Semiconductor substrate and preparation method thereof
A semiconductor and substrate technology, applied in the field of semiconductor substrates and their preparation, can solve the problems of easy cracking, volatility and corrosion of GaN
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0026] An embodiment of preparing a semiconductor substrate of the present invention includes:
[0027] Provide lithium aluminate wafer;
[0028] A semiconductor substrate is obtained by depositing an AlN film layer on the lithium aluminate wafer by using a sputtering method.
[0029] According to the present invention, the lithium aluminate wafer is used as the base of the semiconductor substrate, and the lithium aluminate wafer needs to be polished. For the surface roughness of the lithium aluminate wafer, the root mean square roughness is preferably less than 10 angstroms, more preferably less than 8 angstroms , more preferably less than 5 angstroms. For the polishing method of the lithium aluminate wafer, the present invention is not particularly limited. According to the present invention, a (100) crystal plane lithium aluminate wafer is preferred as the base material of the semiconductor substrate.
[0030] According to the present invention, a sputtering method is us...
Embodiment 1
[0038] Place the polished lithium aluminate wafer with a surface root mean square roughness of 5 Angstroms (100) in the sputtering chamber of the measurement and control sputtering system, and vacuum the sputtering chamber to 2.0×10 -4 Pa; heat the lithium aluminate wafer to 400 °C and keep it warm, with flowing Ar and N 2 As sputtering gas, the flow rate of sputtering gas is about 15 sccm, Ar and N 2 The volume ratio is 3:1.
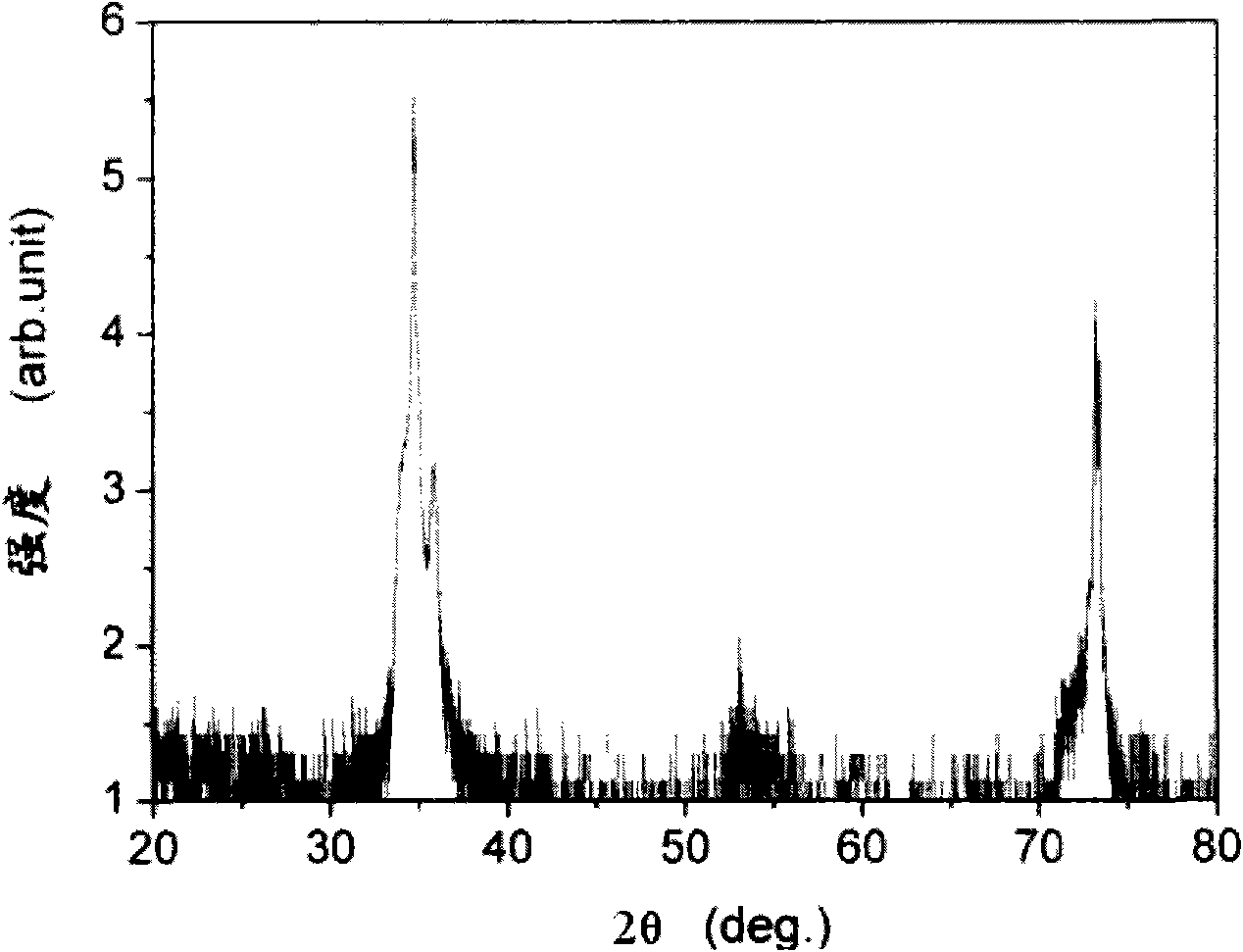
[0039] Using AlN ceramics with a purity of 99.99wt% as the target material, using radio frequency sputtering, the sputtering power is 200W, and the sputtering time is 20 minutes. After the sputtering, the lithium aluminate wafer deposited with AlN is cooled to Remove from room temperature. Carry out XRD test on the semiconductor substrate, the test results are as follows figure 1 As shown, the diffraction peaks located at 34.70°, 35.86°, and 73.19° in the figure correspond to the (200) crystal plane of lithium aluminate, the (0002) crystal plane of A...
Embodiment 2-4
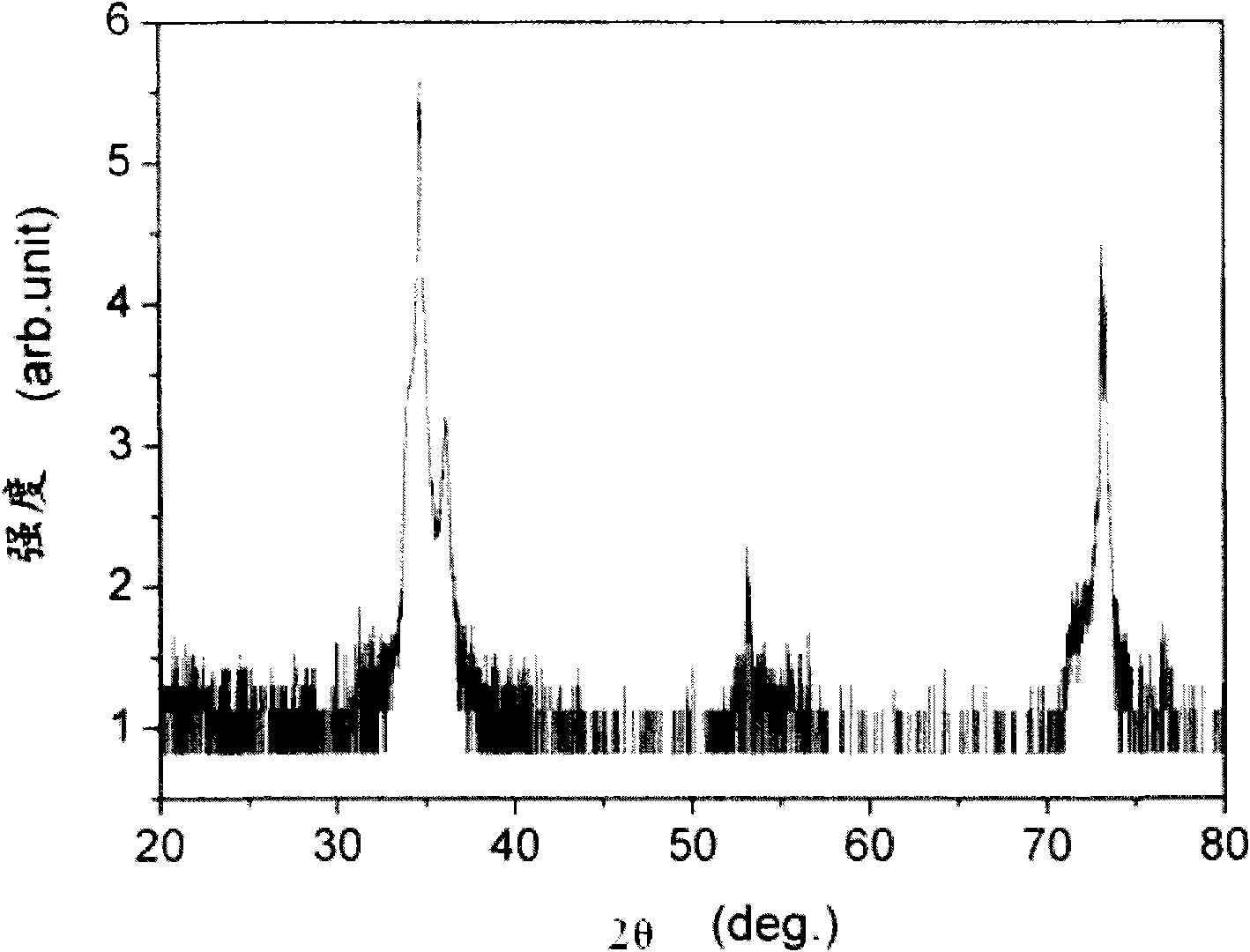
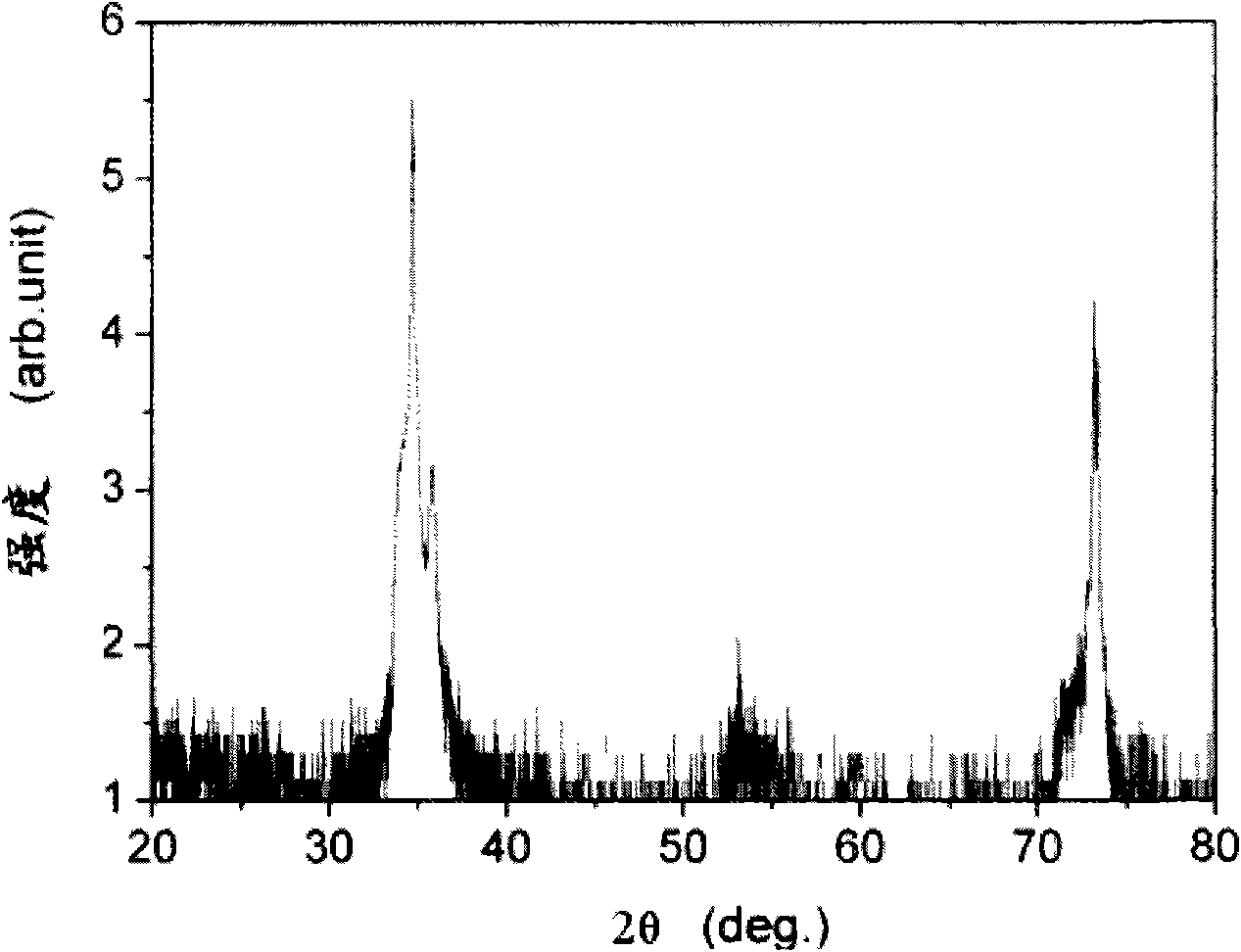
[0041] In these three embodiments, the RF sputtering power in Embodiment 1 was adjusted to 300W, 400W, and 500W, and the sputtering time was 20 minutes, 30 minutes, and 40 minutes, respectively, and the others were the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0042] The three examples also produced (0001) aluminum nitride films with a high c-axis preferred orientation on the (100) plane lithium aluminate wafer.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com