Composition for trapping and inactivating pathogenic microbes and spermatozoa and its pharmaceutical uses
A composition, technology of antimicrobial agent, applied in the field of compositions for capturing and inactivating pathogenic microorganisms and sperm and its pharmaceutical use, can solve the problems of less likely to be used, difficult to use, reduced sexual pleasure and sensitivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Gels were prepared using several methods with the following general recipe.
[0045] Element quantity(%) Alginic acid 4.25 xanthan gum 3.0 glycerin 8.0 lactic acid 2.0
[0046] citric acid 1.0 Potassium hydrogen tartrate 0.4 benzoic acid 0.2 Nonoxynol-9 0-10.0 distilled water balance
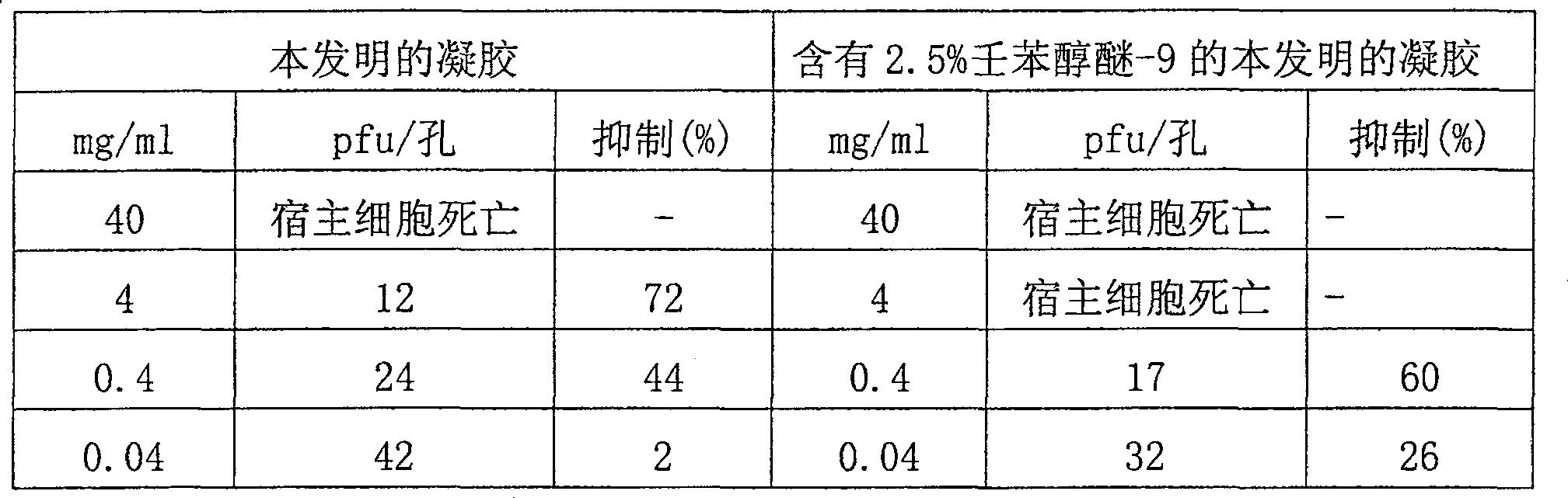
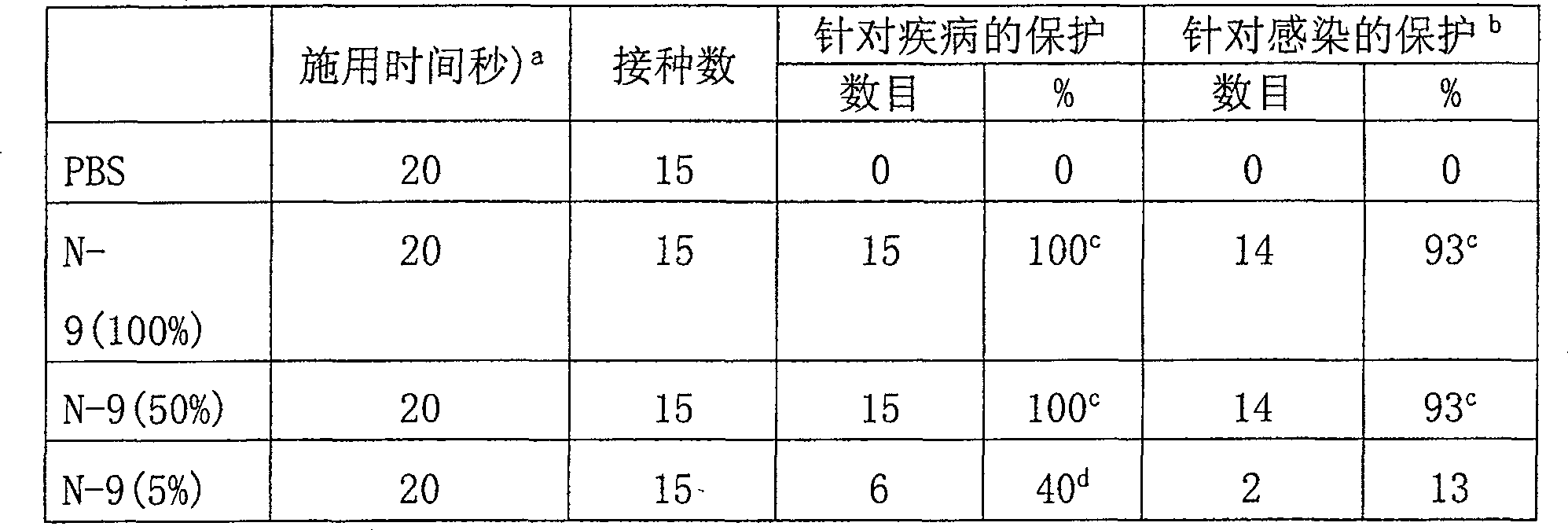
[0047] Gels containing varying levels of nonoxynol-9 (ie, about 0-10%) were prepared. The pH of the formulation was adjusted to pH about 3.5-3.6 with sodium hydroxide. Use this formulation to obtain high-quality capture gels. Additionally, unlike the formulation of Example 2, these formulations showed good stability over time even at levels of nonoxynol-9 up to about 5%.
[0048] As noted above, capture gels of the invention are generally prepared using conventional gel preparation techniques. It is however important to ensure that the buffer is completely soluble in the final product and air entrainment is...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2. Preparation of additional gels using hydroxyethyl cellulose as the second bioadhesive agent. The following general formulations were prepared:
[0057] Element quantity(%) Alginic acid 3.5 xanthan gum 2.0 Hydroxyethyl cellulose 1.75 glycerin 10.0 lactic acid 2.0 citric acid 1.0 Potassium hydrogen tartrate 0.4 benzoic acid 0.2 Nonoxynol-9 0-10.0 distilled water balance
[0058] The gel was prepared in the same general manner as in Example 1, except that the hydroxyethyl cellulose was mixed with the glycerin and xanthan gum mixture.
[0059] Capture gels containing varying levels of nonoxynol-9 (ie, about 0-10.0%) were prepared. The pH of the formulation was adjusted to about 3.5-3.6 with sodium hydroxide. However, formulations prepared with typical levels of nonoxynol-9 (ie, greater than about 5%) were not as stable as desired. Stability studies indicated that these nonoxynol-9 form...
Embodiment 3
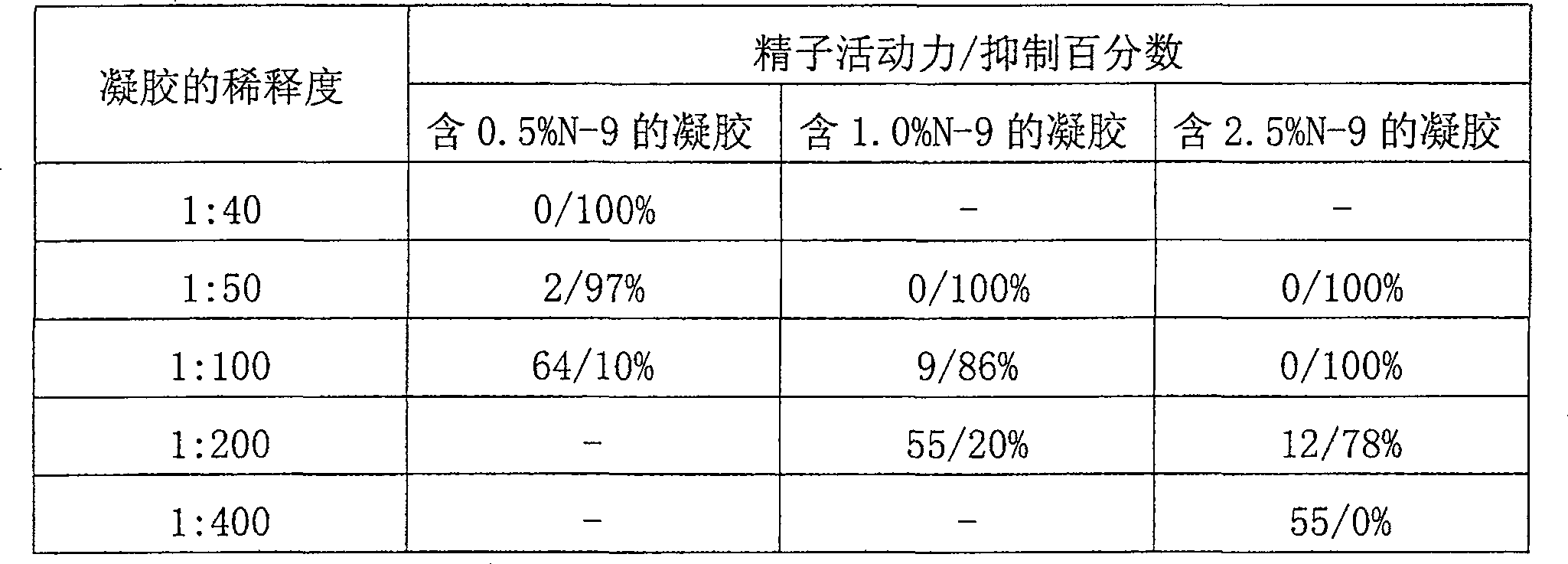
[0060] Example 3. This example illustrates the acid buffering capacity of the gels of the invention. (In addition, and in more detail, a study on the acid buffering capacity of the gels of the present invention is included in Example 10 below). Using the gel prepared in Example 1, the pH of the gel before and after mixing with different amounts of semen was determined. Semen samples were collected from healthy human volunteers and screened for sperm count, motility, pH and volume; the initial pH of semen was about 7.9. The gel is diluted with saline and mixed with semen at the desired gel to semen ratio. The following results were obtained:
[0061] Dilution of gel with saline pH after mixing with semen 1:5 3.97 1:10 4.49 1:20 5.66
[0062] A 1:5 dilution represents approximately 1 part gel to approximately 1 part semen; a 1:10 dilution represents approximately 1 part gel to approximately 2 parts semen. Since the average ejaculate volume is e...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com