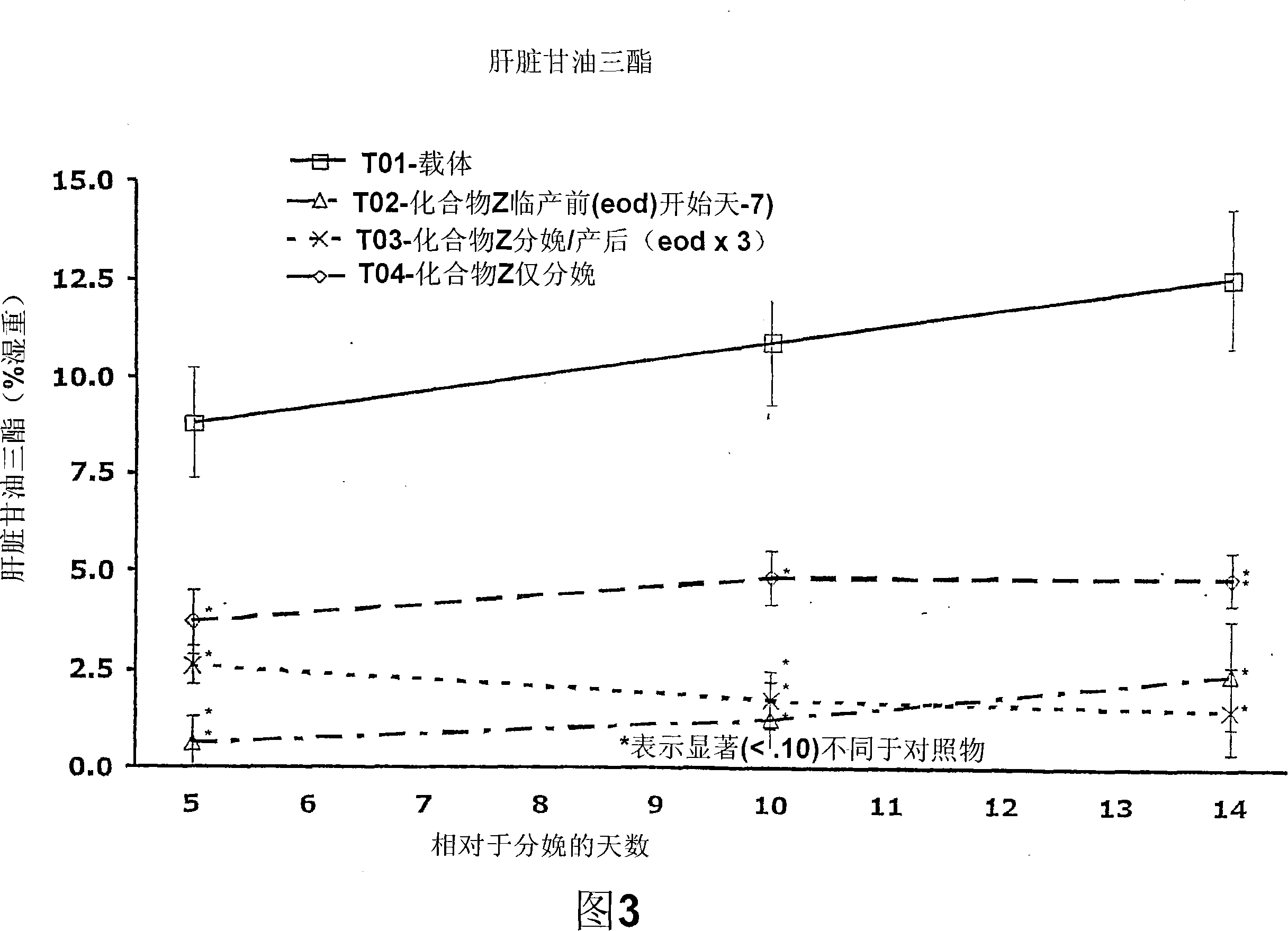
Use of PPAR agonists to treat ruminants
A ruminant and agonist technology, applied in the field of PPAR agonist, treatment of ruminant diseases related to lower blood sugar concentration, and treatment of feline fatty liver, can solve complex interactions, do not know PPAR expression milk production or quality, issues of limited knowledge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
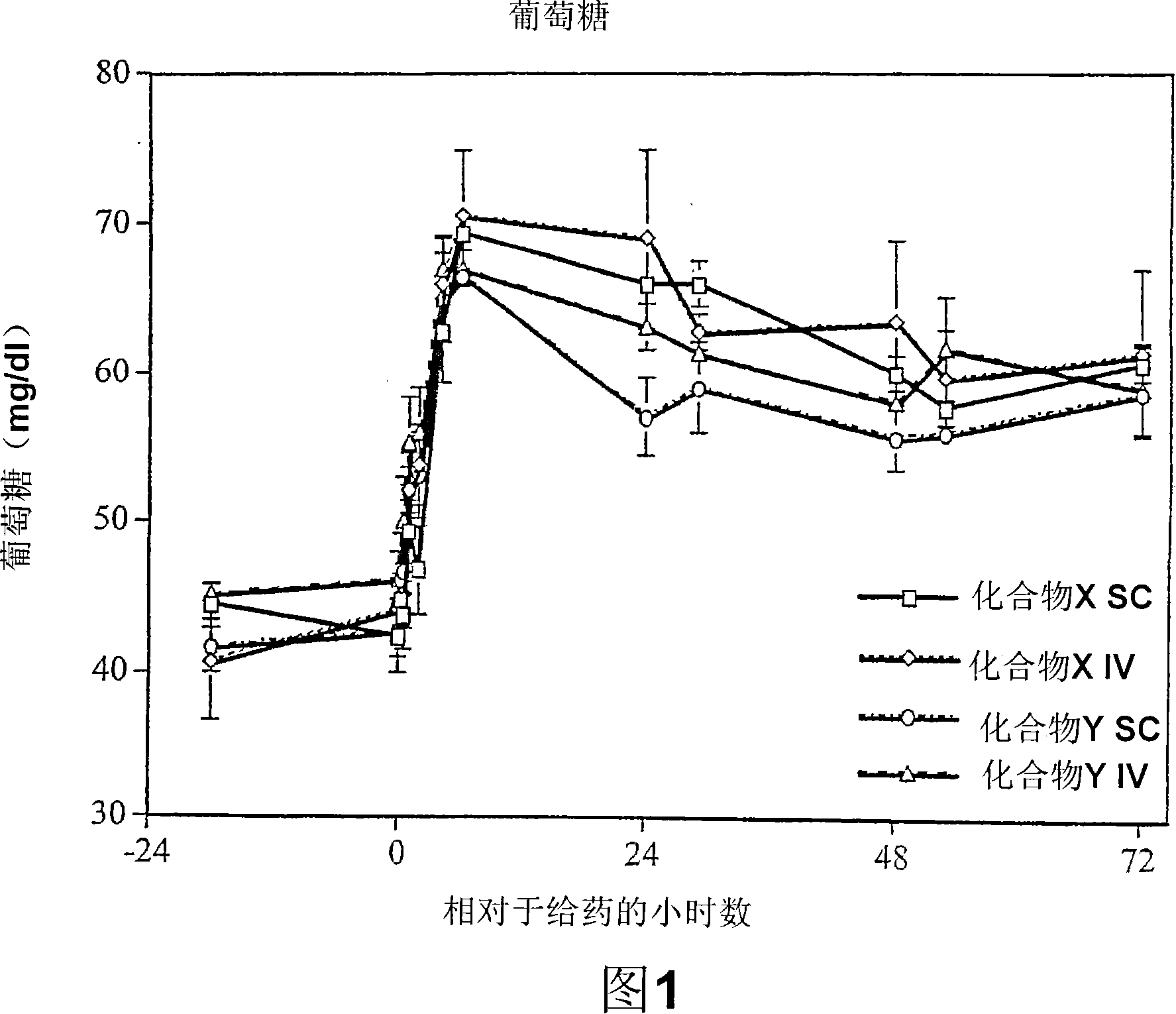
[0121] Twelve lactating cows were selected to study the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of 2 PPARα agonists - Compound "X" and Compound "Y". Both compounds were administered by IV and SC routes as indicated in the table below.
[0122] treat
dosage
Cow No.
T1 compound "X"
T2 compound "X"
T3 compound "Y"
T4 compound "Y"
0.5mg / kg IV
0.5mg / kg SC
0.5mg / kg IV
0.5mg / kg SC
3
3
3
3
[0123] All animals were bled one day, and 15 minutes prior to compound administration. Blood samples were collected from IV-treated animals 5 and 10 minutes after compound administration. Blood samples were collected from all animals at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 24, 30, 48, 54, and 72 hours after compound administration. Samples were analyzed for glucose concentration using a Dade Behring Dimension RXL Serum Chemistry Analyzer. Treatment with both compounds, regardless of route of administration, caused...
Embodiment 2
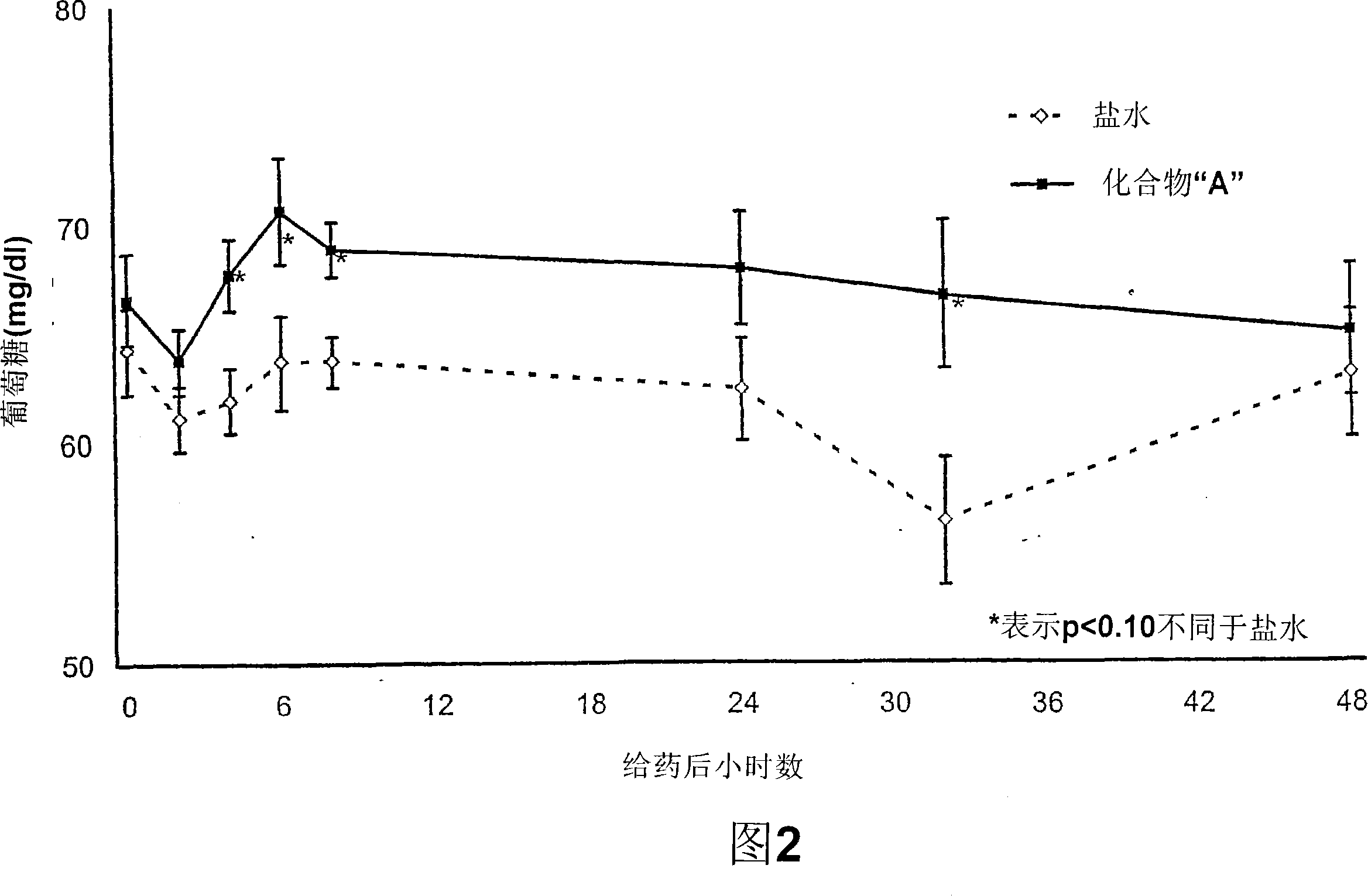
[0127] Ten lactating cows fed a low starch / high fat diet were selected to study the effect of dosing on circulating glucose levels. Animals were fed a low-starch / high-fat diet for one week prior to dosing and remained on the same diet throughout the study.
[0128] treat
dosage
Cow No.
T1 saline
T2 Compound A
3.0mL SC
0.5mg / kg SC
5
5
[0129] All animals were bled 5 minutes prior to compound administration. Blood samples were collected from all animals at 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, 32, and 48 hours after compound administration. In this example, Compound A is the PPAR alpha agonist (3S)-3-[3-(1-carboxy-1-methyl-ethoxy)-phenyl]-piperidine-1-carboxylic acid 4- Trifluoromethyl-benzyl ester.
[0130]
[0131] Samples were analyzed for glucose concentration using an Olympus AU640 analyzer. Treatment with compounds elicited a transient increase in glucose relative to saline controls. The results are shown in Figure 2.
[0...
preparation Embodiment
[0224] In the following formulations, "active ingredient" means a compound used in the present invention.
[0225] Formulation 1: Solution for parenteral administration
[0226] A solution of the active ingredient is prepared as follows:
[0227] Element
Amount (mg / 5ml)
water
1-750
0.1-75
0-50
0-100
0-40
up to 5ml
[0228] or
[0229] Formulation 1a: Solution for Parenteral Administration
[0230] A solution of the active ingredient is prepared as follows:
[0231] Element
Amount (mg / 5ml)
active ingredient
Sodium hydrogen phosphate
pvp
water
1-750
0-75
0-75
0-50
0-100
0-50
0-40
up to 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com