Method for hydrolyzing cellulose-containing plant waste by taking AlCl3 as catalyst in near-critical water
A plant waste and near-critical water technology, which is applied in the field of hydrolyzing cellulose-containing plant waste with AlCl3 as a catalyst in near-critical water, can solve the problems of low glucose yield, environmental pollution, and high energy consumption, and achieve ecological protection Environment, environmental protection, and the effect of resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] (1) Choose 10g of peanut shells (after drying) as raw material, first use a high-speed pulverizer to pulverize it to about 50 mesh particles;
[0023] (2) mix the above particles with a certain amount of catalyst AlCl 3 Mix it with pure water and send it to a near-critical water reactor for hydrolysis; use nitrogen to sweep, empty and leak check the reactor body and pipelines in advance;
[0024] (3) Take 2g of peanut shell particles and send them to a reactor with a volume of 270ml, and heat them with electricity to make the peanut shells in the near-critical water reactor undergo a hydrolysis reaction; the reaction temperature is controlled at 200°C, and the reaction pressure is 1.8MPa. 3 The added amount is 40mg, and the reaction time is 2min.
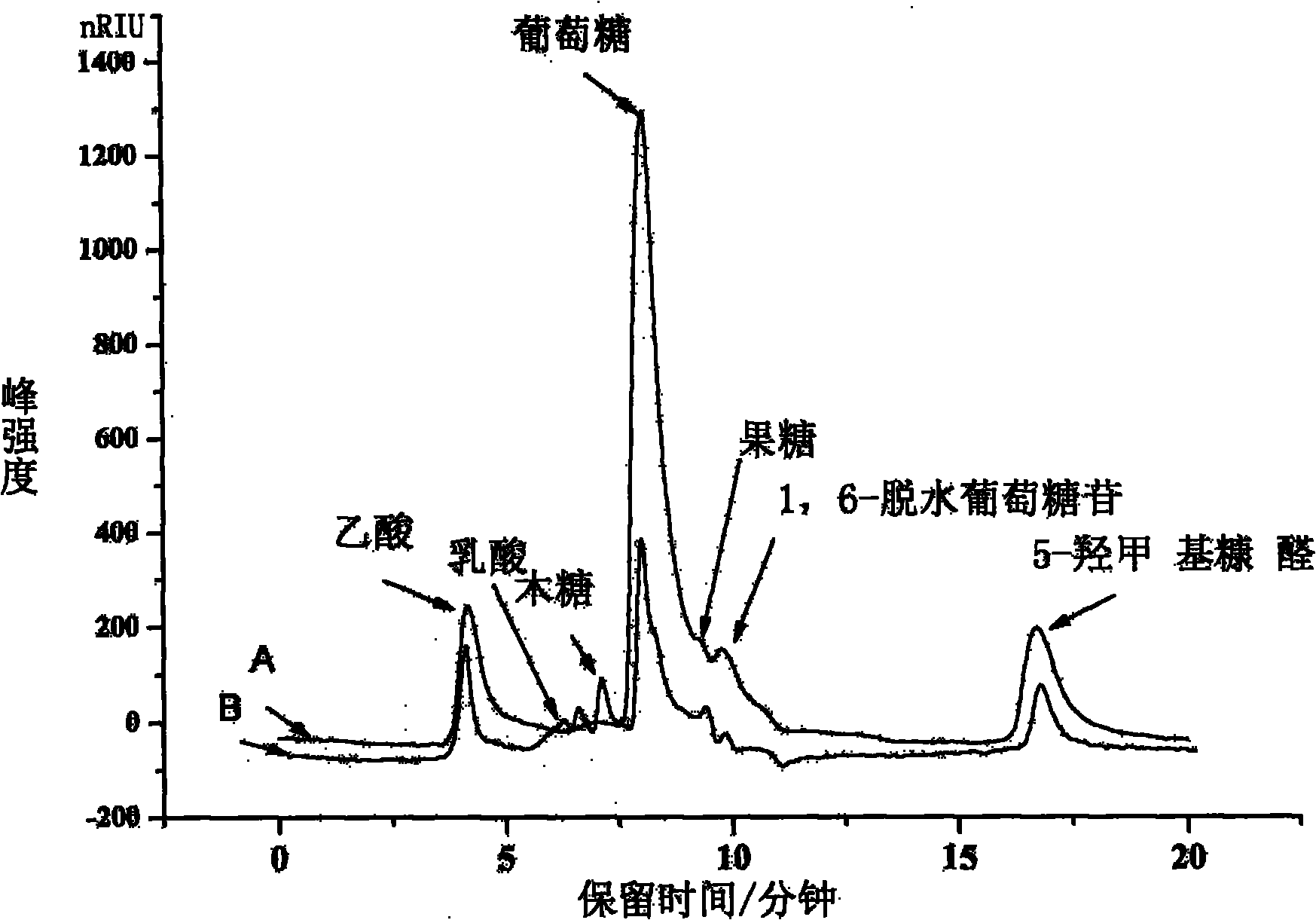
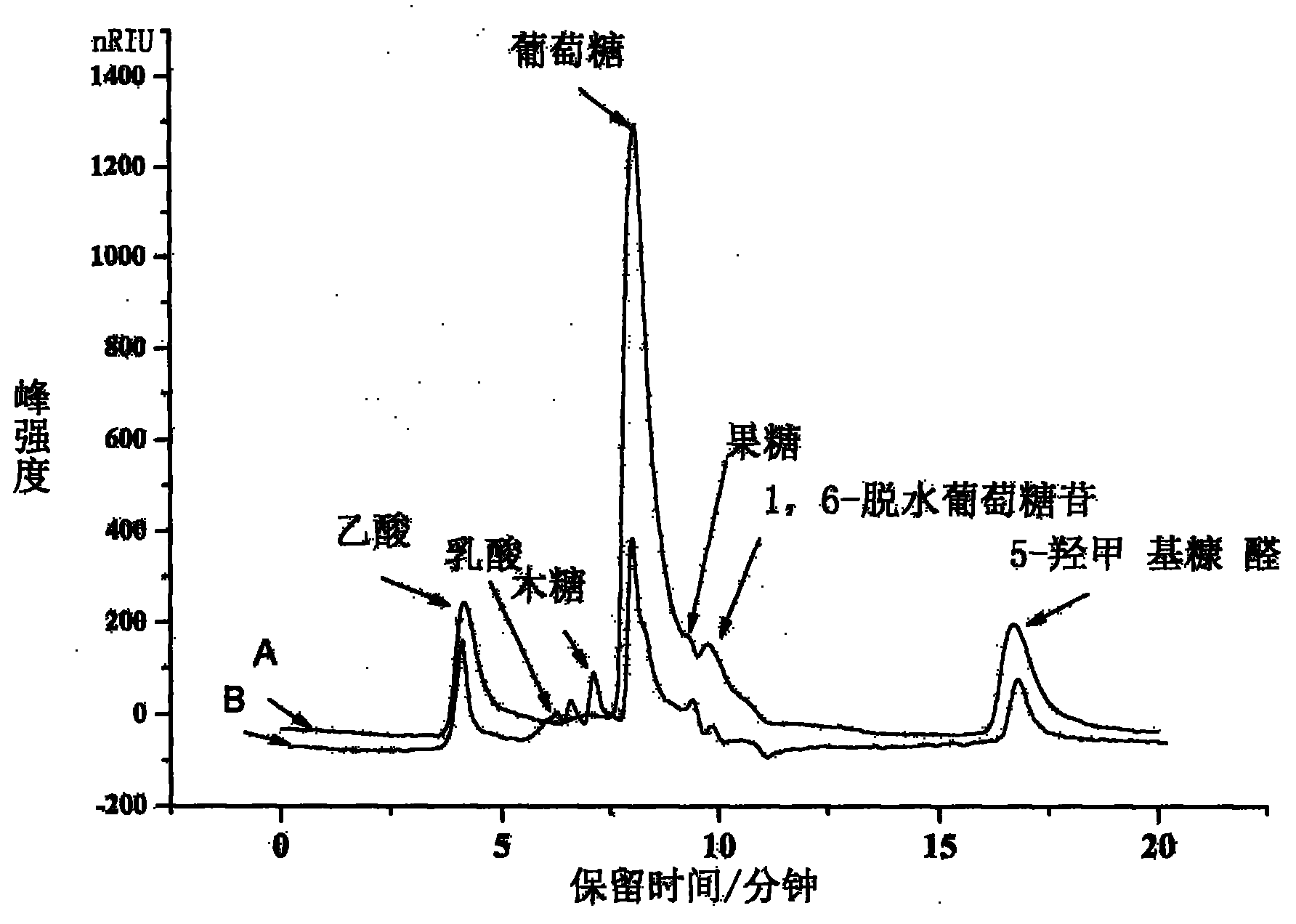
[0025] Finally obtain hydrolyzate and analyze the productive rate of glucose, 5-HMF and acetic acid wherein with HPLC, the yield and the selectivity of each component in the present embodiment are as shown in table 1:
[00...
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) choose 10g corn cob (after drying) as raw material, at first grind it to about 100 mesh particles with a high-speed pulverizer;
[0030] (2) mix the above particles with a certain amount of catalyst AlCl 3Mix it with pure water and send it to a near-critical water reactor for hydrolysis; use nitrogen to sweep, empty and leak check the reactor body and pipelines in advance;
[0031] (3) Take 2g of corncob particles and send them to a reaction kettle with a volume of 270ml, and heat them with electricity to make the corncobs in the near-critical water reaction kettle hydrolyze; the reaction temperature is controlled at 220°C, and the reaction pressure is: 2.0MPa, catalyst AlCl 3 The added amount is 60mg, and the reaction time is 3min.
[0032] Finally obtain hydrolyzate and analyze the productive rate of glucose, 5-HMF and acetic acid wherein with HPLC, the yield and the selectivity of each component in the present embodiment are as shown in table 2:
[0033] The y...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) choose 10g bagasse (after drying) as raw material, at first it is pulverized to about 150 mesh particles with a high-speed pulverizer;
[0037] (2) mix the above particles with a certain amount of catalyst AlCl 3 Mix it with pure water and send it to a near-critical water reactor for hydrolysis; use nitrogen to sweep, empty and leak check the reactor body and pipelines in advance;
[0038] (3) Get 2g of bagasse particles and send them to a reactor with a volume of 270ml, and heat it with electricity, so that the bagasse in the near-critical water reactor is hydrolyzed; the reaction temperature is controlled at 250°C, and the reaction pressure is 3.8MPa. 3 Addition amount: 120mg, reaction time: 3min.
[0039] Finally obtain hydrolyzate and analyze the productive rate of glucose, 5-HMF and acetic acid wherein with HPLC, the yield and the selectivity of each component in the present embodiment are as shown in table 3:
[0040] The yield of each component in the bagas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com