Method for improving antibacterial activity of antifungal protein
A protein, antifungal technology, applied in the field of plant protection and genetic engineering, can solve the problem of no antibacterial activity, and achieve the effect of increasing the effective concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
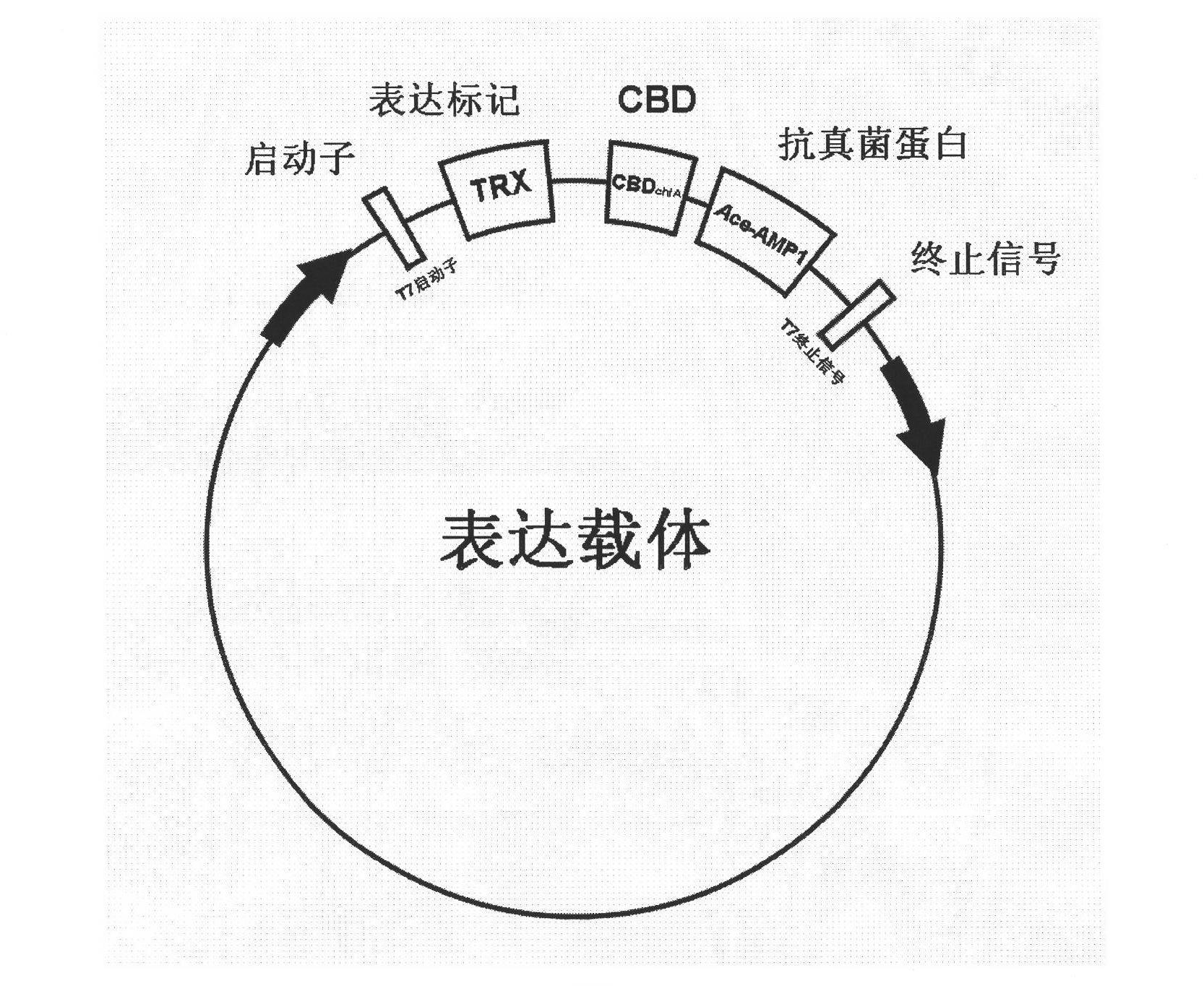
[0025] Example 1 Construction of chitin-binding domain and antifungal protein fusion gene
[0026] 1. Synthetic CBD chiA Fragment (SEQ ID NO.1, the coding nucleic acid sequence derived from the chitin-binding domain of chitinase Al, which can encode a polypeptide whose amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2), it should be noted that this experiment only uses CBD chiAFragments are taken as an example, and the selected chitin-binding domain fragments are not limited thereto. Design primers CBDchiA-F and CBDchiA-R, respectively introduce restriction endonuclease recognition sites at both ends, and obtain fragments with restriction endonuclease sites after PCR (depending on the carrier to be selected, this example The introduced enzyme cutting sites are BglII and KpnI), and the primer sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.5.
[0027] 2. Extract the total RNA in the onion seeds, and obtain the cDNA fragment of the antifungal protein Ace-AMP1 (SEQ ID NO.3, a kind of antifungal prote...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The acquisition of embodiment 2 fusion antifungal protein
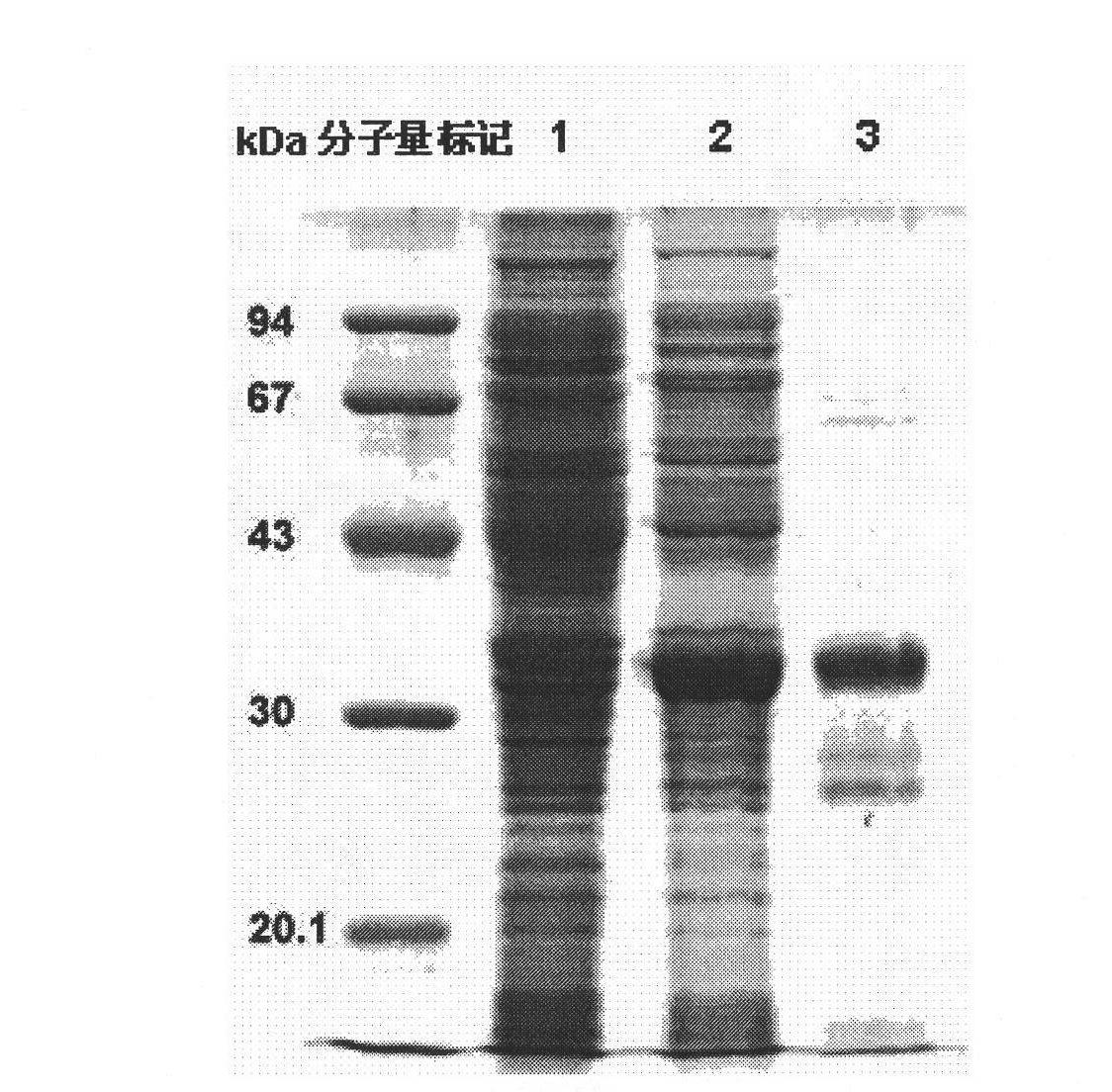
[0030] 1. the CBD-containing product that embodiment 1 obtains chiA Transform the genetically engineered bacteria Origami (DE3) with the fusion protein expression vector of Ace-AMP1. It should be noted that this experiment only uses CBD chiA As a representative of chitin-binding domain, Ace-AMP1 protein is used as a representative of antifungal protein, and is not intended to limit the scope of application of the present invention.
[0031] 2. After the transformed colony grows, inoculate the colony on the plate into 300ml LB liquid medium containing kanamycin, ampicillin and tetracycline, and shake at 37°C until OD 600 =0.6-0.8, add IPTG at a final concentration of 0.05 mM, and culture at 30°C for 4 hours or at 20°C overnight.
[0032] 3. Centrifuge the Escherichia coli liquid obtained in step 2 to remove the supernatant, wash the bacteria with 1×PBS, resuspend in the 1× initial buffer required for His-tag f...
Embodiment 3
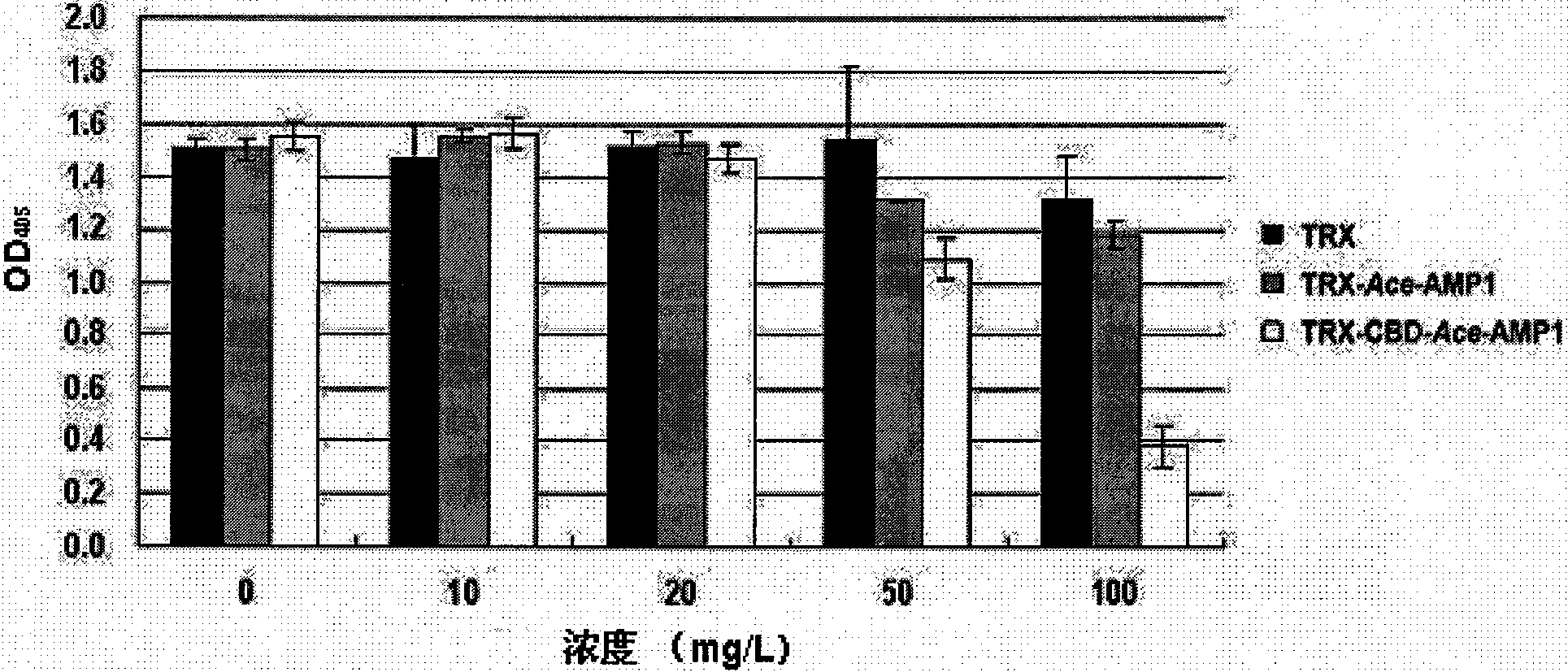
[0033] Embodiment 3 Chitin-binding ability test of fusion antifungal protein
[0034] 1. Express the fusion protein according to the method of steps 1 and 2 in Example 2, it should be noted that only CBD chiA As a representative of chitin-binding domain, Ace-AMP1 protein as a representative of antifungal protein, not intended to limit the scope of application of the present invention.
[0035] 2. After centrifuging the obtained bacterial solution, wash with 1×PBS, and resuspend in 1× binding buffer required for chitin binding. After adding PMSF with a final concentration of 1 mM, the bacteria were ultrasonically disrupted, and the supernatant protein obtained after centrifugation was filtered through a filter membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm. Add chitin beads and incubate the supernatant protein for 1 hour, wash the miscellaneous protein with a large amount of buffer solution for several times, and finally absorb a small amount of chitin beads and mix with 2×SDS loading b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com