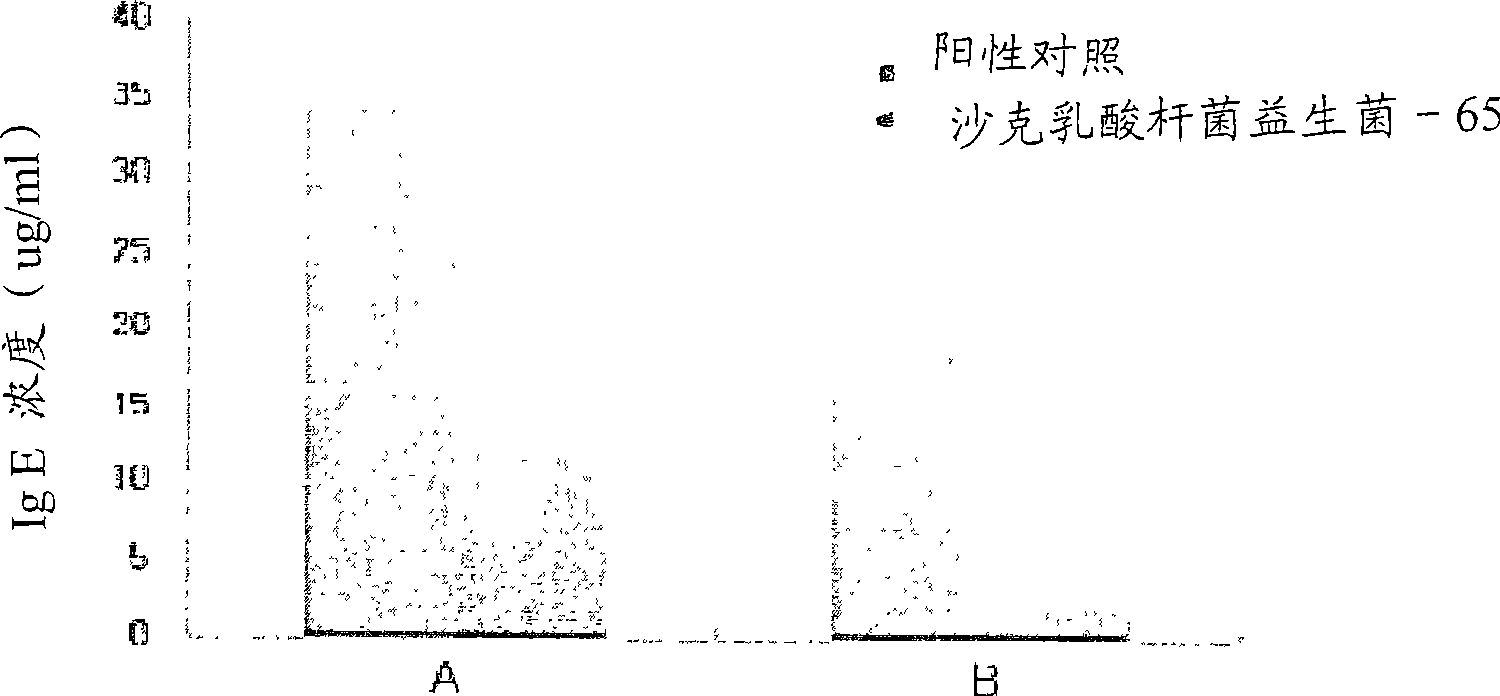
Novel acid tolerant lactobacillus sakei probio- 65 with the ability of growth suppression of pathogenic microorganisms and the anti-allergic effect
A kind of technology of Lactobacillus sack, pathogenic microorganism, applied in the field of new lactic acid bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Isolation of Lactobacillus strains
[0066] The homemade kimchi juice (fermented) was diluted, spread on a BCP solid medium (Eiken Chemical, Japan), and cultured at 37°C for 48 hours. After the bacteria appeared under the microscope, a total of 480 micrococcus and bacilli were selected and cultured on MRS medium (Difco) and stored at -80°C. Finally, a microorganism that inhibits the proliferation of Staphylococcus aureus KCTC1621, which is a factor in the deterioration of atopic diseases, was selected and named Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65 (Figure 6).
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Identification of the isolated Lactobacillus sakei Probio-65 strain
[0068] The Probio-65 strain isolated in Example 1 was cultured at 37°C in MRS medium (Difco). In order to identify the Probio-65 strain, the morphological and physiological characteristics of the Probio-65 strain were used in the literature: Yoon et al., Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 47, 904, 1997 described using the API32A and API CHL system (BioMerieux) Method to determine. The nucleotide sequence of the 16S rDNA gene was determined and analyzed using the method described in Yoon et al., Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 47,933, 1997.
[0069] The Probio-65 strain is a gram-positive bacteria. This strain can survive under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions, does not form spores, is immobile and is a bacillus type. The optimum temperature range for the growth of this strain is 30°C-37°C. The Probio-65 strain does not produce gas and indole, does not show solubility properties, and cannot reduce nitr...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: Evaluation of the inhibitory effect of isolated microorganisms on harmful microorganisms
[0074] The method described by Kuroiwa et al. (Kuroiwa et al., Journal of Infections, 64, 257, 1990) was used to evaluate the growth inhibitory activity of primary isolated microorganisms against harmful pathogenic microorganisms. In this antibiotic activity evaluation, ten microbial strains were used: Escherichia coli KCTC2441, Klebsiella pneumoniae KCTC2208, Staphylococcus aureus KCTC1621, Staphylococcus epidermidis KCTC1917, Shigella freundii KCTC2008, Salmonella gallisepticum, cloacae Bacillus KCTC2361, Salmonella typhimurium, Citrobacter freundii KCTC2006 and Methanosporium KCTC2591.
[0075] The harmful pathogenic microorganisms were cultured in nutrient broth (NB) at 37°C for 18 hours. 0.1 ml of each culture solution was spread on a nutrient agar (NA) plate and air-dried, and a cylinder with a diameter of 8 mm was placed on each plate. The primary isolated microorga...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com