Method for recovering cadmium from waste nickel-cadmium battery
A waste battery, nickel-cadmium technology, applied in the field of waste battery recycling, can solve the problems of complex leaching equipment, long recycling process route, large equipment investment, etc., and achieves a simple and easy recycling method, less equipment investment, and high economic benefits. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
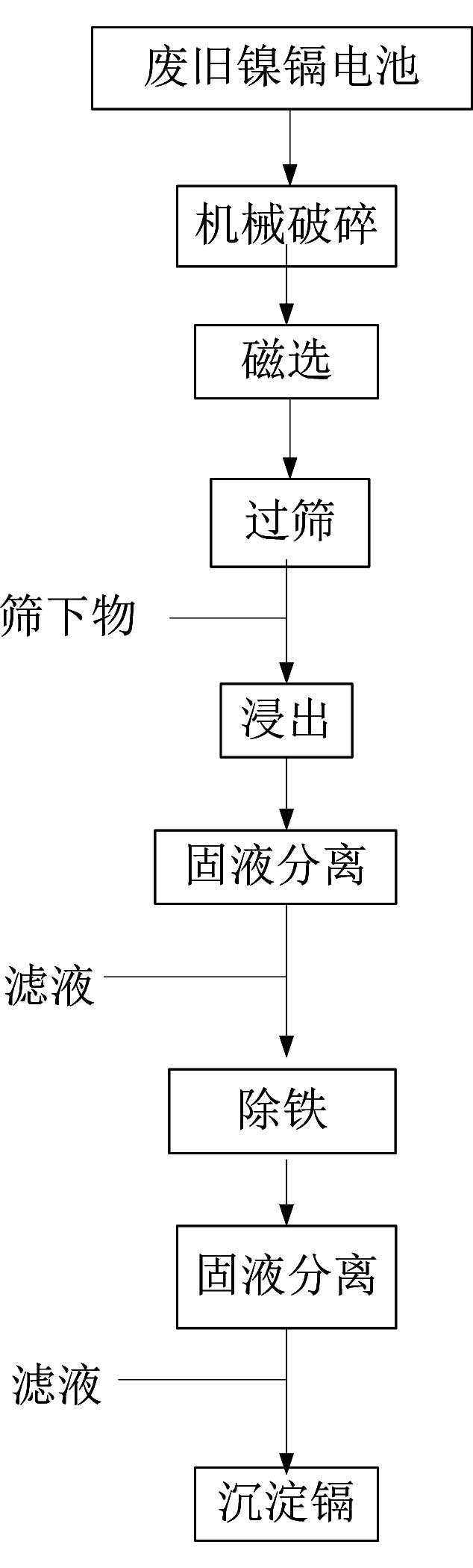
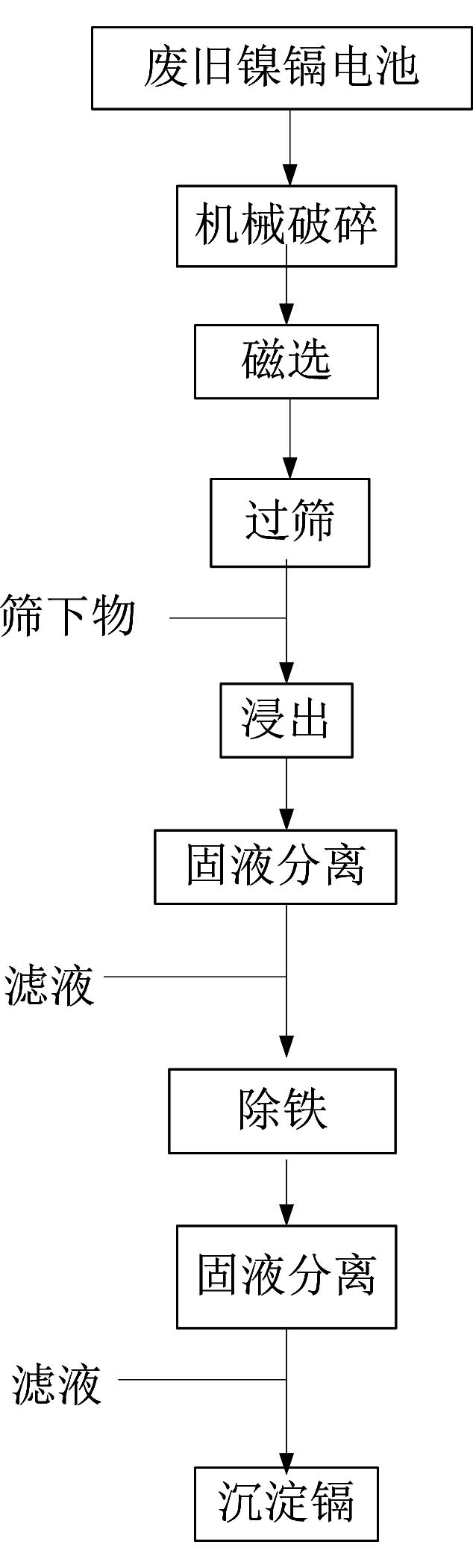
[0035] 1) Put 1000kg of powder into the dissolution kettle, add 5000L of water, 10000mol of sulfuric acid, 6000mol of oxidant sodium chlorate, heat up to 50°C, stir and soak for 3 hours, and take the leachate;
[0036] 2) Add waste nickel hydroxide, adjust the pH of the leaching solution to 3.5, remove iron, and separate solid and liquid;
[0037] 3) After the leachate after solid-liquid separation is passed into H 2 S gas to precipitate cadmium element.
[0038] After testing, the recovery rate of cadmium was 99.8%.
Embodiment 2
[0040] 1) Put 1000kg powder into the dissolution kettle, add 3000L water, 10000mol hydrochloric acid, 10000mol oxidant H 2 o 2 , heated up to 80°C, stirred and soaked for 1 hour, and took the leachate;
[0041] 2) adding sodium hydroxide solution, adjusting the pH of the leaching solution to 5, removing iron, and separating solid and liquid;
[0042] 3) Sodium sulfide is added to the leaching solution after solid-liquid separation to precipitate cadmium element.
[0043] After testing, the recovery rate of cadmium was 99.5%.
Embodiment 3
[0045] 1) Put 1000kg of powder into the dissolution kettle, add 4500L of water, 7500mol of sulfuric acid, and 8000mol of oxidant sodium persulfate, heat up to 60°C, stir and soak for 2 hours, and take the leachate;
[0046] 2) adding sodium carbonate, adjusting the pH of the leachate to 3, iron removal, solid-liquid separation;
[0047] 3) After the leachate after solid-liquid separation is passed into H 2 S gas to precipitate cadmium element.
[0048] After testing, the recovery rate of cadmium was 99.9%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| boiling point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com