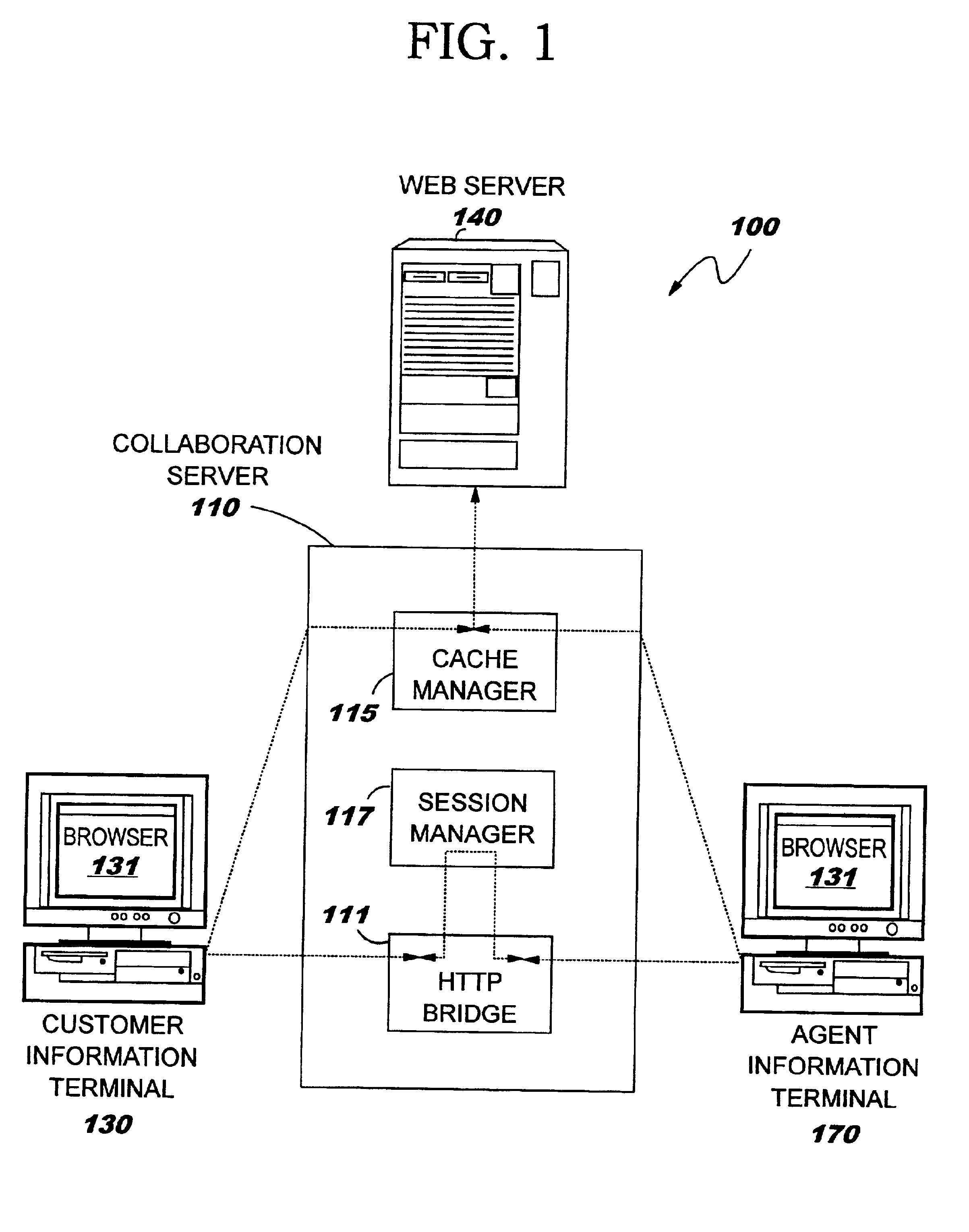
Method for acquiring content information, and software product, collaboration system and collaboration server for acquiring content information
InactiveUS6912573B2Reliable transmissionLow costSynchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb serviceClient-side
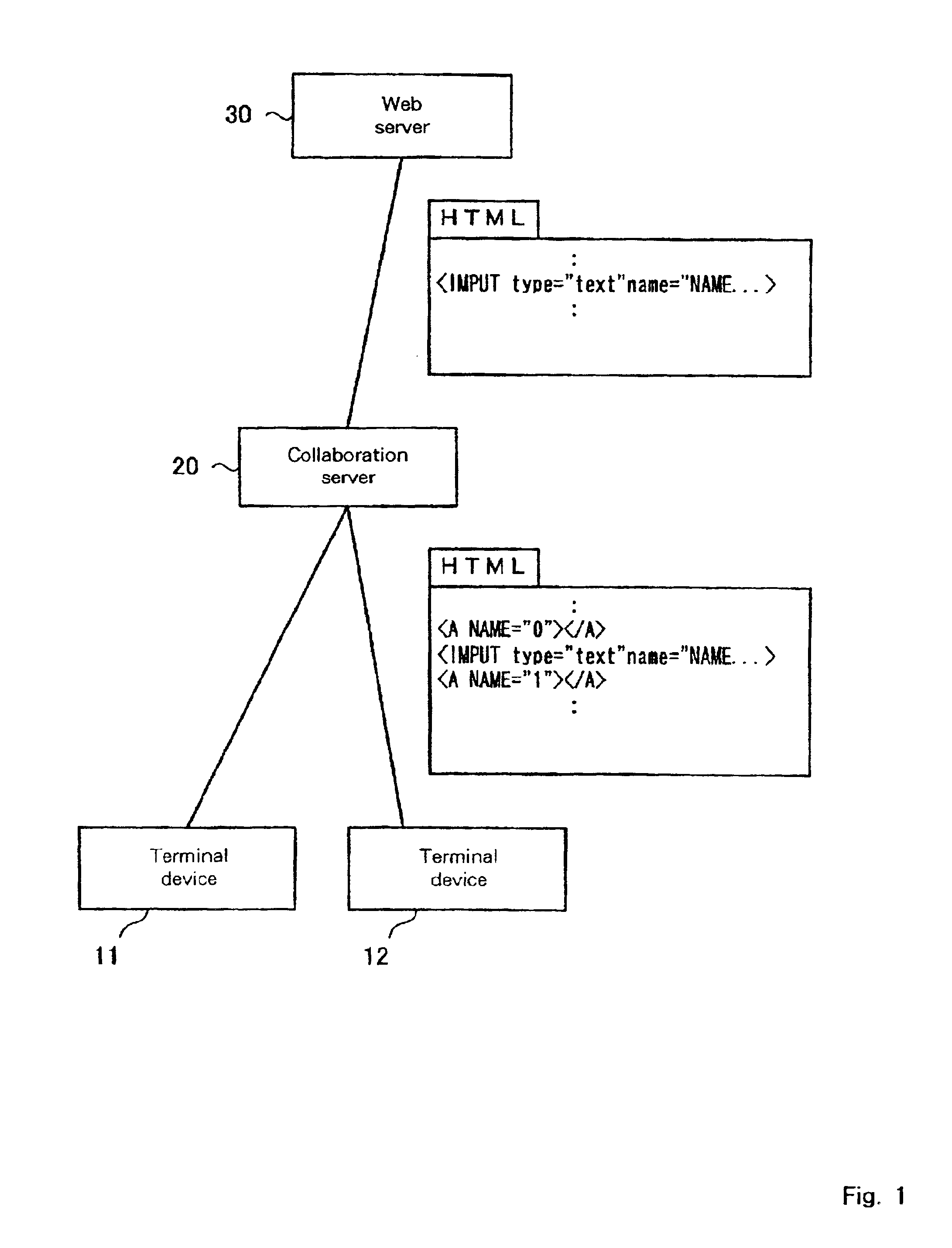
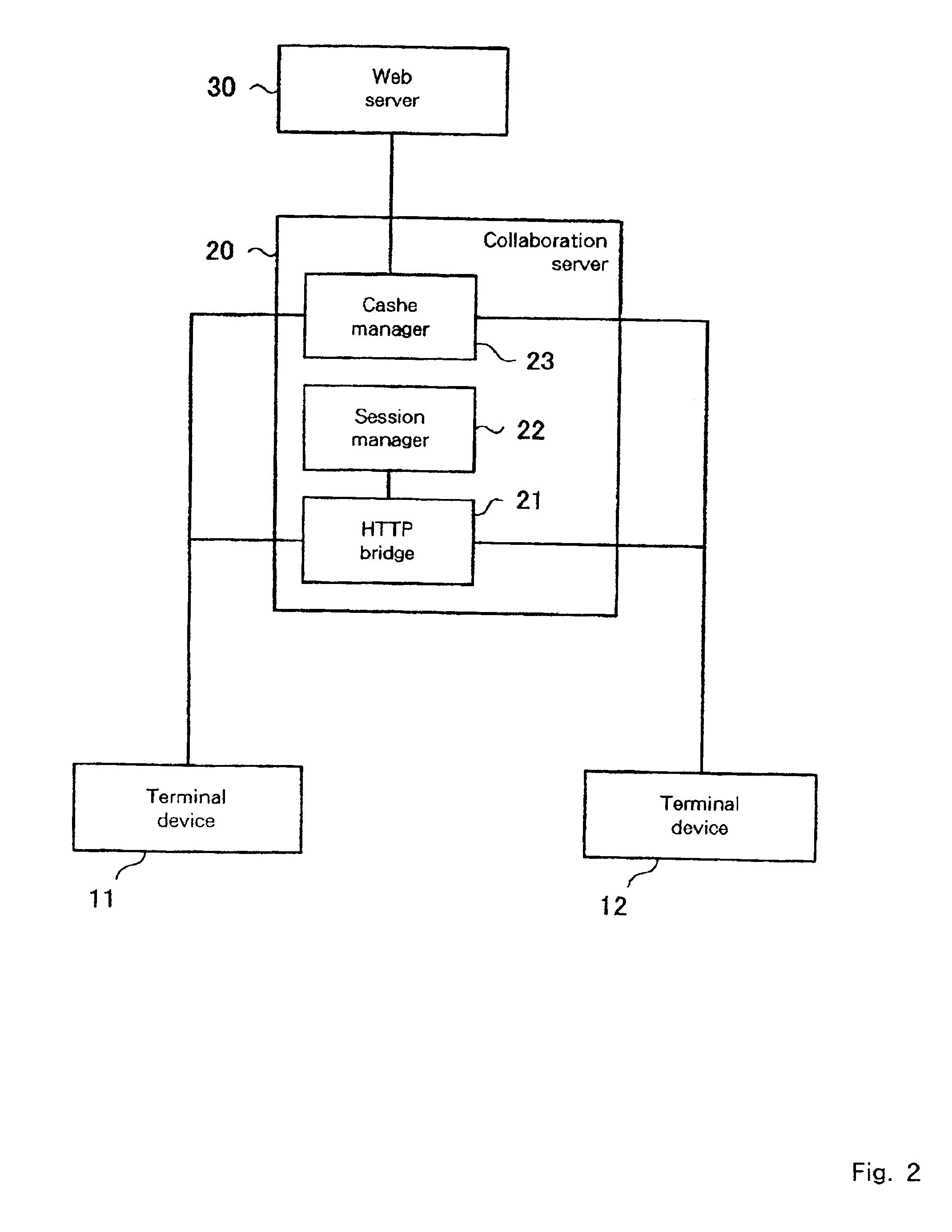
A customer browser and an agent browser are connected to each other through a collaboration server, and a Web server is controlled so as to be accessed through the collaboration server. When the browsers and refer to a page, the collaboration server embeds an applet for detecting a change in the page and a client controller for displaying a page corresponding to changed page information of the other party which performs collaboration. When the customer and agent browsers detect the change in the page, the applet is invoked, and the changed page information is sent to the other party via the collaboration server, and the client controller on the other party controls the browser so as to display the changed page.
Owner:IBM CORP
Web collaboration through synchronization
InactiveUS6938212B2Synchronised browsingCathode-ray tube indicatorsInformation processingWeb browser
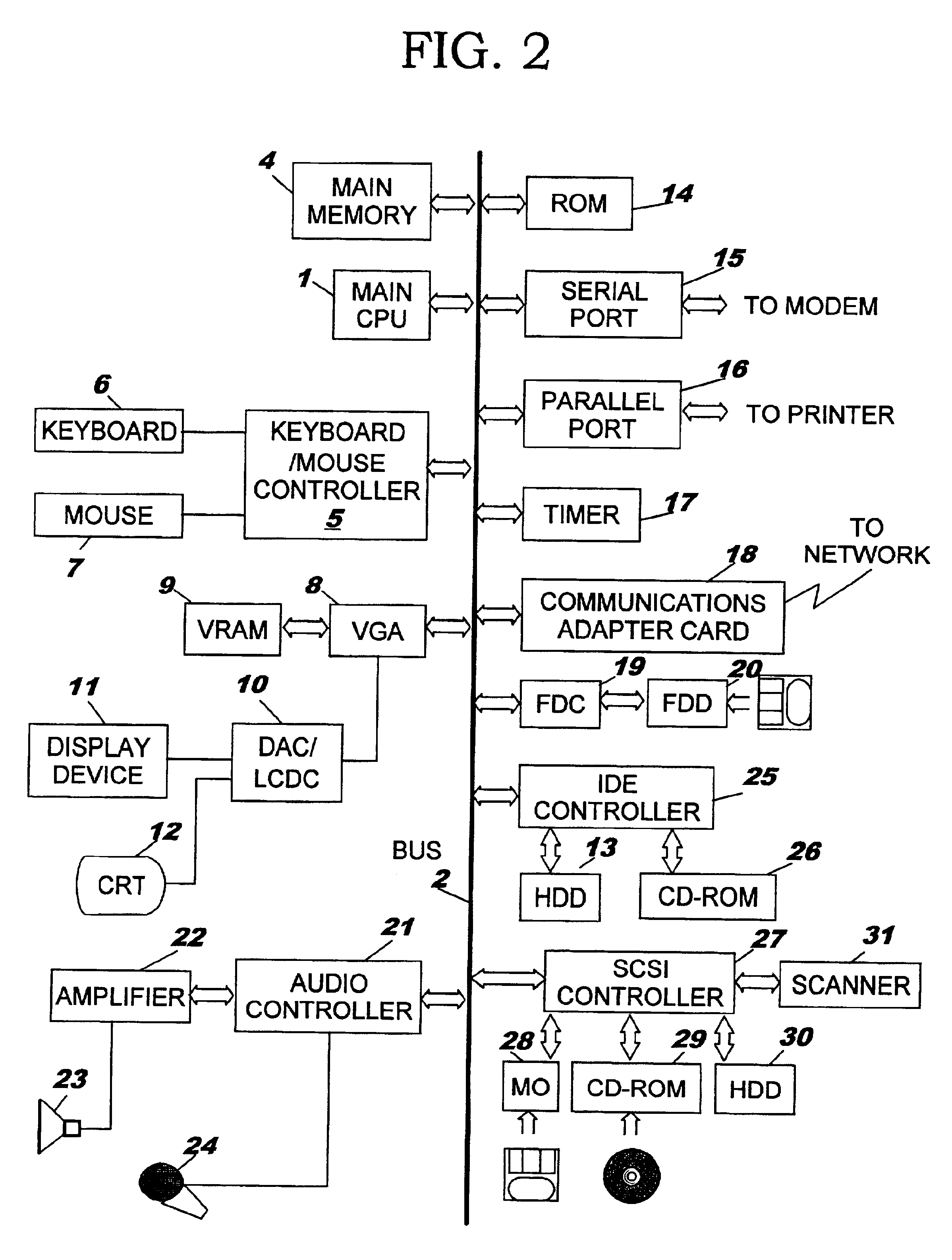
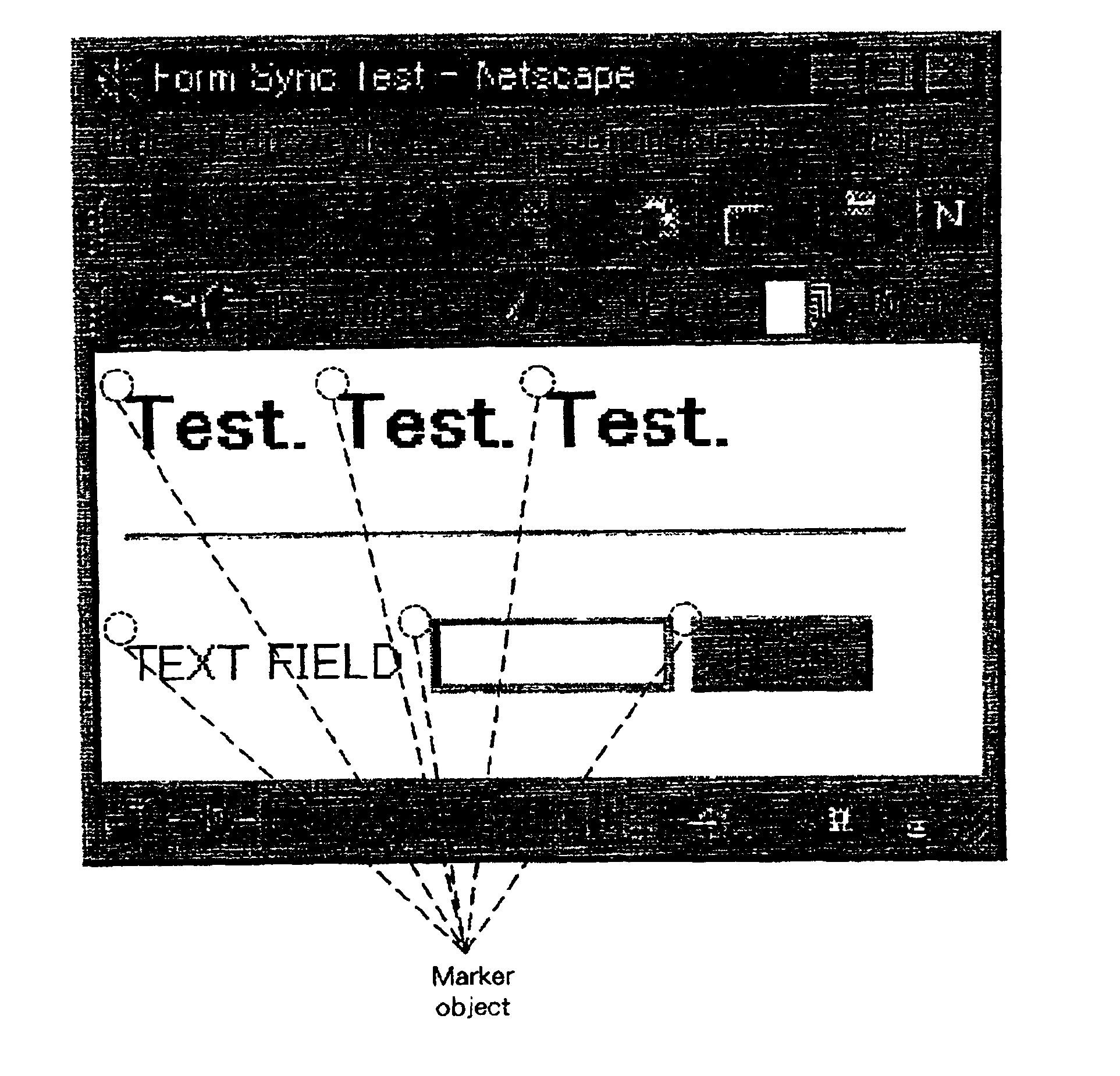
The present invention provides a collaboration technique for synchronizing display scrolling and the locations of remote pointers in the windows of web browsers, independent of the types and the setups of the web browsers. An example embodiment of an information processing system comprises: a collaboration server to be connected to a web server, and a plurality of terminals, for obtaining web content from the collaboration server and for performing a cooperative operation. Terminal devices includes a web browser for displaying web content, and obtains identification information for an object selected as a synchronization reference among objects in the web content, and transmits the information to the other terminal, with which it performs a cooperative operation. The terminal employs the identification information for a predetermined object that it receives, calculates the location of the pertinent object, and controls the web browser in accordance with the location of the object.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for webpage creation and updating
ActiveUS20110219087A1Solve conflictsEffectively integrated with contentSynchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsEmail addressData memory
A computer network system for posting content at a web site includes computer servers configured to host a web site for a group of users, and a data storage configured to store an email address in association with a destination at the website. The computer servers can receive an email message at the email address by the computer servers from a user. A computer processor can automatically extract content from the email message. The computer servers can automatically post the content extracted from the email message at the destination at the website.
Owner:SHUTTERFLY LLC
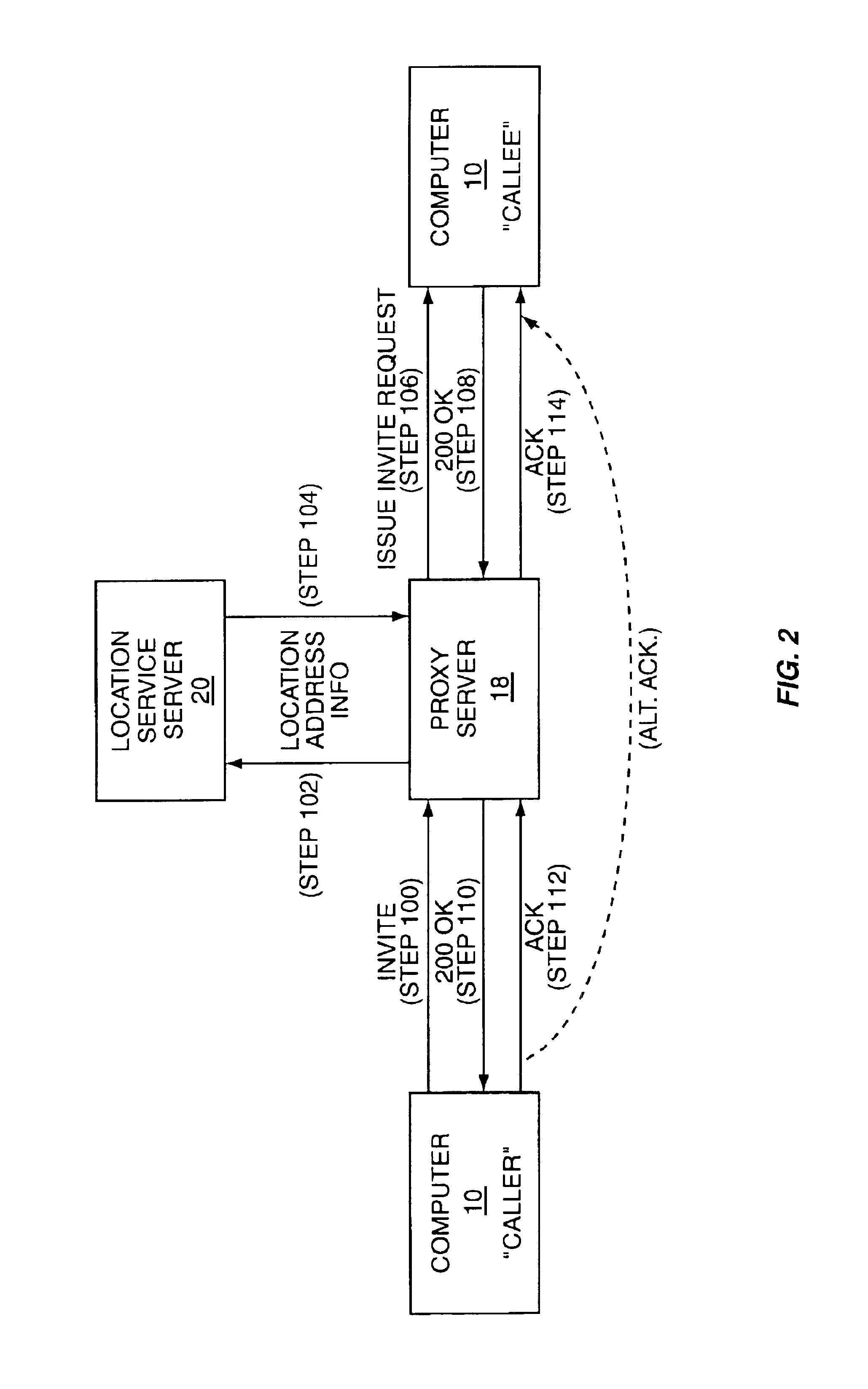
Automated web browser synchronization by using session initiation protocol during a real-time session
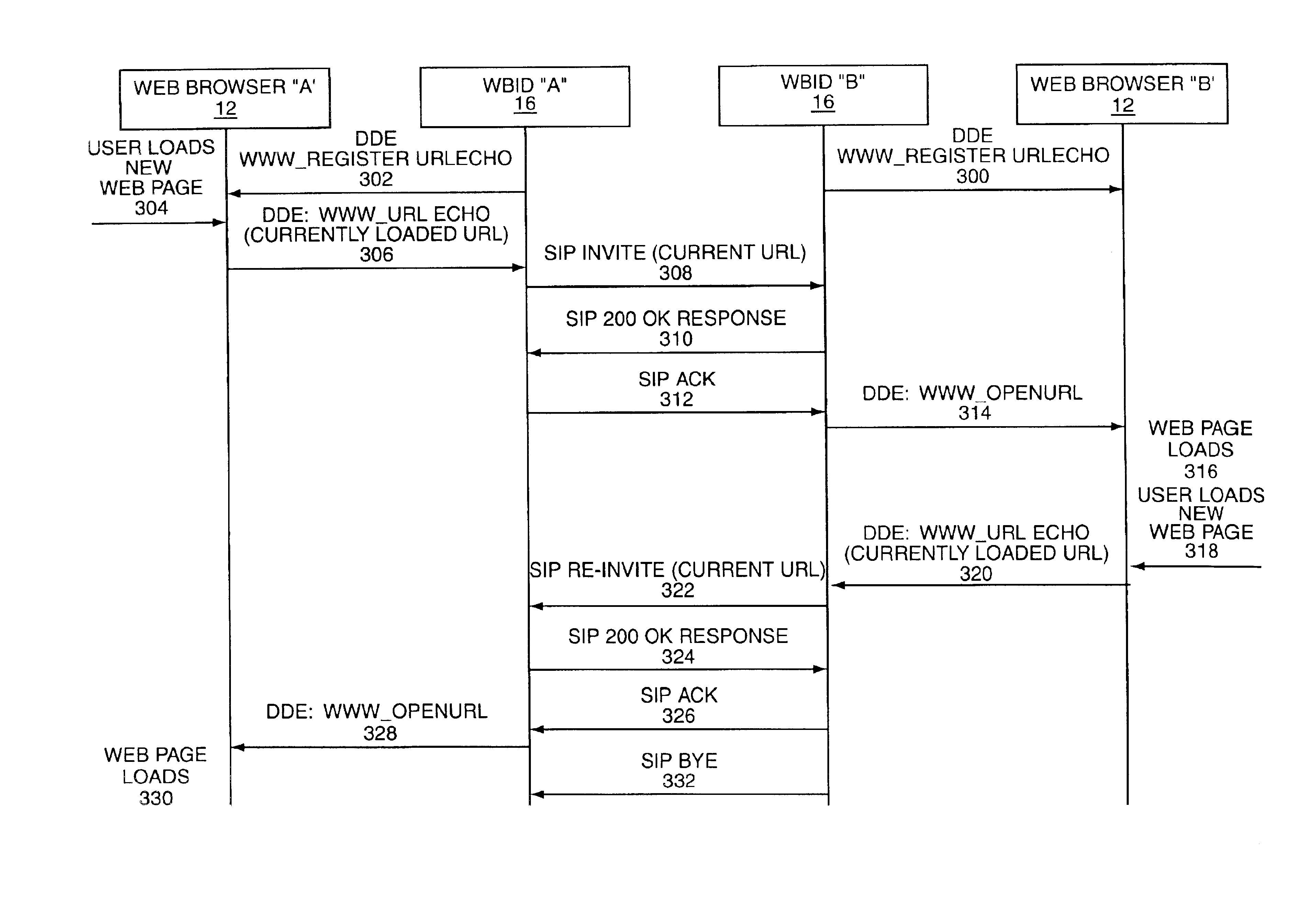
InactiveUS6976094B1Facilitate communicationEasy to transportSynchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsSession Initiation ProtocolWeb browser
The present invention allows synchronization of web browsers to eliminate the need for users to convey uniform resource locators (URLs) or like location indicia. The invention operates with a local user's browser to identify the URL for a newly loaded web page and transmit this newly loaded URL to a remote user's computer for loading on the remote user's browser. Further, the invention also provides for receiving URLs associated with web pages loaded onto the remote user's browser and loading the web pages on the local user's browser using the received URLs.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
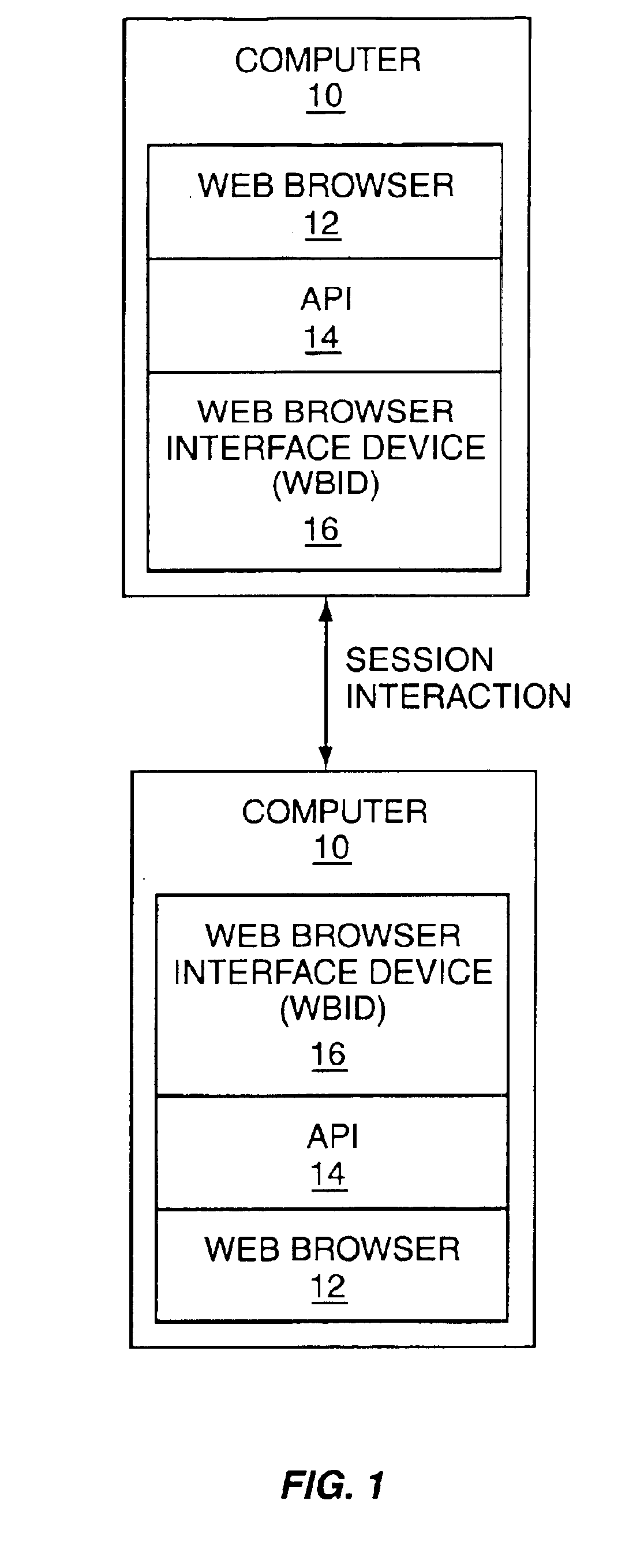
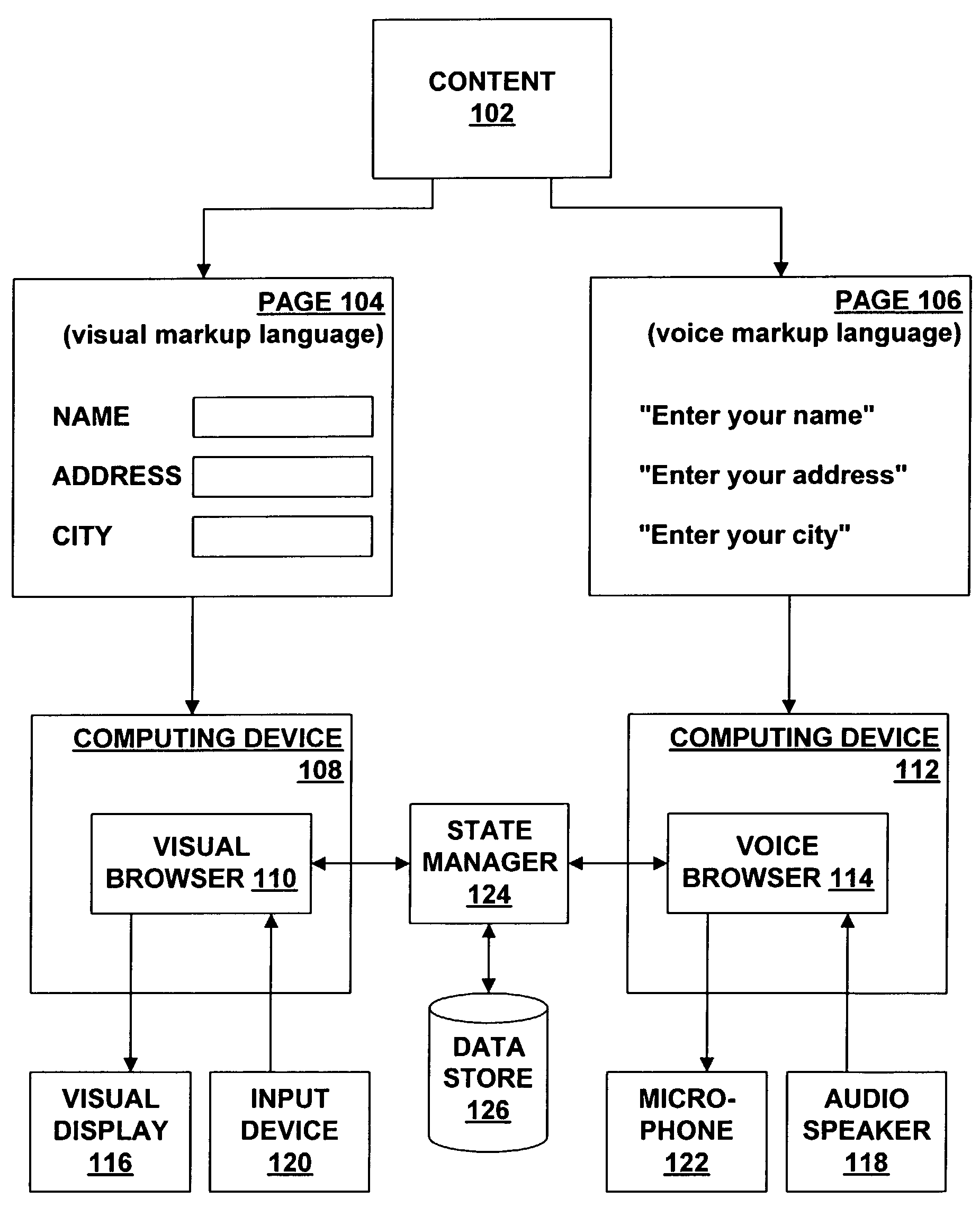
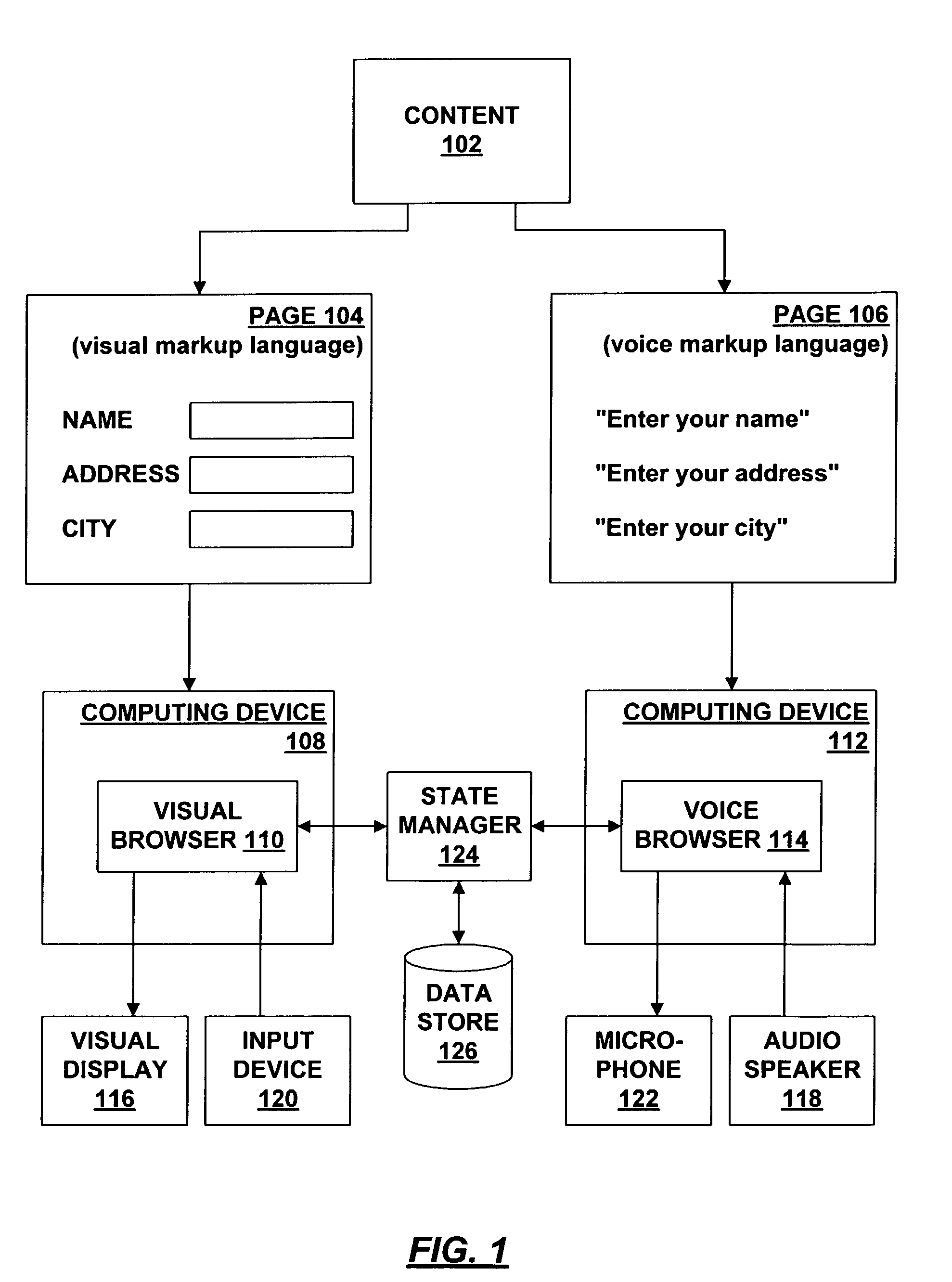
Synchronization among plural browsers
A technique for synchronizing a visual browser and a voice browser. A visual browser is used to navigate through visual content, such as WML pages. During the navigation, the visual browser creates a historical record of events that have occurred during the navigation. The voice browser uses this historical record to navigate the content in the same manner as occurred on the visual browser, thereby synchronizing to a state equivalent to that of the visual browser. The creation of the historical record may be performed by using a script to trap events, where the script contains code that records the trapped events. The synchronization technique may be used with a multi-modal application that permits the mode of input / output (I / O) to be changed between visual and voice browsers. When the mode is changed from visual to voice, the record of events captured by the visual browser is provided to the voice browser, thereby allowing the I / O mode to change seamlessly from visual to voice. Likewise, the voice browser captures events which may be provided to the visual browser when the I / O mode is changed from voice to visual.
Owner:GULA CONSULTING LLC
System and method for record and playback of collaborative web browsing session
InactiveUS20040054728A1Cost effectiveSynchronised browsingWeb data retrievalNetwork connectionWorld Wide Web
A collaborative Web browsing session may take place over a network, allowing the presenter on a first computer to direct the audio and visual components of a browser on one or more second computers. The second computer is instructed to log into a control site that downloads an active control, such as an applet, to the second computer. The present invention allows a collaborative Web browsing session ("session"), as created by the presenter and witnesses by one or more users on second computers, to be recorded and archived by the control site. When a user of a computer is connected to the control site through a communication network such as the World Wide Web, that user may log into the control site and request to view an archived session. The session will then be replayed by the control site on the user's computer, directing the audio and visual components of the browser on the user's computer as if the user was attending the live session. The recorded session replays the events of the live session in real time such that they playback experience contains the same audio and visual events that took place when the session was originally being recorded.
Owner:RED HAT
Group-browsing system
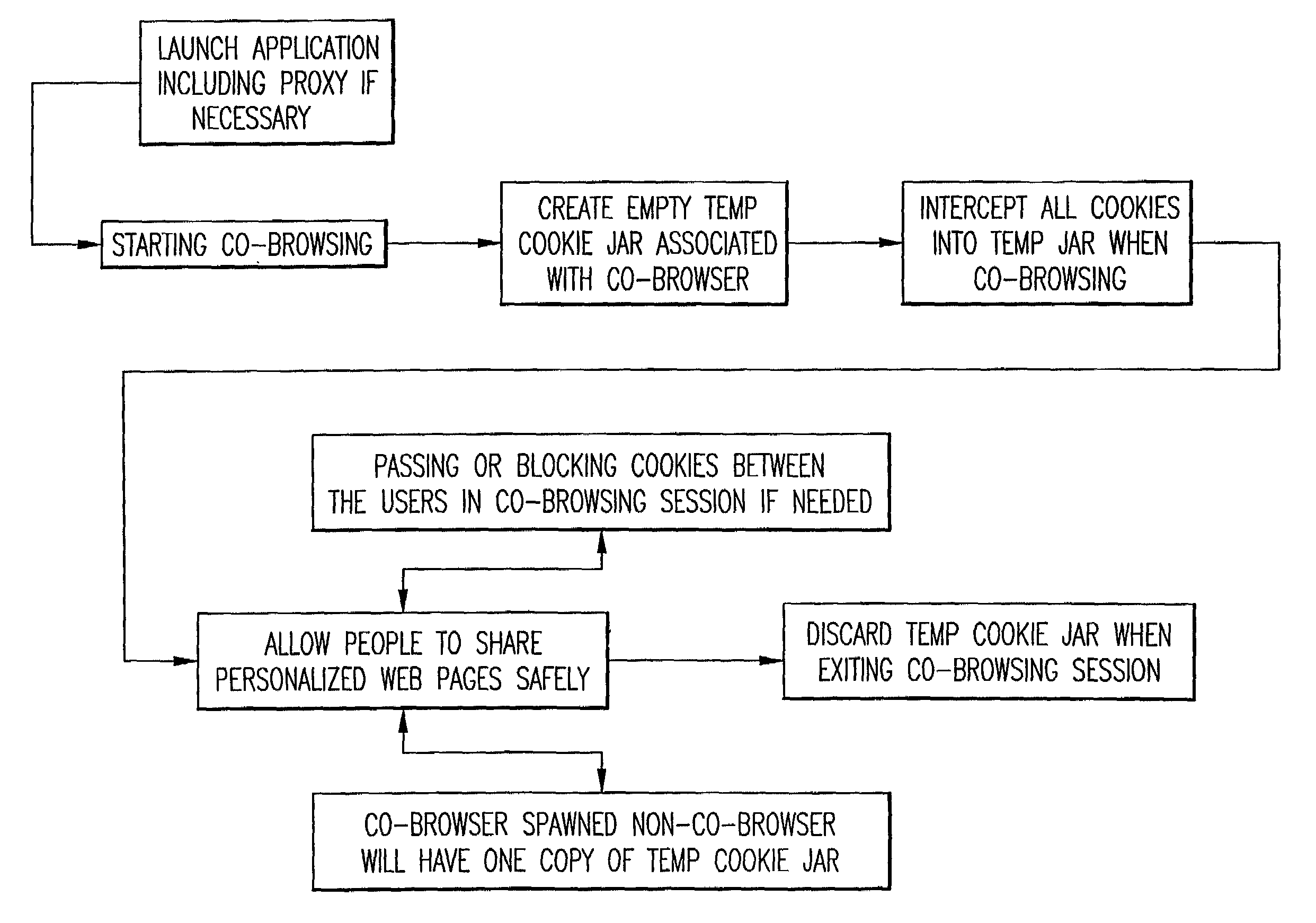
InactiveUS20060129642A1Synchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideWeb page
A group-browsing system for a plurality of clients each including a shared web browser. A server is linked to the shared web browser of each client and is configured to monitor the transmission of the web site URL request from the shared web browser of one client of the group and to direct the request to the shared web browser of other clients in the group. A gatekeeper module is configured to first mask the identity of each client's computer on the shared browser. This prevents the web site from retrieving any client's actual identifier. Second, the gatekeeper is also configured to create a same temporary identifier for each client when any client logs on to the web site so that the same web page is displayed for all the clients in the group.
Owner:NET2PHONE
Facilitating interaction between web browsers
ActiveUS20070288563A1Easy accessSynchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsWeb siteWeb browser
Users browsing the same website may join in a single communication forum by navigating to a predefined communication web server or website. Navigating to the predefined communication web server includes transmitting an access request to the web server. The access request includes various information including identification information associated with the referring website. Based on the identity of the referring website, the web server joins users into an appropriate communication forum. If a pre-existing communication forum corresponding to the referring website is unavailable, a new communication forum corresponding to the referring website may be created. The communication forum allows users viewing the same referring website to interact and communicate in a variety of ways.
Owner:GLOBAL INFORMATION SOLUTIONS
System for enabling multiple clients to interact together over a network with a secure web page
A group-browsing system for a plurality of clients each including a shared web browser. A server is linked to the shared web browser of each client and is configured to monitor the transmission of the web site URL request from the shared web browser of one client of the group and to direct the request to the shared web browser of other clients in the group. A gatekeeper module is configured to first mask the identity of each client's computer on the shared browser. This prevents the web site from retrieving any client's actual identifier. Second, the gatekeeper is also configured to create a same temporary identifier for each client when any client logs on to the web site so that the same web page is displayed for all the clients in the group.
Owner:NET2PHONE
Web site cobrowsing
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Collaborative browsing
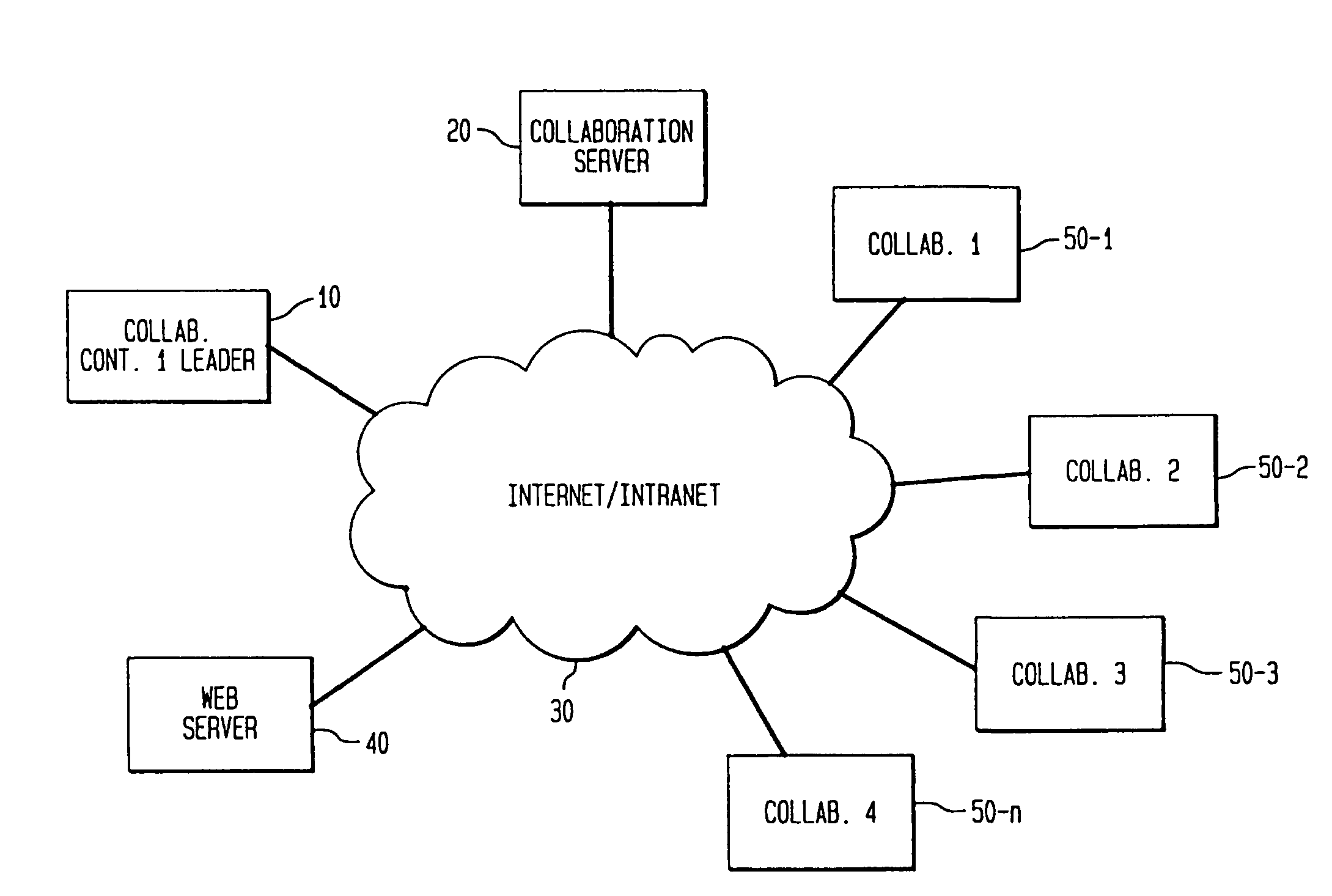
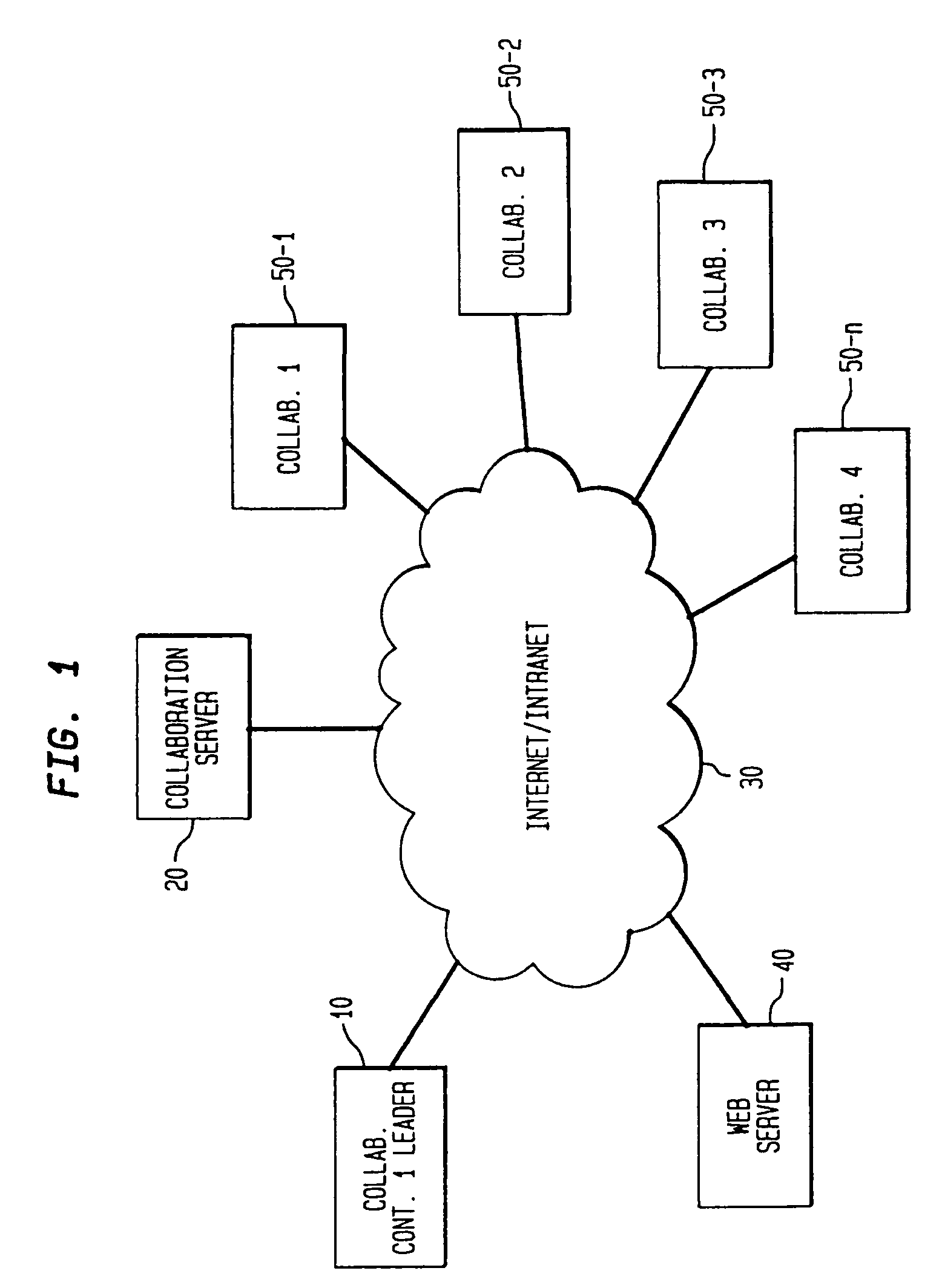
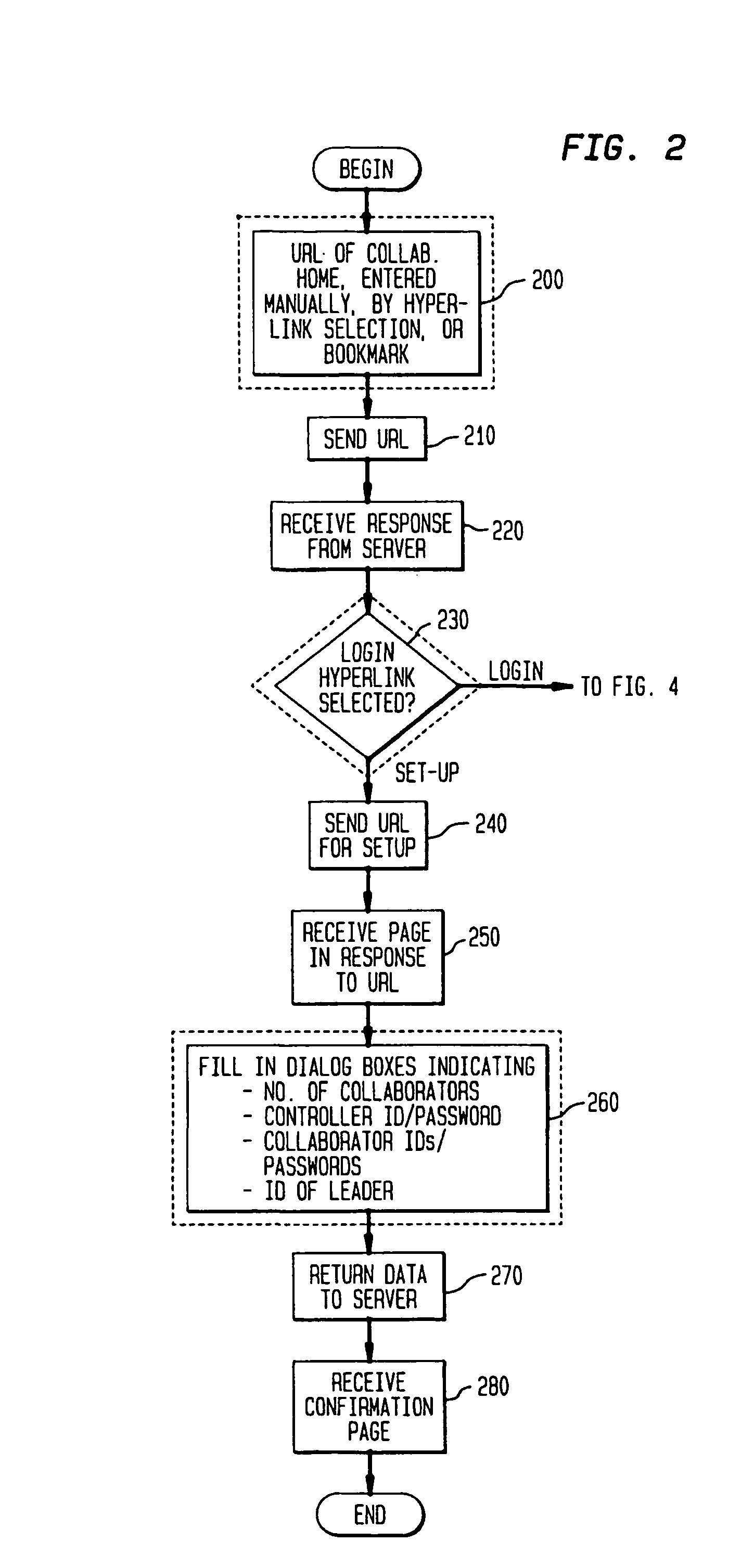
The present invention is directed to a technique for collaborative browsing among users at two or more different PCs. In an illustrative system in accordance with the present invention, copies of selected URLs are shared among collaborating PCs, each of which uses the URL to retrieve the corresponding document. In this system, a PC is configured to select hyperlinks for itself and one or more other PCs. Each URL corresponding to a selected hyperlink is communicated via the Internet (using standard Internet protocols) to a server. The server broadcasts the URL to the collaborating PCs each of which retrieves the corresponding document in conventional fashion. The server knows the IP addresses of the collaborating PCs through a collaboration set-up process which occurs in advance of the actual collaborative browsing session.
Owner:KNAPP INVESTMENT
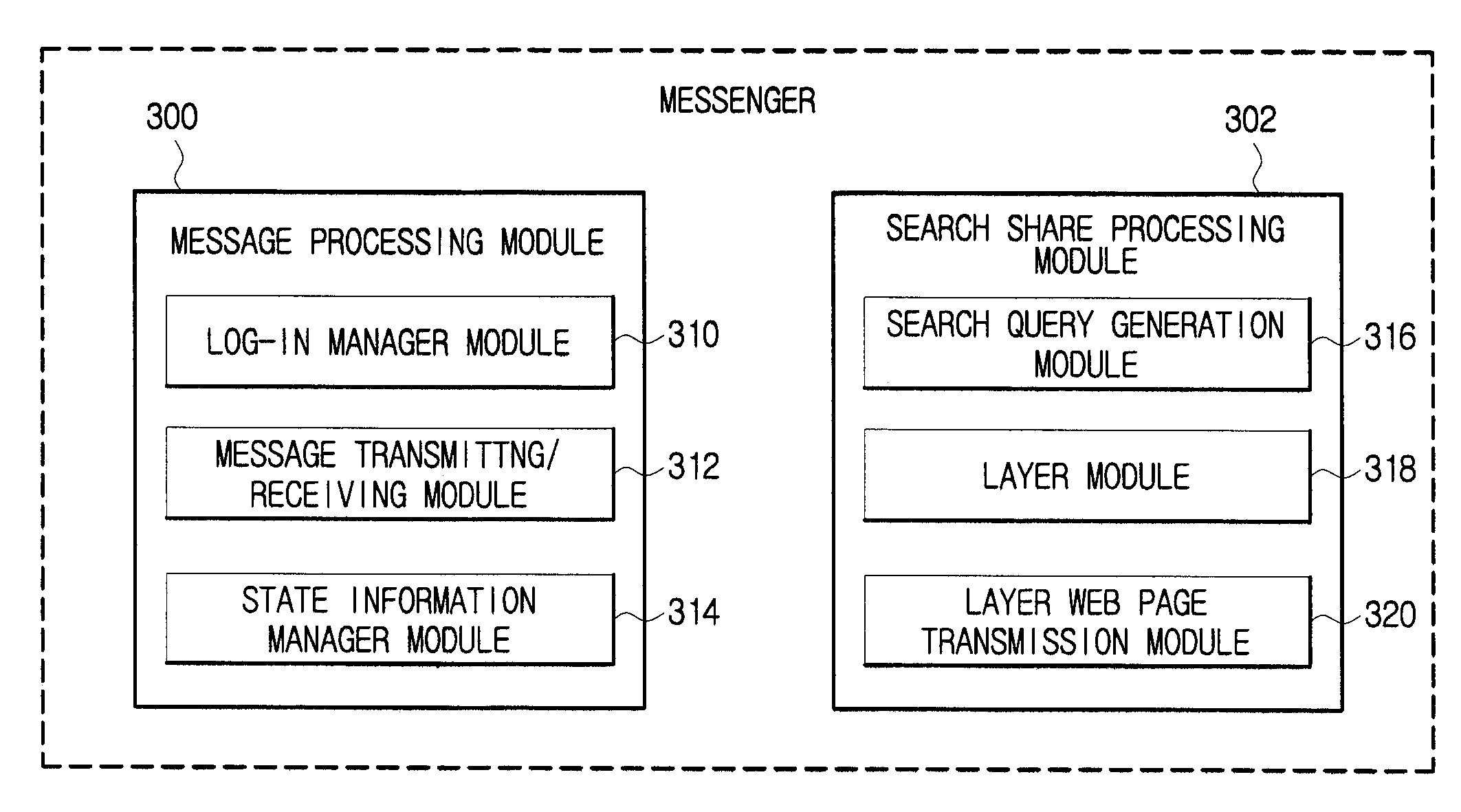
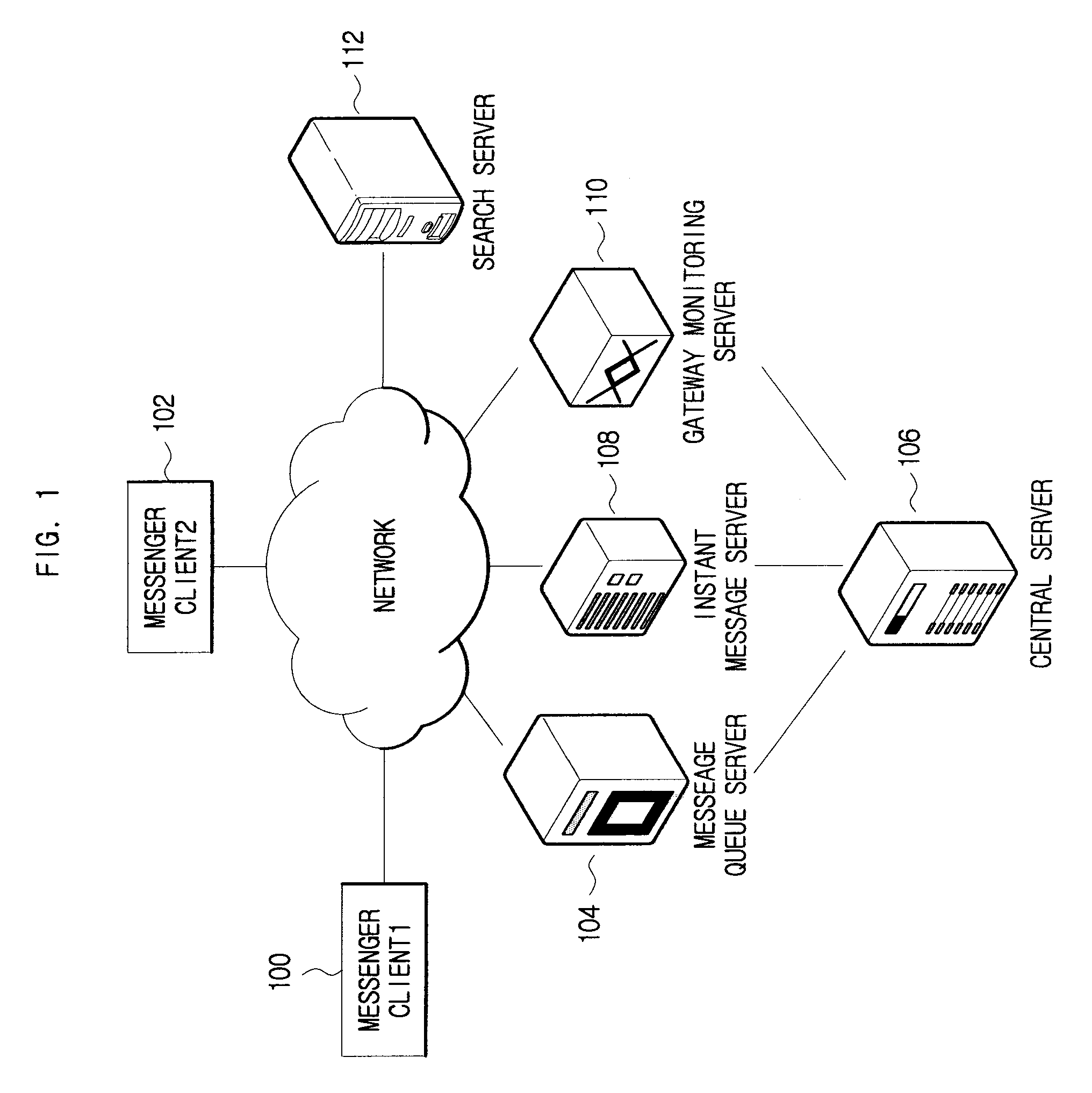
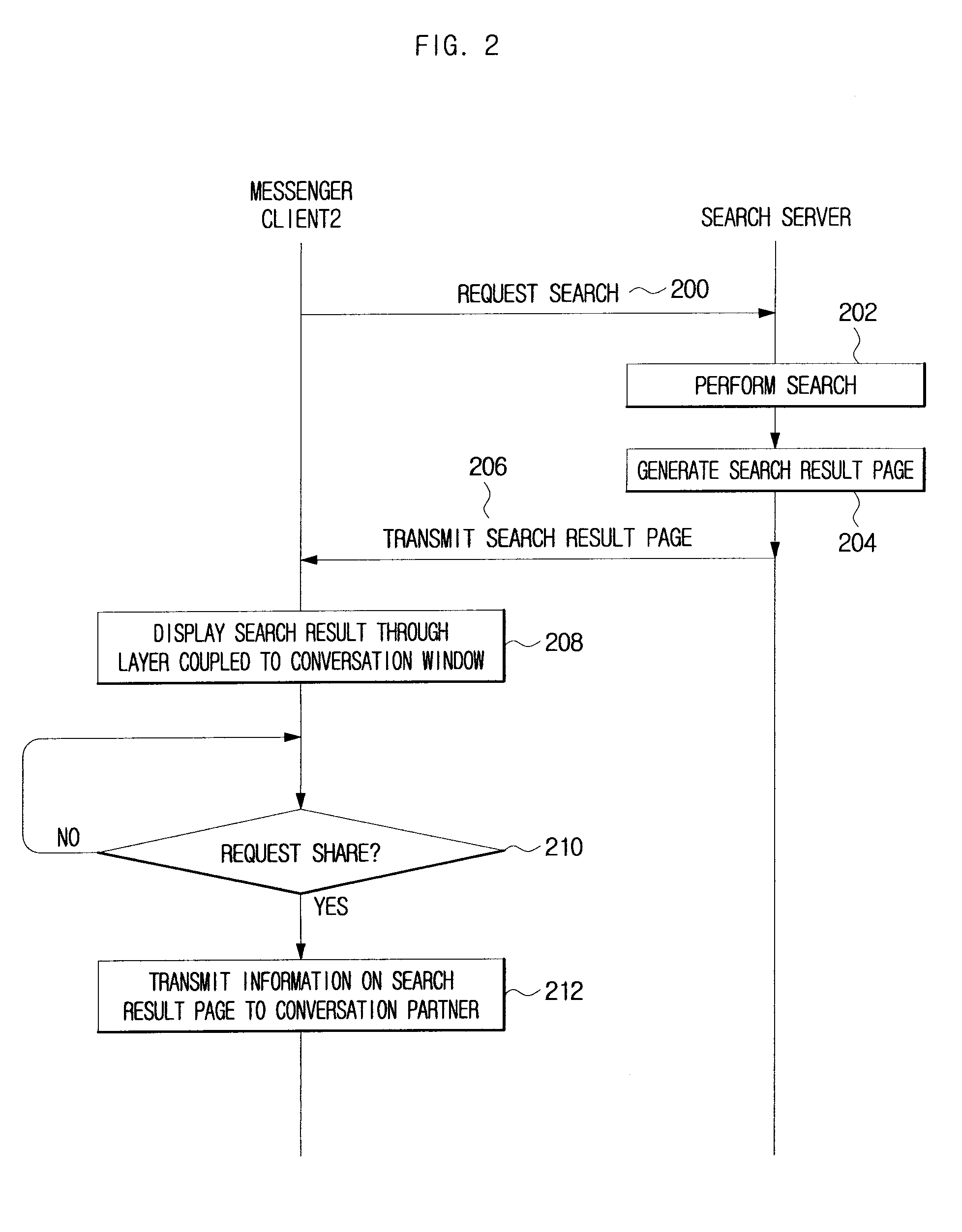
System And Method For Sharing Search Result Using Messenger
ActiveUS20080140779A1Easy to shareSynchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideWeb page
Disclose is a method and system for sharing search result using messenger. A messenger client generates search request information and receives web page data corresponding to the search request information. A search server receives the search request information from the messenger client and performs a search for one or more keywords included in the search request information to transmit search result page data to the messenger client. When the search result page is transmitted from the search server, a layer coupled to a conversation window is formed to display the search result page and allow users to share the information on web page corresponding to the search results when requested.
Owner:NHN CORP
Method and system for collaborative web browsing
ActiveUS7401294B2Improve experienceSynchronised browsingWeb data navigationDocumentation procedureWeb browser
A Web browser is augmented with collaborative features to support community aware browsing sessions. The augmentation provided includes a data mining plug-in for the browser to establish collaborative context based on Uniform Resource Locator (URL) meta data keywords, or mined topics, and a collaboration co-browser (explorer bar) which displays a collaboration space, called CollabSpace, corresponding to the document that is displayed in the main browser. With this augmented browser, a user can perform various collaboration functions from the collaboration explorer bar, including viewing the online status of members of the CollabSpace, communicate with members of the CollabSpace via electronic mail (e-mail), instant messaging or discussion threads, and register as a member of the CollabSpace. CollabSpaces can be established and associated with one or more Web documents, meta data keywords or topics.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for web page co-browsing
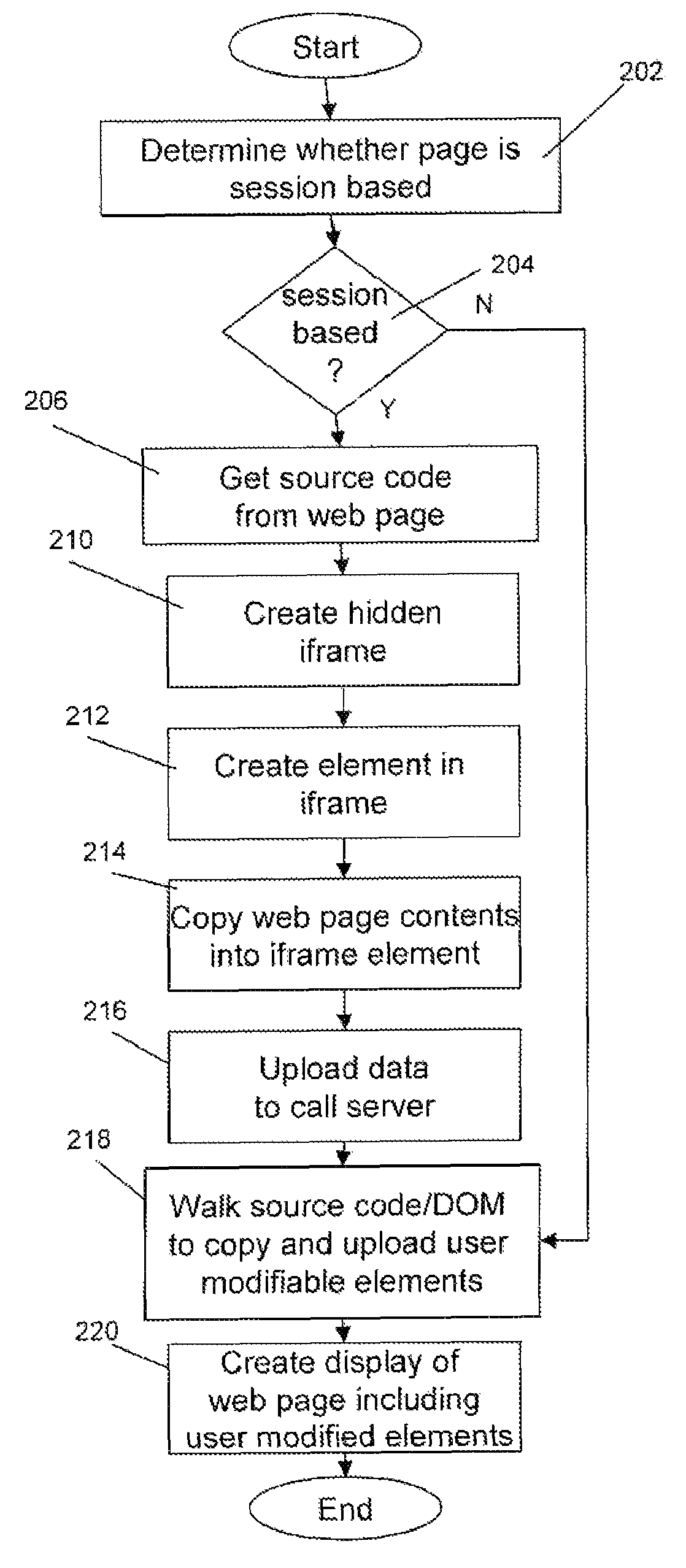
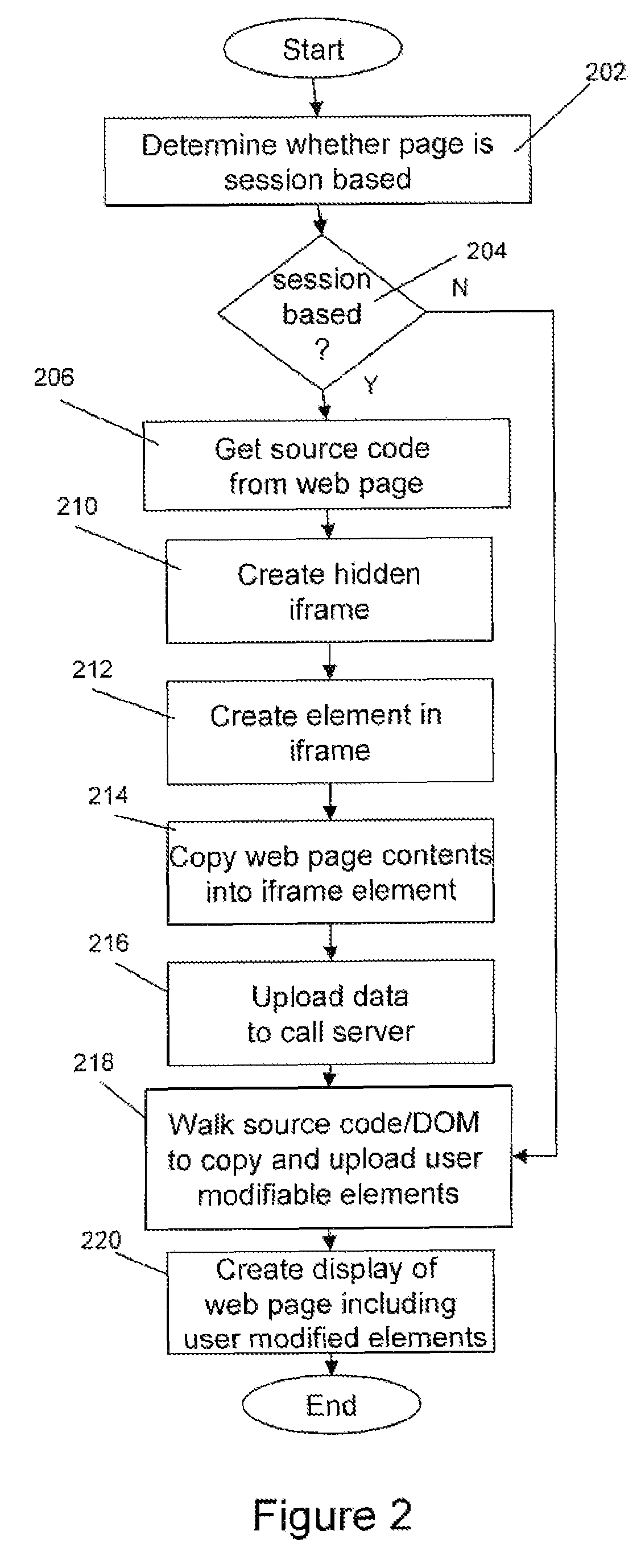
A method and apparatus for extracting information from a web page on a standard end user browser without plug-ins, includes the steps of dynamically creating an element on a web page being viewed by an end user, copying at least a portion of the contents of the web page or form field values, and uploading the data to a target domain, wherein the target domain may be different from the domain of the web page. In co-browsing applications, the data uploaded is used to create a copy of the website for display to a third party.
Owner:ORACLE OTC SUBSIDIARY
Selective sharing for collaborative application usage
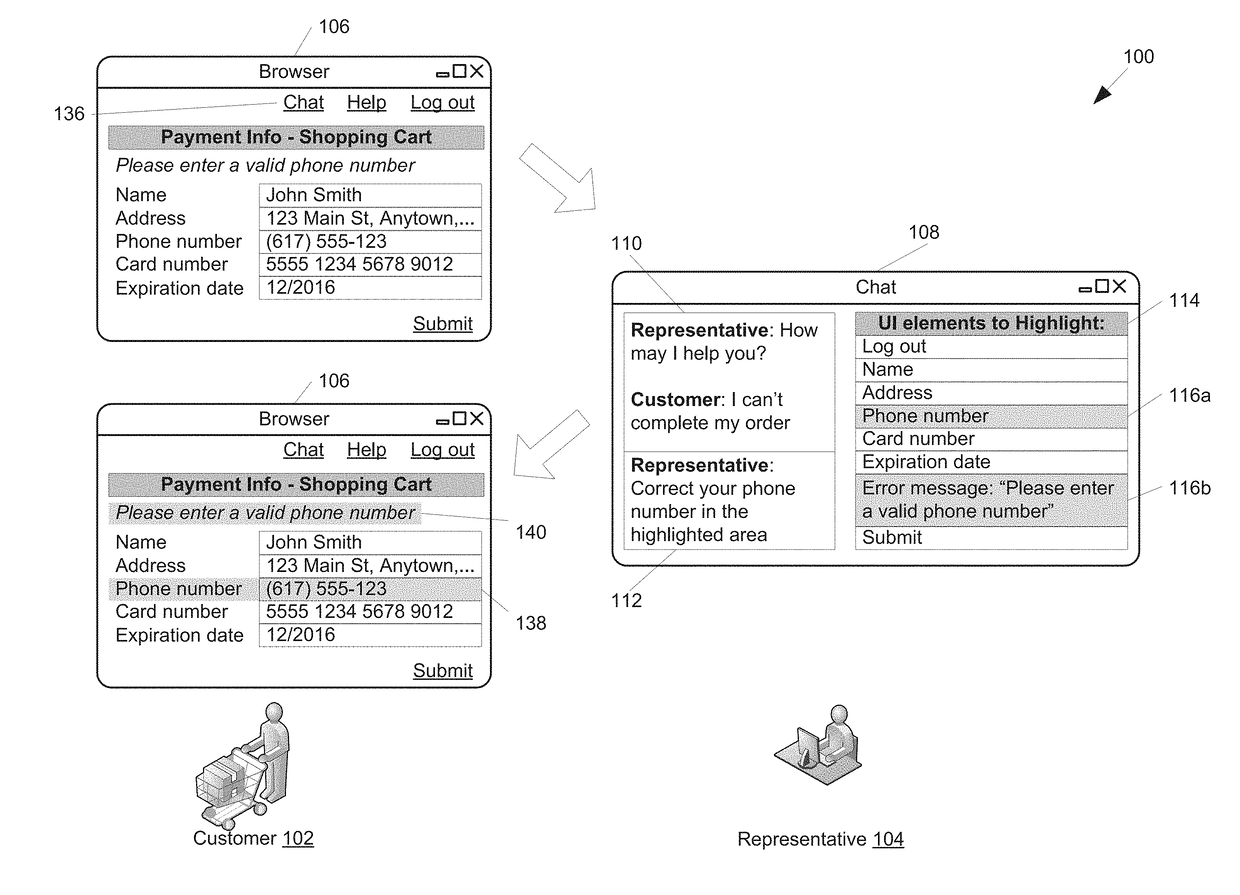
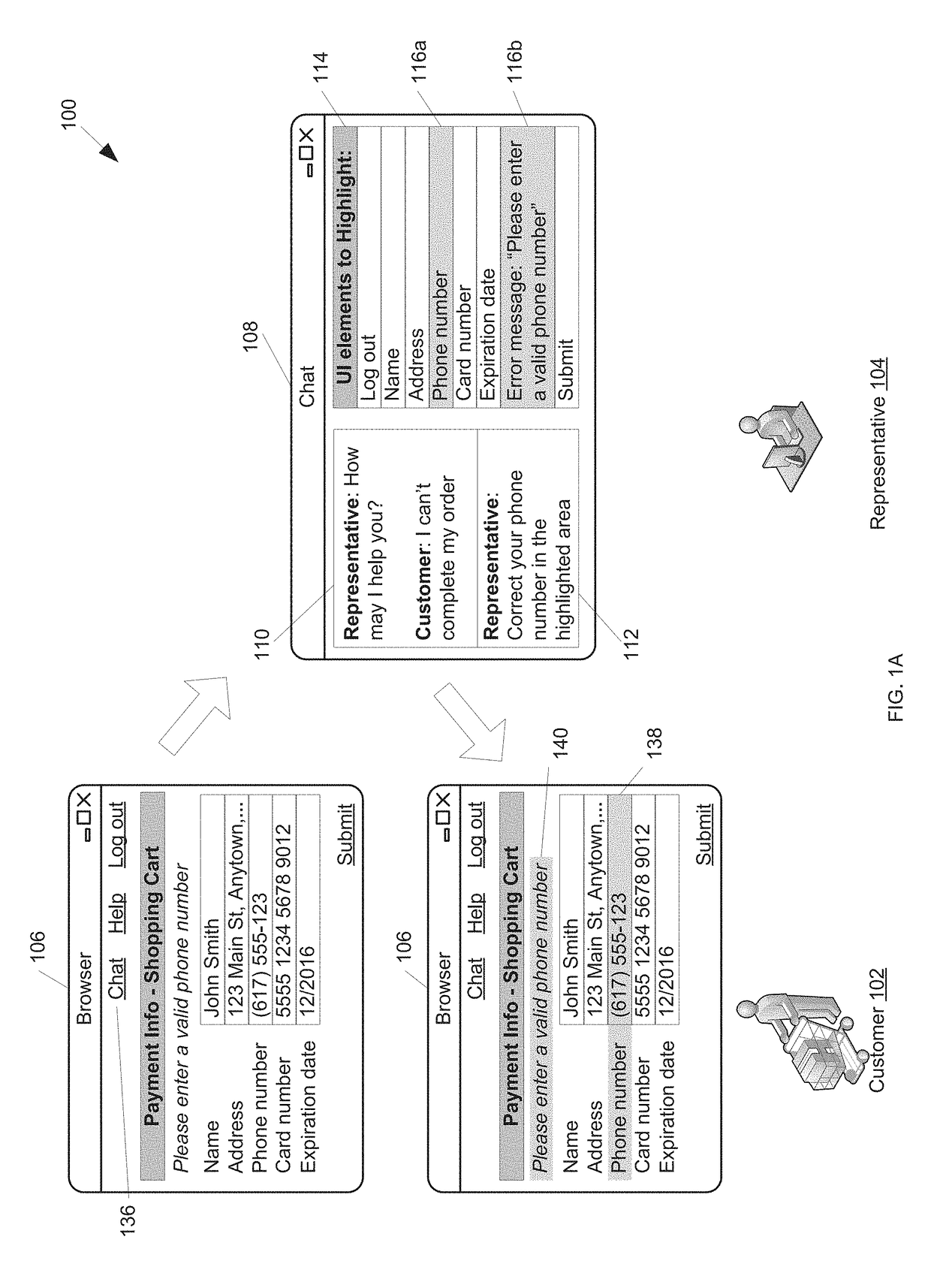
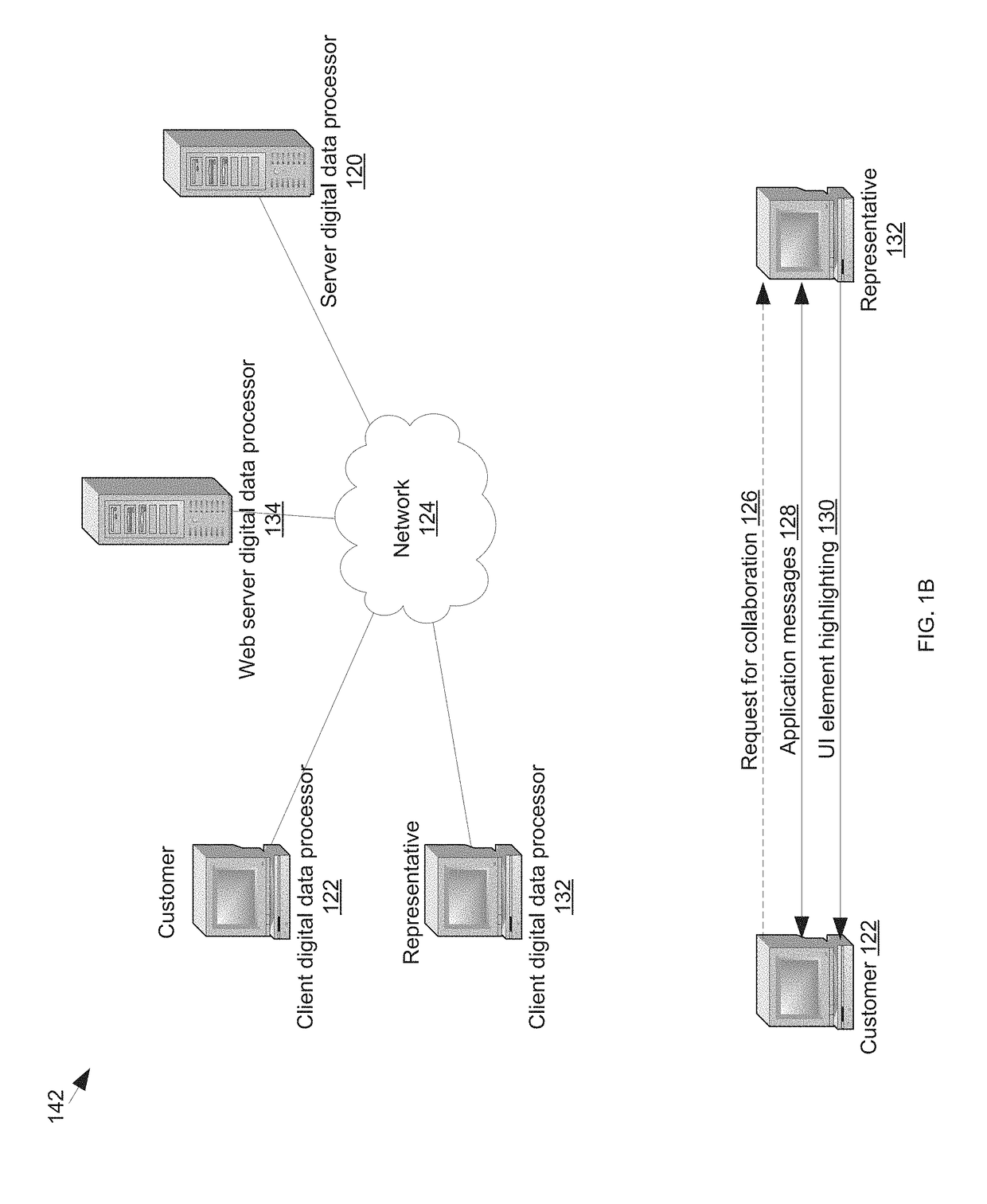
ActiveUS20180011678A1Facilitate remote highlightingSynchronised browsingNatural language data processingDigital dataData treatment
The present disclosure describes systems, methods, computer-readable media, and apparatuses for selective sharing during collaborative application usage. The selective sharing system is configured for selectively sharing UI elements in a UI running on a first digital data processor. The system includes a server digital data processor configured to receive, from the first digital data processor, a collection of UI elements. The collection of UI elements may be identified based on at least one of: on one or more markup attributes corresponding to the UI elements, a content position of the UI elements, a UI definition, historical data about the UI running on the first digital data processor, and historical data about a UI running on a second digital data processor. The server digital data processor is configured to transmit, to the second digital data processor, the collection of UI elements.
Owner:PEGASYSTEMS
Method and system of collaborative browsing
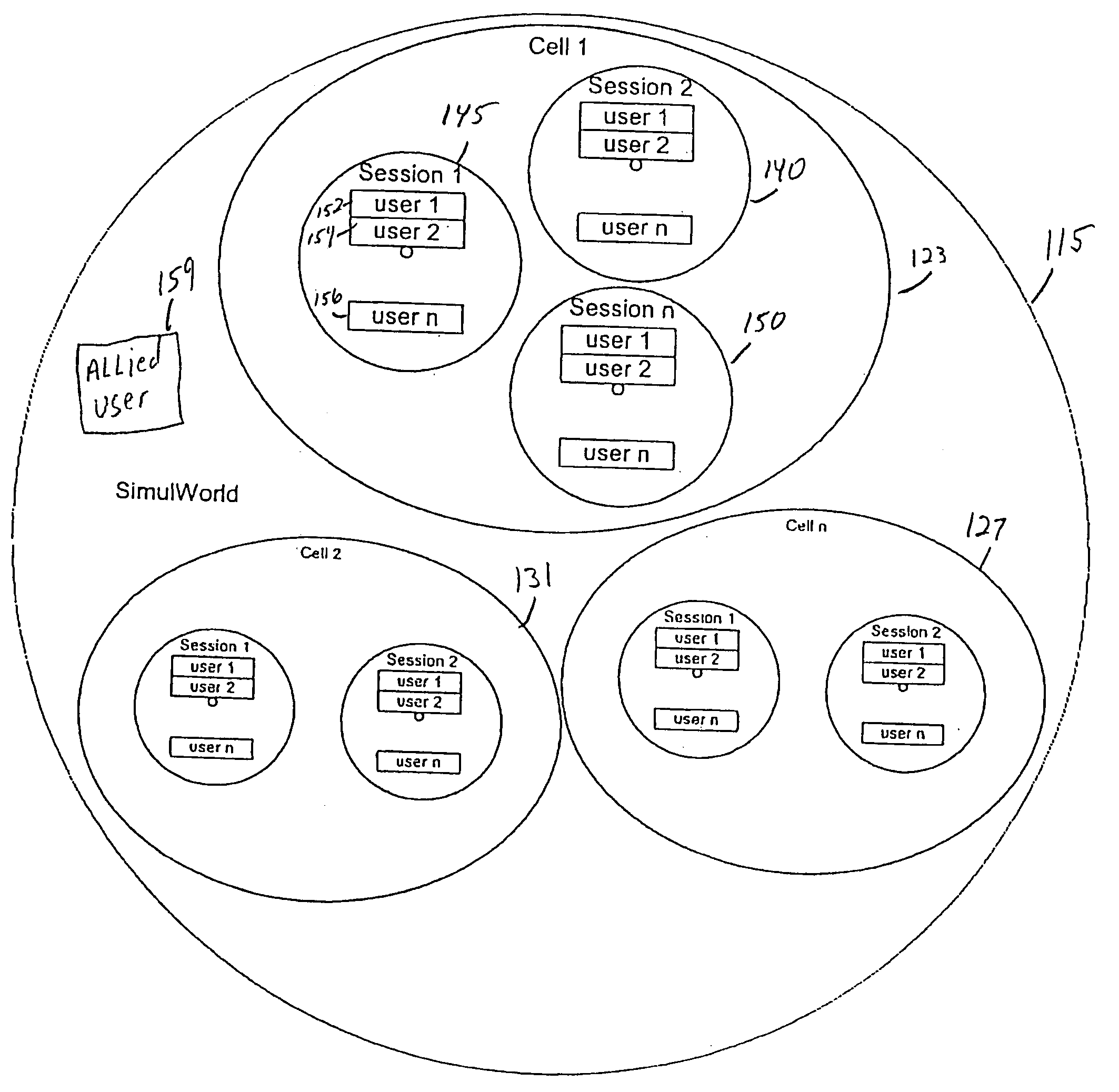
InactiveUS20050198162A1Disadvantages of and of reduced eliminatedSynchronised browsingMultiple digital computer combinationsClient-sideFacilitated communication
A dynamic collaborative-browsing system enables client programs connected to a computer network to join and leave groups or sessions, to collaboratively browse together as a session, to communicate with other client programs in the session. Each client program in the session may act as a session leader, or may just follow a session leader as it browses network sites of the computer network. The system includes client programs, typically executing on client computers and server software, typically executing on one or more main servers. Network servers, such as Web servers, host a number of network sites each having a location or uniform resource locator (URL). The main server groups into server-defined cells. One or more client programs interact with the server software to cause the server to create a session, to cause the client program to connect to a network site, to notify the server software of the network site's location or URL, and to notify other client programs in the session of the network site's location or URL so that other client programs in the session become connected to the same network site. The server software facilitates the formation of client programs into sessions and allows the client programs to communicate, to connect to and view a same network site, and to perform other collaborative activities. The server software also groups sessions currently connected to network sites in a same cell, and notifies each session and the client programs of the sessions of all of the other sessions and client programs in the same cell. The server software also facilitates communication between the sessions and client programs connected to network sites in the same cell.
Owner:PROFICIENT SYST
Popular searches
Special data processing applications Securing communication Digital data processing details Color television details Lower station broadcast interaction arrangement Program/content distribution protection Selective content distribution Transmission Input/output processes for data processing Television systems
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com