Escherichia coli detection method based on time-resolved fluorescence method and DNA hybridization
A time-resolved fluorescence technology for Escherichia coli, which is applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve problems such as general constraints, cumbersome operation, and sensitivity limitations, and achieve the effects of reducing the probability of DNA degradation, simplifying the experimental process, and reducing pollutants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
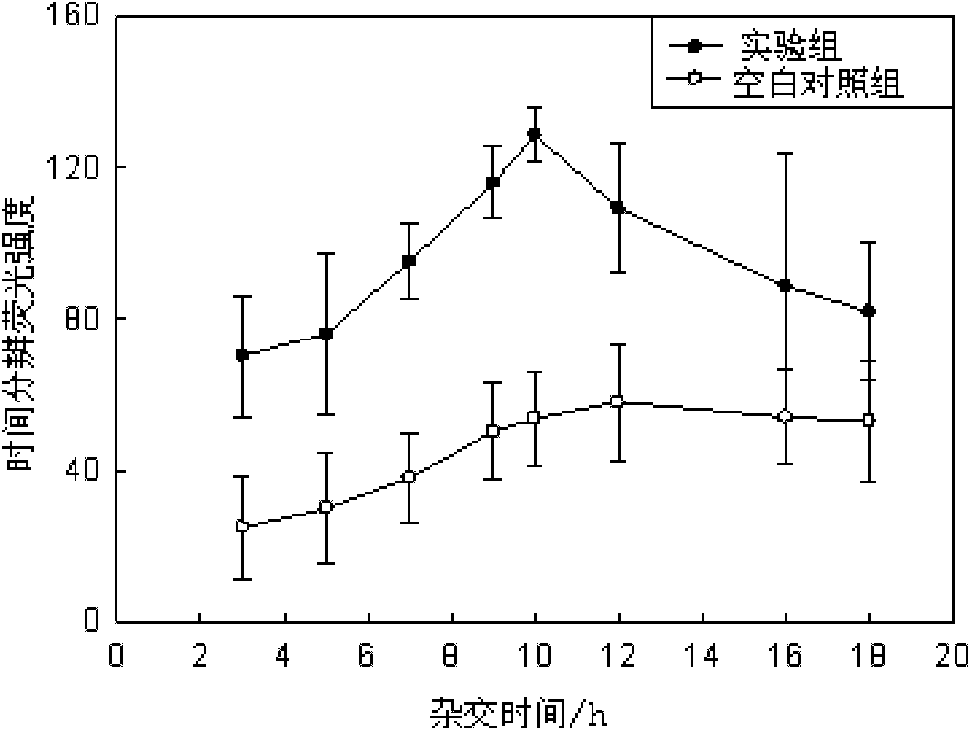
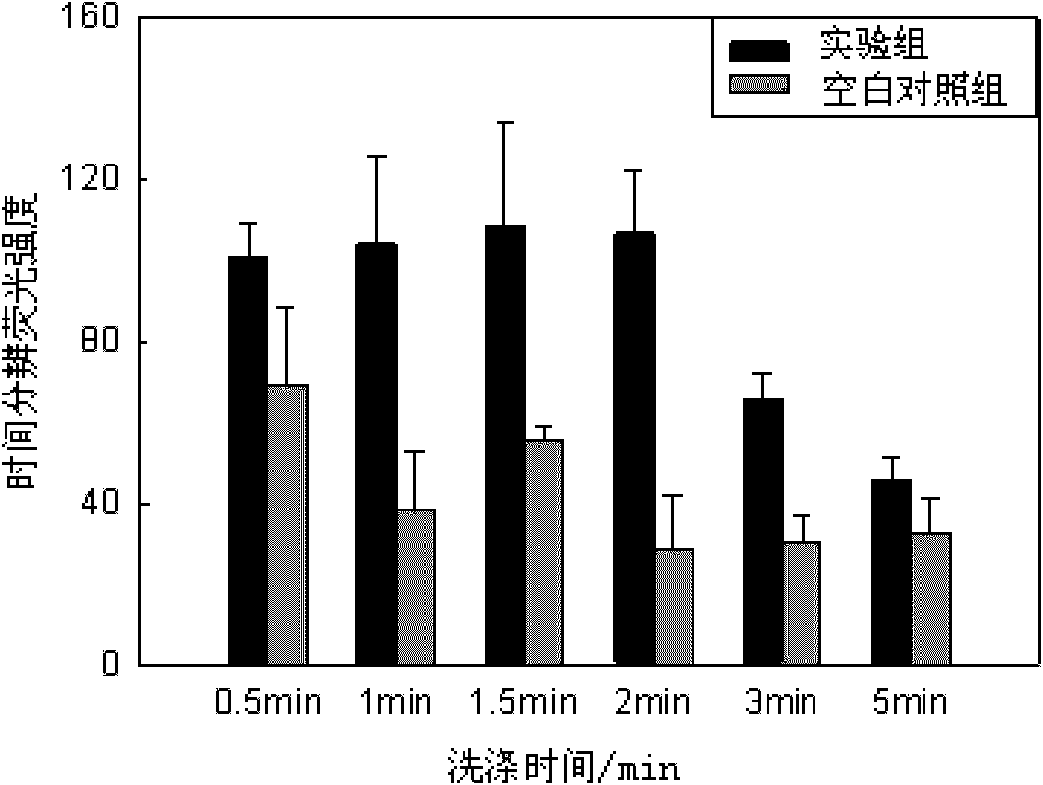
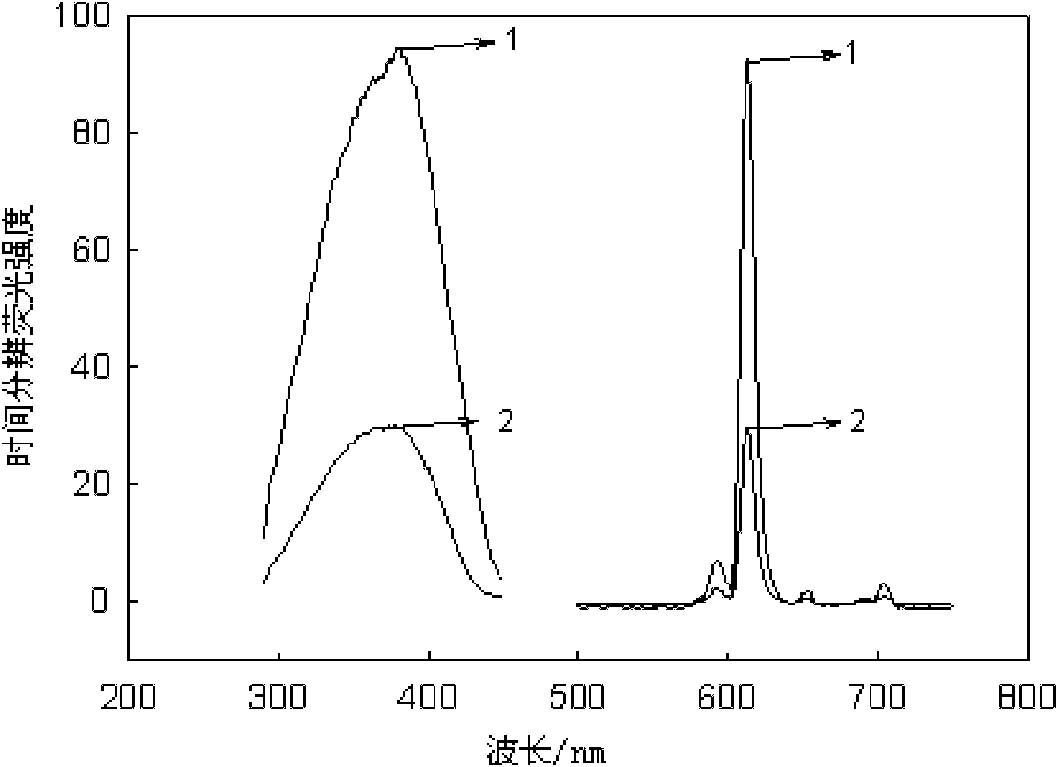
[0036] The following is intended to illustrate the present invention rather than to further limit the present invention, and the present invention can be implemented in any manner described in the summary of the present invention.
[0037] 1. Design of capture probes and recognition probes
[0038] The DNA probe sequence of the present invention is based on published patents (Yao Zhijian, Yu Yong, Ma Liren, etc., gene chips, preparation methods, and test kits for detecting various common bacterial pathogens, Chinese patent, public date October 3, 2007, public number CN101045945A ) in Escherichia coli 16S rRNA gene conservation sequence screening.
[0039] After literature search and sequence comparison in the National Center for Biological Information (NCBI) database, the target DNA sequence that is conserved within a species and specific among species is 5'-CGT CCG ATC ACC TGC GTC AAT GTA ATG TTC TGC GAC GCTCAC ACC GAT AC-3'. DNA sequence complementary to target sequence: 5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com