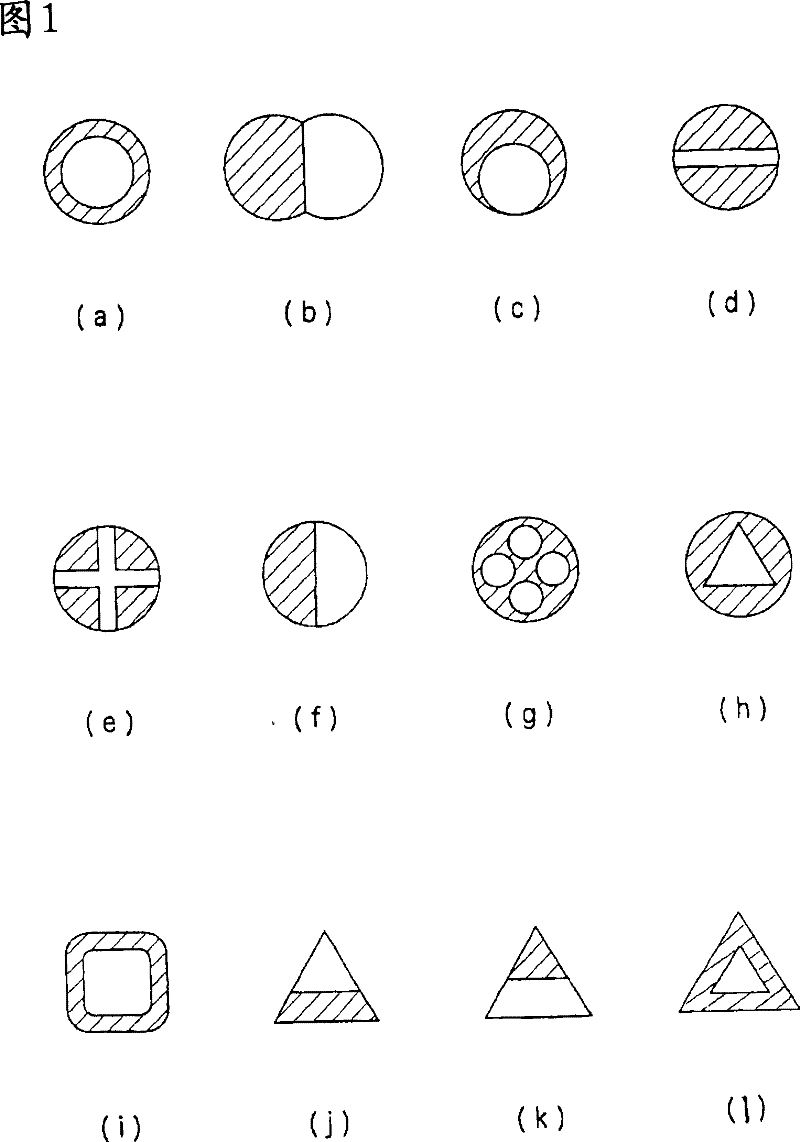Woven structure of belt form and method for production thereof
A technology of structures and fabrics, applied in fabrics, structures of seat belts/slings, textiles, etc., can solve the problems of easy yarn cutting, poor bending, and poor productivity, and achieve excellent anti-twisting effects and excellent wearing Good feeling and usability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
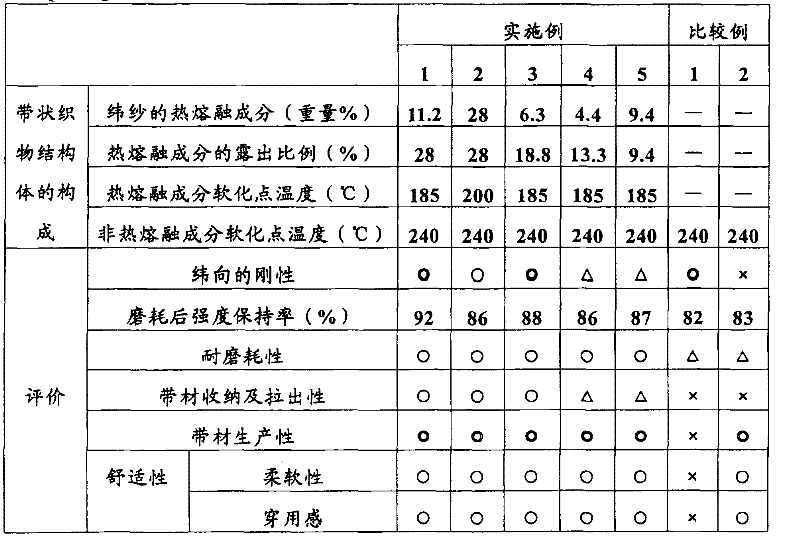
[0089] As the warp yarn, 1670dtex / 144f, a breaking strength of 8.4cN / dtex, and an elongation of 12% were dyed black polyester multifilaments, and the warp density was 390 threads / 2.54cm. As the weft yarn, a sheath component of 280dtex / 16f was used. The core is polyethylene terephthalate (softening point 185°C) copolymerized with 25 mol% isophthalic acid, and the core component is polyethylene terephthalate (softening point 240°C) with an intrinsic viscosity of 0.68 Sheath type thermal fusion polyester yarn (manufactured by Kanebo Co., Ltd., Bellcouple [registered trademark], core / sheath ratio = 3 / 2), and 720dtex / 72f (softening point 240°C), breaking strength 6.5cN / dtex, elongation Polyester fibers with a rate of 20% are paralleled, and a tape is woven by a knitting machine with a width of 5 cm and a weft density of 20 / 2.54 cm. Next, the tape was heat-treated at a temperature of 200° C. to melt the sheath component and melt and fix the surrounding polyester fibers, whereby the ...
Embodiment 2
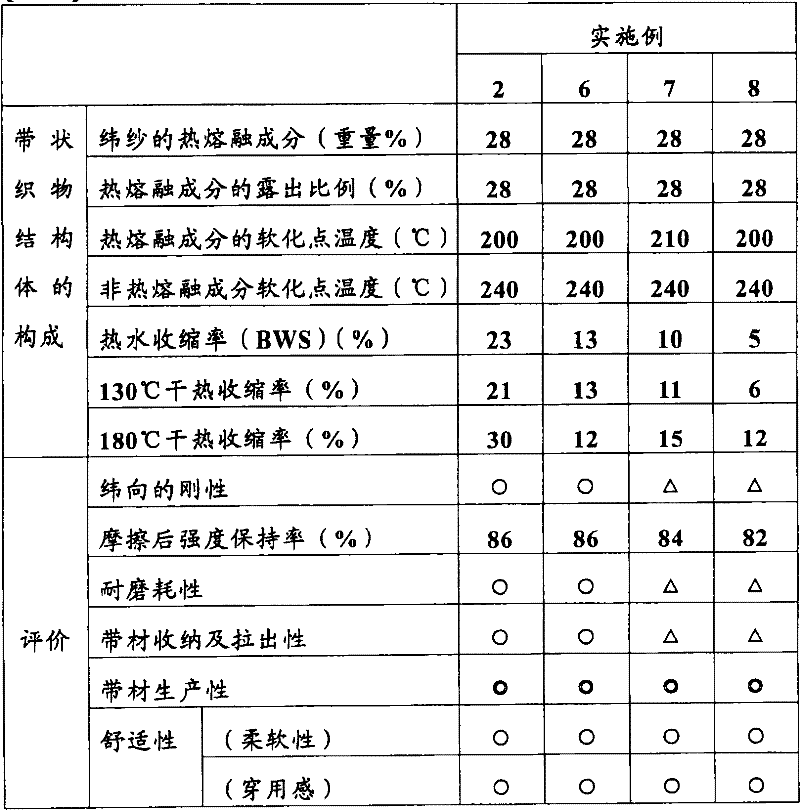
[0091] As the weft yarn, instead of the core-sheath type heat-melting polyester yarn of the above-mentioned Example 1, 2,2-bis[4-(2 -Carboxyethoxy)phenyl]propane polyester multifilament (softening point 200°C, intrinsic viscosity 0.69, maximum thermal shrinkage stress 0.23cN / dtex, BWS 23%, 130°C dry heat shrinkage 21%, 180 °C dry heat shrinkage rate of 30%), except that it was the same as the above-mentioned Example 1 to obtain the target belt-shaped fabric structure.
Embodiment 3
[0093] Instead of the core-sheath type hot-melt polyester yarn of Example 1, 167dtex / 48f, the sheath component was polyethylene terephthalate (softening point 185° C.) copolymerized with 25 mol% isophthalic acid, and the core component was A core-sheath heat-melt polyester yarn (manufactured by Kanebo Co-woven Co., Ltd., Bellcouple [registered trademark], core / sheath ratio = 2 / 1) of polyethylene terephthalate (softening point: 240° C.) with an intrinsic viscosity of 0.68 ), except that it was the same as in the above-mentioned Example 1, and the target belt-shaped fabric structure was obtained.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| softening point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com