Protein flocculant for treating printing and dyeing wastewater
A printing and dyeing wastewater and protein technology, which is applied in the field of polymer chemicals and its application, can solve the problems of less protein research, increased environmental burden, and underutilization, etc., to achieve increased environmental burden, reduced secondary pollution, and low cost. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Synthetic example
[0040] The raw material for preparing water-soluble protein in the synthesis example is commercially available animal protein powder with a protein content of 80%. The water-soluble protein is prepared by alkaline hydrolysis, and the preparation method is as follows:
[0041] Add 1 part by weight of animal protein powder, 3.3 parts by weight of deionized water and 0.1 part by weight of ammonia water (weight concentration 20%) into the autoclave. The temperature was raised slowly under stirring, and the temperature rose to 140° C. in about 1 hour. Keep this temperature to carry out the hydrolysis reaction for 2 hours, and the reaction ends. Cool down and filter and wash the filter residue, combine the filtrate and washing liquid to obtain a hydrolyzed protein solution. The filter residue was weighed after drying, and the protein hydrolysis rate was calculated according to the following formula:
[0042] Hydrolysis rate (%) = [(m 0 -m 1 ) / (80%*m 0 )]*100%
[0043] In the ...
Embodiment 1
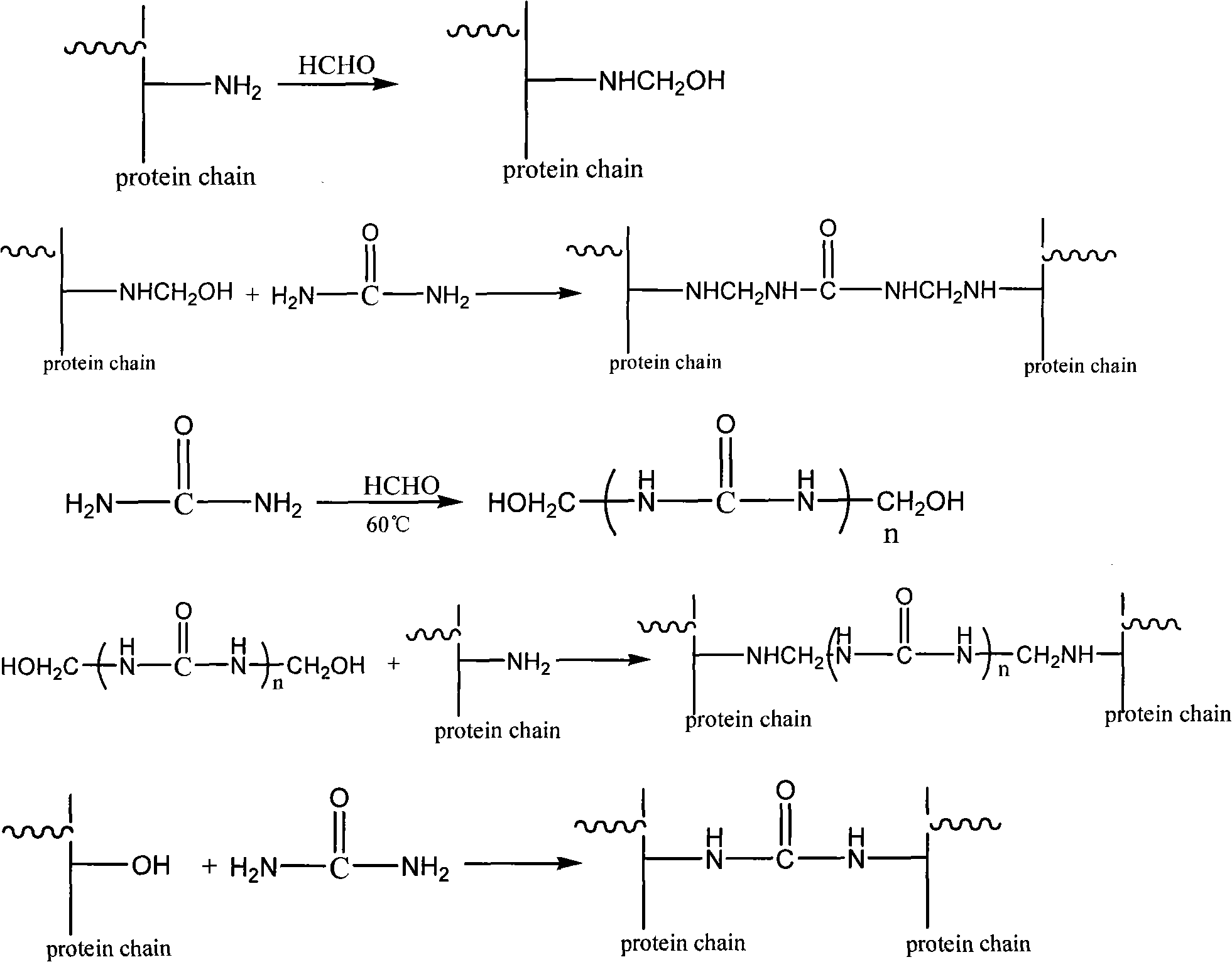
[0046] Add 100 grams of hydrolyzed protein solution into a four-necked glass reaction flask with a stirrer and a thermometer, start stirring and add 30 grams (0.37 moles) of formaldehyde solution (37% content), 23 grams (0.38 moles) of urea, and an aqueous solution of sodium carbonate to adjust the reaction System pH≈9. The temperature was raised to 60° C., and the reaction was kept for 5 hours. Sampling analysis After the formaldehyde reaction is complete, the material is cooled and discharged to obtain a yellow viscous liquid.
Embodiment 2
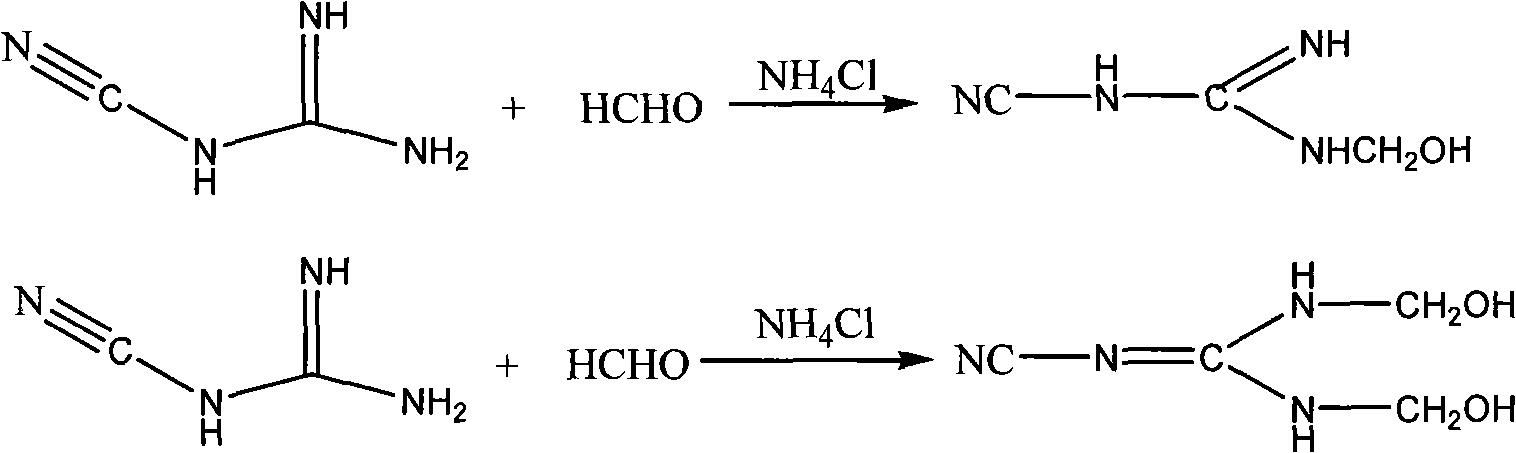
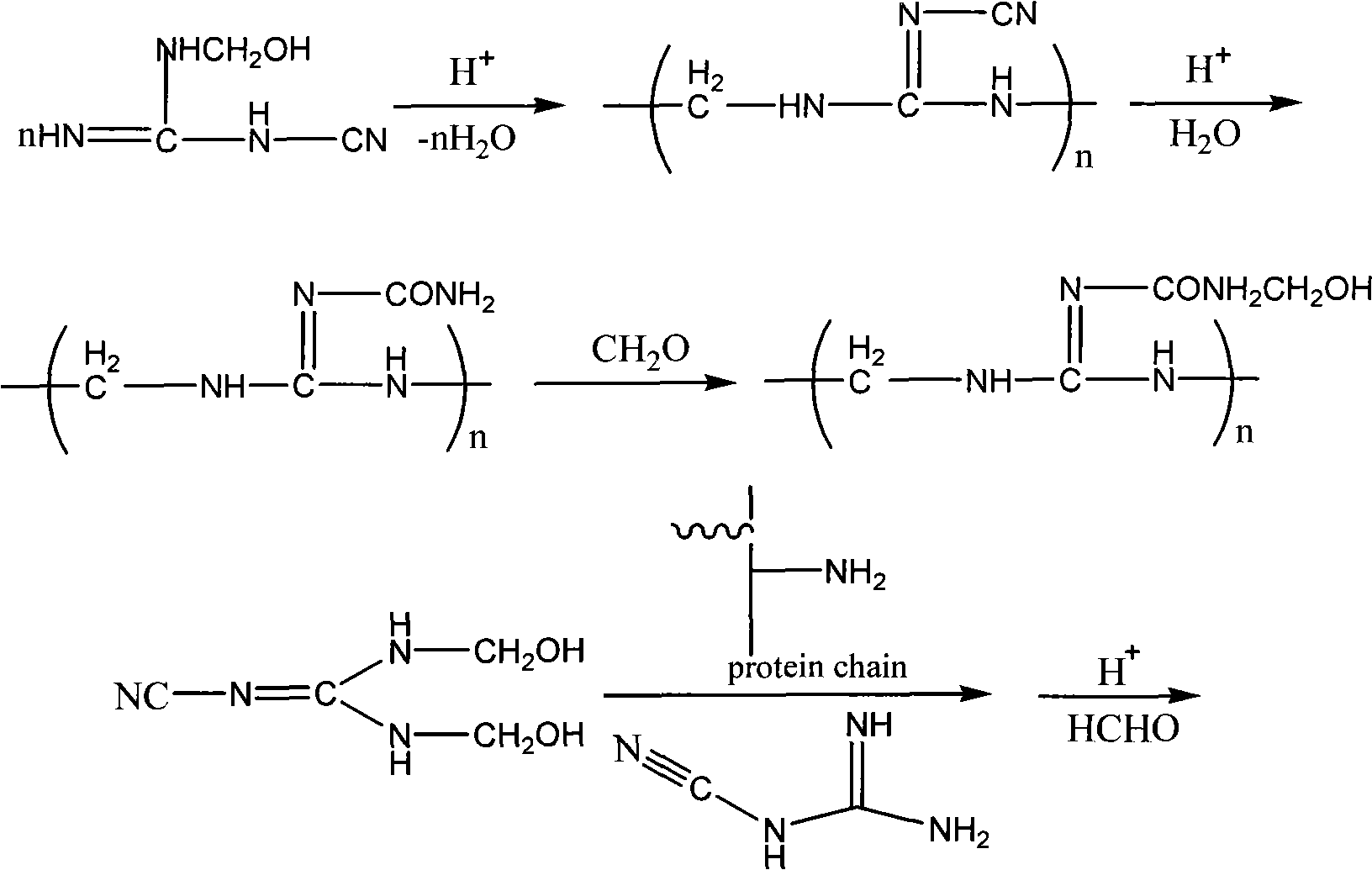
[0048] The reaction device is the same as above. Add 150 grams of hydrolyzed protein solution, 8.4 grams (0.1 mole) of dicyandiamide, and 8.1 grams (0.1 mole) of 37% formaldehyde solution. First use sodium carbonate aqueous solution to adjust pH ≈ 9, and react at 60°C; after 3 hours, use hydrochloric acid to adjust pH = 4-5, continue to react for 4 hours, and analyze until all formaldehyde reacts, then cool and discharge to obtain a yellow viscous liquid .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| absorption wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com