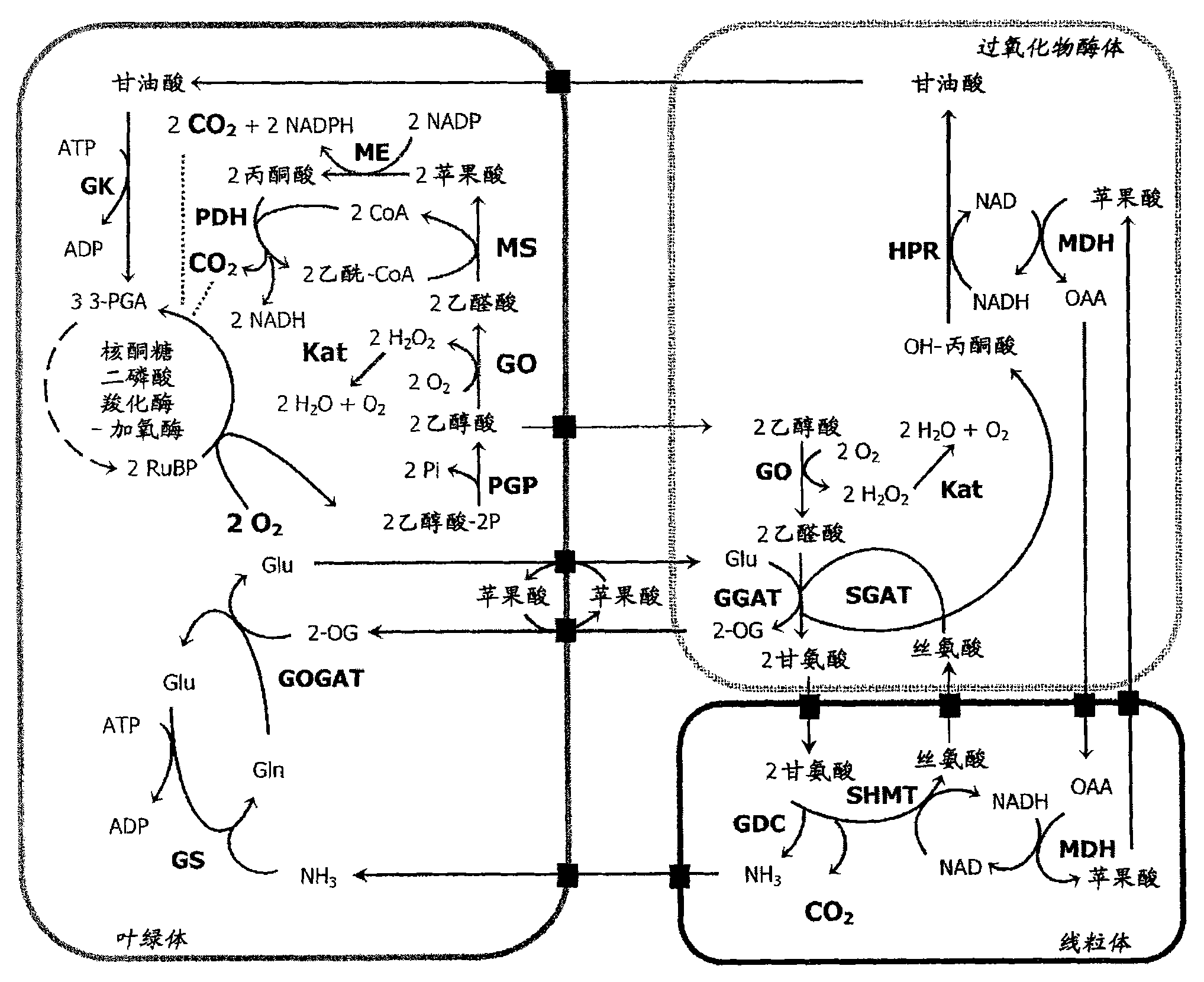
Means for improving agrobiological traits in a plant by providing a plant cell comprising in its chloroplasts enzymatic activities for converting glycolate into malate
A plant cell, malate synthase technology, applied in the field of yield transgenic plants or plant cells, can solve the problems of weakened photorespiration, endogenous enzyme patterns and changes in the content of UV protectants
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0133] Example 1: PCR Amplification of Transgene
[0134] The cDNAs corresponding to glycolate oxidase 2 (GO, At3g14420) in Arabidopsis leaves and malate synthase (MS, X56948) in pumpkin cotyledon and E. coli catalase (KatE; M55161) genomic sequence and cloned into pGEMT-Easy (Promega, Mannheim, Germany) or pCR-Blunt II-TOPO (Invitrogen). For the case of GO and MS, the nucleotides encoding the last amino acids (A / SRL) were omitted, which were estimated to represent peroxisome targeting signals (31, 32). The following primer combinations were used: GO forward primer: (5'-TACAATTGGAGATCACTAACGTTACCGAGT-3' SEQ ID NO: 9) and GO reverse primer: (5'-TGGGACACTCCACGTCCTTAGTCTAGACTAGTA-3' SEQ ID NO: 10); MS forward primer: (5'-ACACCGGTCGCTGGGAATGTATTCTGAATCGGCA-3'SEQ ID NO: 11) and MS reverse primer: (5'-CACATAGGCATACATCATCCAGGTGAGTCGACGTT-3'SEQ ID NO: 12); KatE forward primer: (5'-ACACCGGTCGCAACATAACGAAAAGAACCCA-3'SEQ ID NO : 13) and KatE reverse primer: (5'-ACGTCGACTCAGGCAGGAATTTTG...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment 2: Construction of binary vector
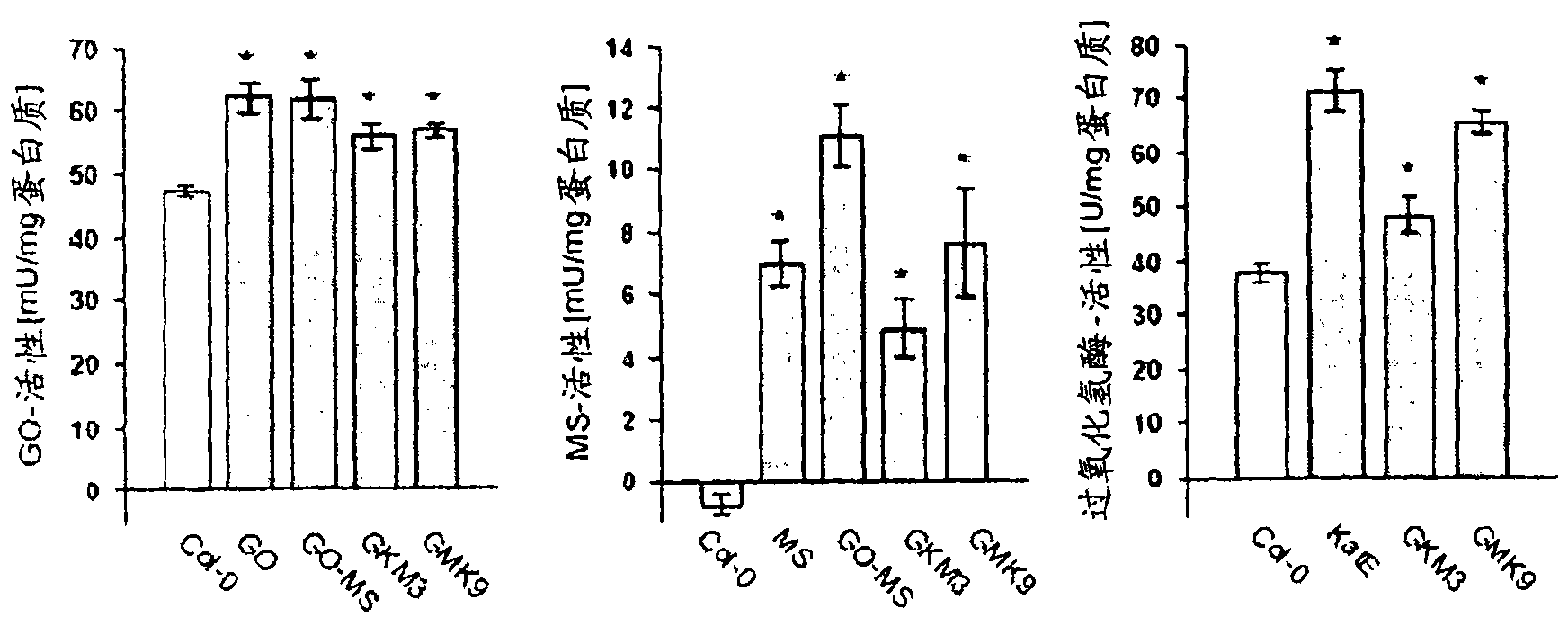
[0136] To direct expression in Arabidopsis, DNA encoding the plastid precursors of these enzymes was cloned into a modified form of the binary vector pGreenII [33, 34]. DNA encoding these enzymes was cloned into binary vectors using different strategies. For MS and KatE, the CaMV35S promoter was excised from the vector and expression was directed by the tomato-rbcS3C promoter. The selectable marker genes nosKan (kanamycin resistance), nosHyg (hygromycin resistance) and nosBAR 18 (BASTA resistance) were cloned into the StuI-site in the basic pGreenII vector. GO was cloned into pGreenII 35S-nosKan vector, MS was cloned into pGreenII rbcS3C-nosHyg vector, and KatE was cloned into pGreenII rbcS3C-nosBAR vector, and the resulting plasmids were called 35S:GO, rbcS3C:MS and rbcS3C:KatE.
Embodiment 3
[0137] Example 3: Transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana and selection of transformants
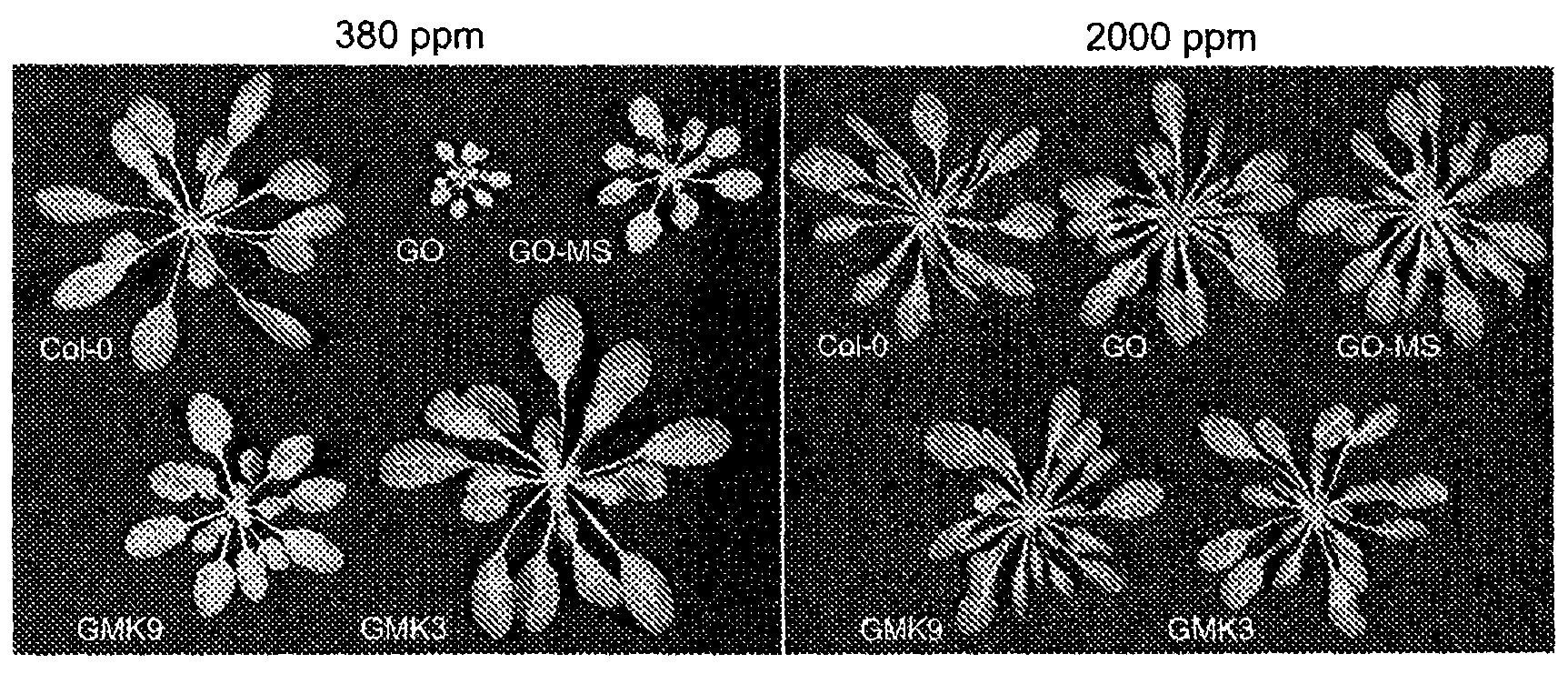
[0138] The binary vectors 35S:GO, rbcS3C:MS, and rbcS3C:KatE were electroporated into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 carrying the helper plasmid pSoup for transformation of Arabidopsis plants (Ecotype Columbia, Col-0) by vacuum invasion [35 ]. Transformed seeds were selected for resistance to kanamycin, hygromycin or BASTA. Leaf material was collected from selected plants and DNA was extracted for PCR analysis. Plants containing the transgene are capable of self-pollinating. The transgenic lines underwent two more rounds of screening and characterization using PCR and enzyme activity detection.
[0139] Generally, plants are grown under the conditions of 8 hours of light / 16 hours of darkness, and the photosynthetically active photon flux density (PPFD) is 100 or 600 μmol quantum m-2s-1 (normal and increased light intensity, respectively), and the temperature is adjusted to 22°C duri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com