Sn-Cu base leadless solder alloy and preparation method
A lead-free solder and alloy technology, applied in the field of lead-free brazing materials and non-ferrous alloy materials, can solve the problems of poor comprehensive mechanical properties, poor oxidation resistance, poor corrosion resistance, and limited use of alloys.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] 1. Weigh P 4% and Sn 96% according to the mass ratio, which is 50 grams in total, then put the two into a graphite crucible, and cover the above-mentioned molten salt on it, place the crucible in a resistance furnace, Keep the temperature at 450°C for 45 minutes, stir evenly and then cast to obtain the Sn-P master alloy;
[0020] 2. Based on the total mass as 100%, weigh the Sn-P master alloy with the amount of P accounting for 0.1%, then weigh Cu 0.7%, the balance is Sn, and the total weight is 100 grams. Put the ingredients into a graphite crucible, cover it with the above-mentioned protective molten salt, place the crucible in a resistance furnace, keep it warm at 450°C for 60 minutes, stir it evenly and cast it into an ingot to obtain the required solder alloy.
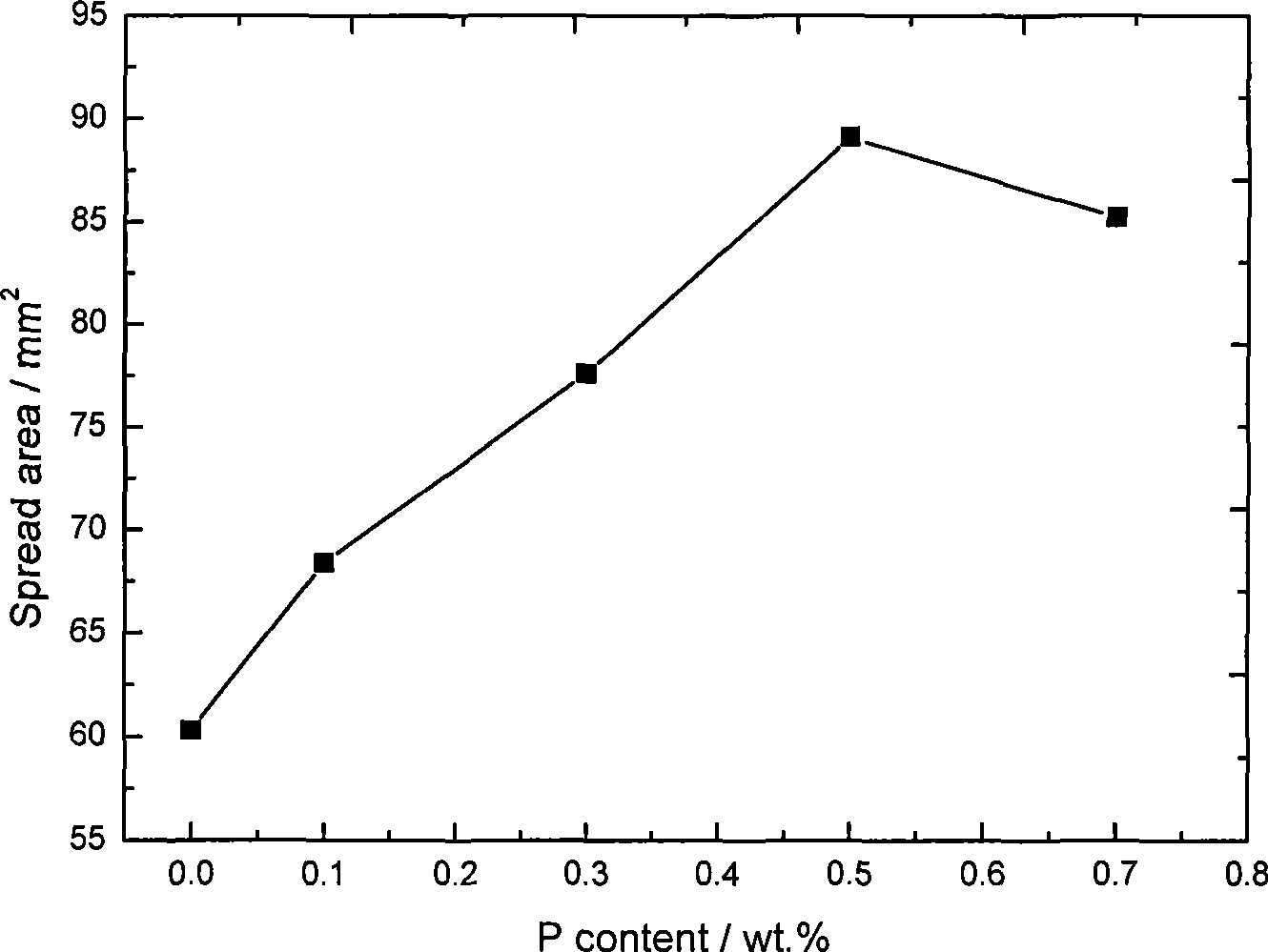
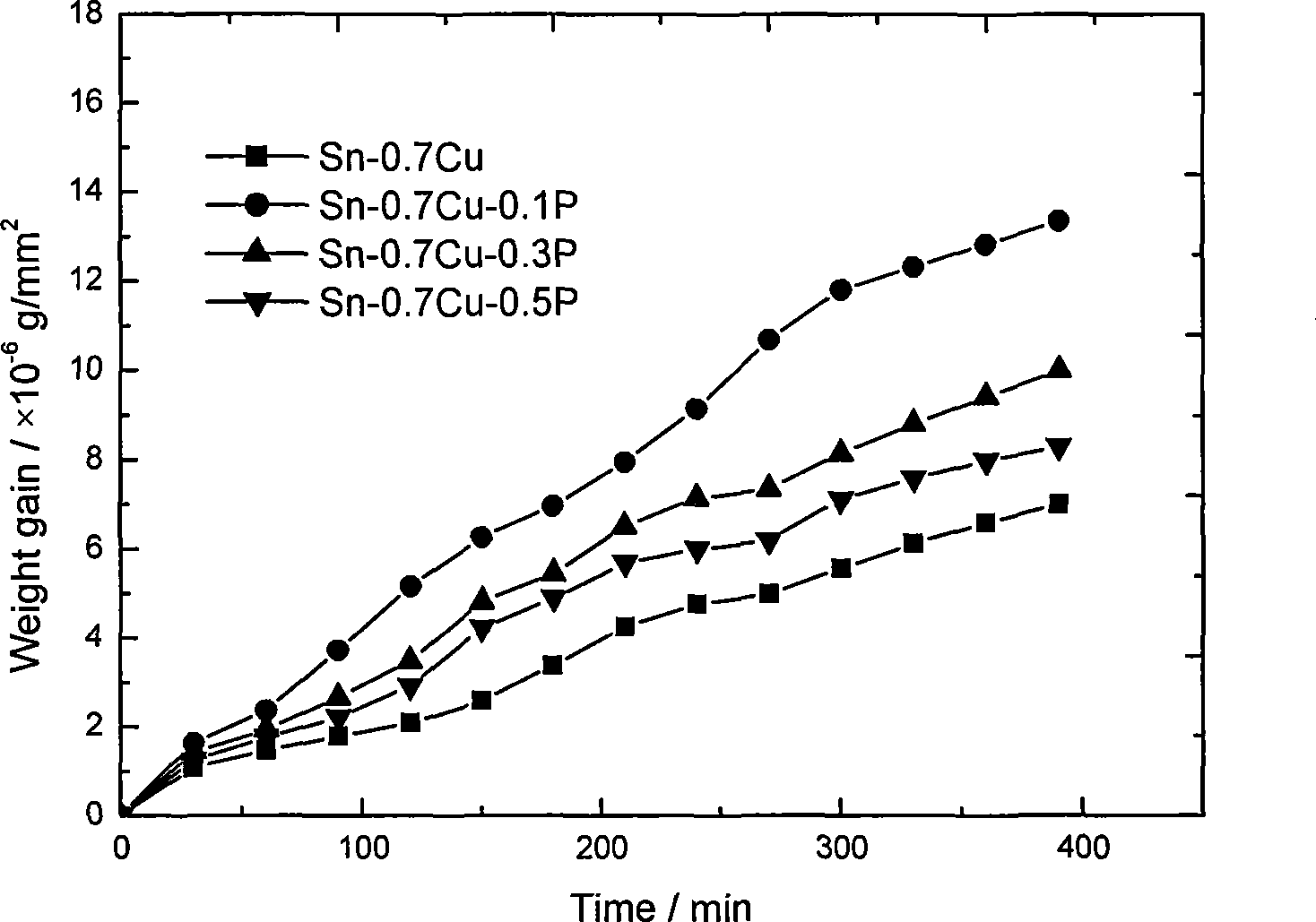
[0021] According to the above method, a series of Sn-Cu alloys with different P contents were welded for the measurement of wettability and oxidation resistance; the influence of solder alloys with differen...
Embodiment 2
[0025] 1. Take P 4% and Sn 96% according to the mass ratio, which is 50 grams in total, then put the two into a graphite crucible, and cover the above-mentioned molten salt on it, place the crucible in an induction furnace, Insulate at a temperature of 500°C for 30 minutes, stir evenly and then cast to obtain a Sn-P master alloy;
[0026] 2. Based on the total mass of 100%, weigh the Sn-P master alloy with the amount of P accounting for 0.05%, then weigh Cu 0.7%, P 0.05%, Bi 1%, the balance is Sn, and the total weight is 100 gram. Put the ingredients into a graphite crucible, cover it with the above-mentioned protective molten salt, place the crucible in an induction furnace, keep it warm at 500°C for 30 minutes, stir it evenly, and cast it into an ingot to obtain the required solder alloy.
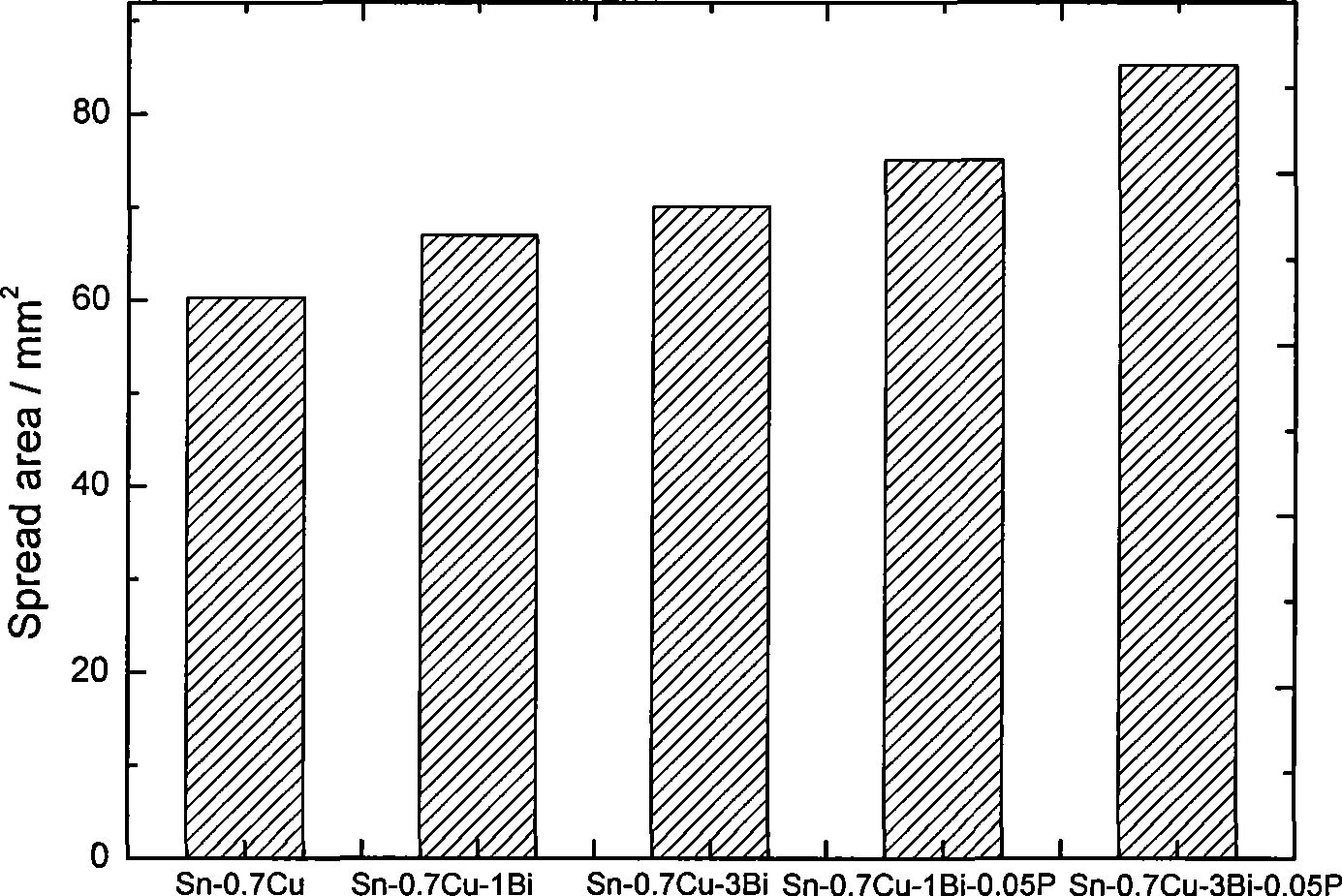
[0027] A series of Sn-0.7Cu-based alloys with different Bi content and P content were melted according to the above method for wettability and melting point measurement. The wettability...
Embodiment 3
[0029] 1. Take P 4% and Sn 96% according to the mass ratio, which is 50 grams in total, then put the two into a graphite crucible, and cover the above-mentioned molten salt on it, place the crucible in an induction furnace, Keep the temperature at 400°C for 60 minutes, stir evenly and then cast to obtain the Sn-P master alloy;
[0030] 2. Based on the total mass of 100%, weigh the Sn-P master alloy with the amount of P accounting for 0.05%, and then weigh Cu 0.7%, P0.05%, Bi1%, Zn1%, the balance is Sn, the total The weight is 100 grams. Put the ingredients into a graphite crucible, cover it with the above-mentioned protective molten salt, place the crucible in an induction furnace, keep it warm at 500°C for 30 minutes, stir it evenly, and cast it into an ingot to obtain the required solder alloy.
[0031] A series of Sn-0.7Cu-1Bi-1Zn alloys with P content were welded according to the above method for wettability measurement. The wettability of each alloy to Cu is characterized...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com