Method for producing nano-fibre bracket material with levorotation polylactic acid as base material
A technology of L-polylactic acid and nanofibers, applied in the direction of scaffolds, fiber types, fiber treatment, etc., can solve the problems of long degradation time, degradation products easily cause tissue inflammation, and cannot be widely used, and achieve simple preparation process and excellent biophase Capacitance and mechanical properties, the effect of excellent tissue compatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] 1. Preparation of spinning solution: Dissolve L-polylactic acid (PLLA) in a mixed solution of dichloromethane and dimethylformamide (volume ratio = 3: 1), magnetically stir for two hours and centrifuge at 5000 rap / min to obtain By removing the air bubbles in the solution, a uniform and stable spinning solution can be obtained.
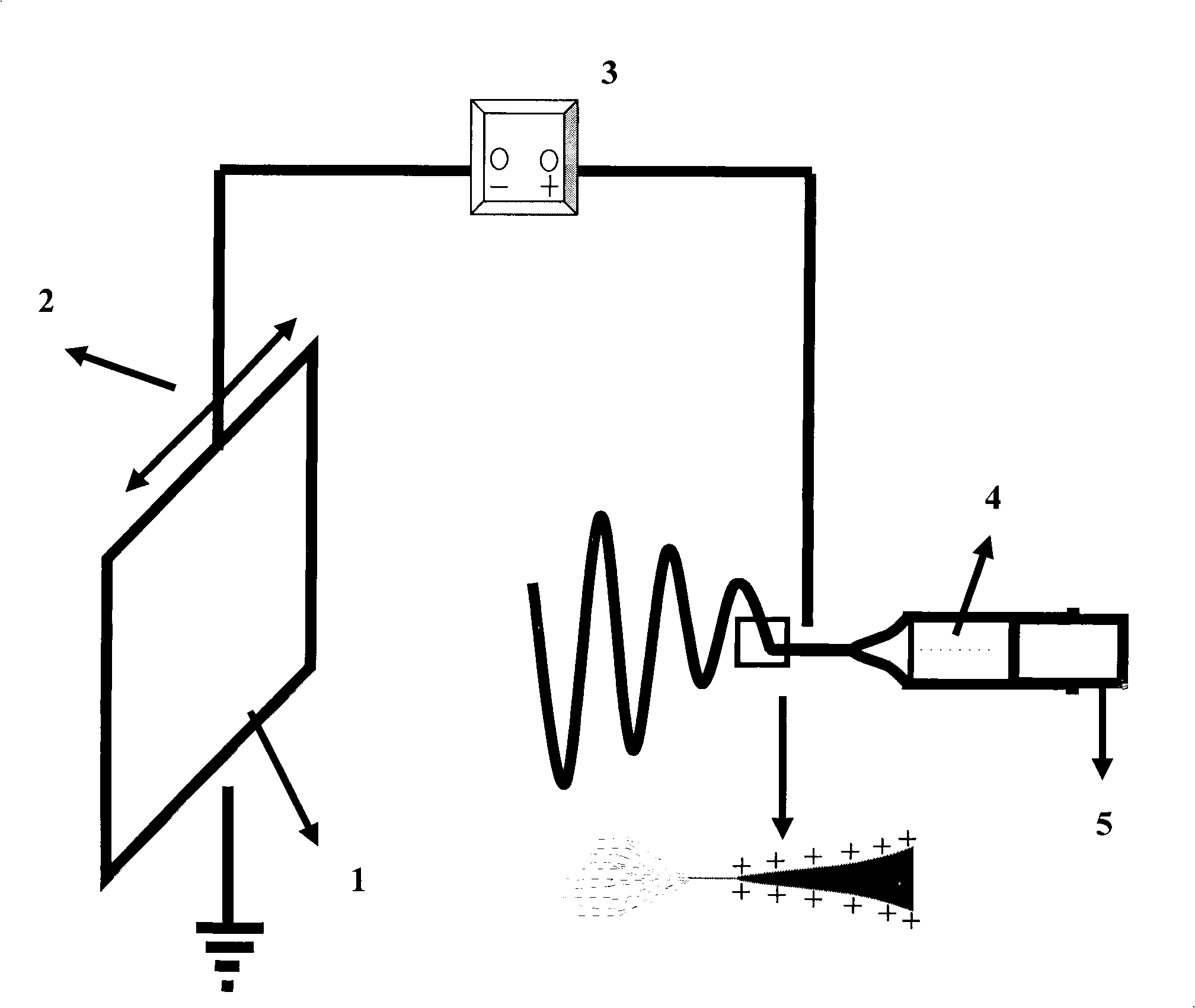
[0024] 2. Preparation of nanofibrous membrane: as figure 1 As shown, the above-mentioned L-polylactic acid solution is placed in the driving device 5, in the glass syringe of 5ml (No. For the polylactic acid solution, the flat receiver 1 is used as a collection device for nanofibers, and the distance between the collection device and the needle is kept between 15-20 cm. The prepared L-polylactic acid nano-super ordered fiber membrane was stored at room temperature and dried under vacuum for future use.
[0025] 3. Modification of nanofibrous scaffold materials: the nano-super ordered fiber material obtained in step 2 is modified by low-tempera...
Embodiment 2
[0027] 1. As in step 1 in Example 1.
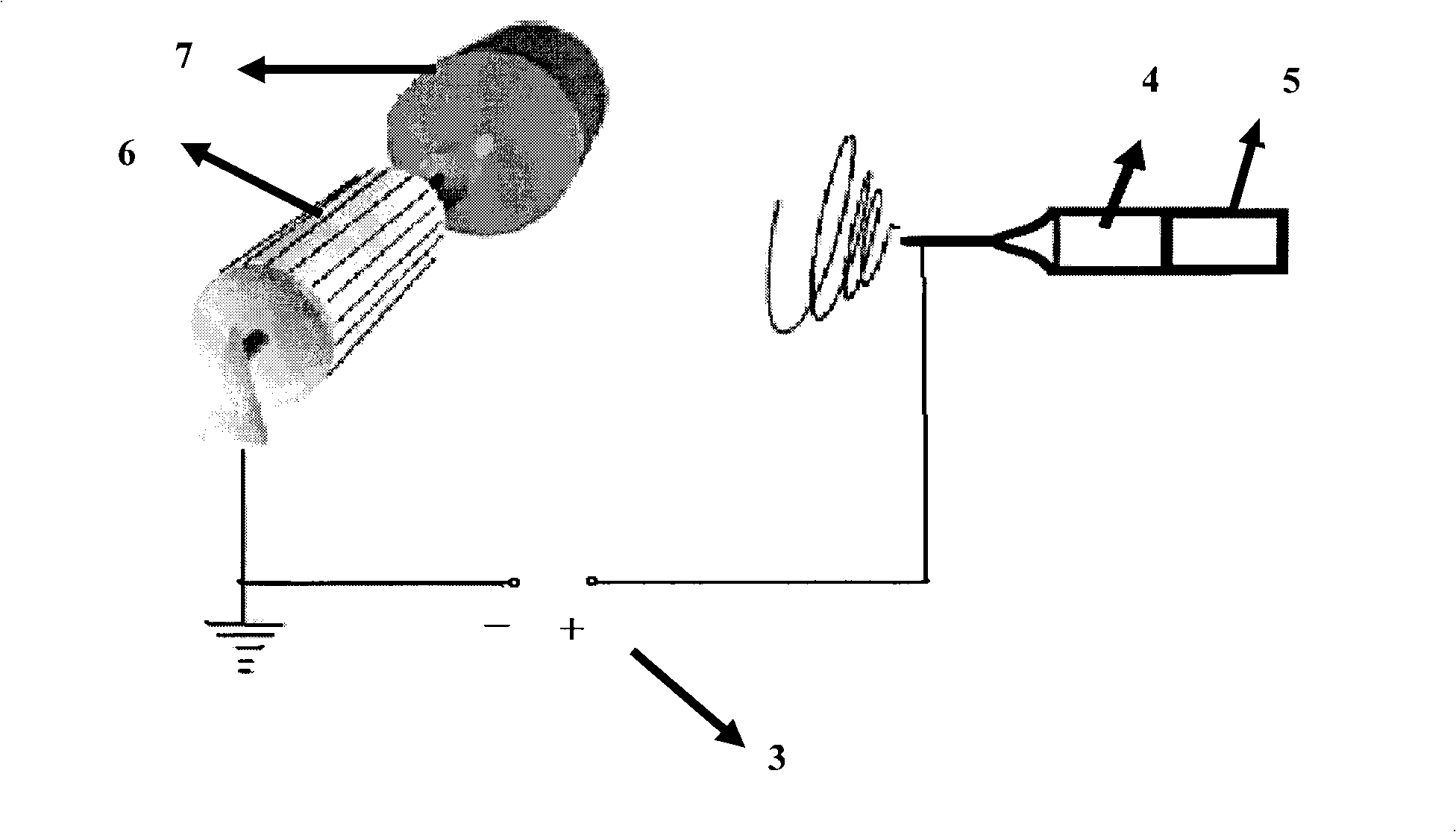
[0028] 2. Preparation of nanofibrous membrane: as figure 2 As shown, the above-mentioned L-polylactic acid solution was placed in a 5ml glass syringe (No. The high-speed rotation of motor 7, insulated high-speed (wire) drum 6 receiver 1000r / min is used as the collecting device of nanofiber, and the distance between collecting device and needle head remains between 15-20cm. The prepared L-polylactic acid nano-super ordered fiber membrane was stored at room temperature and dried under vacuum for future use.
[0029] 3. Modification of nanofibrous scaffold material: as step 3 in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0031] 1. As in step 1 in Example 1.
[0032] 2. Preparation of nanofibrous membrane: as figure 2 As shown, the above-mentioned L-polylactic acid solution was placed in a 5ml glass syringe (No. The high-speed rotation of the motor 7, the insulating high-speed (wire) drum 6 receiver is used as the collecting device of nanofiber at 2000r / min, and the distance between the collecting device and the needle remains between 15-20cm. The prepared L-polylactic acid nano-super ordered fiber membrane was stored at room temperature and dried under vacuum for future use.
[0033] 3. Modification of nanofibrous scaffold material: as step 3 in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| porosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com