Fluidity improver for aromatic polycarbonate resin, process for producing the fluidity improver for aromatic polycarbonate resin, aromatic polycarbonate resin composition, and molded product
一种聚碳酸酯树脂、芳香族的技术,应用在芳香族聚碳酸酯树脂组合物及其成型体领域,能够解决成型体外观不良、残留单体、聚合性低等问题,达到外观优异、机械特性优异、熔融流动性优异的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
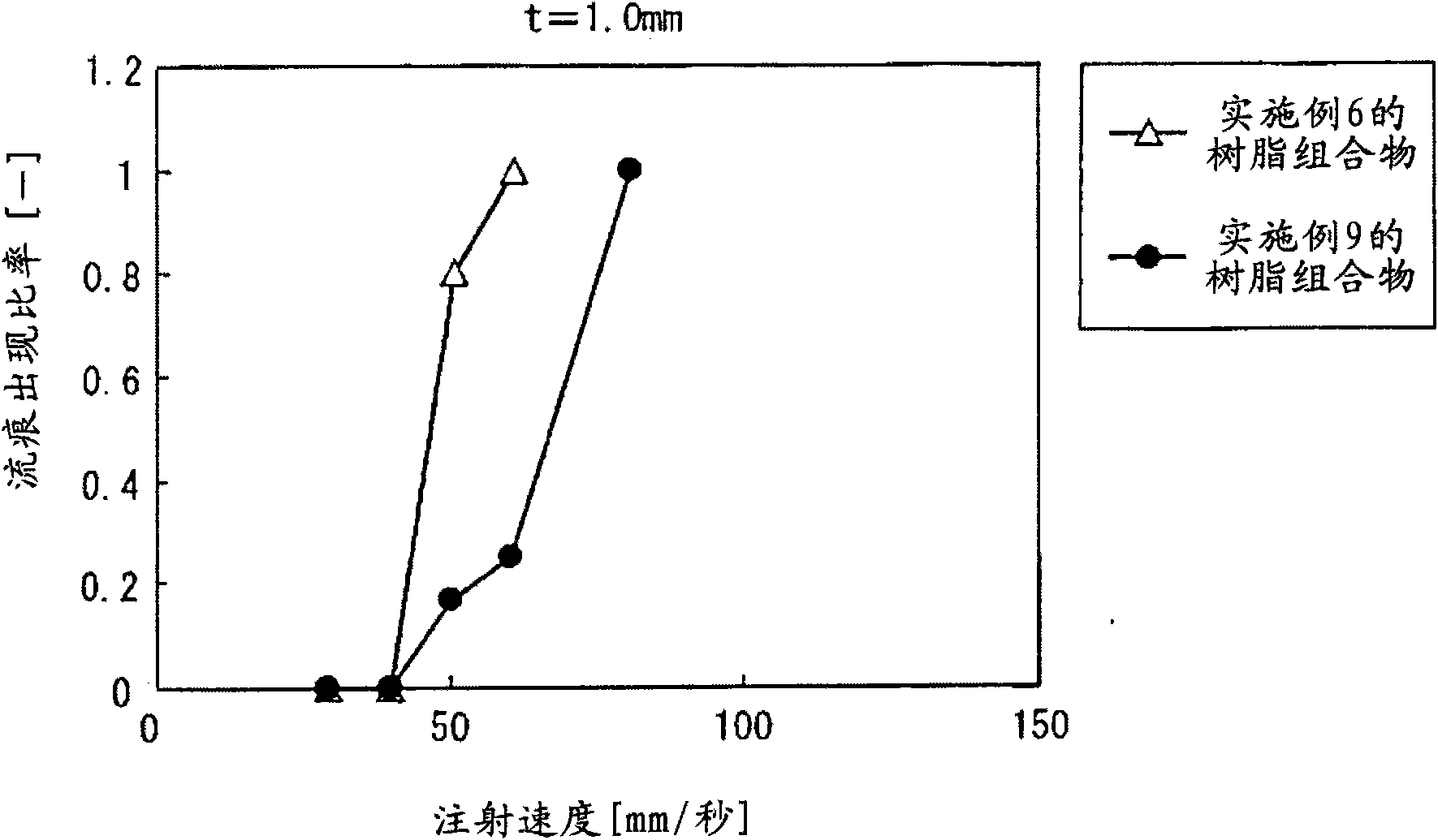
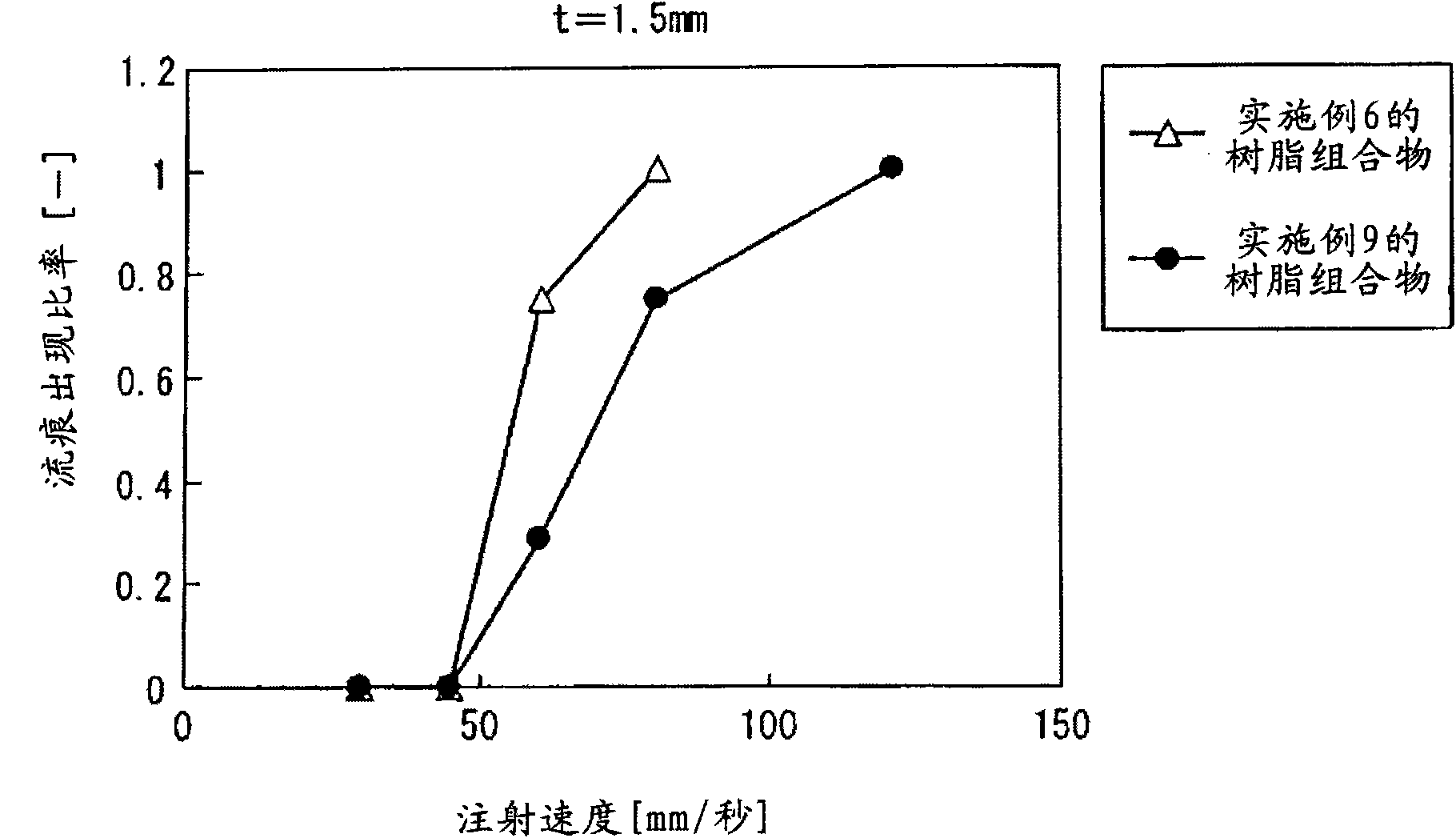
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0139] Hereinafter, although an Example demonstrates this invention more concretely, this invention is not limited by these Examples.
[0140] In addition, "part" and "%" in an Example and a comparative example represent "part by mass" and "% by mass", respectively.
[0141] In addition, the polymerization rate and average molecular weight in the following examples were measured as follows.
[0142] (1) Polymerization rate
[0143] The polymerization rate at the end of the second step was measured in the following procedure.
[0144] (i) Measure the mass (x) of the aluminum dish to a unit of 0.1 mg.
[0145] (ii) About 1 g of the emulsion of the polymer (X) was put in the aluminum dish, and the mass (y) of the aluminum dish after putting the polymer (X) emulsion was measured to the unit of 0.1 mg.
[0146] (iii) Put the aluminum pan containing the polymer (X) emulsion in a dryer at 180° C., and heat for 45 minutes.
[0147] (iv) Take out the aluminum dish from the desiccat...
Embodiment 2
[0202] Production of Polymer (X-2)
[0203] Polymer (X-2) was produced in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the compositions of the monomer mixture (b), the chain transfer agent, and the polymerization initiator were changed as follows.
[0204] Monomer mixture (b):
[0205] Styrene 20.0 parts
[0206] Phenyl methacrylate 29.75 parts
[0207] Allyl methacrylate 0.25 parts
[0208] Chain transfer agent:
[0209] n-octyl mercaptan 0.375 parts
[0210] Polymerization Initiator:
[0211] 0.1 parts of tert-butyl hydroperoxide
[0212] The polymerization rate at the time of producing the polymer (X-2) was 100%, the Mw of the polymer (X-2) was 43000, the Mn was 16500, and the molecular weight distribution (Mw / Mn) was 2.6.
Embodiment 3
[0214] Manufacture of polymer (X-3)
[0215] In a separable flask equipped with a thermometer, a nitrogen gas introduction pipe, a cooling pipe, and a stirring device, the following emulsifier mixture was added, stirred, and the internal temperature of the separable flask was raised to 60° C. under a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0216] Emulsifier Blend:
[0217]PELEX SS-L (manufactured by Kao Corporation, anionic emulsifier) 2.4 parts
[0218] 295 parts of deionized water
[0219] Then, the following reducing agent mixture was added in a separable flask.
[0220] Reductant mixture:
[0221] Ferrous sulfate 0.0001 parts
[0222] EDTA disodium salt 0.0003 parts
[0223] Sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate 0.3 parts
[0224] 5 parts of deionized water
[0225] Then, the following monomer mixture (a), a chain transfer agent, and a polymerization initiator were mixed, and the resulting mixture was dropped into a separable flask over 270 minutes, and stirred 15 minutes after the comp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight-average Molecular Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight-average Molecular Weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com