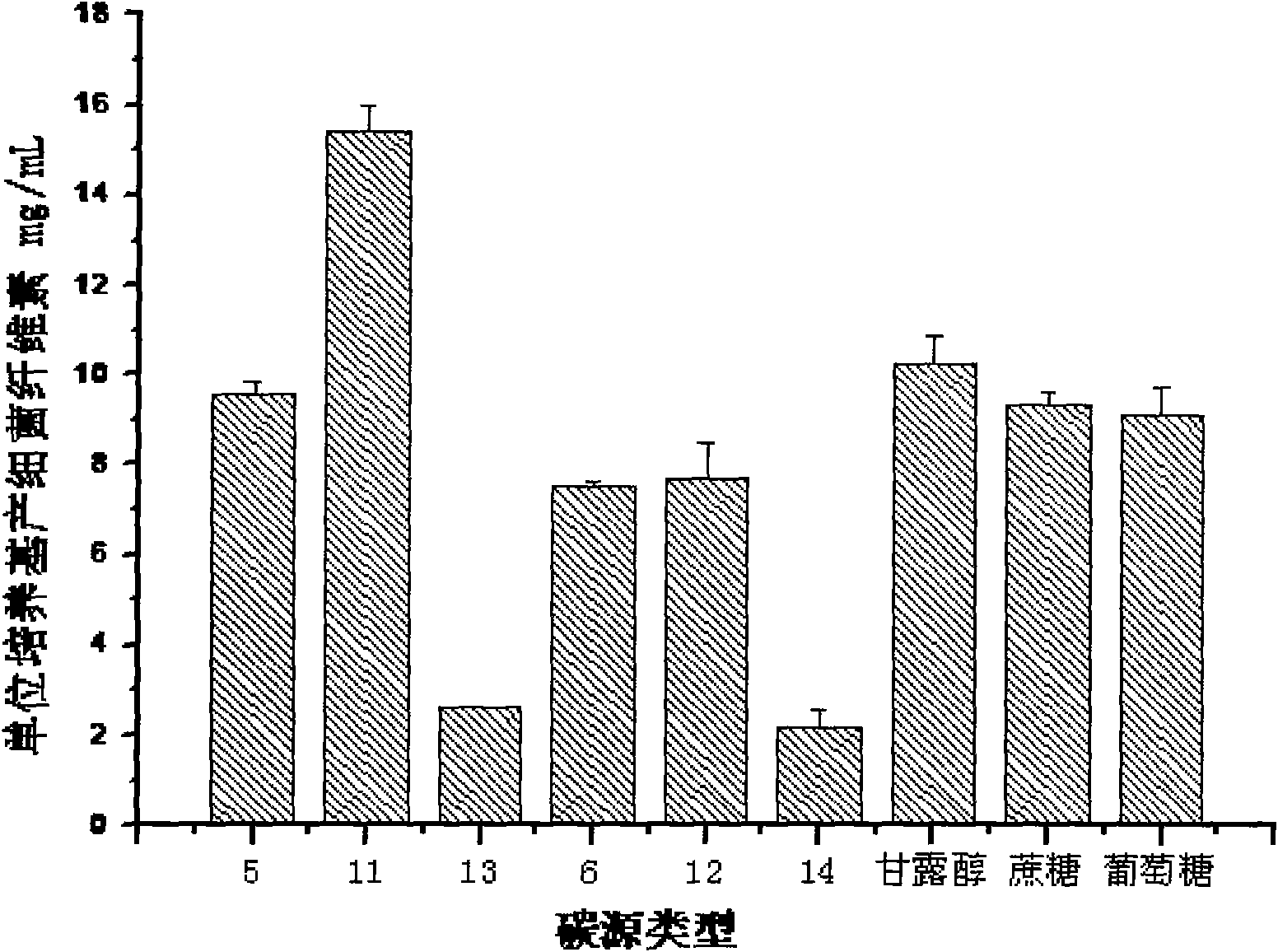
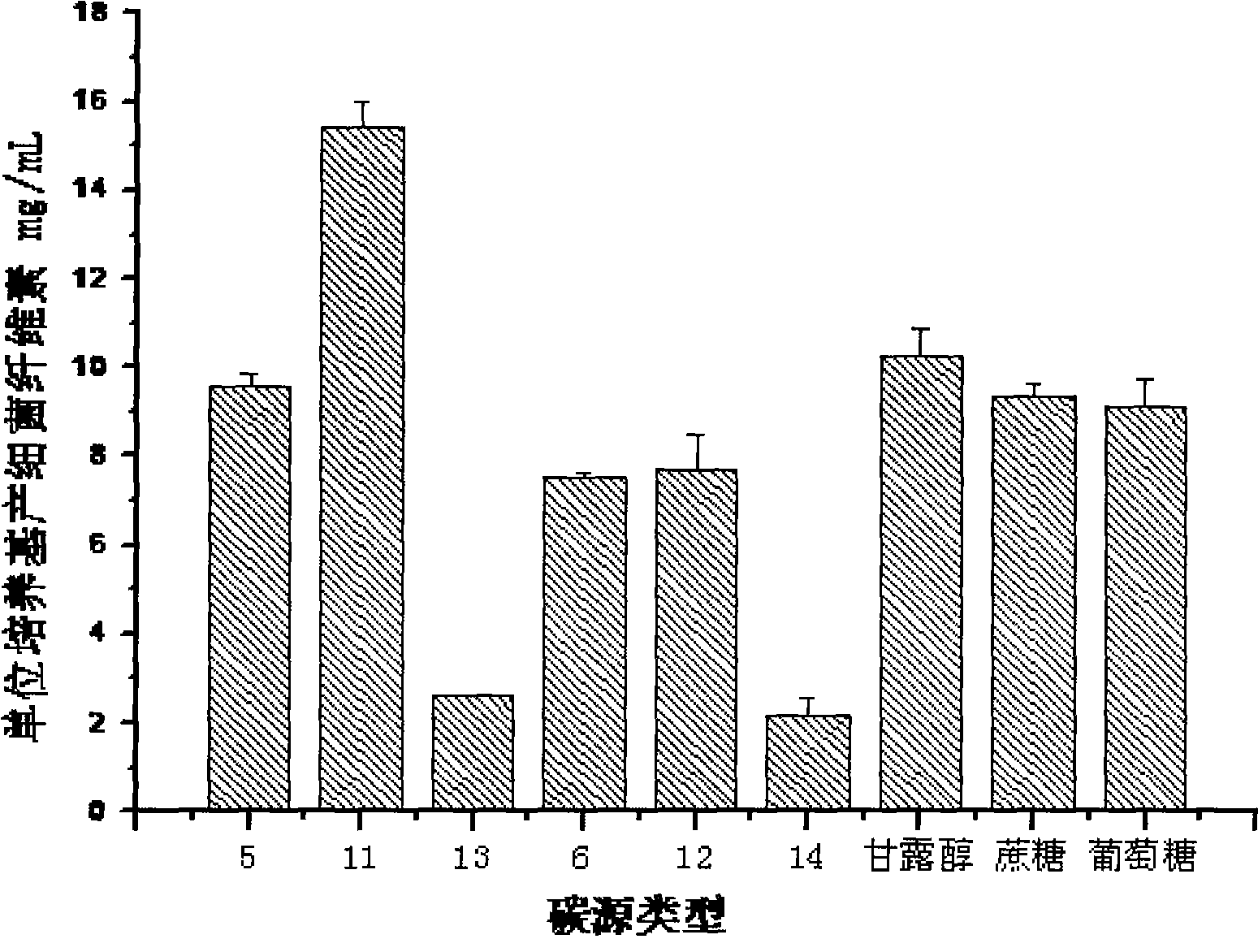
Method for producing bacterial cellulose with wheat straws/maize straws
A bacterial cellulose and corn stalk technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low cellulose production and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Wheat straw is first ground with a plant pulverizer, then soaked overnight (12-24h) with dilute sulfuric acid (3%, w / v) in a reactor at a solid / liquid ratio of 1:6 between the straw and dilute acid solution, Then react at a temperature of 121° C. for 60 minutes, then separate the straw residue and acid solution by suction filtration, collect the hydrolyzate, and refrigerate at 4° C. for later use.
[0067] Add NaOH to adjust the pH value of the hydrolyzed liquid to about 10, filter the precipitate with filter paper to obtain the treated hydrolyzed liquid, and then fine-tune the pH value to 10.0. Then seal it with a film, place it in a 30°C water bath for 12-24 overnight, and finally adjust the pH value of the hydrolyzate to 5.0 with dilute acid. Then add 2% (mass percentage) activated carbon, stir (at room temperature for 5-10min), filter out the activated carbon with filter paper to obtain detoxified hydrolyzed clear liquid, and fine-tune the pH value to 5.5 with dilut...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Wheat straw is first ground with a plant grinder, and then soaked overnight (12-24h) in a reactor with dilute hydrochloric acid (1%, w / v) at a solid / liquid ratio of 1:10 straw to dilute acid solution, Then react at a temperature of 121° C. for 75 minutes, then separate the straw residue and acid solution by suction filtration, collect the hydrolyzate, and refrigerate at 4° C. for later use.
[0070] Add Ca(OH) 2Adjust the pH value of the hydrolyzed liquid to about 10, filter out the precipitate with filter paper to obtain the treated hydrolyzed liquid, and then fine-tune the pH value to 10.0. Then seal it with a film, place it in a 40°C water bath for 12-24 overnight, and finally adjust the pH value of the hydrolyzate to 5.0 with dilute acid. Then add 2% (mass percentage) activated carbon, stir (at room temperature for 5-10min), filter out the activated carbon with filter paper to obtain detoxified hydrolyzed clear liquid, and fine-tune the pH value to 5.5 with dilute ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Wheat straw is first ground with a plant pulverizer, and then soaked overnight (12-24h) with dilute sulfuric acid (2%, w / v) in a reactor with a solid / liquid ratio of 1:15 straw to dilute acid solution, Then react at a temperature of 100° C. for 80 minutes, then separate the straw residue and acid solution by suction filtration, collect the hydrolyzate, and refrigerate at 4° C. for later use.
[0073] Add 25% ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the hydrolyzed liquid to 10, filter out the precipitate with filter paper to obtain the treated hydrolyzed liquid, and fine-tune the pH value to 10. Then seal it with a film, place it in a 25°C water bath to react overnight, and finally adjust the pH value of the hydrolyzate to 5.0 with dilute acid. Then add 2% (mass percentage) activated carbon, stir (at room temperature for 5-10min), filter out the activated carbon with filter paper to obtain detoxified hydrolyzed clear liquid, and fine-tune the pH value to 5.5 with dilute s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com