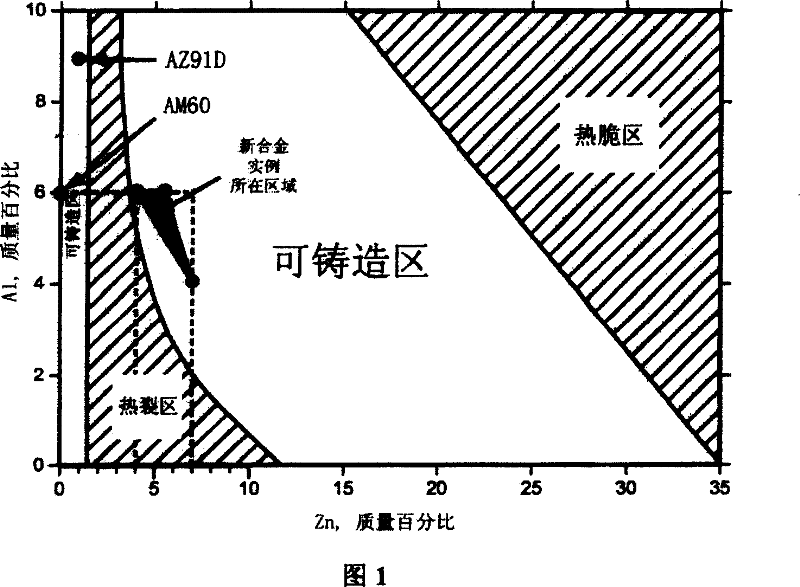
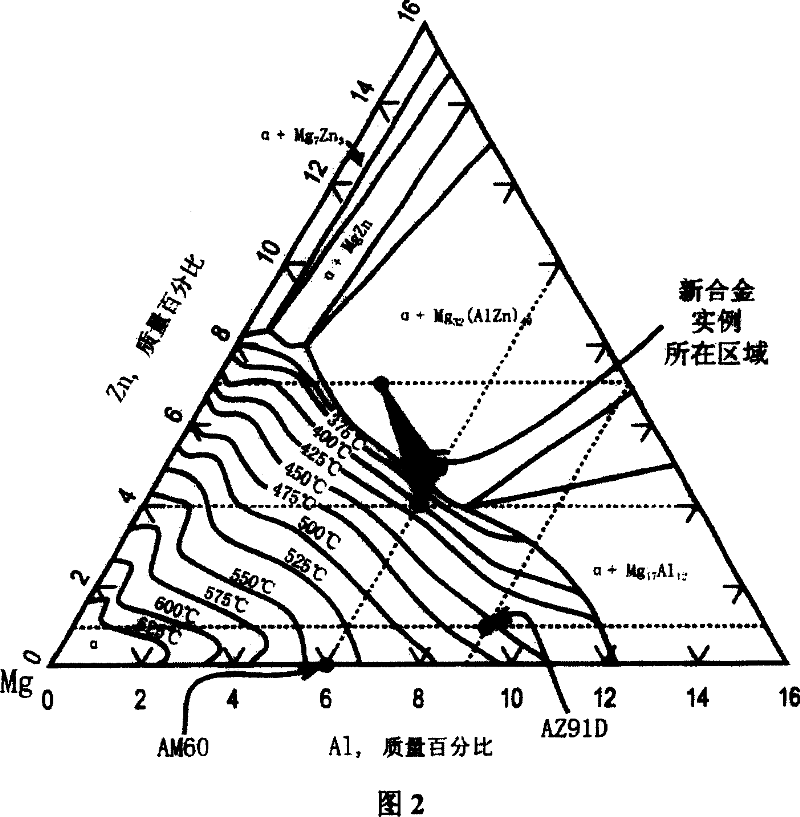
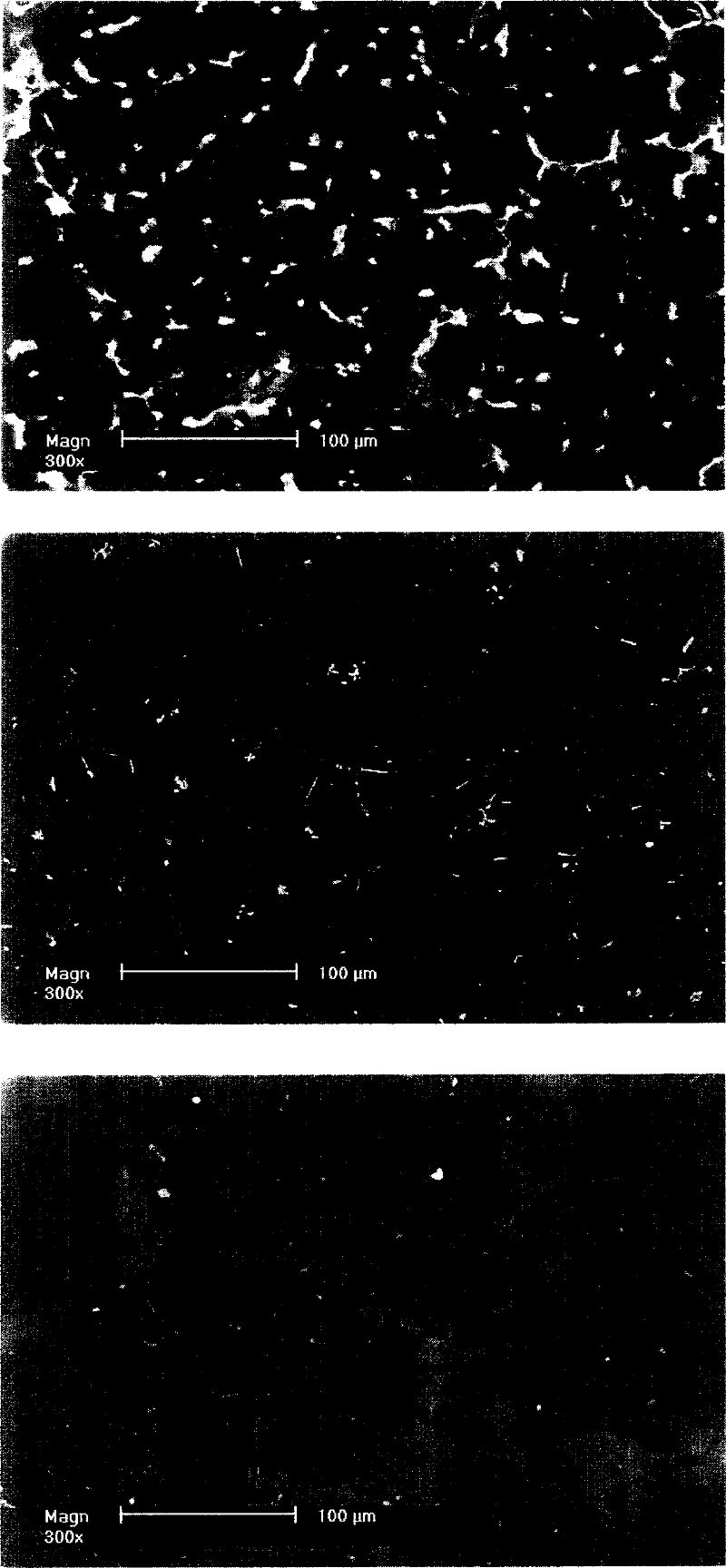
High strength and high toughness cast magnesium alloy and preparing process thereof
A technology for casting magnesium alloys and high toughness is applied in the field of casting magnesium alloys, which can solve the problems of low efficiency and high cost, and achieve the effects of low cost, high cost performance and stable process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The basic operation steps of the present embodiment 1 alloy (comparative example 1 alloy AZ91, comparative example 2 alloy AM60) are as follows:
[0038]
Alloy grade
Element content (weight percent %)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminum (Al)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Antimony (Sb)
Example 1
89.2
6
4
0.3
0.5
AZ91
89.7
9
1
0.3
0
AM60
93.7
6
0
0.3
0
[0039] II), alloy smelting and casting molding:
[0040] The smelting work of Example 1 is carried out in a pit furnace, and the crucible is made of carbon steel; the casting of the alloy is completed in a metal mold. The detailed procedure is as follows:
[0041] 1) Preheat various ingredients such as pure magnesium, pure aluminum, aluminum-manganese intermediate alloy, pure zinc, antimony powder, etc. Preheat to 350°C in a box-type furnace, then set the target temperature of ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0069] The basic operation steps of the alloy in this embodiment are as follows:
[0070]
Alloy grade
Element content (weight percent %)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminum (Al)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Example 2
88.7
6
5
0.3
[0071] II), alloy smelting and casting molding:
[0072] Refer to Example 1. In the third step of the smelting process, the alloy of this embodiment does not need to add antimony powder ingredients wrapped in aluminum foil.
[0073] III), heat treatment of castings:
[0074] Refer to the heat treatment section in Example 1. The temperature of the T4 solid solution treatment of the alloy in this embodiment is preferably 370° C. This temperature is determined by referring to the phase diagram of the magnesium-aluminum-zinc ternary alloy and finally determined by experiments. If the temperature is too high, phase transformation and precipitation...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The difference from Example 1 is:
[0088] The basic operation steps of the alloy in this embodiment are as follows:
[0089]
Alloy grade
Element content (weight percent %)
Magnesium (Mg)
Aluminum (Al)
Zinc (Zn)
Manganese (Mn)
Yttrium (Yt)
Example 2
88.2
4
7
0.3
0.5
[0090] II), alloy smelting and casting molding:
[0091] Refer to Example 1. In the third step of the smelting process of the alloy in this embodiment, after the addition of pure aluminum and aluminum-manganese master alloy ingredients, the magnesium-yttrium master alloy ingredients are added, and finally the pure zinc ingredients are added.
[0092] III), heat treatment of castings:
[0093] Refer to the heat treatment section in Example 1. The temperature of the T4 solid solution treatment of the alloy in this embodiment is preferably 360° C. This temperature is determined by referring to the phase diagram of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com