Method of bonding resins by light irradiation and process for producing resin article
A technology of bonding method and manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of resin bonding based on light irradiation and the manufacture of resin parts, can solve flow path blockage, difficult microchip manufacturing method, difficulty in coping with narrow flow path width and flow path pattern Complications and other problems, to achieve the effect of suppressing deformation, suppressing the blockage of the flow path, and facilitating the narrowing of the flow path width
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
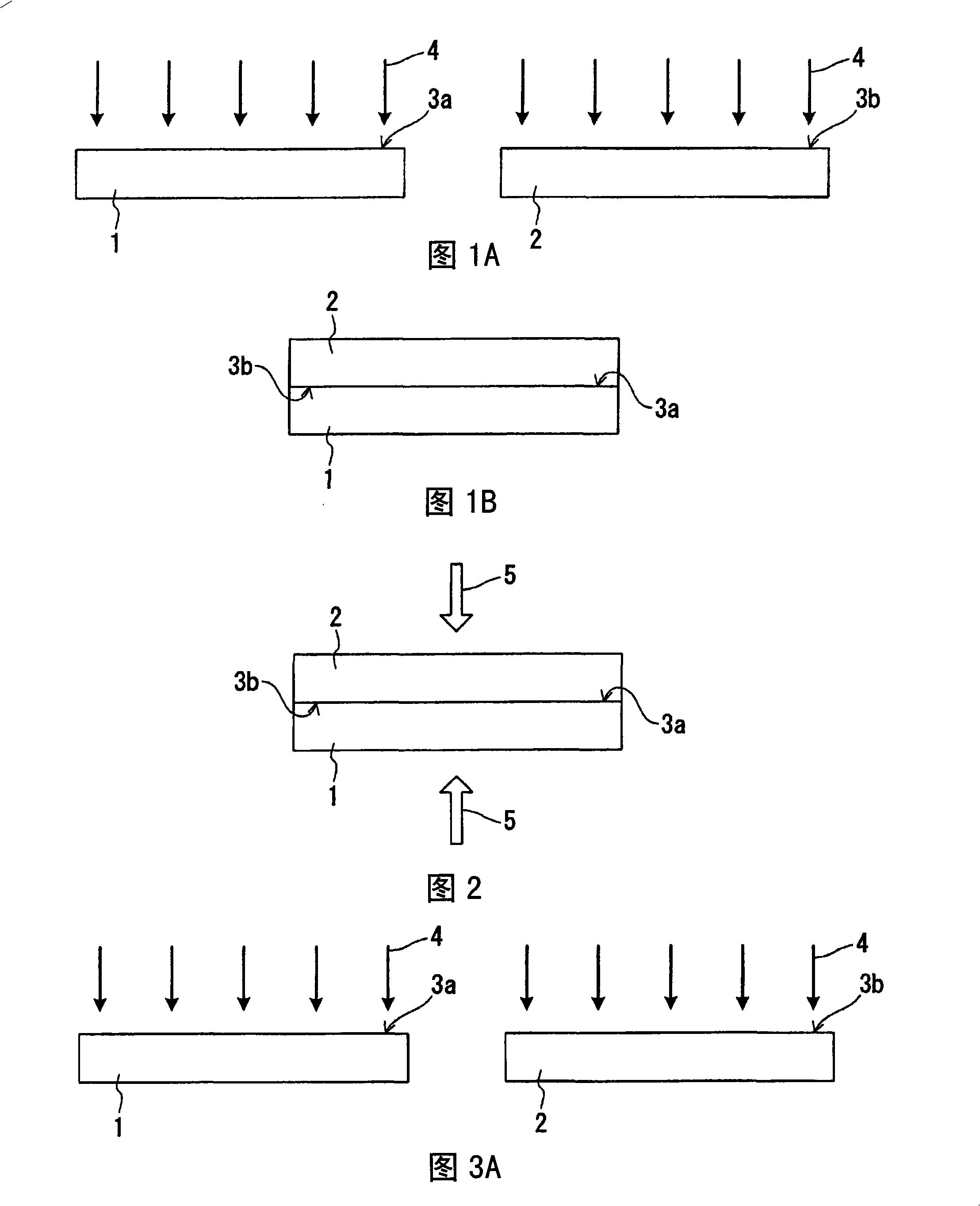
[0075] Using a Xe excimer lamp (manufactured by Usio Electric, UER20-172A), each of a pair of resin substrates (70mm×20mm, thickness 2mm) composed of a cycloolefin polymer (ZEONEX330R manufactured by Nippon Zeon Co., Ltd., glass transition temperature 123°C) The surface is irradiated with ultraviolet light (wavelength 172nm). The irradiation of ultraviolet light is carried out in the atmosphere, the distance between the lamp and the surface of the substrate is 5mm, and the irradiation intensity is 10mW / cm 2 , The irradiation time is 10 minutes. The irradiated surface of ultraviolet light is the whole of one main surface of each substrate.
[0076] When X-ray excitation photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurement was performed on the substrate surface (irradiated surface) before and after ultraviolet light irradiation, it was found that the signal derived from oxygen in the Ols spectrum increased significantly after irradiation compared with before ultraviolet light irradiati...
Embodiment 2
[0083] In the same manner as in Example 1, ultraviolet light was irradiated to the respective surfaces of a pair of resin substrates made of a cycloolefin polymer used in Example 1.
[0084] Next, N-(2-aminoethyl)-3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (AEAPS), which is a kind of aminosilane as a silane coupling agent, is applied to the irradiated surface of one resin substrate (resin substrate A). . On the other hand, 3-glycidyl ether aminopropyl trimethoxysilane (GPS) having an epoxy group as a terminal group was applied to the irradiated surface of another resin substrate (resin substrate B). The following formulas (1) and (2) represent the structural formulas of AEAPS and GPS.
[0085] [chemical formula 1]
[0086]
[0087] [chemical formula 2]
[0088]
[0089] Resin substrates A and B surface-treated with a silane coupling agent are opposed in such a way that the respective irradiated surfaces (surface-treated surfaces) are in contact with each other, and a pressure of 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com