Method for reclaiming precious metal palladium from waste palladium-carbon catalyst
A palladium-carbon catalyst and precious metal technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of low palladium recovery rate, long process, high cost, etc., and achieve the effect of good product quality, high recovery rate and low production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
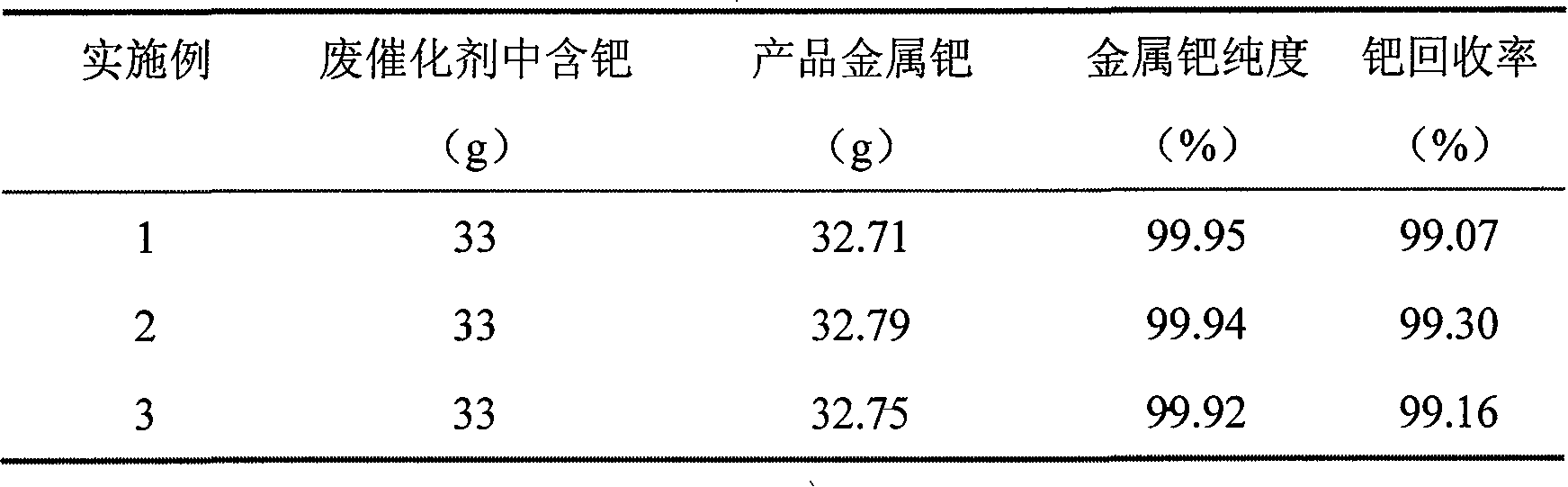
[0017] Get waste palladium-carbon catalyst 10kg (dry), palladium content is 0.33% (wt), puts into tube furnace and roasts, and roasting temperature is 600 ℃, fully gas supply, and roasting ash adds formic acid reduction, and add-on is every kilogram of palladium ash Add 300 milliliters of formic acid, heat to 70 DEG C, keep for 3 hours, filter, filter residue is leached with aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, wherein palladium ash: hydrochloric acid: sodium hypochlorite: hydrogen peroxide: water=1:5:5:5:3, temperature 75°C, 4 hours, filtration, recovery of filter residue, ion exchange of filtrate, ammonia complexation, filtration, recovery of complexation slag, acidification of complexation liquid, collection of acidification tail liquid, acidification precipitation and drying, then put into roasting furnace, 600°C Calcined at lower temperature for 4 hours, and reduced with hydrogen to obtain 32.71 g of product metal palladium.
Embodiment 2
[0019] Get spent catalyst 10kg (dry), palladium content is 0.33% (wt), puts into tube furnace and roasts, and roasting temperature is 650 ℃, fully gas supply, roasting ash is added formic acid reduction, and add-on is every kilogram of palladium ash plus 400 Milliliter of formic acid, heated to 75°C, kept for 4 hours, filtered, and the filter residue was leached with aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, sodium hypochlorite, and hydrogen peroxide, wherein palladium ash: hydrochloric acid: sodium hypochlorite: hydrogen peroxide: water=1:6:5:8:4, temperature 80°C , time 5 hours, filtration, filter residue recovery, filtrate ion exchange, ammonia complexation, filtration, complexation slag recovery, complexation liquid acidification, acidification tail liquid collection, acidification precipitation, drying, put into roasting furnace, roasting at 550 °C After 4.5 hours, it was reduced with hydrogen to obtain 32.79 g of the product metal palladium.
Embodiment 3
[0021] Get spent catalyst 10kg (dry), palladium content is 0.33% (wt), puts into tube furnace and roasts, and roasting temperature is 700 ℃, fully gas supply, and roasting ashes adds formic acid reduction, and add-on is every kilogram of palladium ashes and adds 500 Milliliter of formic acid, heated to 80 ° C, kept for 5 hours, filtered, and the filter residue was leached with aqueous solution of hydrochloric acid, sodium hypochlorite, hydrogen peroxide, wherein palladium ash: hydrochloric acid: sodium chlorate: hydrogen peroxide: water=1:7:5:10:3, temperature 85°C, time 6 hours, filtration, recovery of filter residue, ion exchange of filtrate, ammonia complexation, filtration, recovery of complexation slag, acidification of complexation liquid, collection of acidification tail liquid, acidification precipitation and drying, then put into roasting furnace, 550°C Calcined at lower temperature for 4 hours, and reduced with hydrogen to obtain 32.75 g of product metal palladium.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com