An organic luminescence part
A technology for organic light-emitting devices and light-emitting layers, which is applied in the manufacture of electrical solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, and semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc., and can solve the problems of increasing device thickness, cathode damage, and complex preparation processes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
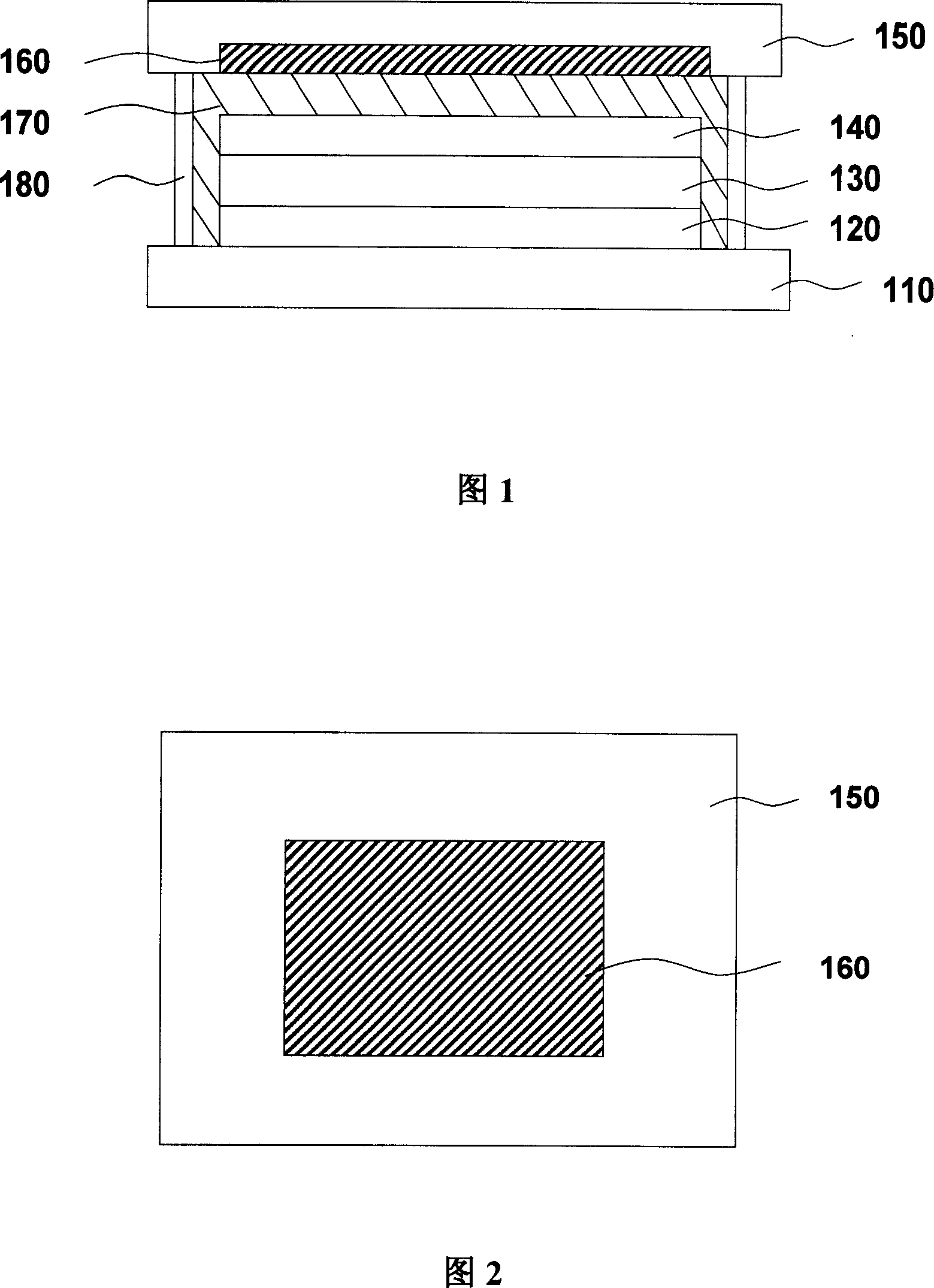
[0032] 1 is a cross-sectional view of the structure of the first embodiment of the organic light-emitting device of the present invention. An anode layer 120, a light-emitting layer 130, and a cathode layer 140 are sequentially arranged on a substrate 110, wherein the substrate 110 is generally a glass substrate, and the anode 120 is a transparent electrode. Metal oxides such as indium tin oxide (ITO), zinc oxide, and zinc tin oxide, or metals with higher work functions such as gold, copper, and silver, preferably ITO, and the light-emitting layer 130 may also include a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer, One or more layers of the electron injection layer and the electron transport layer. The hole transport layer is made of p-type organic semiconductor materials with strong hole transport ability, generally triphenylamine compounds, such as NPB, TPD, MTDATA and other materials. One, the electron transport layer is generally a metal-organic complex, such as Alq 3 , BA...
Embodiment 2
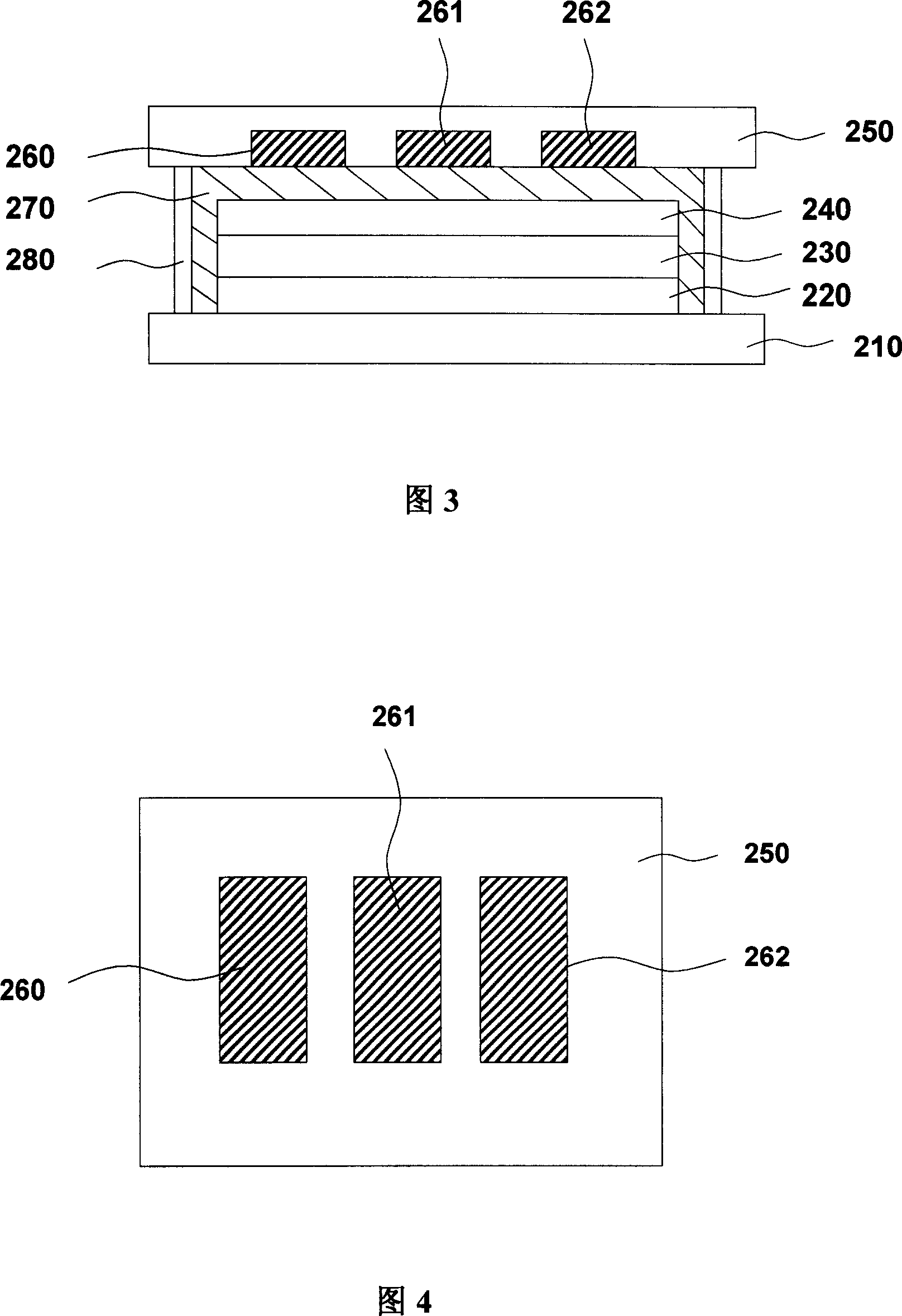
[0036]2 is a cross-sectional view of the structure of the second embodiment of the organic light-emitting device of the present invention. An anode layer 220, a light-emitting layer 230, and a cathode layer 240 are sequentially arranged on a substrate 210. The material selection of each layer is the same as in Example 1, and the cathode layer 240 is arranged above. There is a packaging board 250, and the packaging board 250 and the substrate 210 are bonded and fixed by the packaging glue 280. The packaging board 250 contains three independent low-melting point metal layers 260, 261 and 262, which are respectively filled with metals with different melting points. In this embodiment, glass is selected as the packaging plate. During preparation, three cube-shaped grooves are sequentially formed on a plane inside the glass plate by means of stamping. The plan view of the structure is shown in Figure 4. Load three kinds of metal particles with different melting points, and then use ...
Embodiment 3
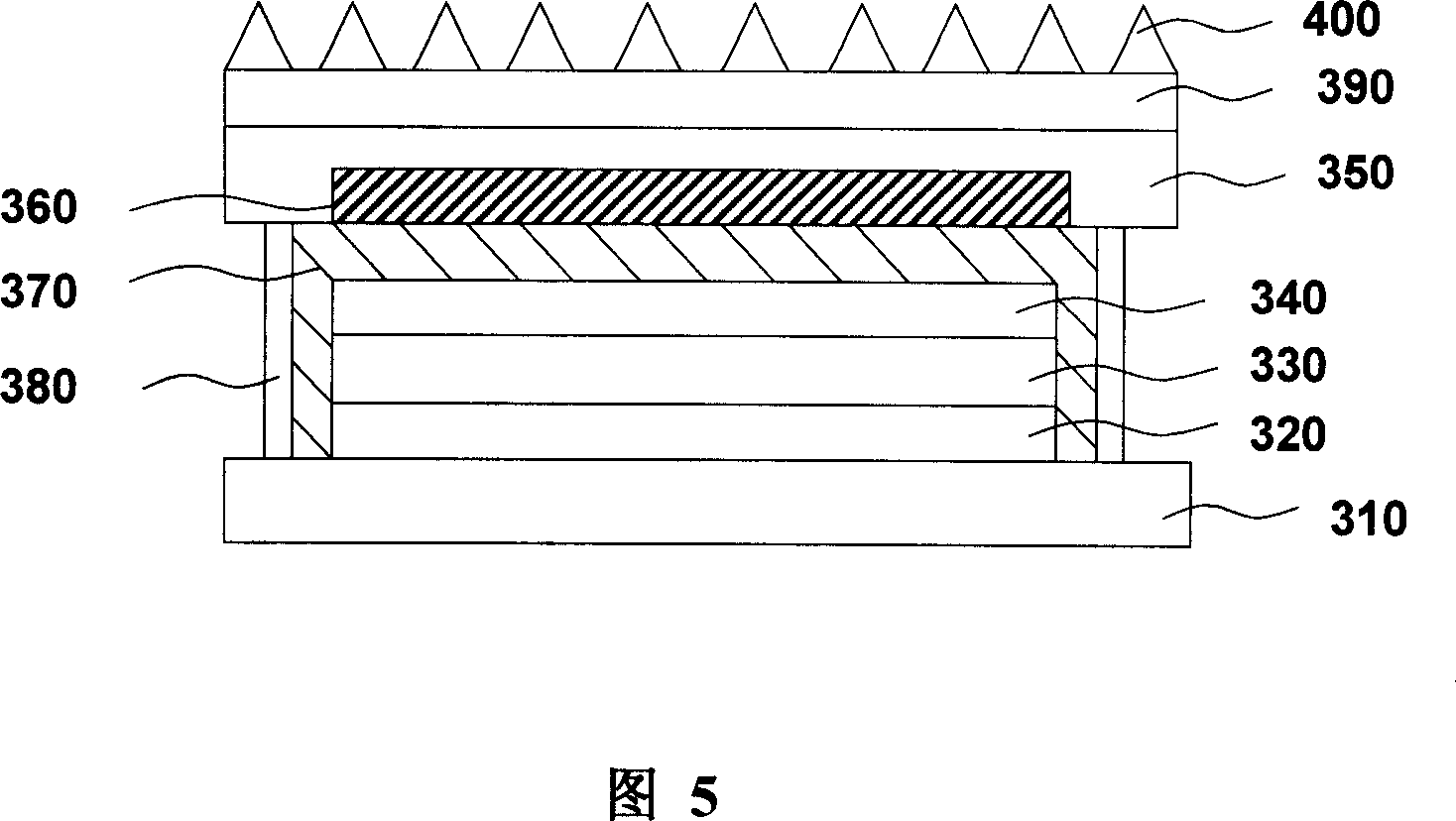
[0039] 3 is a cross-sectional view of the structure of the third embodiment of the organic light-emitting device of the present invention. An anode 320, a light-emitting layer 330, and a cathode 340 are sequentially arranged on a substrate 310. The selection of materials for each layer is the same as in Example 1, including a low-melting point metal layer 360. The packaging board 350 is arranged on the cathode layer 340, and the packaging board 350 and the substrate 310 are bonded and packaged by the packaging adhesive 380. The difference from Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 lies in the outer side of the packaging board 350 of this embodiment Also be provided with a metal heat dissipation plate 390 with heat dissipation protrusions 400, the metal heat dissipation plate 390 is a thermally conductive material, and its function is to help transfer the heat inside the device to the external environment better, and the heat dissipation protrusions 400 The effect is to increase the sur...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com