Method for etching semiconductor structure and method for forming metal interconnection layer
A metal interconnection layer and semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of rough trench line edges, insufficient protection of trench edges, and inability to effectively protect the underlying structure, etc., to achieve Effects of improving line edge roughness and improving breakdown voltage characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
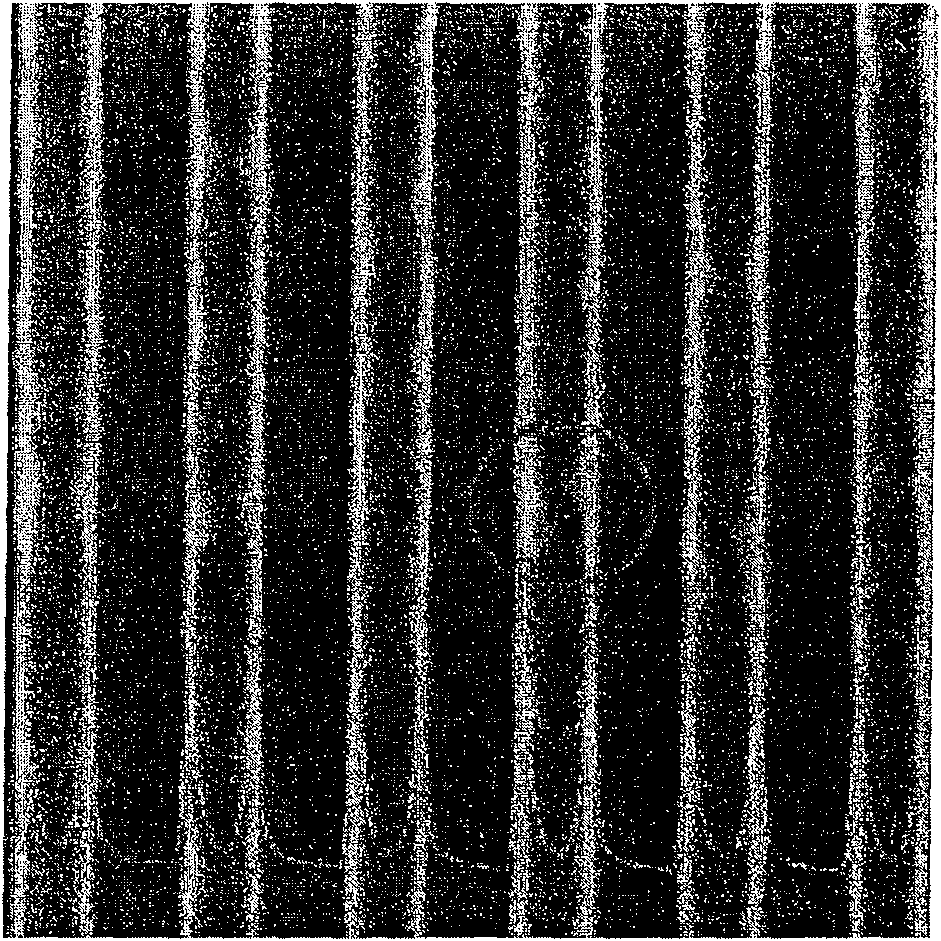
[0060] This example combines the attached Figure 3 to Figure 8 , taking the copper interconnection process as an example, describe in detail the trenches formed by etching the semiconductor structure provided by the present invention for filling the first layer of metal interconnection layer, and describe in detail the metal interconnection provided by the present invention Layer Formation Method Form the first layer of metal interconnection layer.
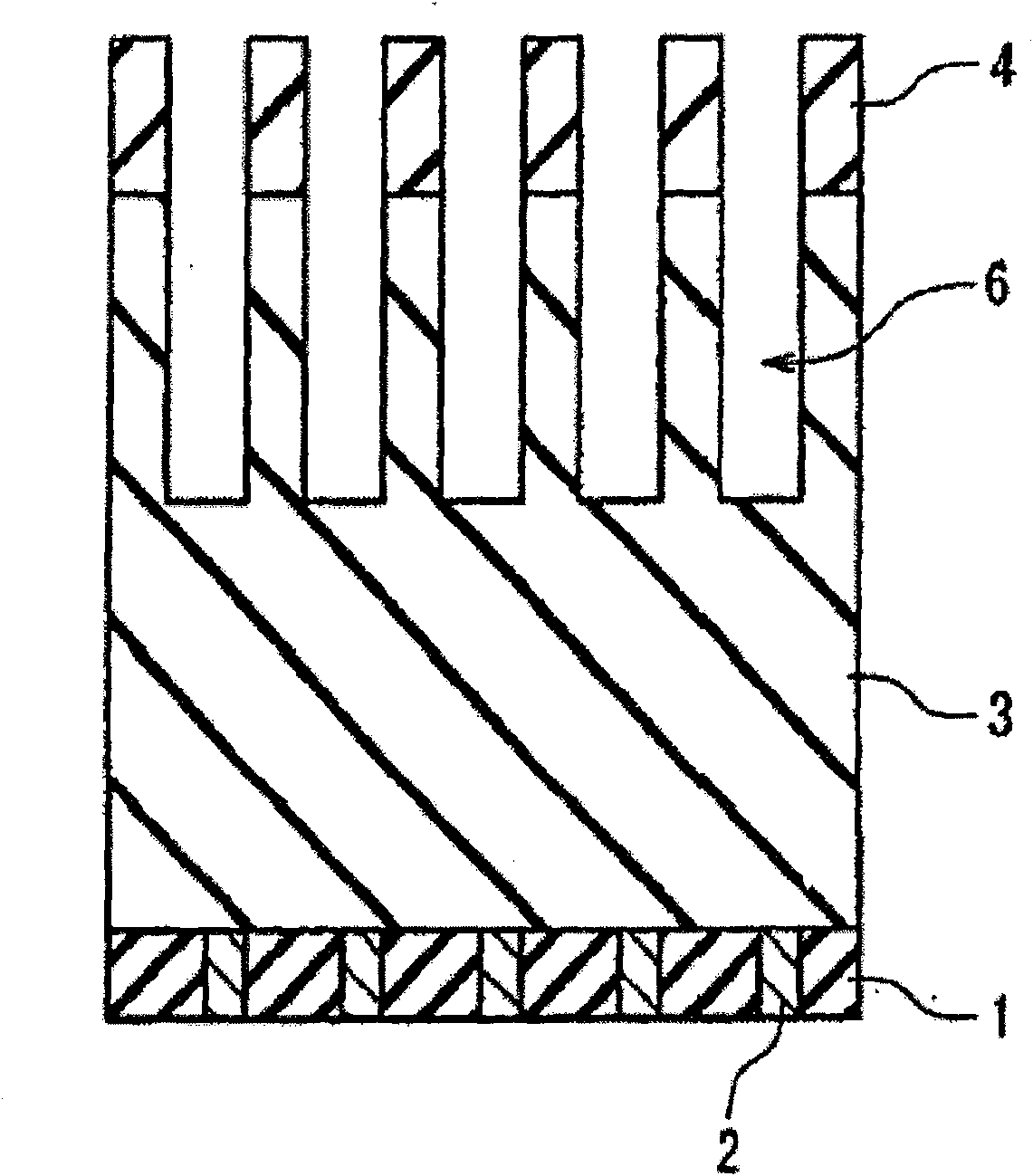
[0061] refer to image 3 As shown, a substrate 100 with a semiconductor device is provided, an active region (not shown) and a metal tungsten plug (not shown) on the active region are provided in the substrate 100, and the metal tungsten plug is used to make the described The active region is electrically connected to the first metal interconnection layer;
[0062] An etch stop layer 105 is formed on the substrate 100 to determine the end point of the etching process and avoid over-etching the tungsten plug in the lower substra...
Embodiment 2
[0080] This embodiment combines the attached Figure 13 to Figure 15 Describe in detail that the gate structure is etched by using the semiconductor structure etching method provided by the technical solution of the present invention.
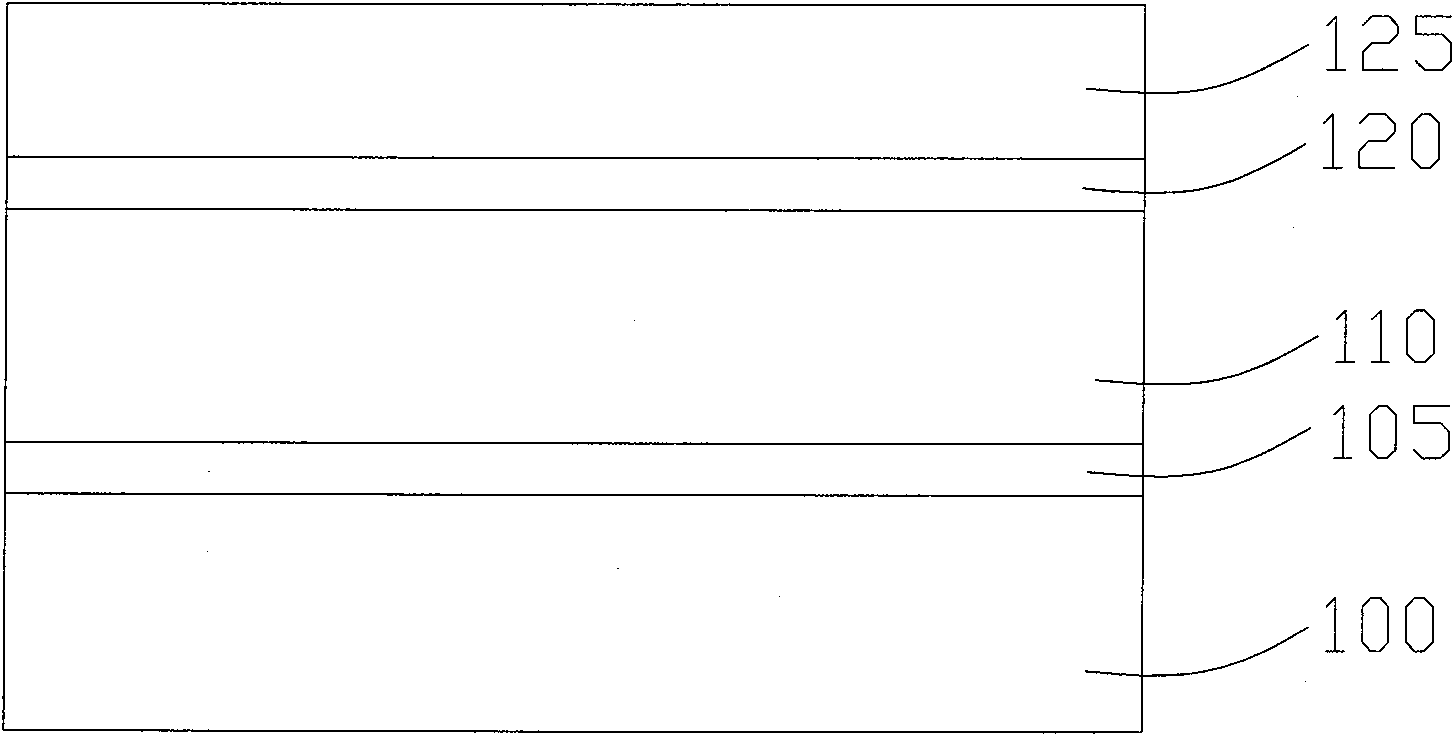
[0081] refer to Figure 13 As shown, a semiconductor substrate 200 having an active region 203 and a shallow trench isolation structure (not shown in the figure) is provided, and a gate dielectric layer 205 is formed on the active region 203. The material of the gate dielectric layer 205 includes but Not limited to silicon oxide, it is prepared by thermal oxidation in an oxidation furnace.
[0082] A gate layer 210 is formed on the gate dielectric layer 205. The material of the gate layer 210 is doped polysilicon. The polysilicon is prepared by low pressure chemical vapor deposition (LPCVD) through silane decomposition reaction, and then doped with polysilicon.
[0083] A bottom anti-reflective coating 215 (Bottom Anti-reflective Coating, BAR...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com