Application of rice OsRPA1a gene in fertility control
A gene and rice technology, applied in the field of rice hybrid seed production and fertility control, can solve problems such as non-detection, and achieve the effect of improving product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
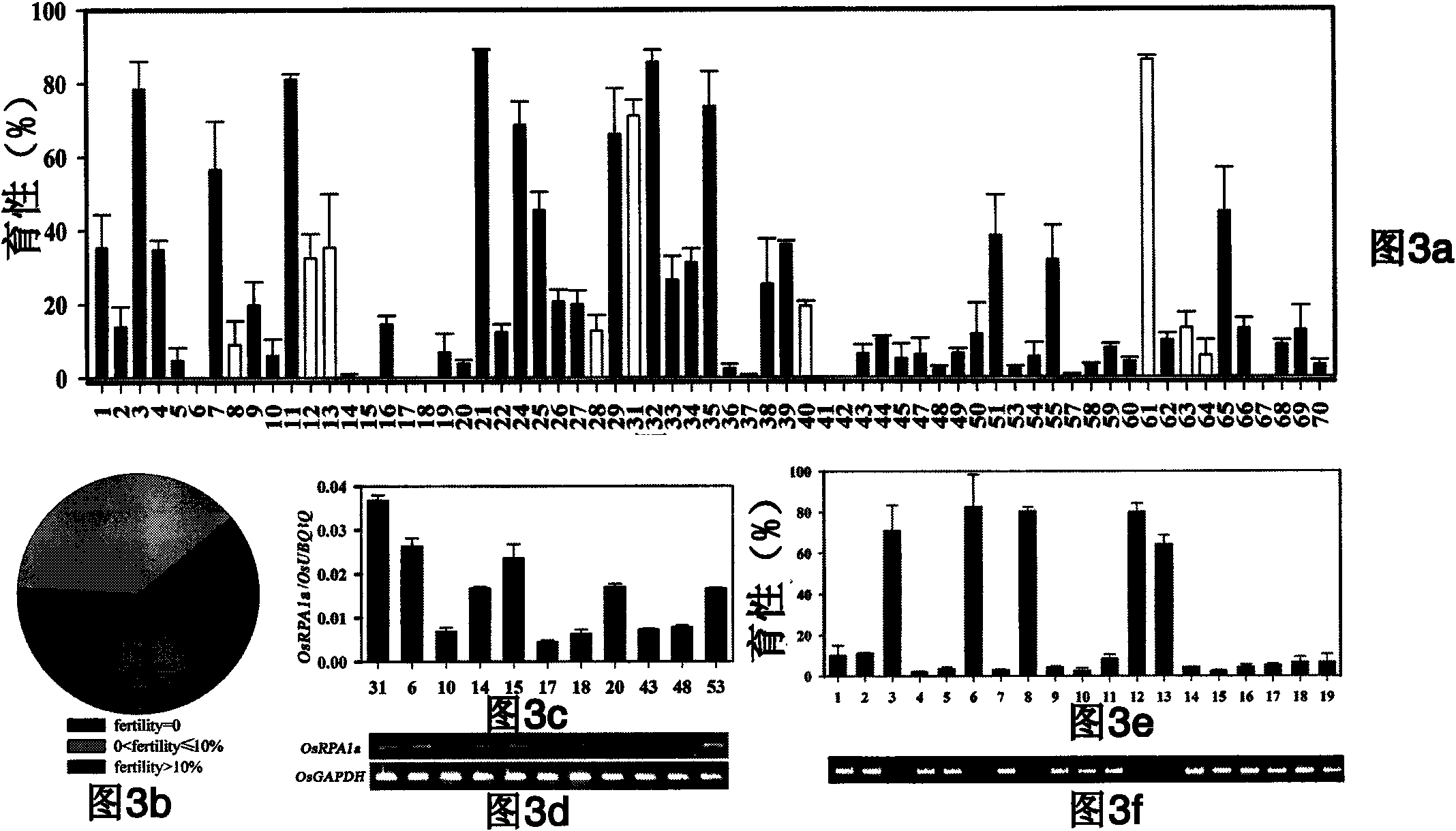
[0061] Example 1: Screening and Character Identification of Mutants
[0062] mutant library T 0 After the generation plants were harvested separately, the next generation, namely T, was planted under normal cultivation conditions. 1 In the second generation, each material was planted in 2 rows, with 10 plants in each row, and a total of 20 plants were planted at a planting density of 15×24 cm. The phenotypes of the mutants were recorded in the field during the entire growth period of rice, and the phenotypes of the mutant plants in the same family were consistent and conformed to the typical 3:1 segregation. The DNA of each individual plant was extracted in time for PCR positive detection. Families with positive PCR results for all mutants were used as materials for follow-up studies. The primers for positive detection by PCR are located on the T-DNA segment. A pair of primers are GV-F: 5-ggc atc ggt aaa cat ctg ct-3, GV-R: 5-gcc tca aga agc tca agt gc-3, The size of the PC...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Example 2: Isolation of mutant T-DNA flanking rice genome sequence
[0068] For the mutation family obtained in Example 1, this example utilizes the TAIL-PCR method (refer to Zhang et al., Non-random distribution of T-DNA insertions at various levels of the genome hierarchy as revealed by analyzing 13,804 T-DNA flanking sequences from an enhancer-trap mutant library. 2007, Plant J, 49: 947-959 method and steps) isolated the flanking sequence of the mutant T-DNA insertion site.
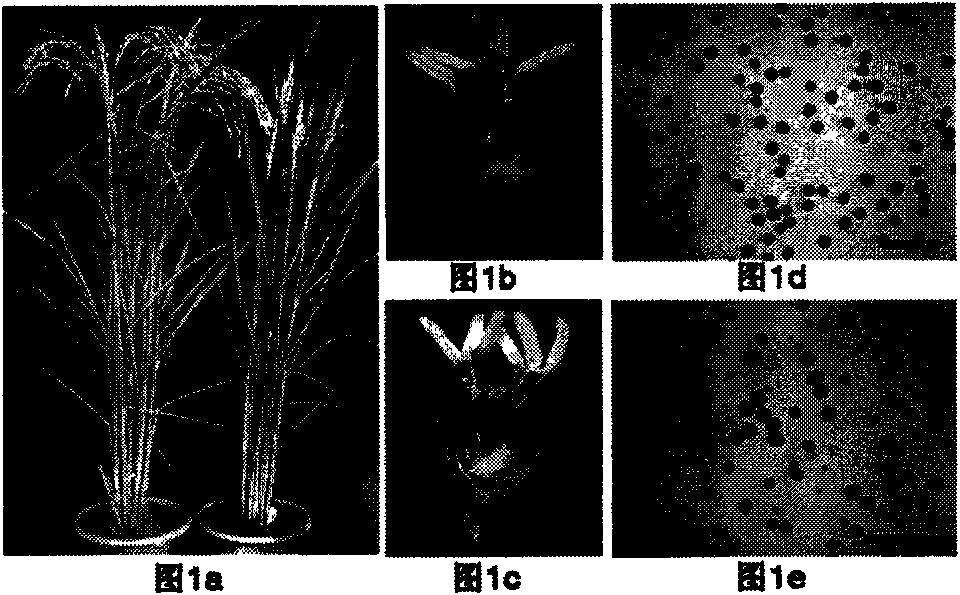
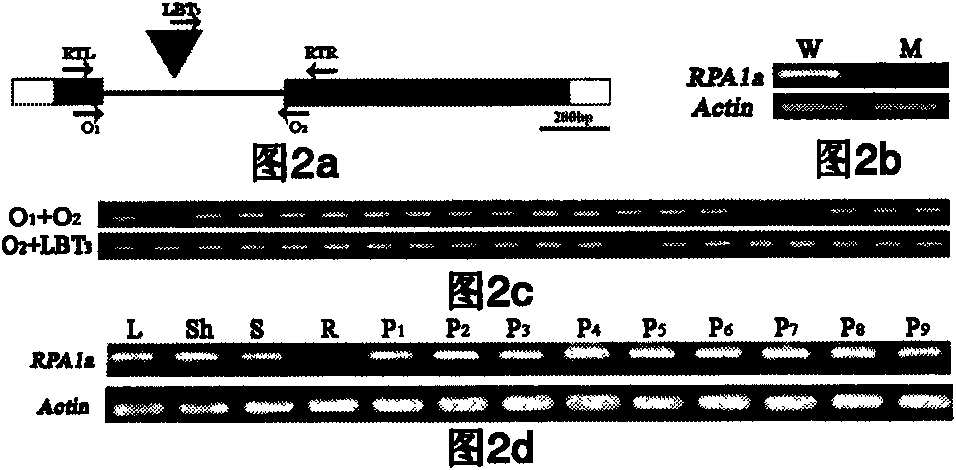
[0069] Through this example, the flanking sequence of the insertion site of the family's T-DNA was obtained, and the balast search tool provided on the Rice Genome Annotation Project website ( http: / / rice.plantbiology.msu.edu / blast.shtml ), the isolated flanking sequence was located in the intron of the Os02g53680 gene of rice chromosome 2. Such as figure 2 As shown in a, on the KOME website ( http: / / cdna01.dna.affrc.go.jp / cDNA / ) has a full-length cDNA J033031B02 corresponding to it. The...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3: Co-segregation verification of T-DNA and mutant traits
[0073] According to the mutant Osrpala family T-DNA localization result that embodiment 2 obtains, design genome primer O 1 (5'-agc gag tac gtc atcaac ga-3') and O 2 (5'-ccg aaa caa gaa ctt cca gg-3') with primer LBT on the left border of T-DNA 3 (5'-cca gta cta aaa tcc aga tccccc gaa t-3,) paired amplification to verify the genotypes of each individual plant in the T1 and T2 generations, such as figure 2 as shown in c. Corresponding genotype and phenotype to see if co-segregation is consistent. Primer O 1 +O 2 The product size is about 1.1kb, primer O 2 +LBT 3 The size of the product is about 0.9kb. Since the fragment of T-DNA transferred into the genome is about 10kb, when the T-DNA is inserted into the O 1 with O 2 Between, it cannot be amplified because the fragment is too large. Therefore, when a single plant is respectively used with primer O 1 +O 2 and primer O 2 +LBT 3 There are t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com