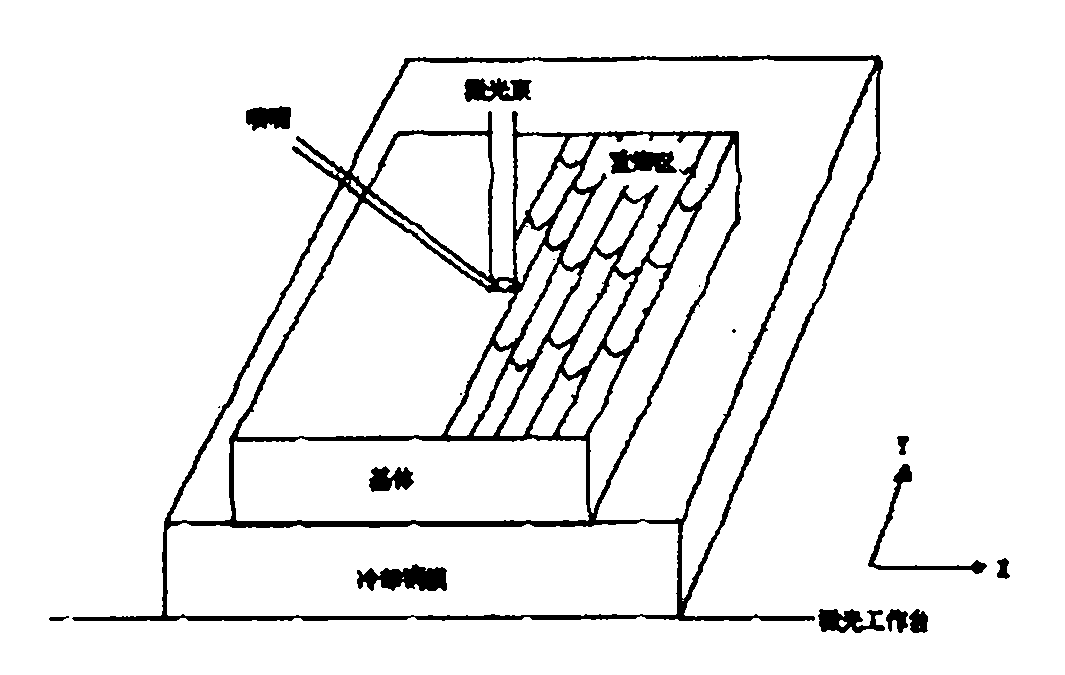
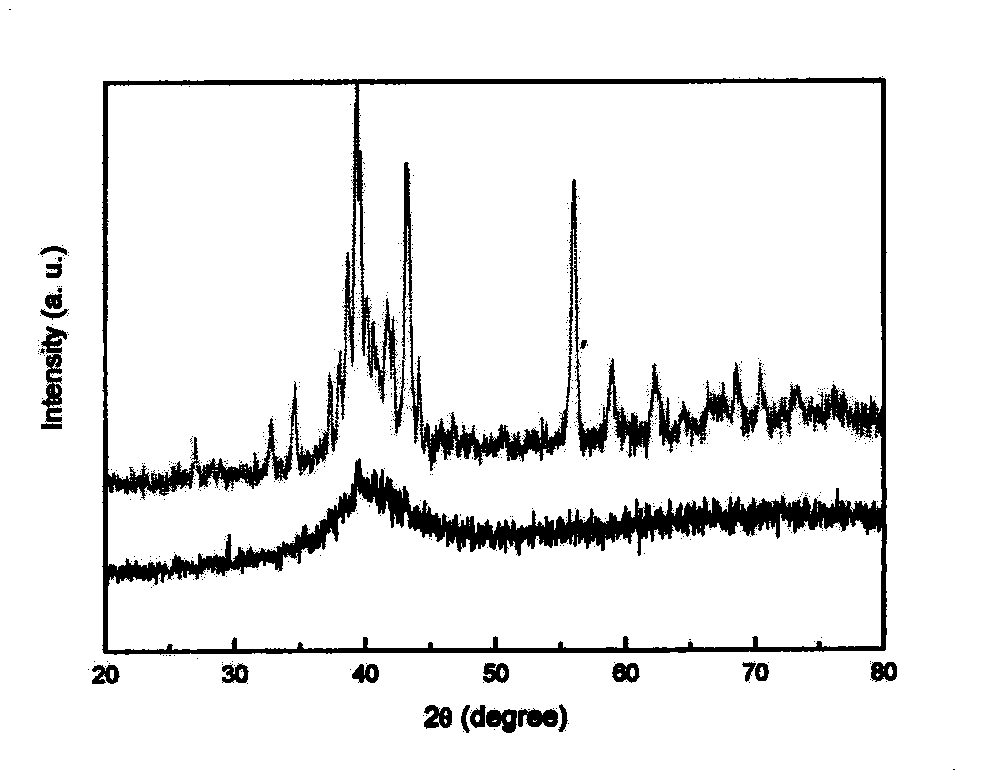
Method for preparing high-hardness Cu base amorphous alloy coating by using laser surface treatment
A technology of amorphous alloy and amorphous layer, applied in metal material coating process, coating and other directions, can solve the problems of slow deposition speed, complex processing procedure, poor repeatability, etc., to achieve simple cooling system, high energy density, processing short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0034] Example 1: Preparation of 120 μm thick Cu by laser surface treatment 60 Zr 30 Ti 10 Amorphous Alloy Coating
[0035] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0036] The first step: Cu 60 Zr 30 Ti 10 Alloy Preparation
[0037] Select Cu, Zr, and Ti elements with a purity of 99.9% as raw materials, and mix them according to atomic percentages. Place the prepared raw materials in a vacuum electric arc furnace, and vacuumize to 5×10 -3Pa, filled with argon protective gas with a pressure of 0.05MPa; adjust the current to 200A, smelt 4 times and take it out with the furnace cooling to obtain uniform Cu 60 Zr 30 Ti 10 alloy.
[0038] Step 2: Sample Preparation
[0039] The prepared alloy was cut into a sample of 15mm×10mm×2mm, and the surface was treated with sandpaper and acetone to increase the laser absorption rate of the material surface.
[0040] Step Three: Laser Treatment
[0041] The sample was placed on the copper mold of the workbench, and the prot...
example 2
[0045] Example 2: Preparation of 185 μm thick Cu by laser surface treatment 60 Zr 30 Ti 10 Amorphous Alloy Coating
[0046] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0047] The first step: Cu 60 Zr 30 Ti 10 Alloy Preparation
[0048] Select Cu, Zr, and Ti elements with a purity of 99.9% as raw materials, and mix them according to atomic percentages. Place the prepared raw materials in a vacuum electric arc furnace, and vacuumize to 5×10 -3 Pa, fill in the argon protective gas with a pressure of 0.01MPa; adjust the current to 220A, smelt 5 times and take it out with the furnace cooling to obtain uniform Cu 60 Zr 30 Ti 10 alloy.
[0049] Step 2: Sample Preparation
[0050] The prepared alloy was cut into a sample of 15mm×10mm×2mm, and the surface was treated with sandpaper and acetone to increase the laser absorption rate of the material surface.
[0051] Step Three: Laser Treatment
[0052] The sample was placed on the copper mold of the workbench, and the pro...
example 3
[0057] Example 3: Preparation of 135 μm thick Cu by laser surface treatment 50 Zr 10 Ti 40 Amorphous Alloy Coating
[0058] The specific operation steps are as follows:
[0059] The first step: Cu 50 Zr 10 Ti 40 Alloy Preparation
[0060] Select Cu, Zr, and Ti elements with a purity of 99.9% as raw materials, and mix the ingredients according to atomic percentages. Place the prepared raw materials in a vacuum electric arc furnace, and repeatedly smelt them in a high-purity argon atmosphere, and vacuumize to 4×10 -3 Pa, filled with argon protective gas with a pressure of 0.06MPa; adjust the current to 250A, smelt 4 times and take it out with the furnace cooling to obtain uniform Cu 50 Zr 10 Ti 40 alloy.
[0061] Step 2: Sample Preparation
[0062] The prepared alloy was cut into a sample of 15mm×10mm×2mm, and the surface was treated with sandpaper and acetone to increase the laser absorption rate of the material surface.
[0063] Step Three: Laser Treatment
[0064...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| microhardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| microhardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com