Method for screening new drug for lowering cholesterol based on analysis of change of NPC1L1 protein subcellular localization
A technology for lowering cholesterol and cholesterol, applied in the field of cell biology and pharmacology, can solve the problems of drug research and development limitations, unclear drug mechanism of cholesterol, unclear mechanism of cholesterol absorption, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0198] Example 1 Cholesterol regulates the transport of NPC1L1 protein between endocytic recycling body (ERC) and plasma membrane
[0199] The pEGFP-N1 vector containing the NPC1L1 protein coding region was transfected into the rat liver cell line CRL1601 to obtain a stable expression strain of NPC1L1-EGFP, which was named CRL1601 / NPC1L1-EGFP.
[0200] The results of conventional Western Blot experiments showed that the expression level of NPC1L1-EGFP in the stable expression strain was similar to the expression level of endogenous NPC1L1 protein in some human liver cell lines (HepG2, huh7 and L02). Therefore, the inventors used this cell line to study the localization of NPC1L1 protein.
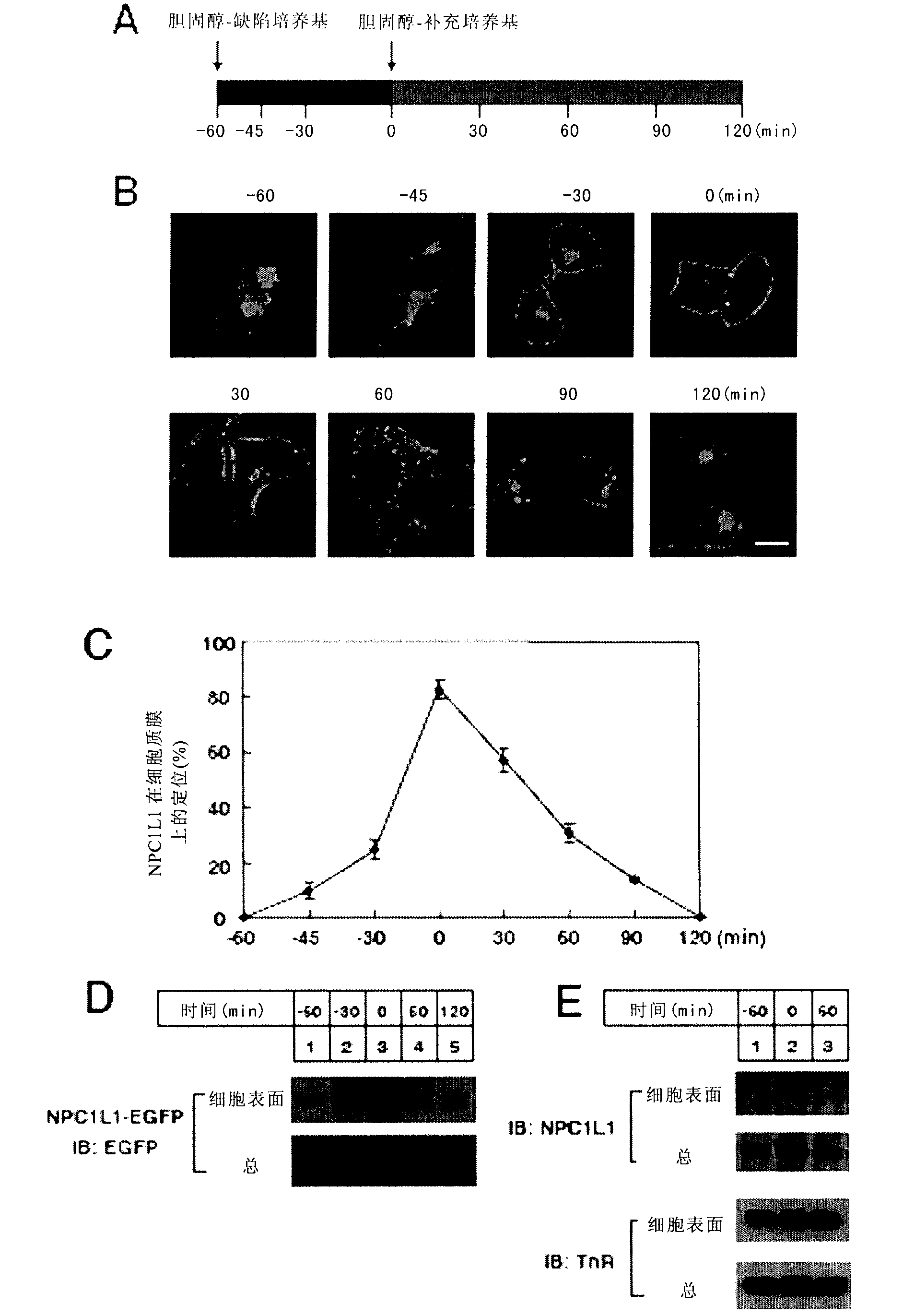
[0201] For the process of processing CRL1601 / NPC1L1-EGFP cells, see figure 1A, Cholesterol (Chol)-deficient medium was used to culture cells at -60 min, the aforementioned medium was removed at 0 min, and cells were cultured with cholesterol (Chol)-supplemented medium until 120 min. That i...
Embodiment 2
[0205] Example 2 NPC1L1 protein is necessary for the absorption of free cholesterol
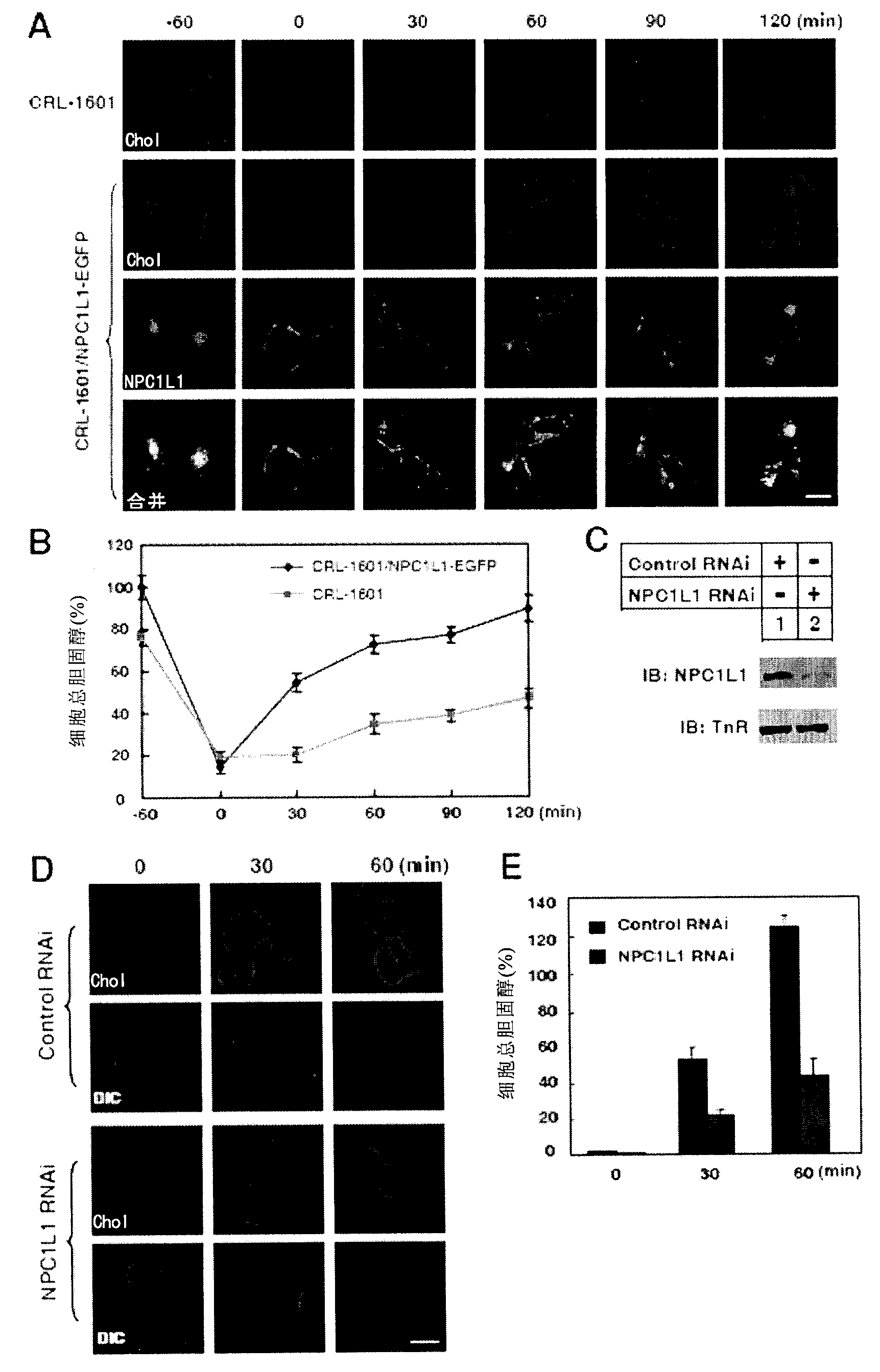
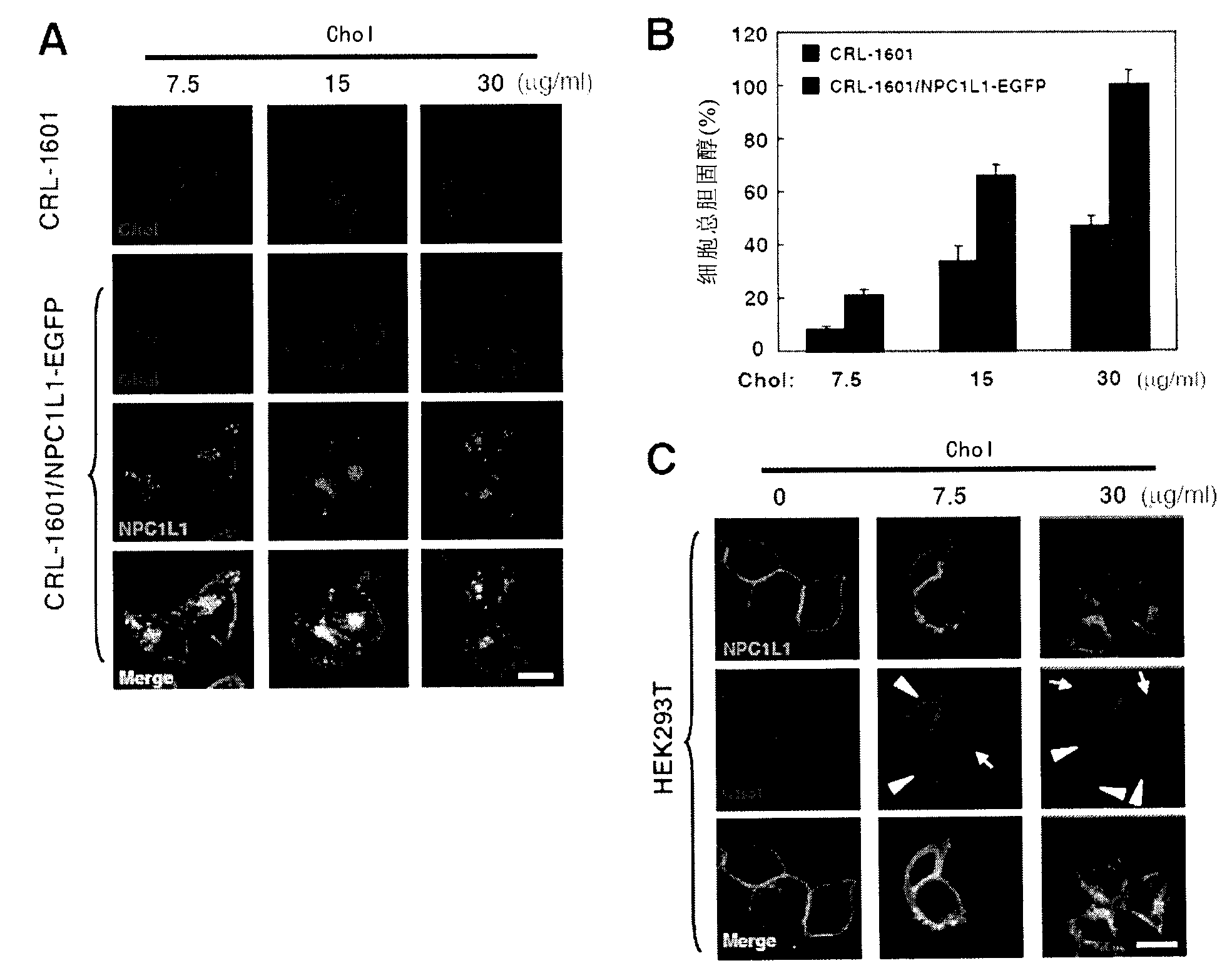
[0206] Cellular uptake of cholesterol from low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is achieved through endocytosis of LDL receptors. The endocytosis of NPC1L1 protein suggests that NPC1L1 protein may mediate cholesterol absorption through a similar process. To test this idea, the inventors used Filipin to stain intracellular cholesterol. CRL-1601 and CRL-1601 / NPC1L1-EGFP cells as figure 1 Treatments shown in A, fixed at different time points, stained with Filipin, and visualized with two-photon confocal fluorescence localization. The result is as figure 2 As shown in A, after the cells were treated with cyclodextrin (CDX) to reduce cholesterol, the signal of Filipin was hardly seen, indicating that the amount of cholesterol in the cells was very low; at the same time, the NPC1L1 protein was also localized in the plasma membrane (time point: 0min). When the cells were treated with the cholesterol-...
Embodiment 3
[0210] Example 3 Deletion of clathrin / AP2 reduces endocytosis and cholesterol uptake of NPC1L1 protein
[0211] In order to find the factors involved in the endocytosis of NPC1L1 protein, the present inventors performed a large number of co-immunoprecipitation. Bands specific for the NPC1L1 protein were identified using tandem mass spectrometry. One of these proteins is the μ2 subunit of the AP2 complex. The AP2 complex is composed of α, β2, μ2 and σ2, etc. It is known that its function is to bind proteins into clathrin-coated vesicles to participate in endocytosis. Co-immunoprecipitation confirmed the results of mass spectrometry, indicating that NPC1L1-EGFP, μ2 and CHC are in the same complex, see Figure 4 .
[0212] right Figure 4 The mass spectrometric identification of each NPC1L1 protein-binding protein (Band1-7) in A is shown in Table 1, where Band5 is the μ2 subunit of the AP2 complex.
[0213] Table 1
[0214]
[0215] Next, the inventors used the RNAi meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com